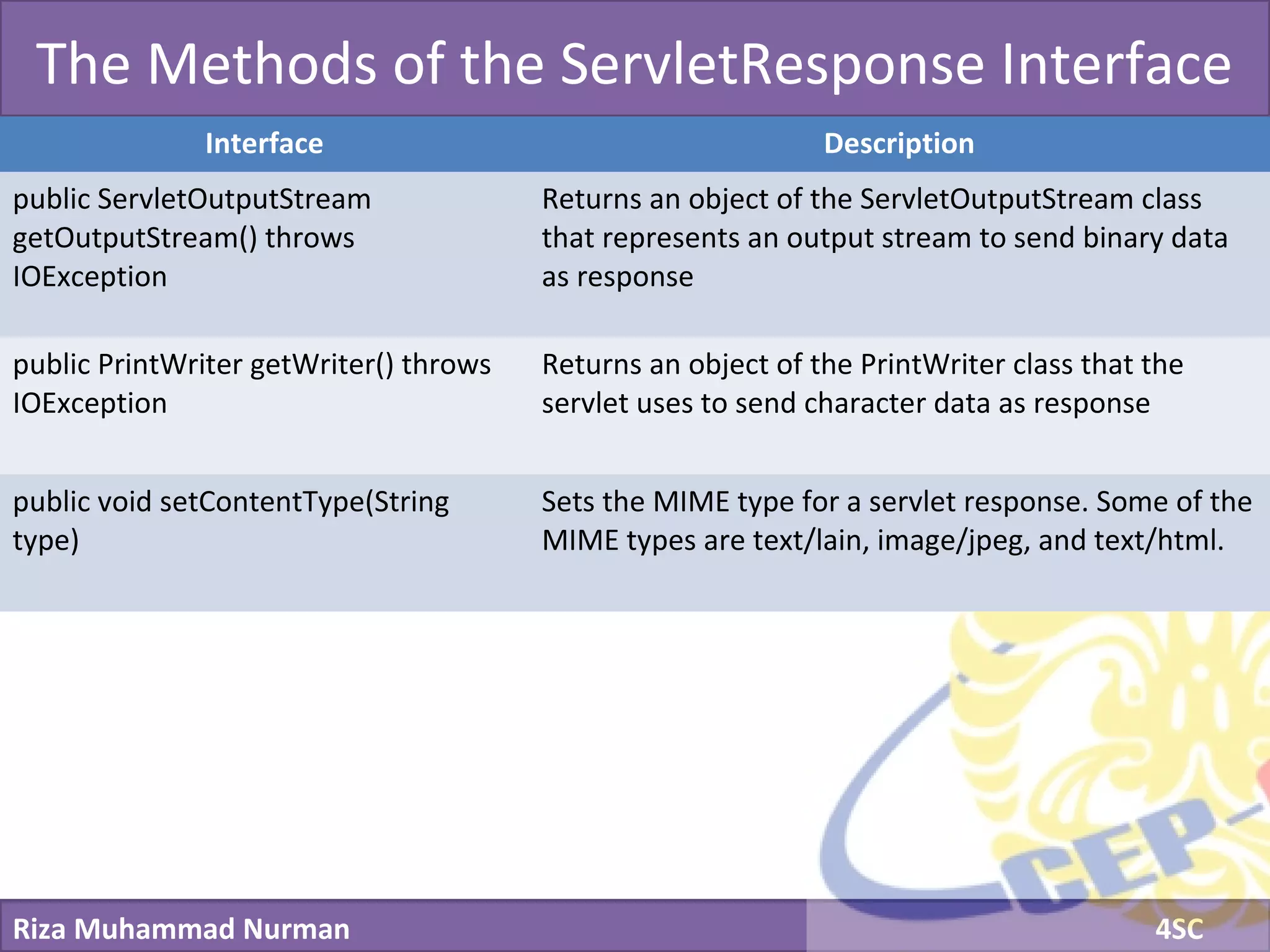
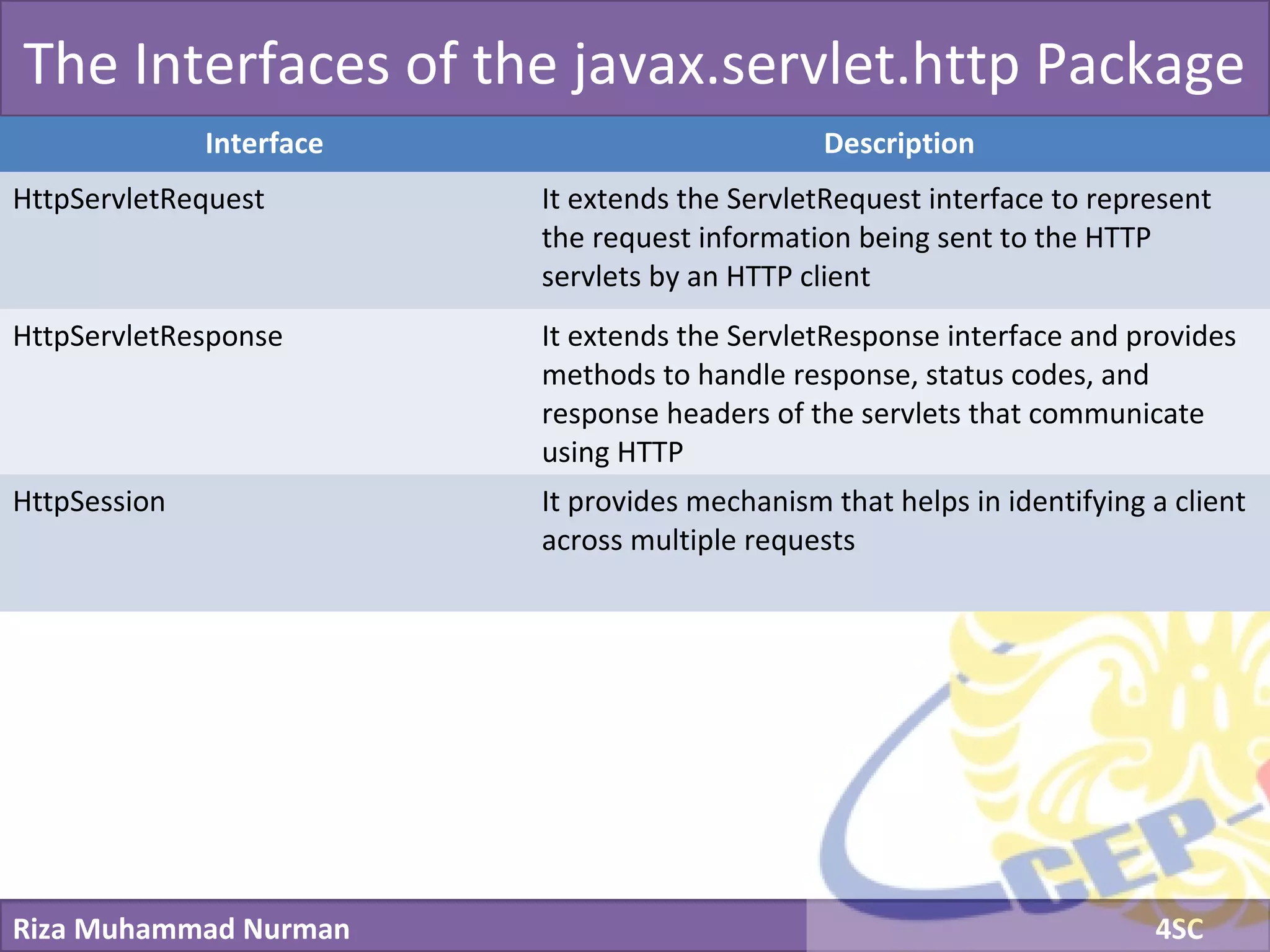
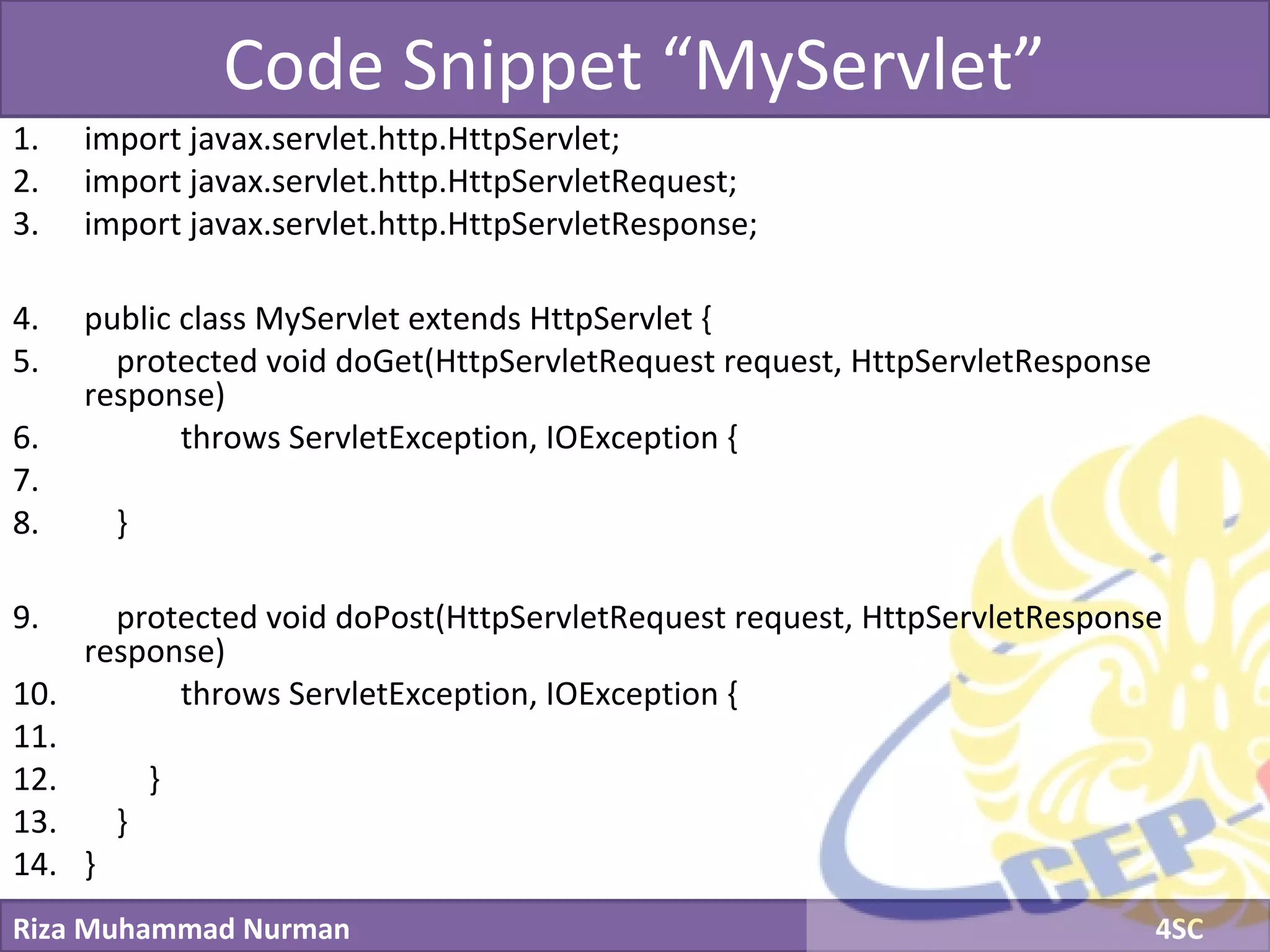
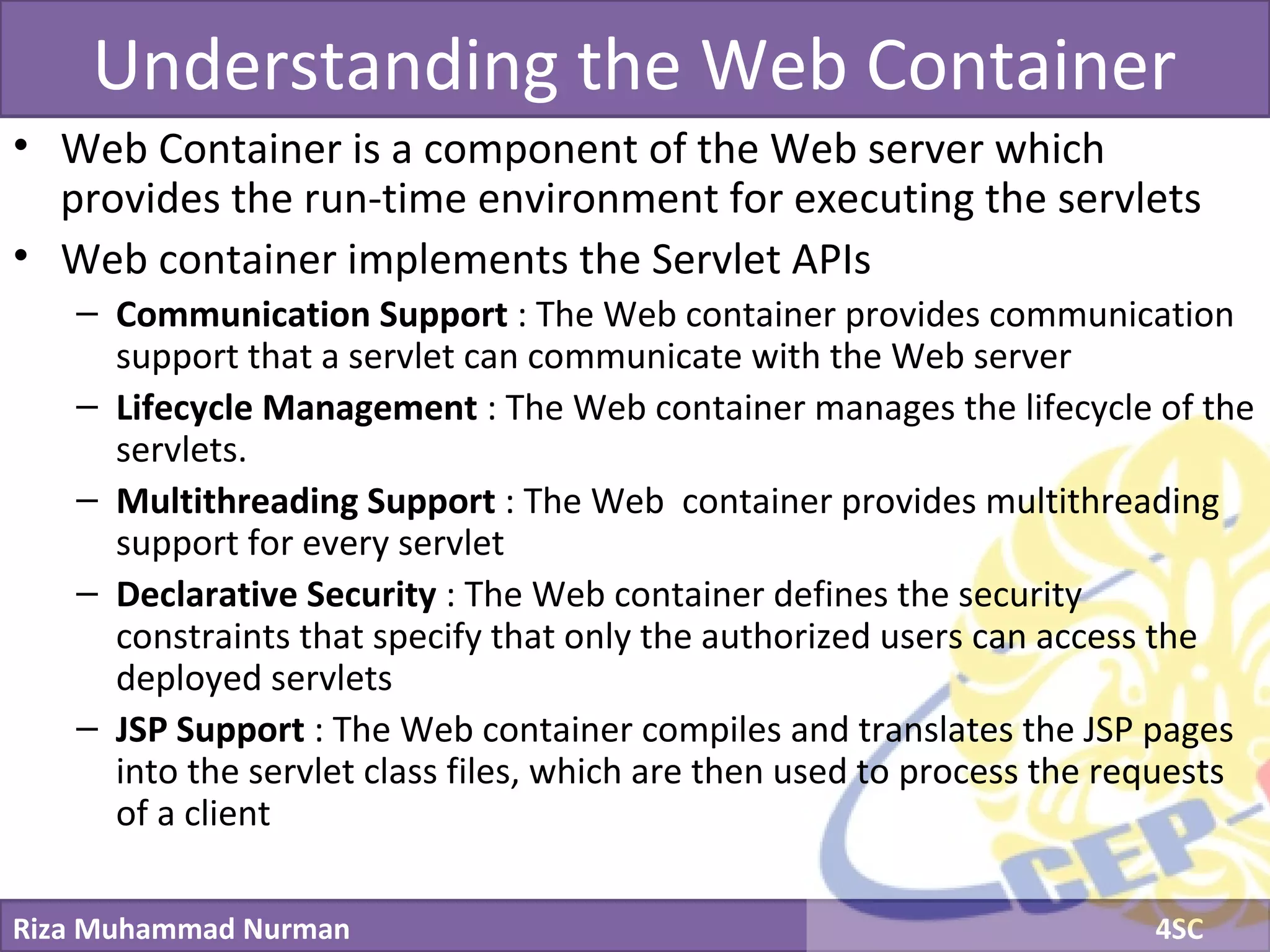
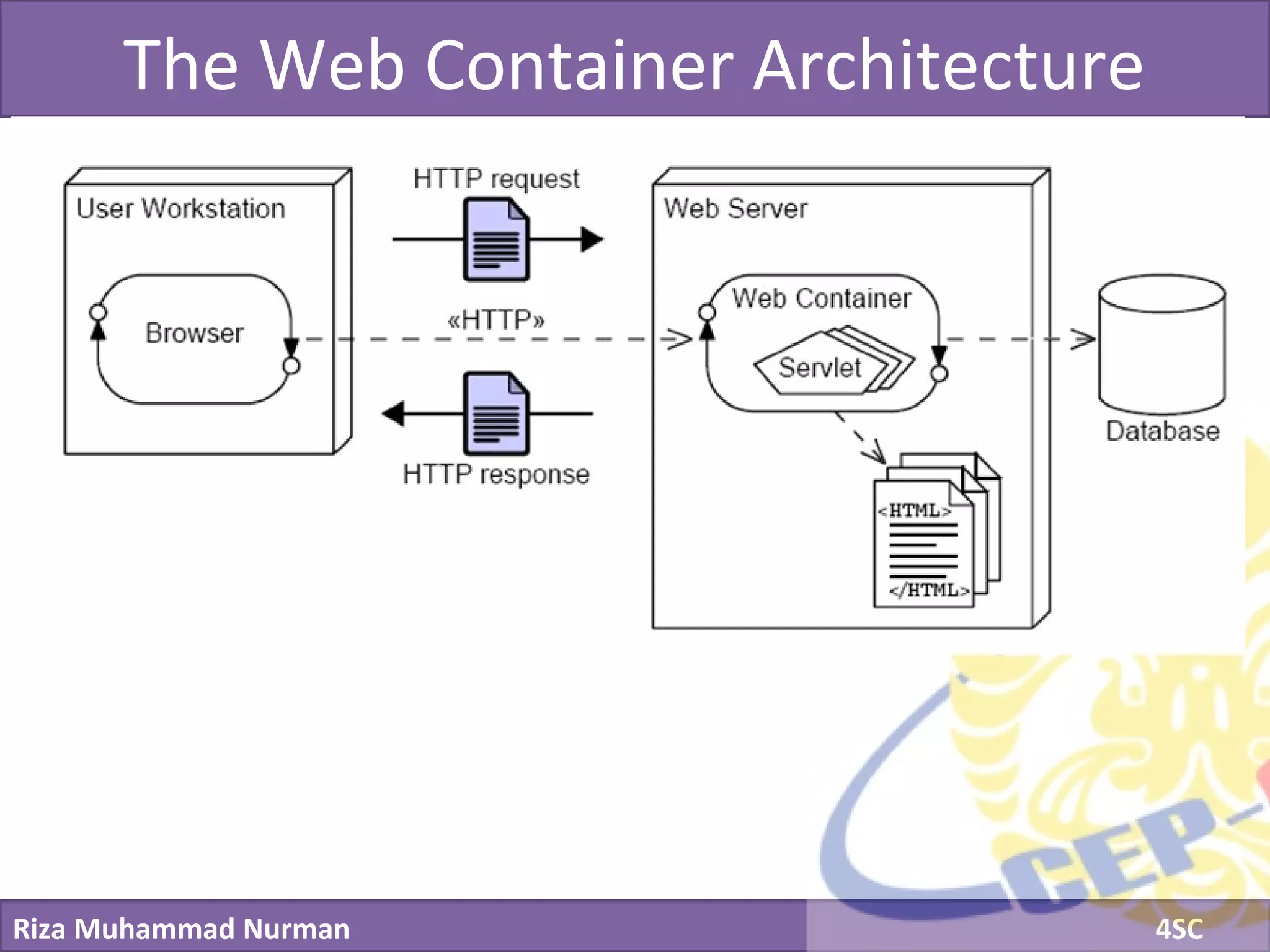
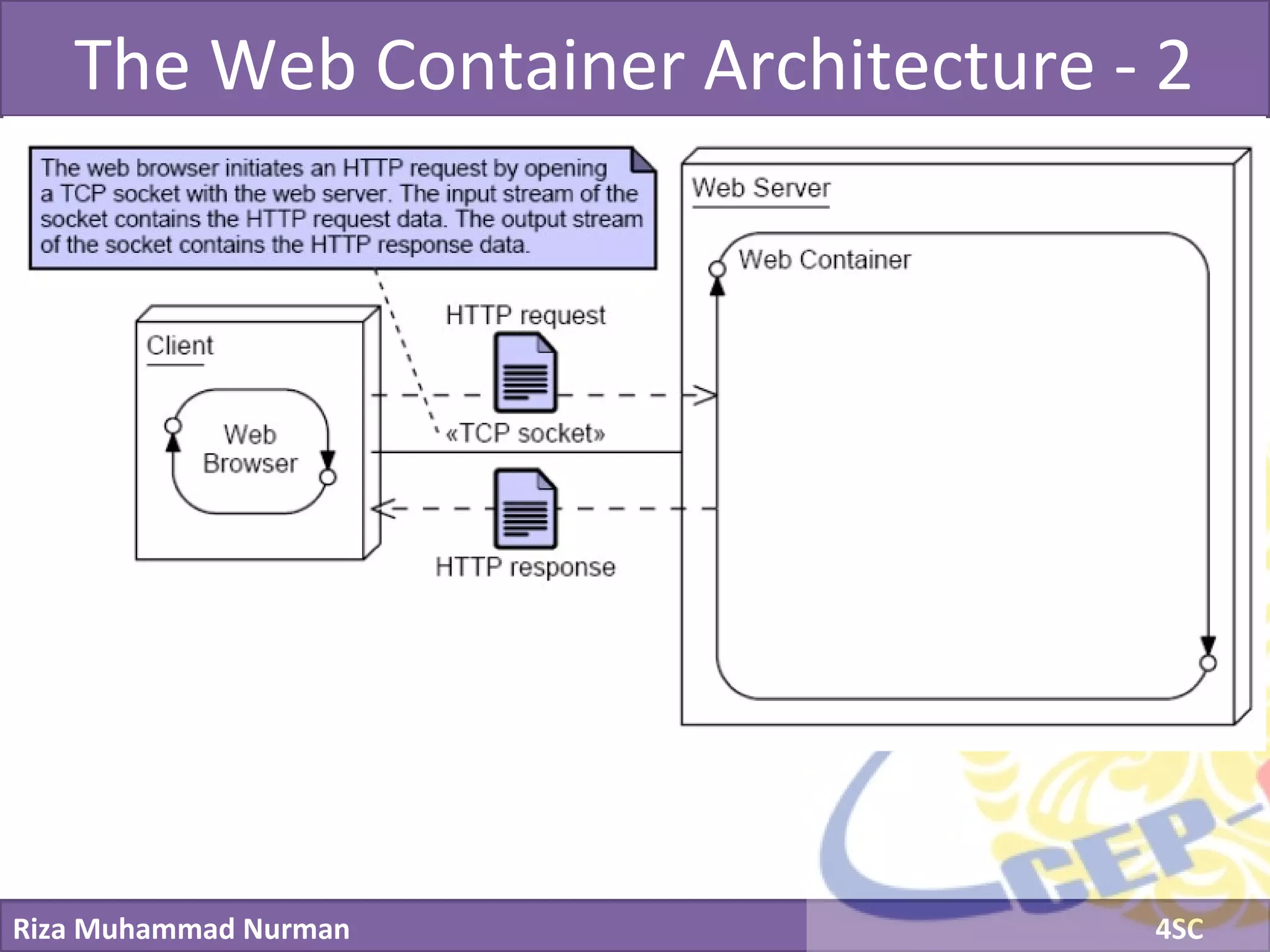
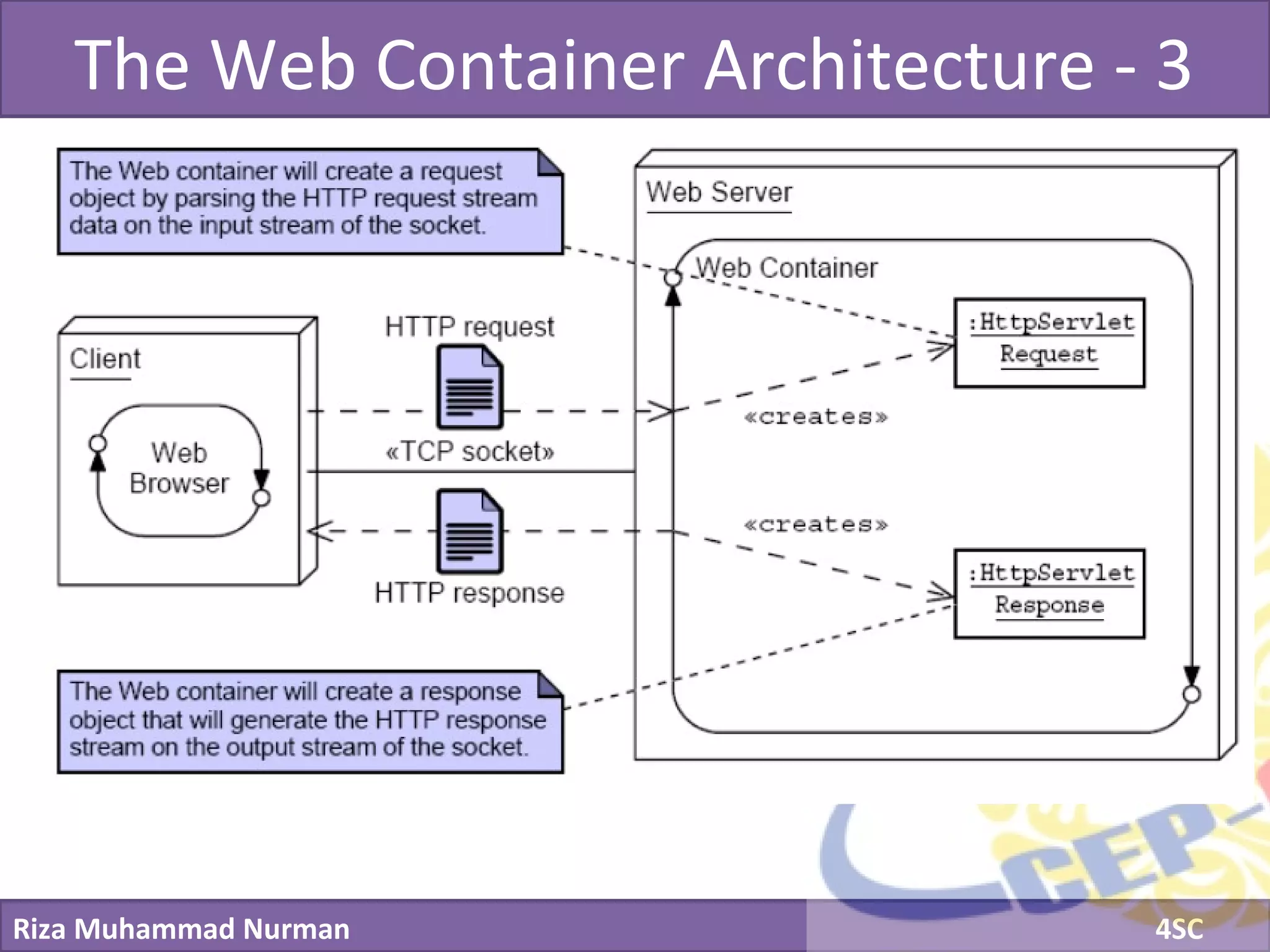
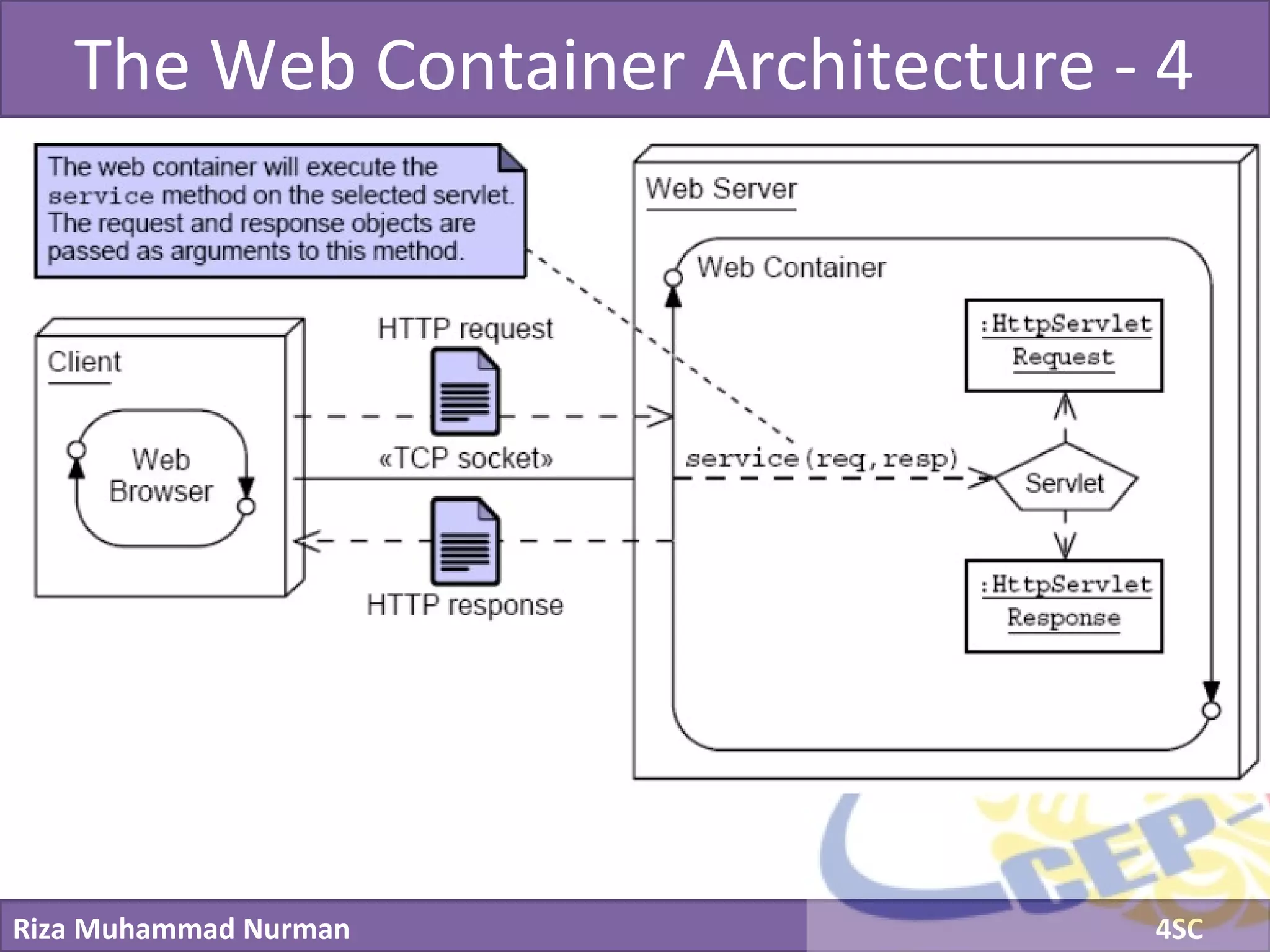
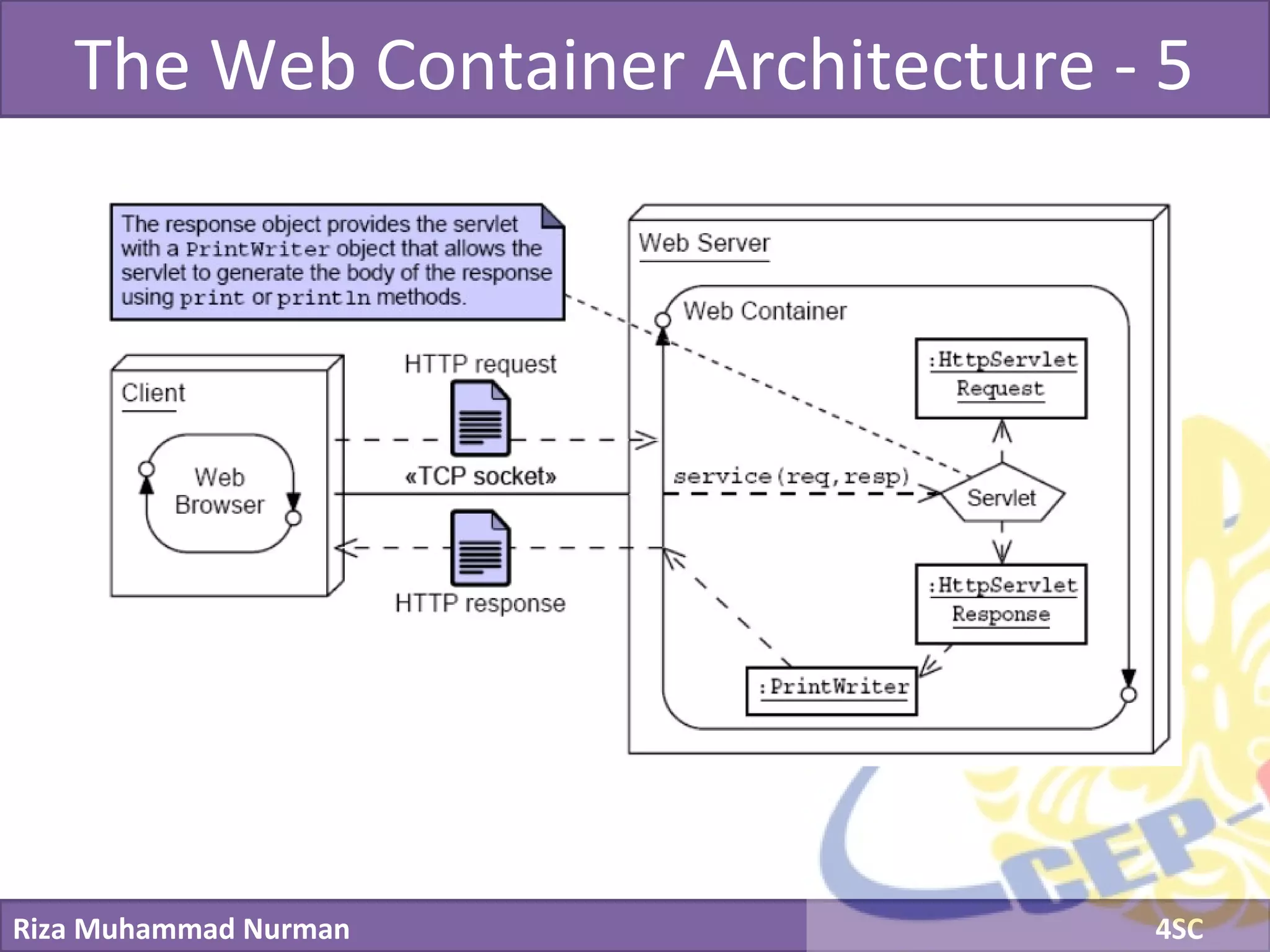
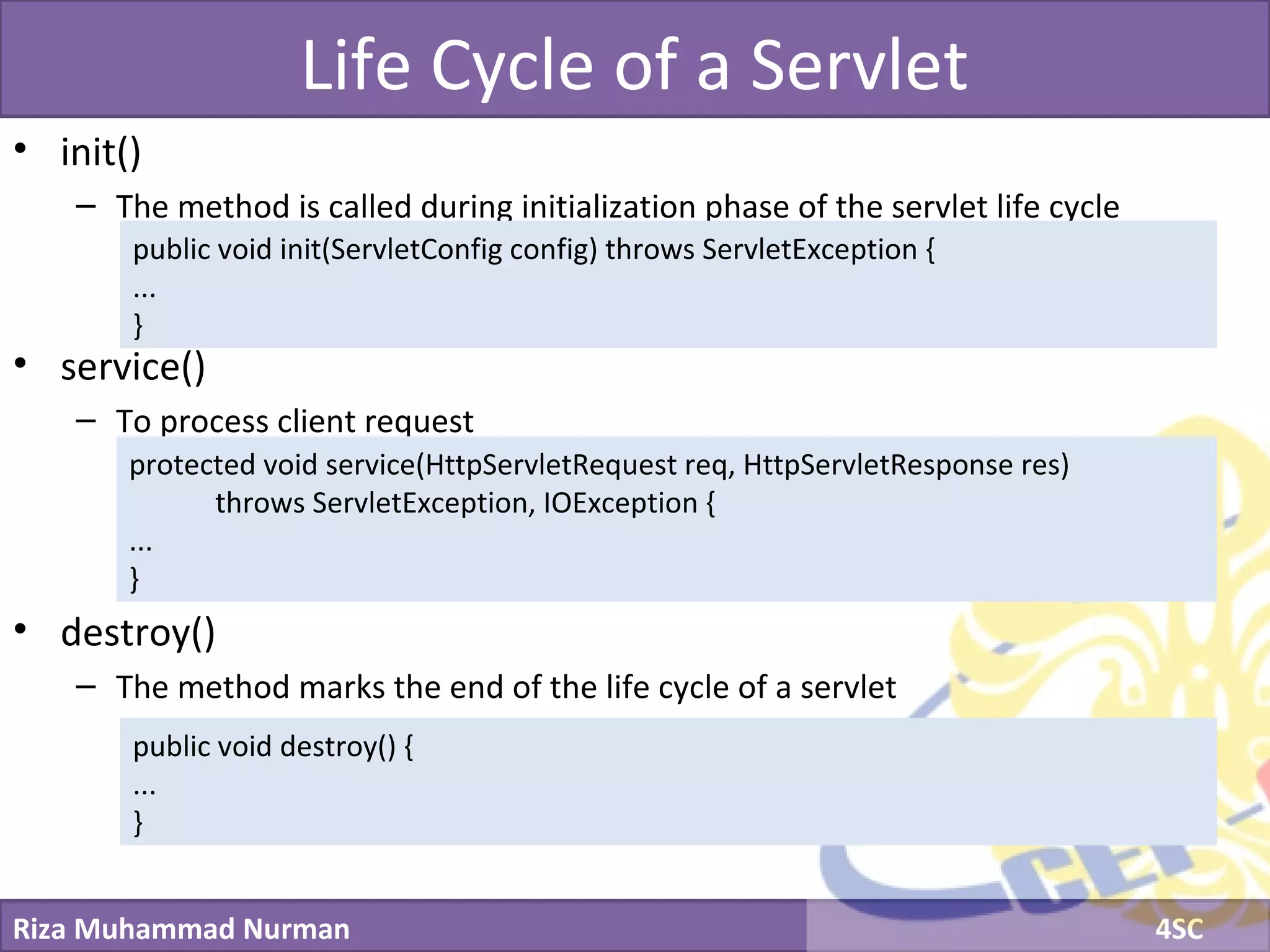
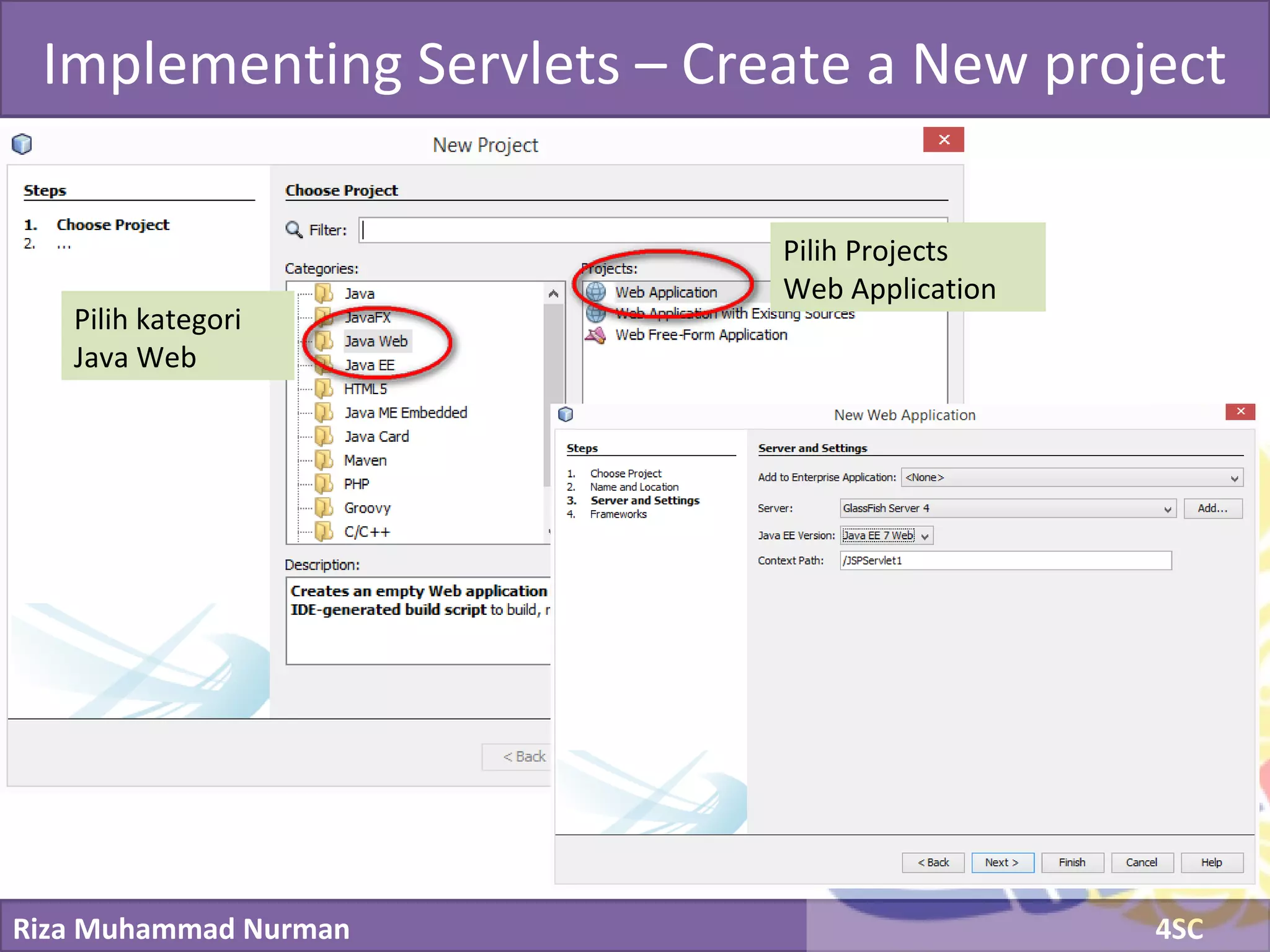
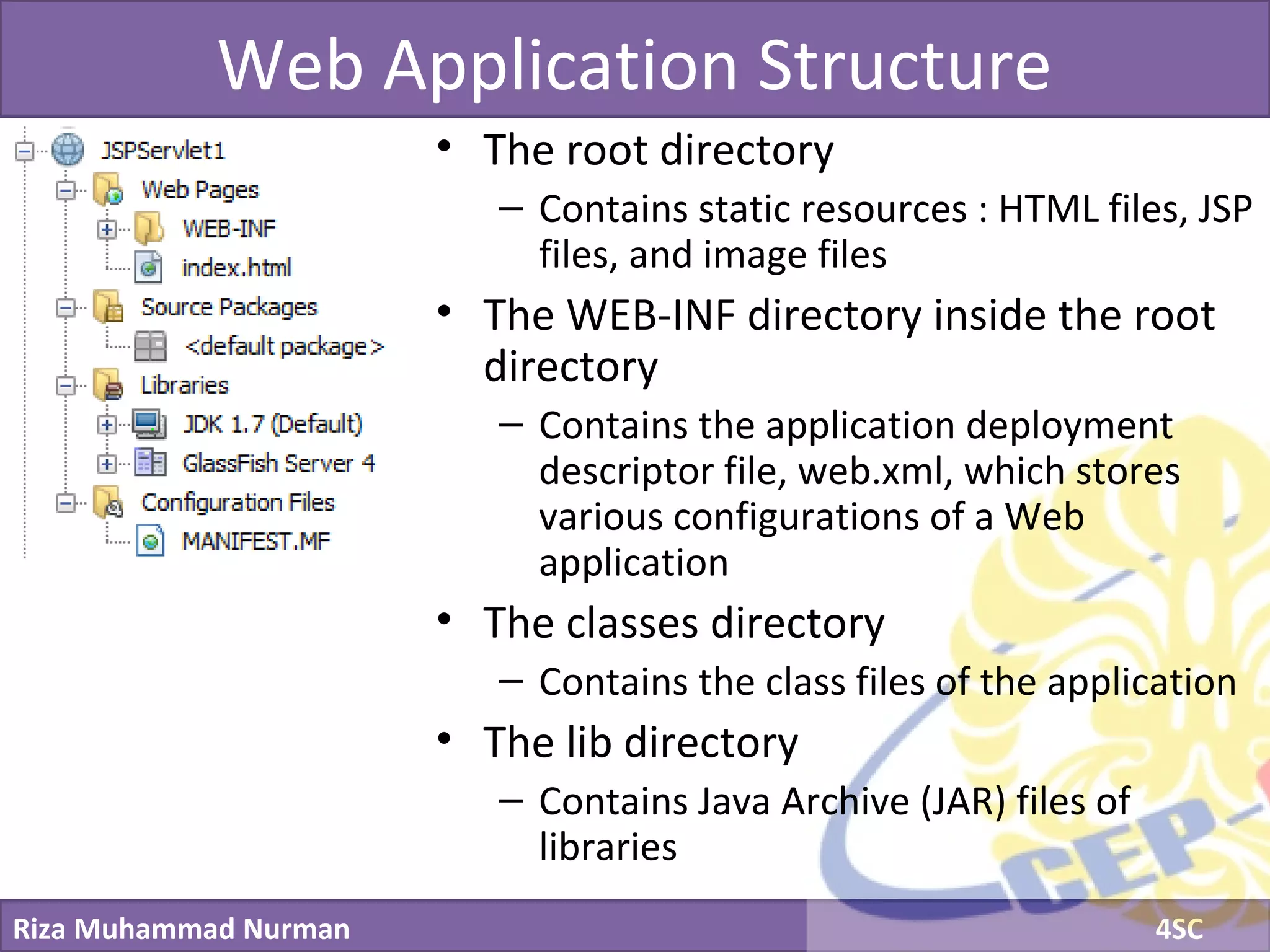
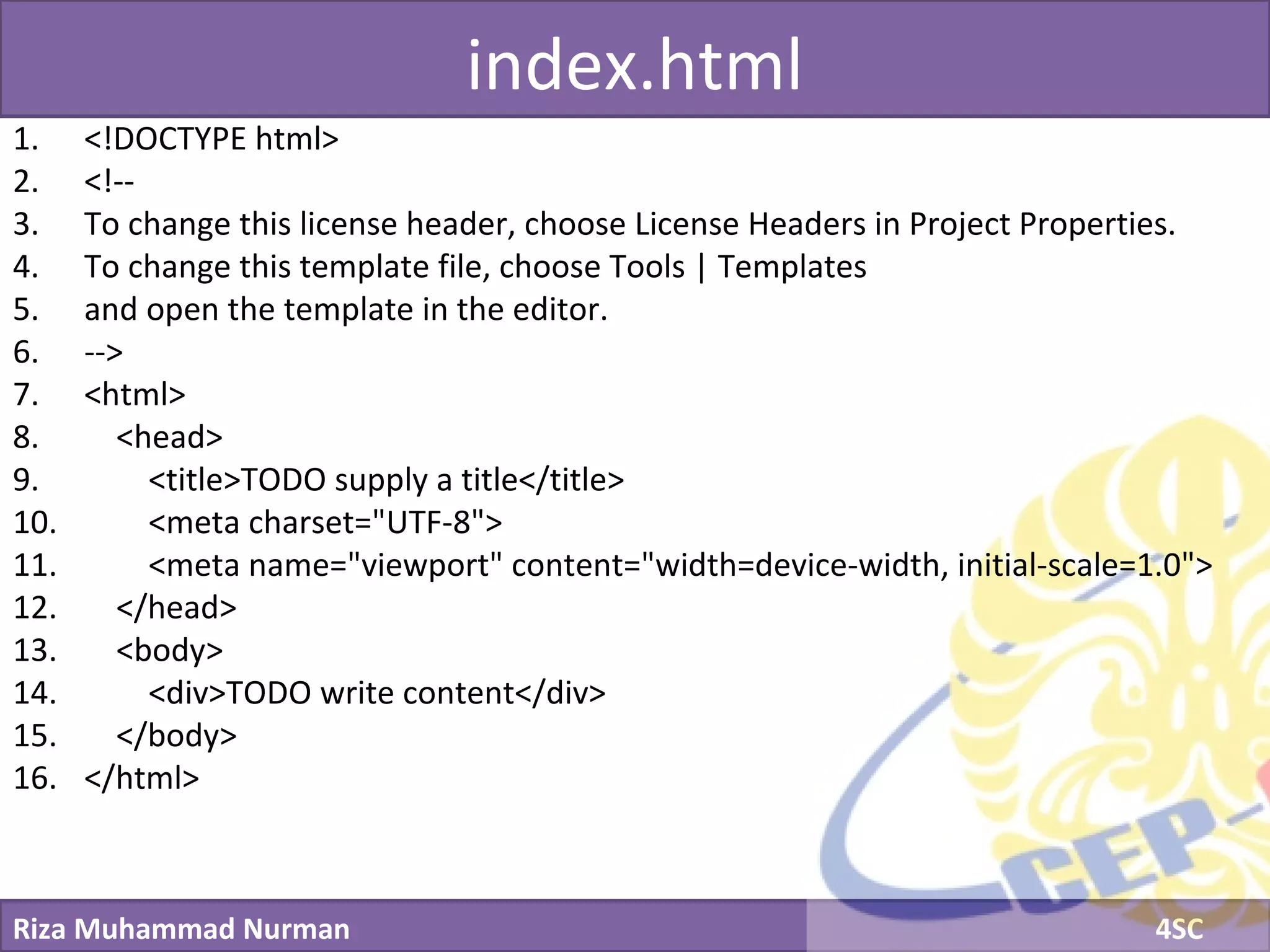
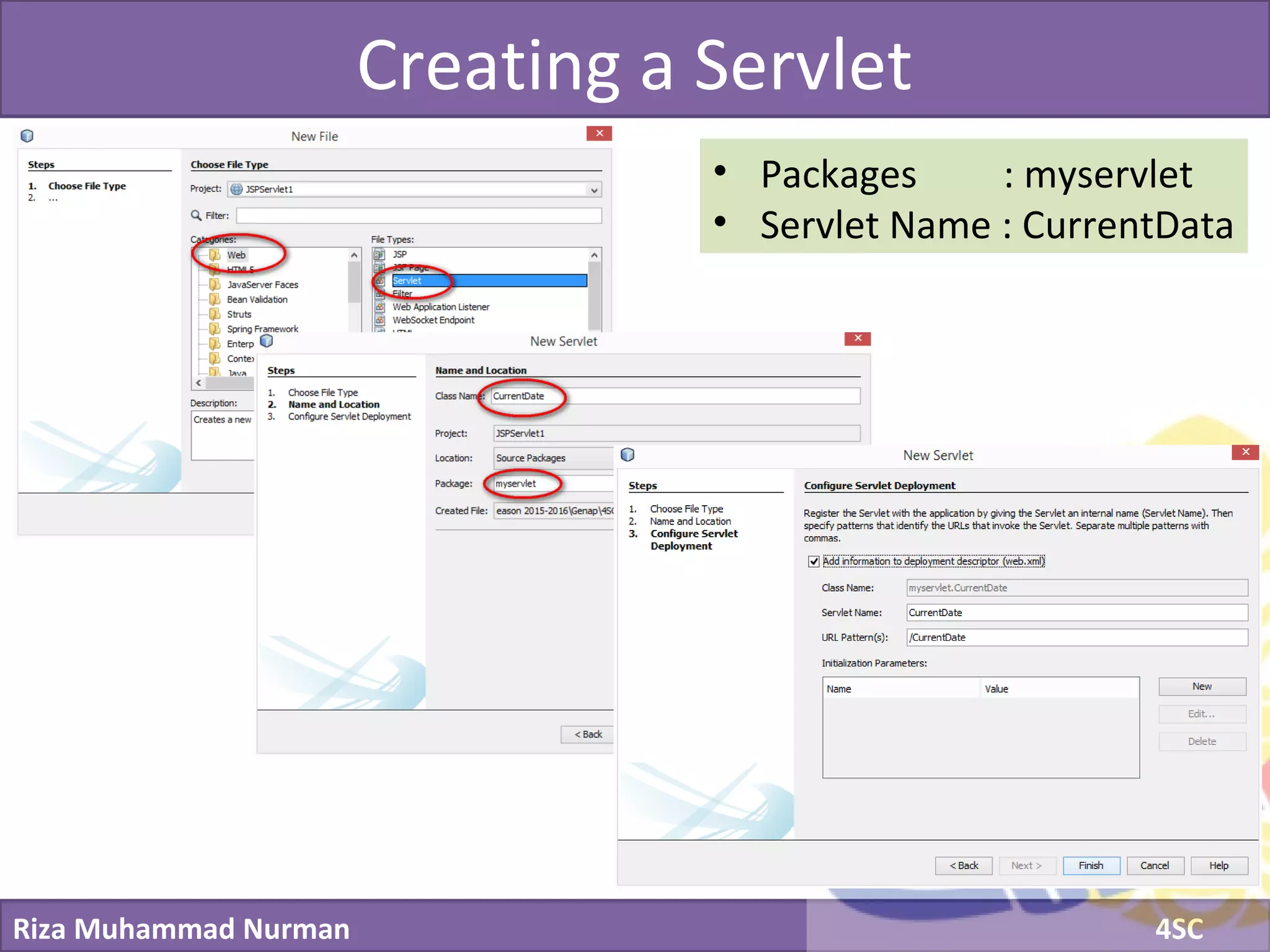
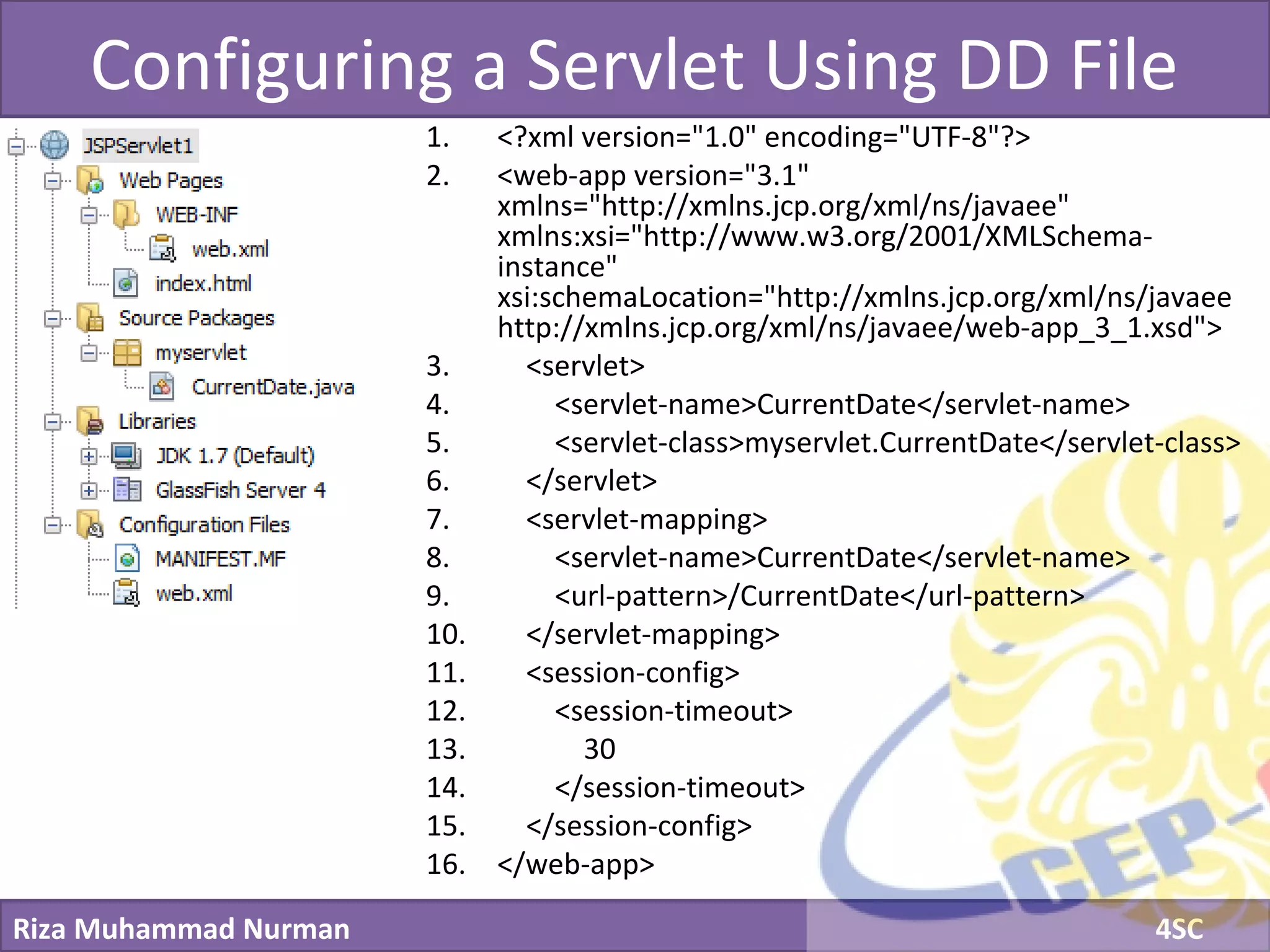
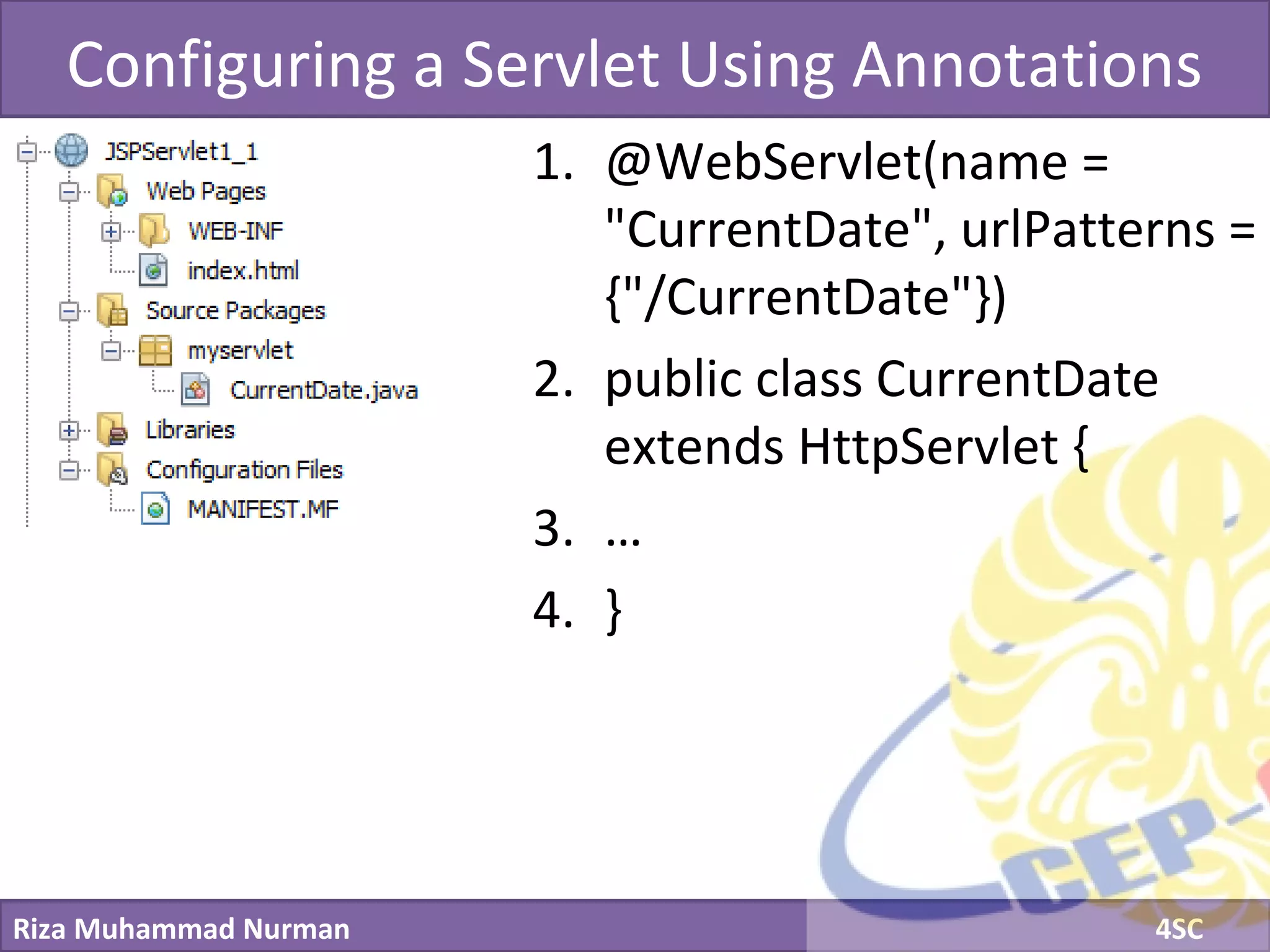
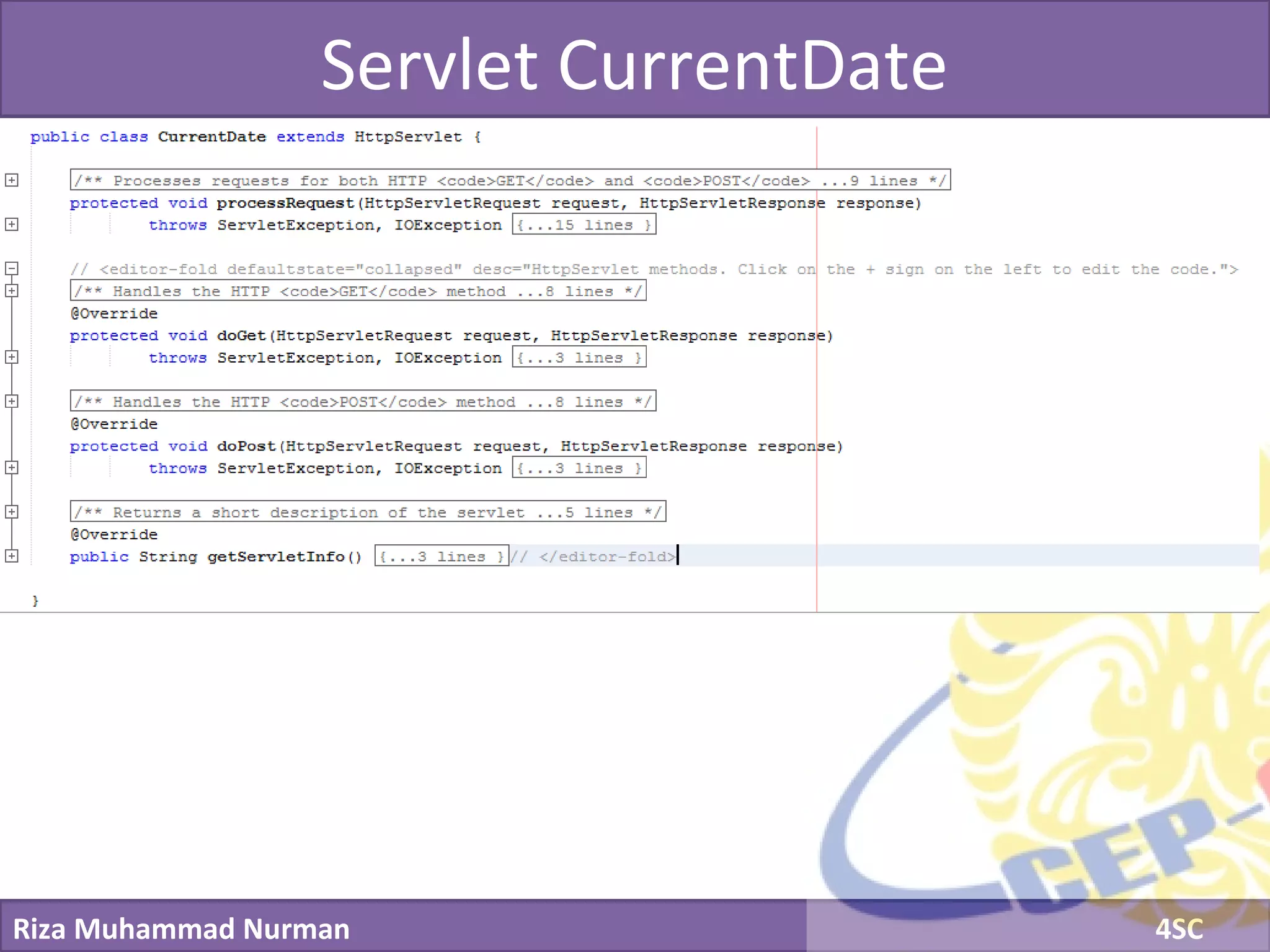
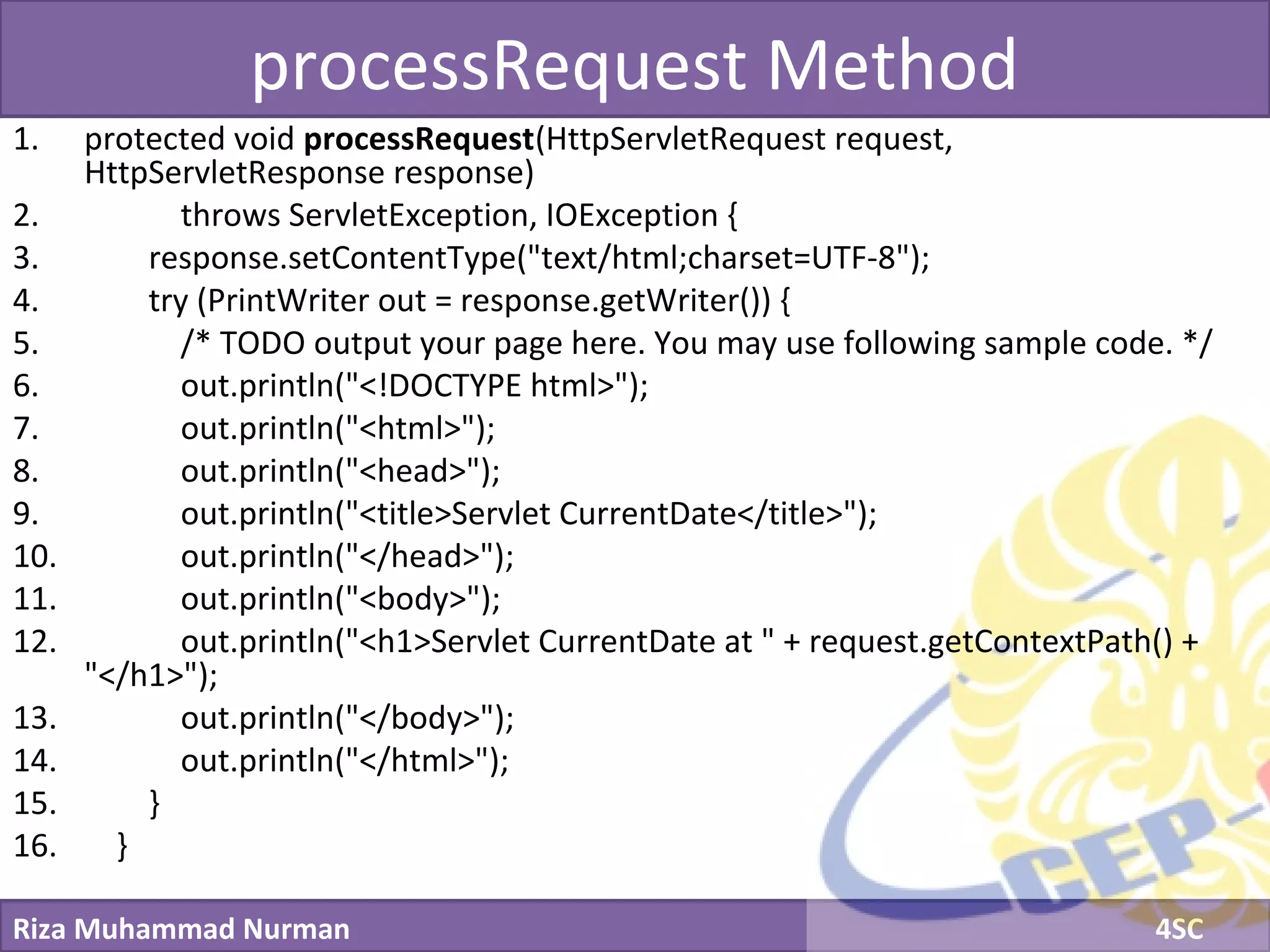
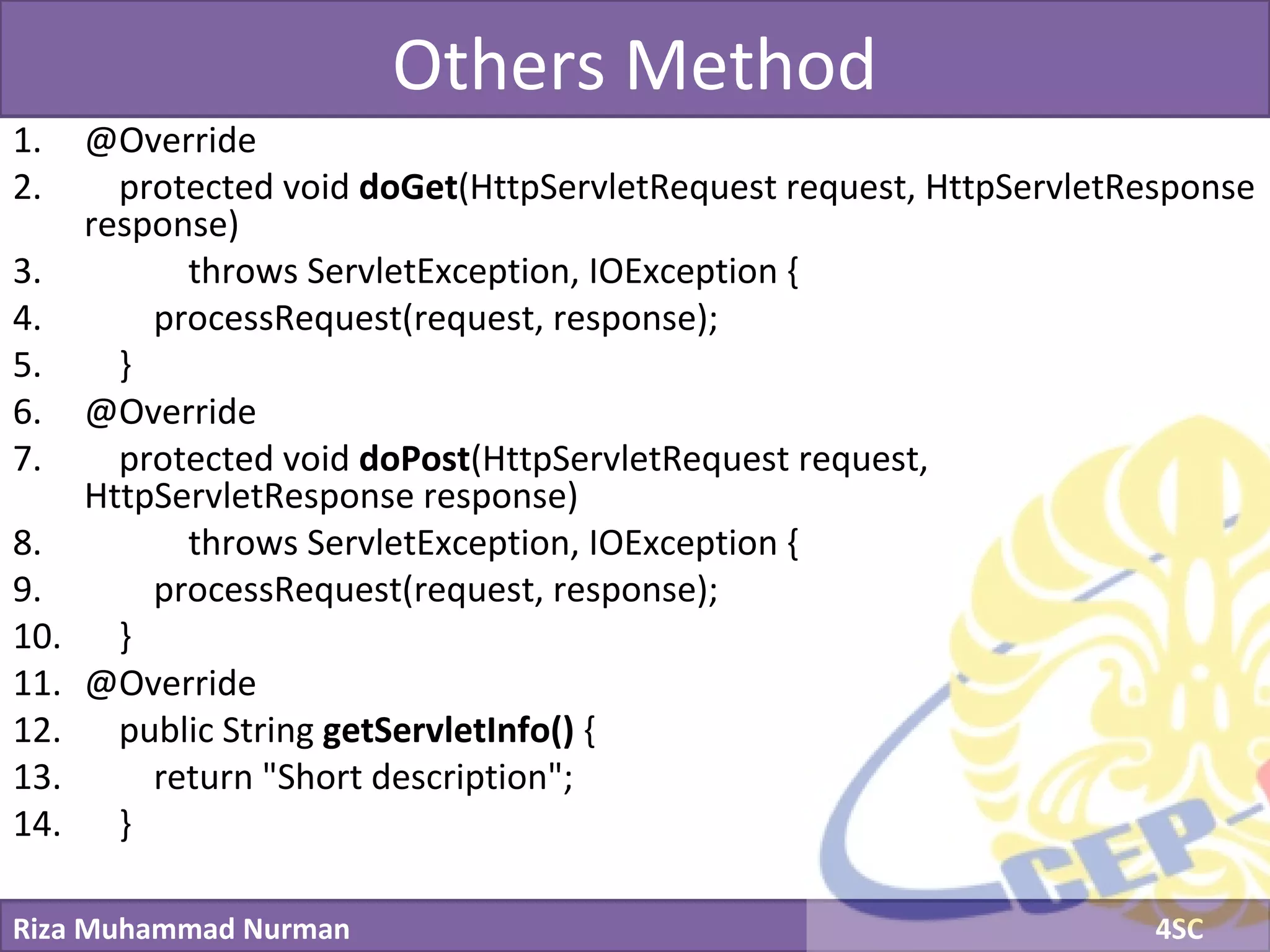
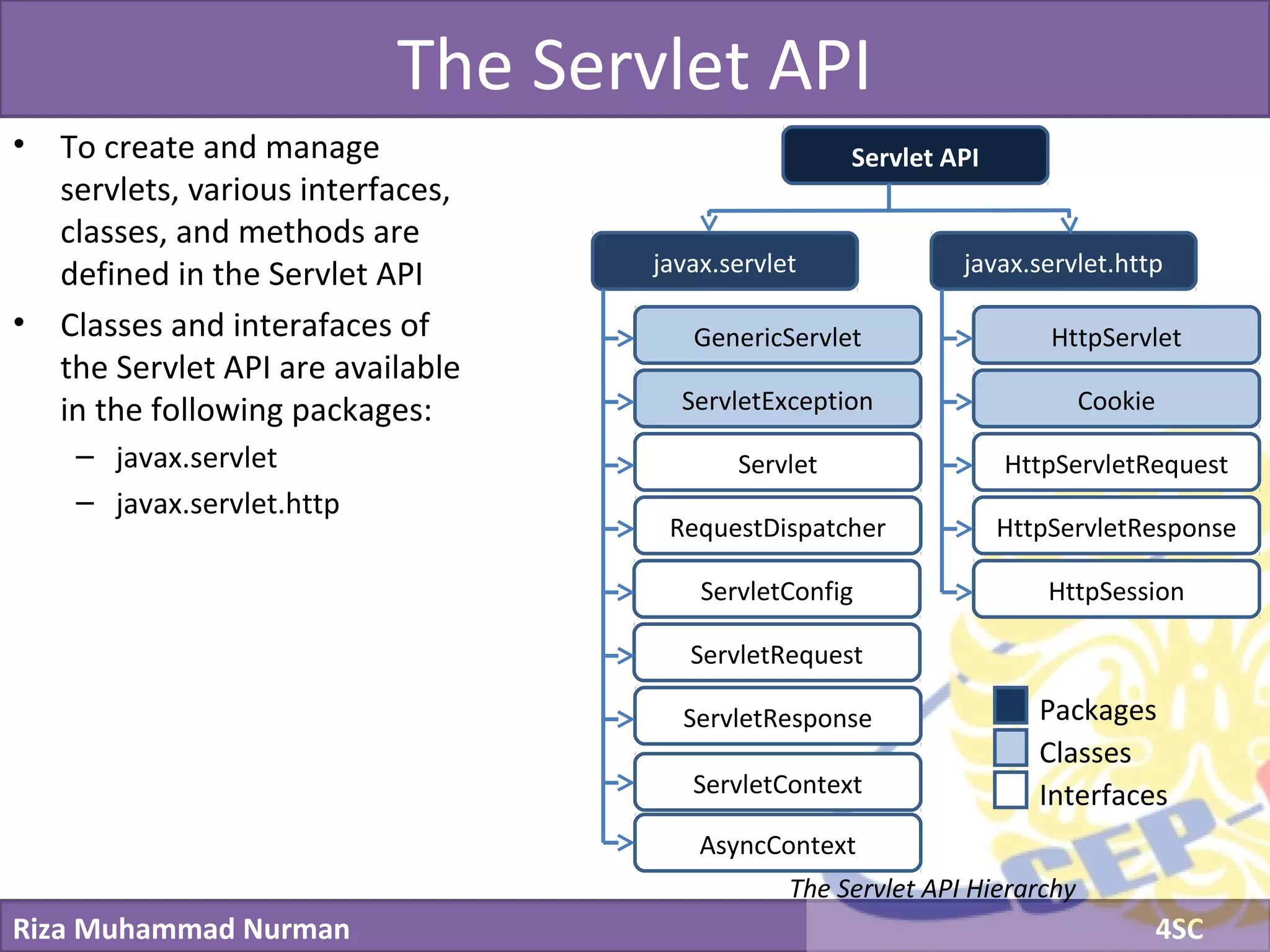
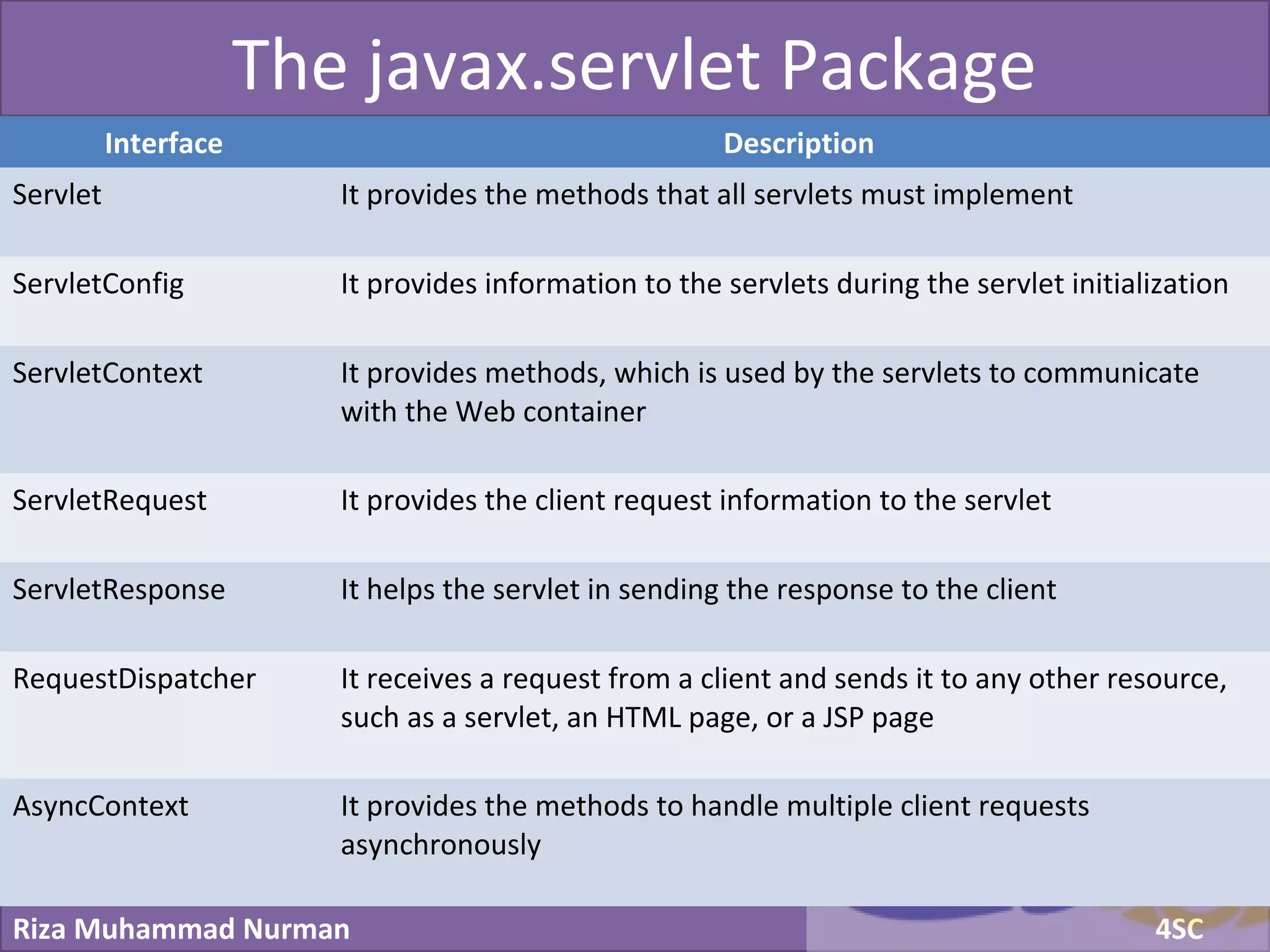
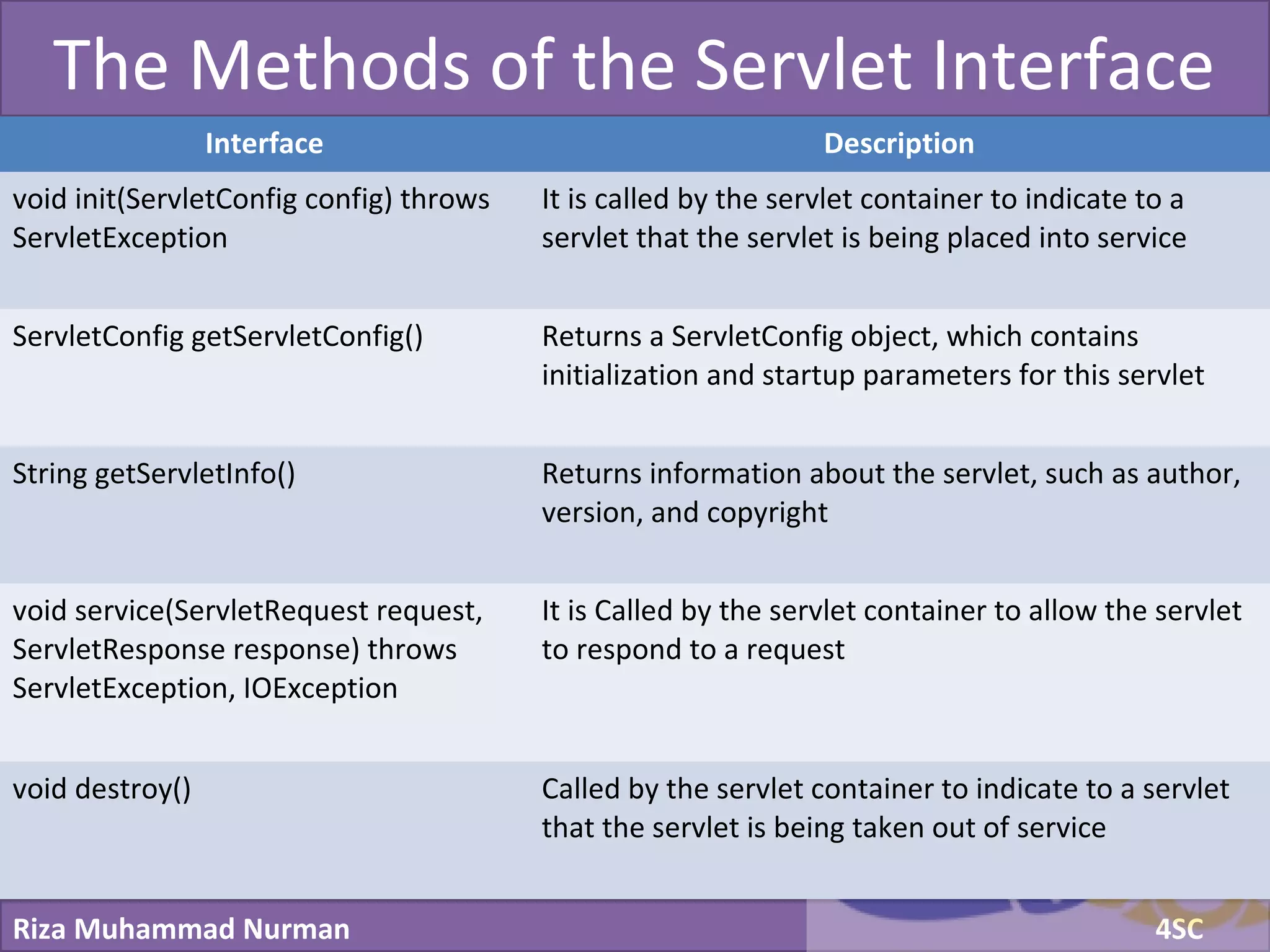
The document discusses servlets and provides examples of implementing servlets. It introduces servlets and their features like being efficient and supporting asynchronous programming. It describes the Servlet API including important interfaces like Servlet, ServletRequest, and ServletResponse. Code snippets show how to create a basic servlet that displays the current date and time. The document also discusses the web container and its role in servlet execution and lifecycle.


![Riza Muhammad Nurman 4SC Click to edit Master title styleThe Methods of the ServletRequest Interface Interface Description String getParameter(String paramName) Returns a String object that specifies the value of a particular request parameter public String[] getParameterValues(String paramName) Returns an array of String objects that contains all the values of the request parameter public Enumeration getParameterNames() Returns an Enumeration object containing all the parameter names as String objects that `request contains public String getRemoteHost() Returns a String object that specifies the full-qualified name of the computer from which the request is sent public String getRemoteAddr() Returns a String object that specifies the IP address of the computer from which the request is sent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/q7m2chapter2-160322015257/75/Exploring-the-Java-Servlet-Technology-7-2048.jpg)