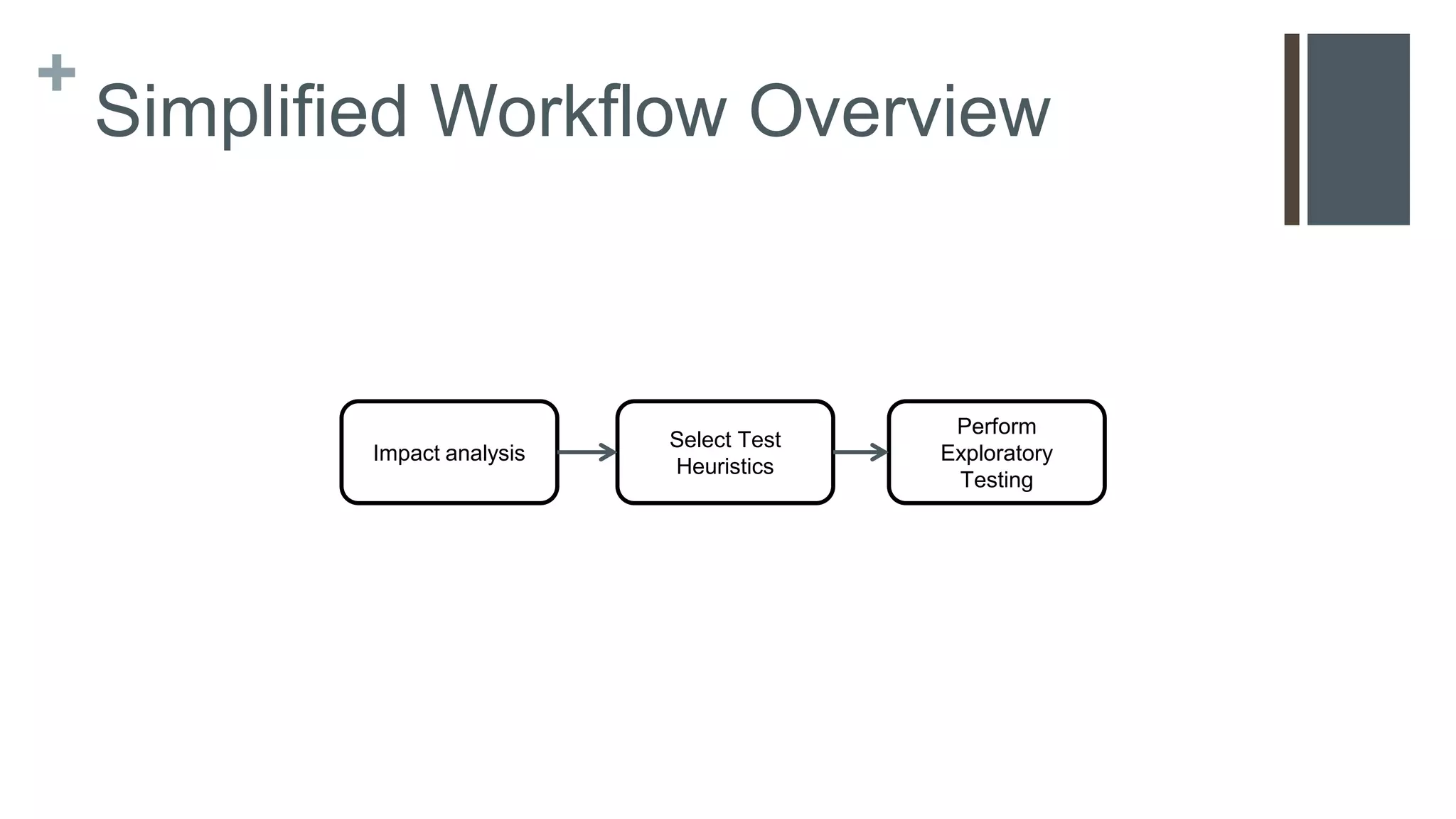
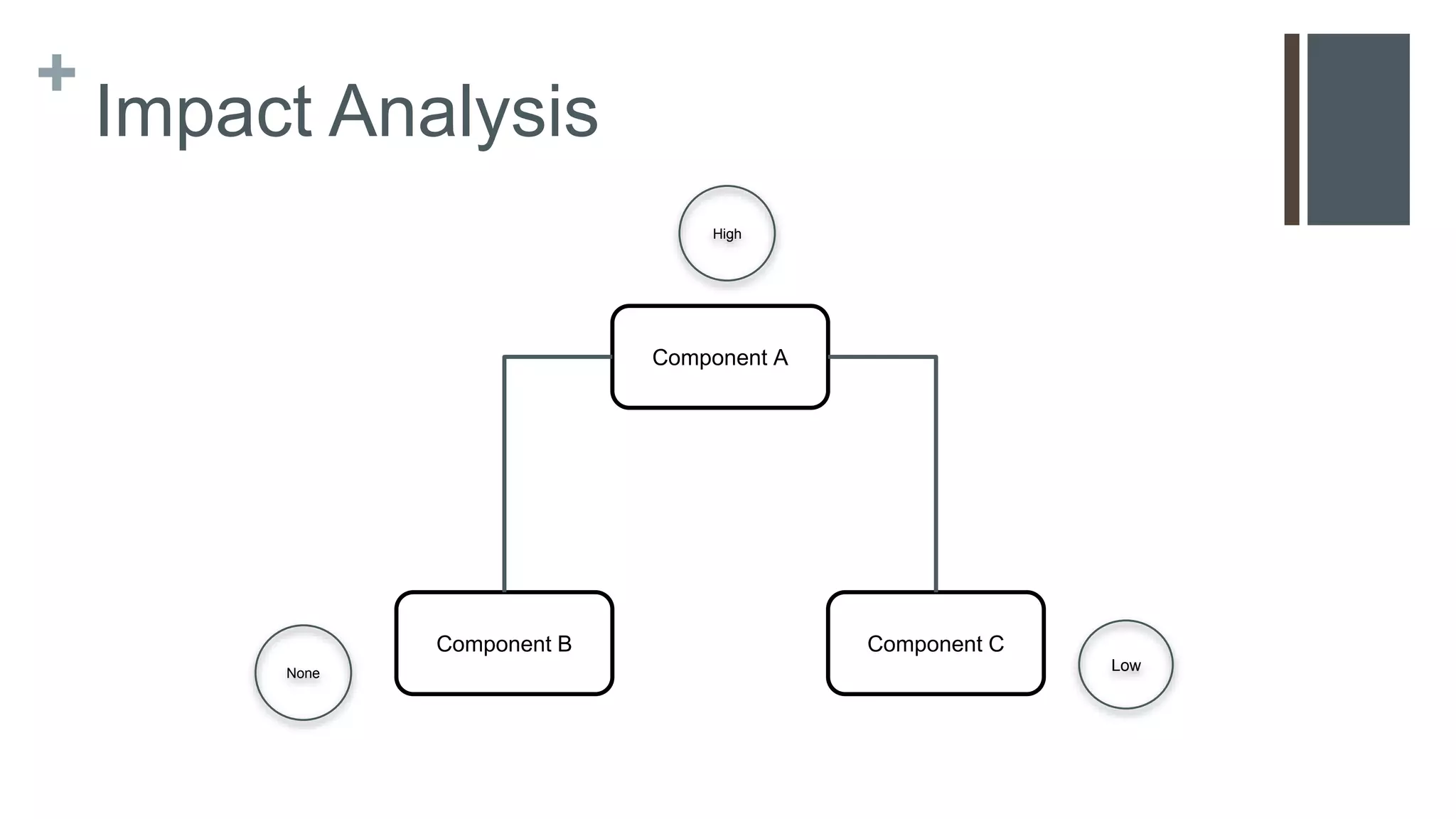
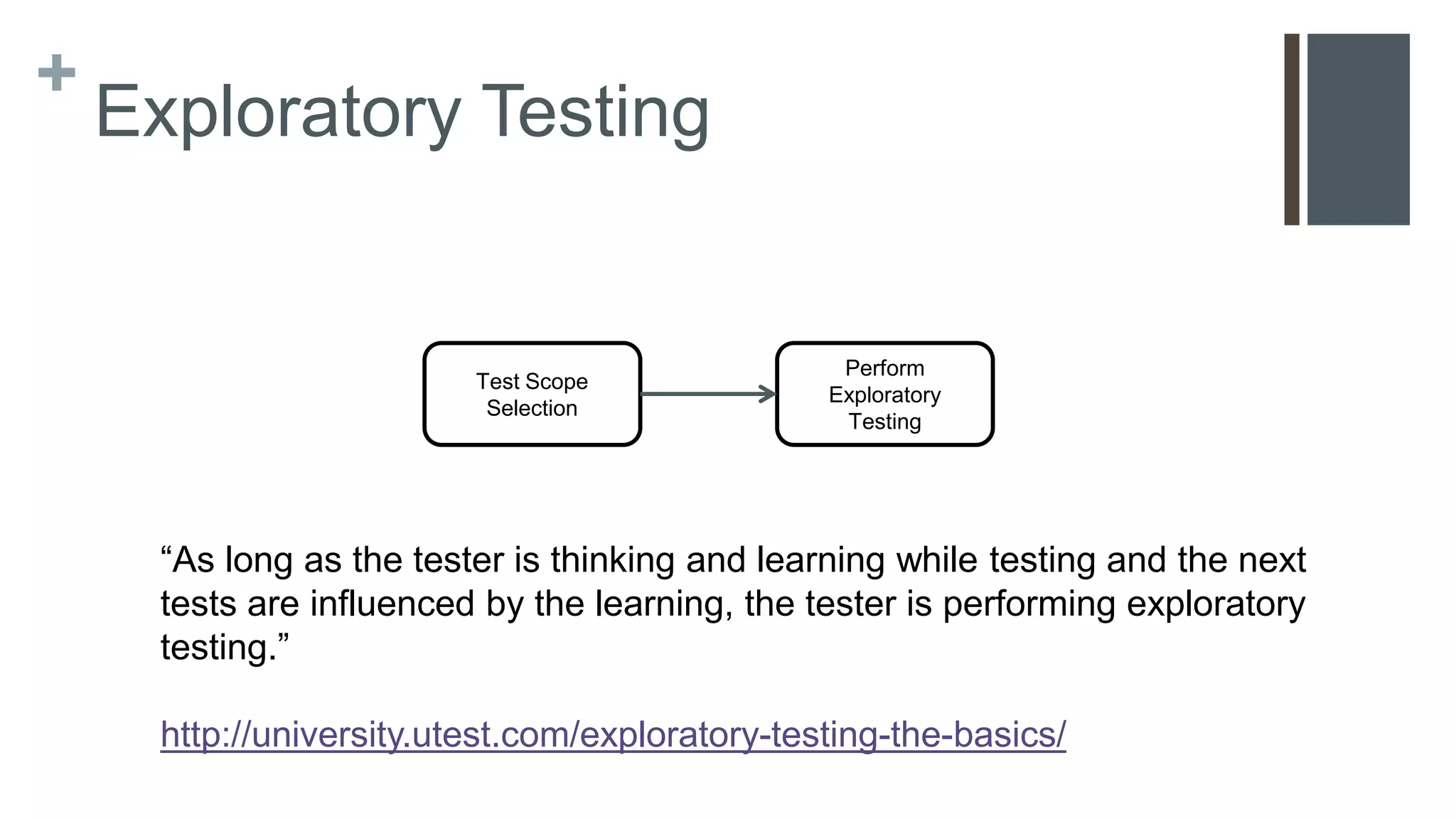
This document provides a simplified introduction to exploratory testing for developers in an agile context, focusing on practical steps to begin testing their code. It outlines a workflow involving impact analysis and the selection of relevant test techniques based on the extent of changes made to features. The conclusion emphasizes that this is a foundational overview with additional resources for further learning.