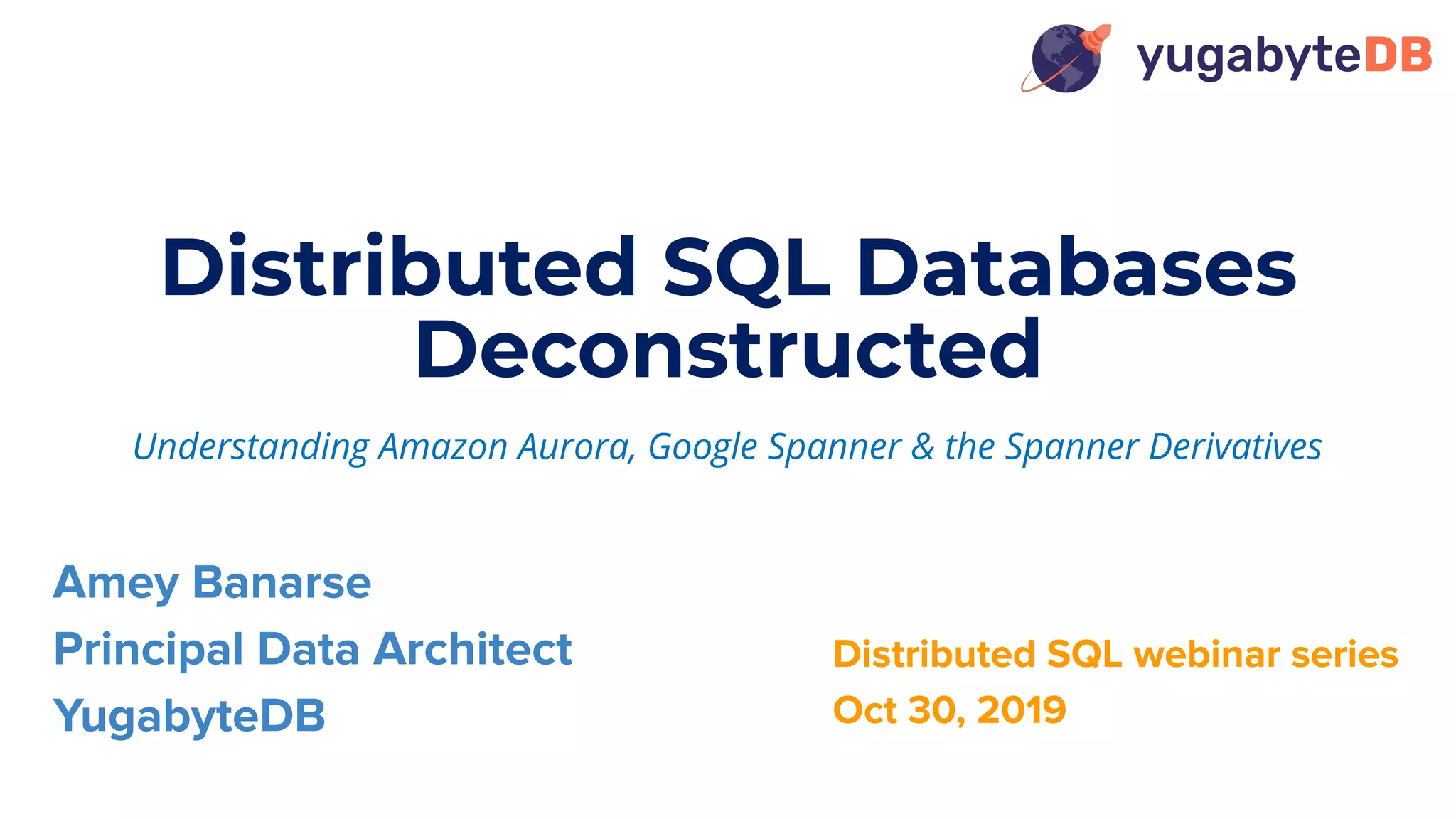
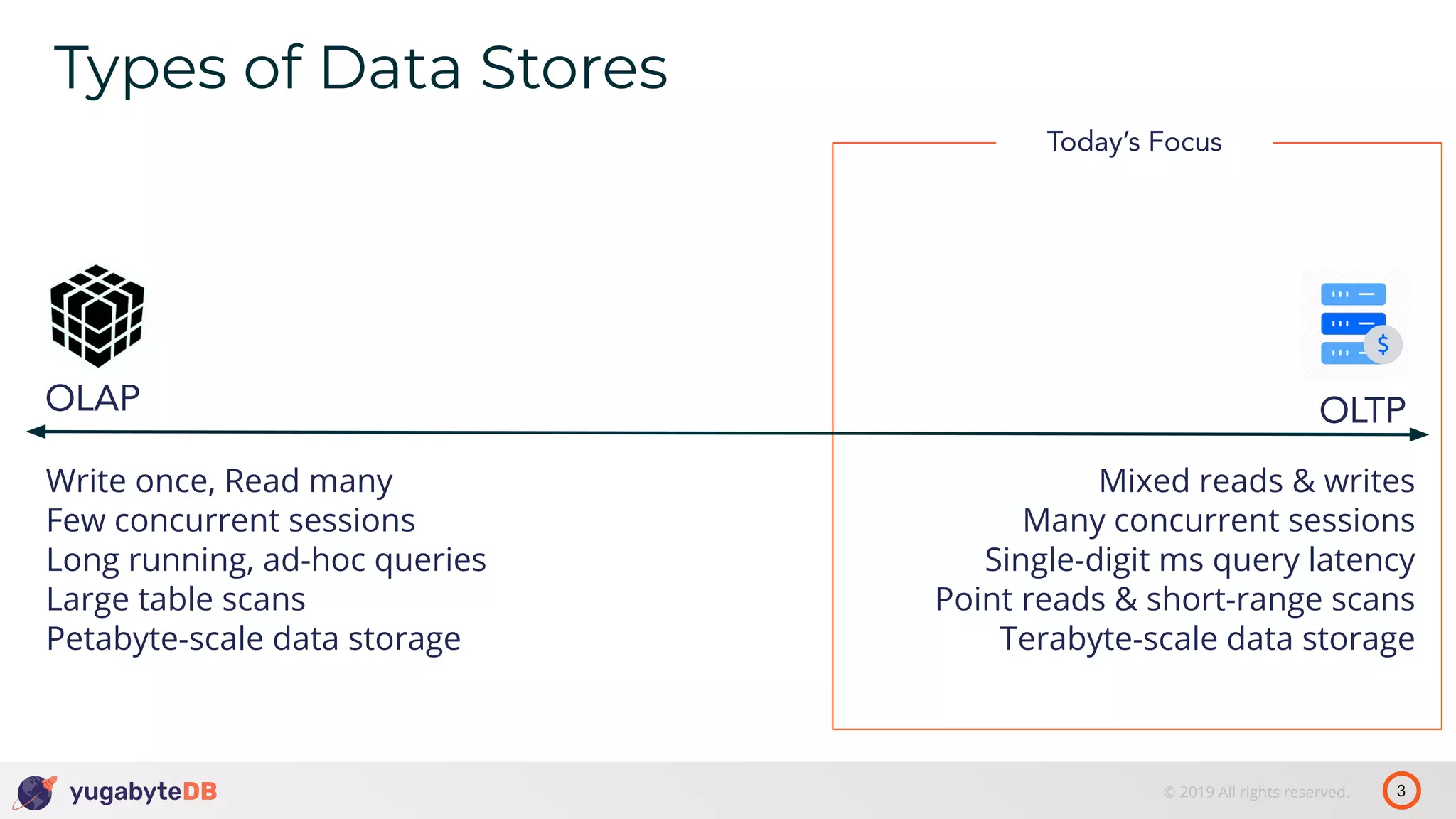
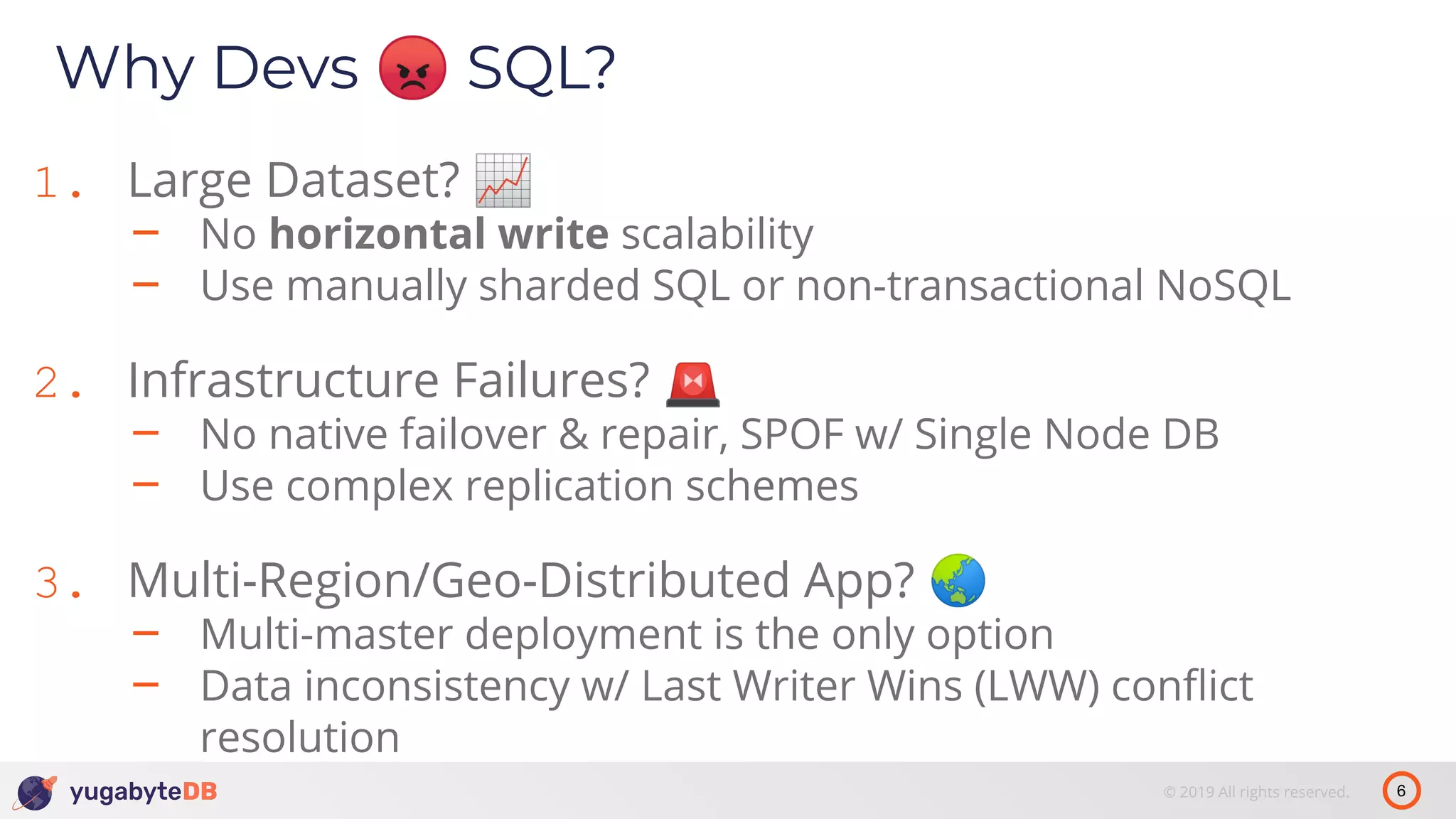
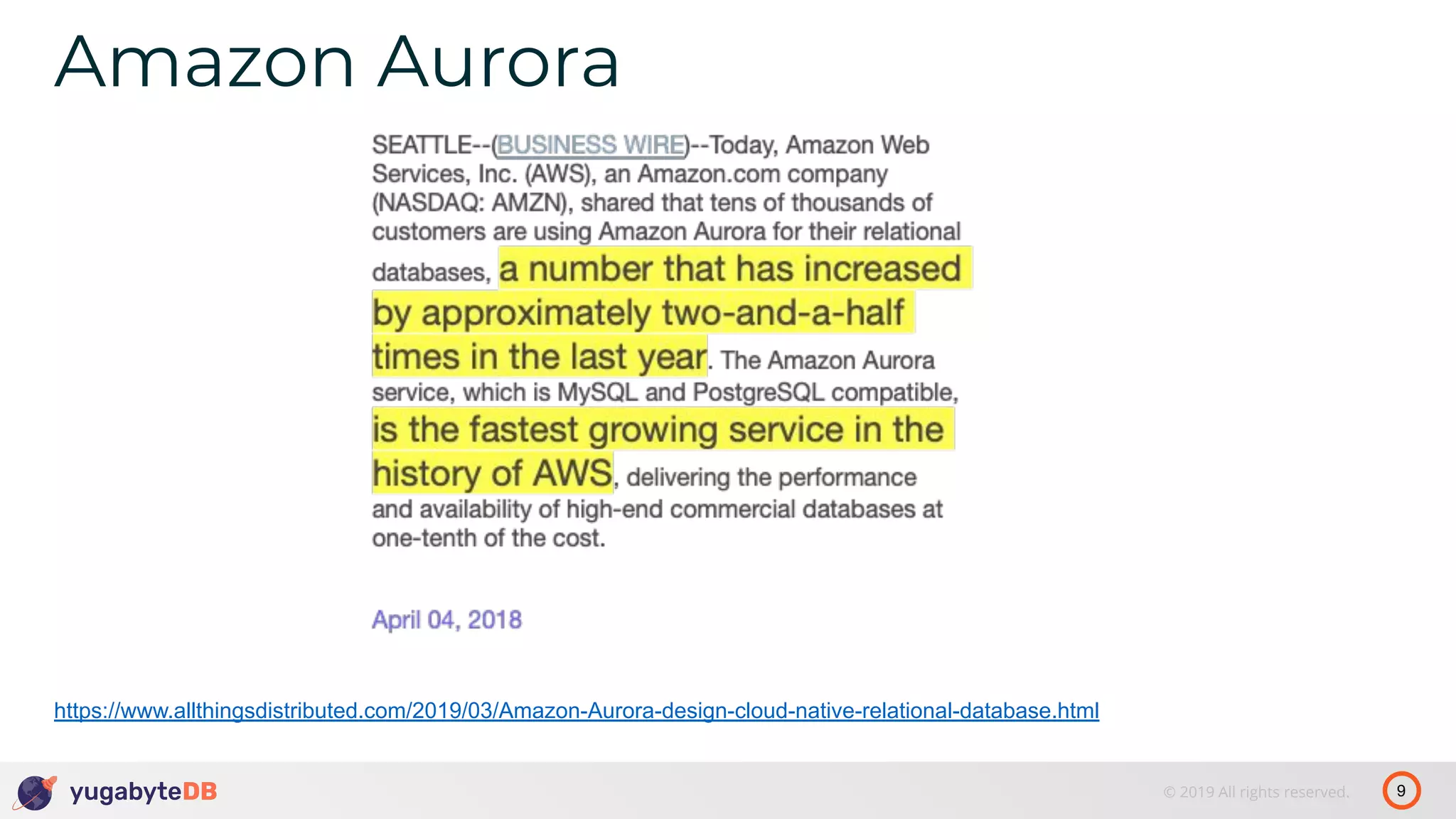
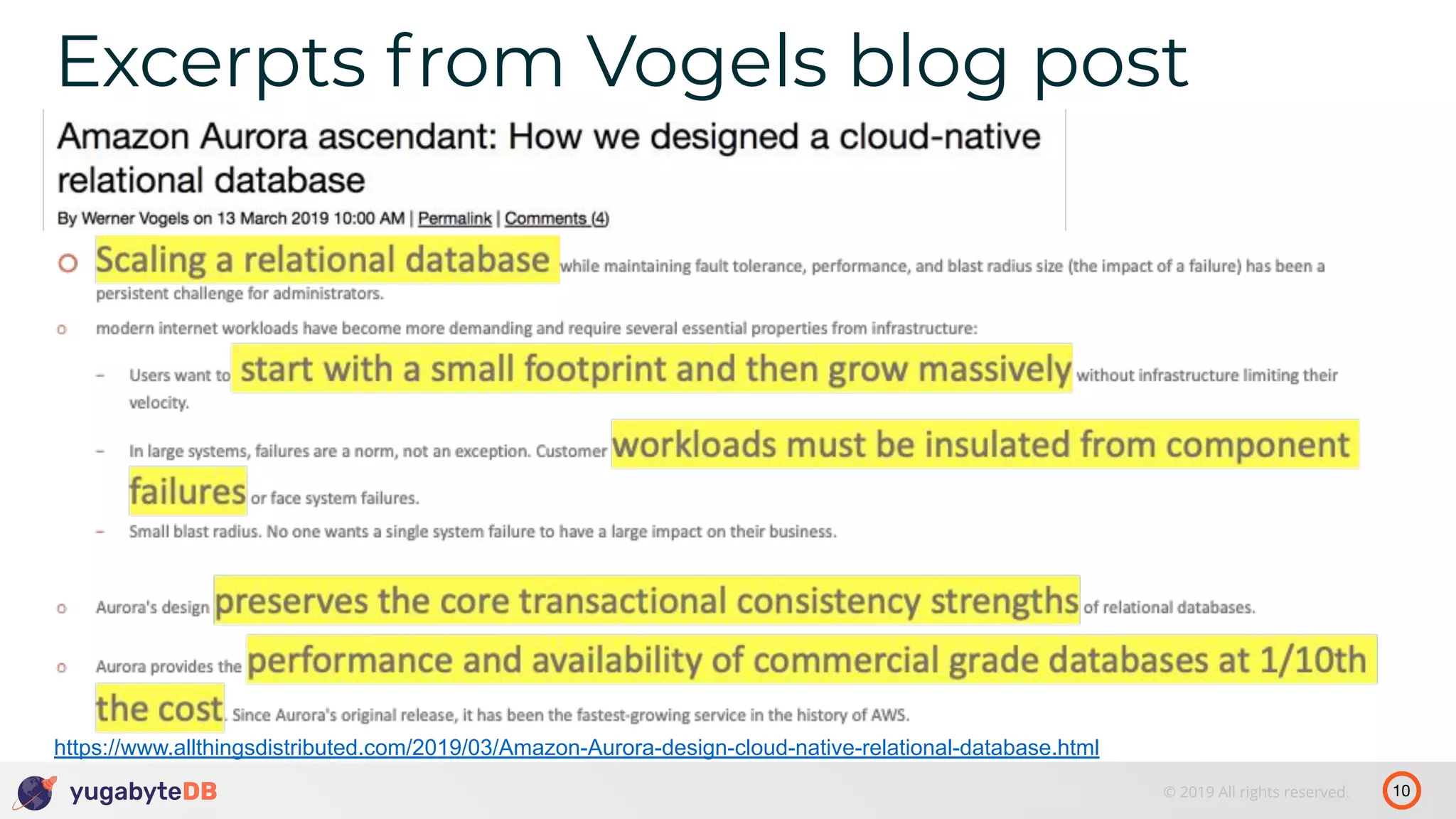
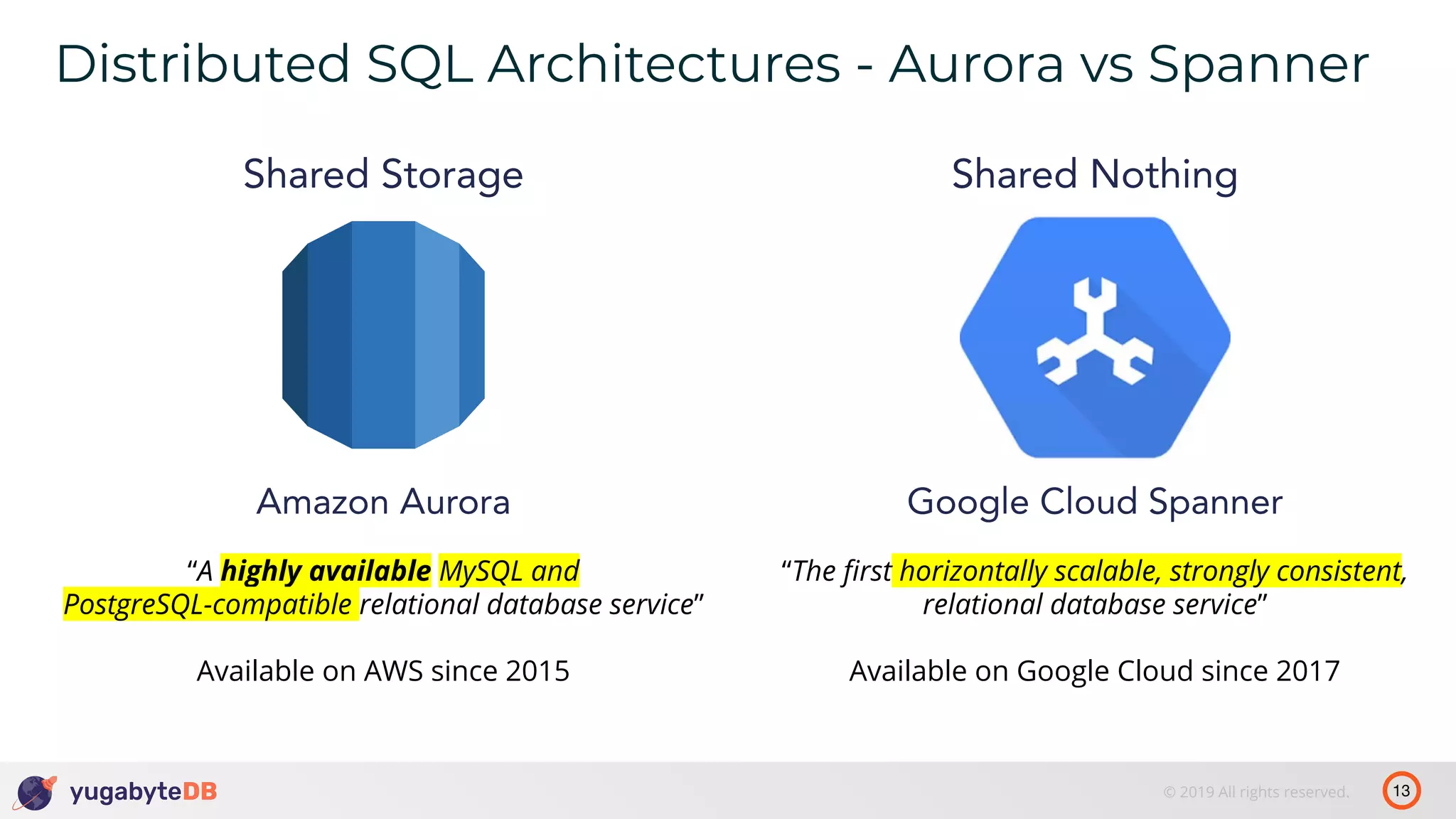
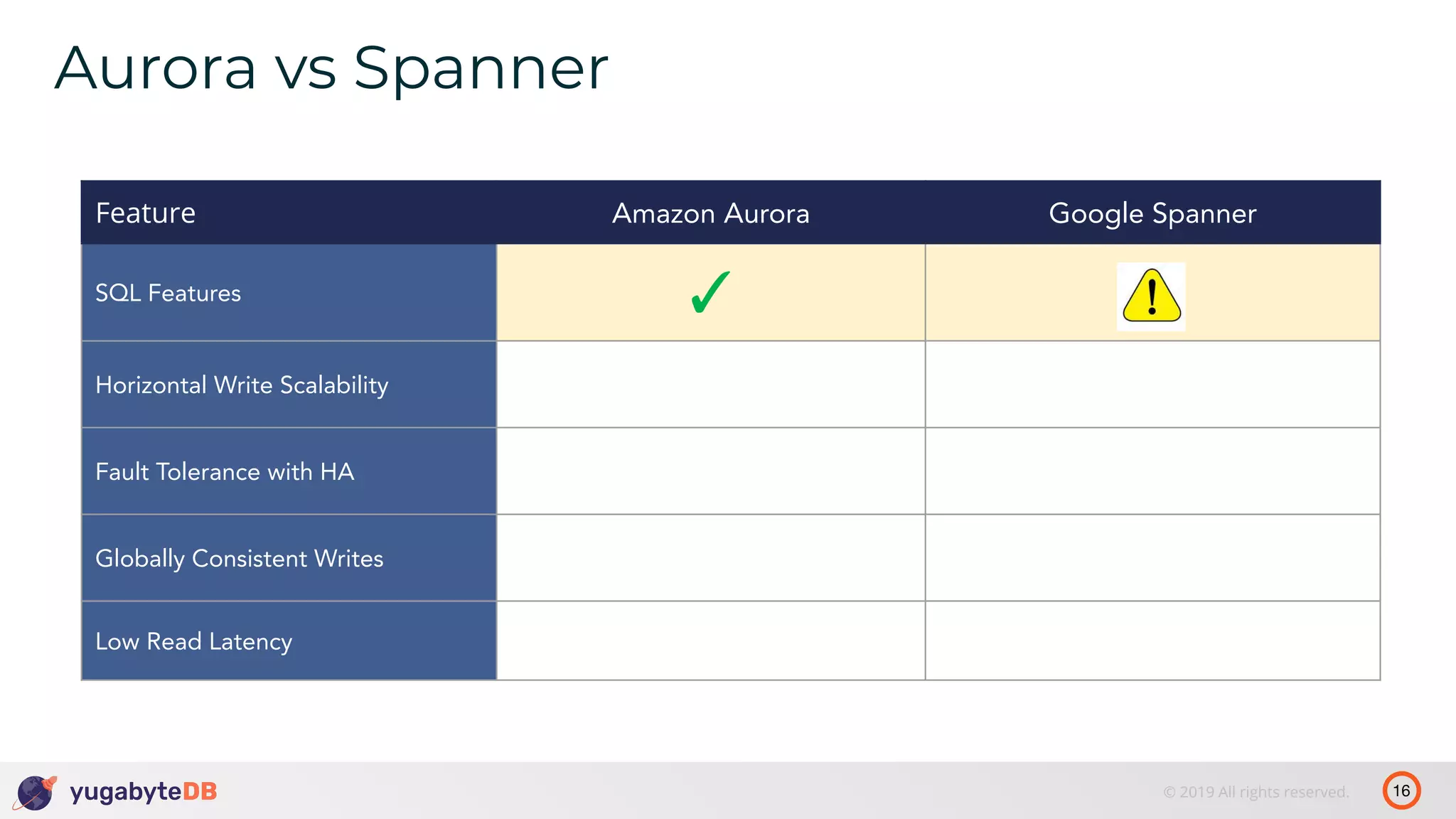
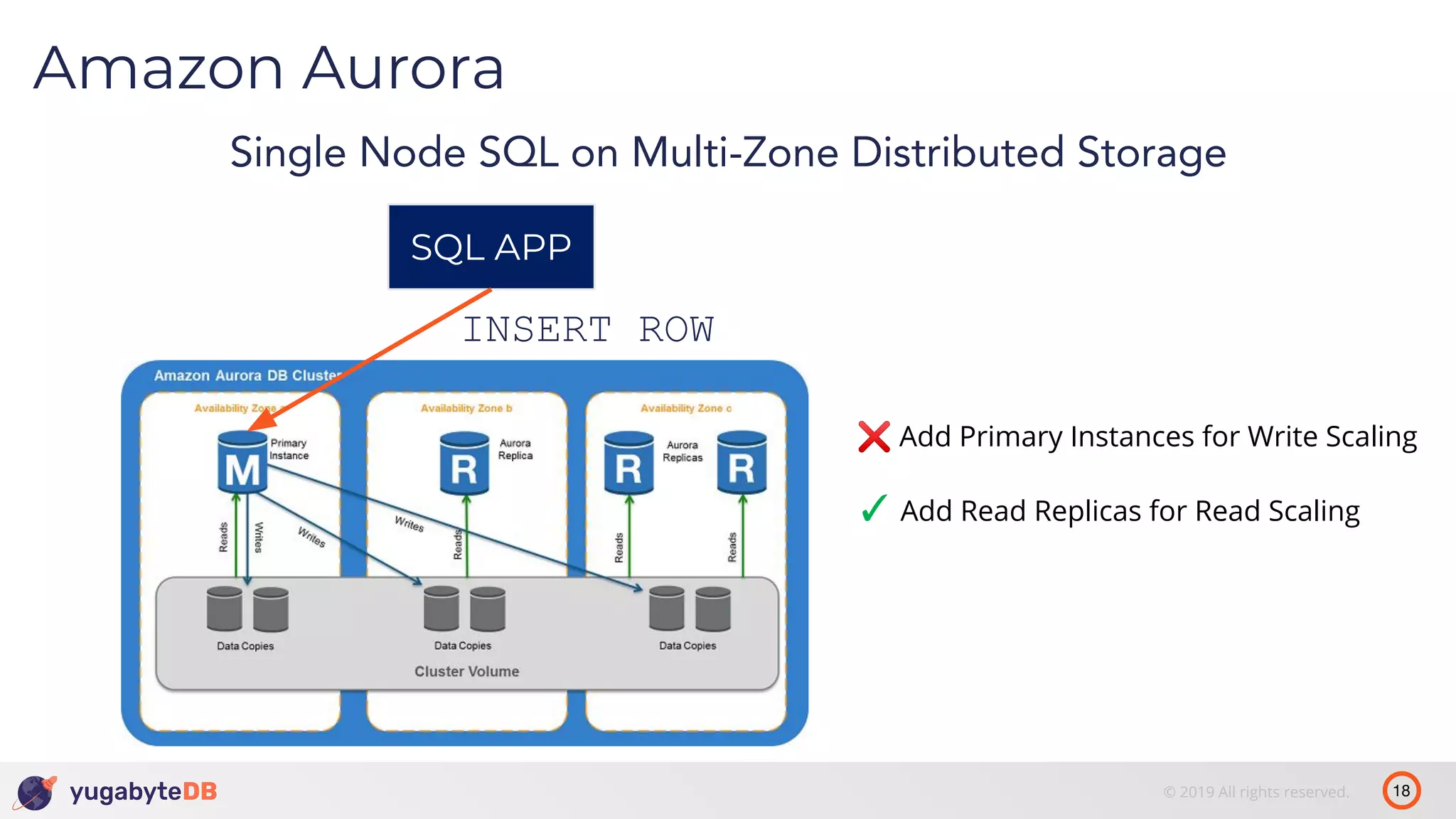
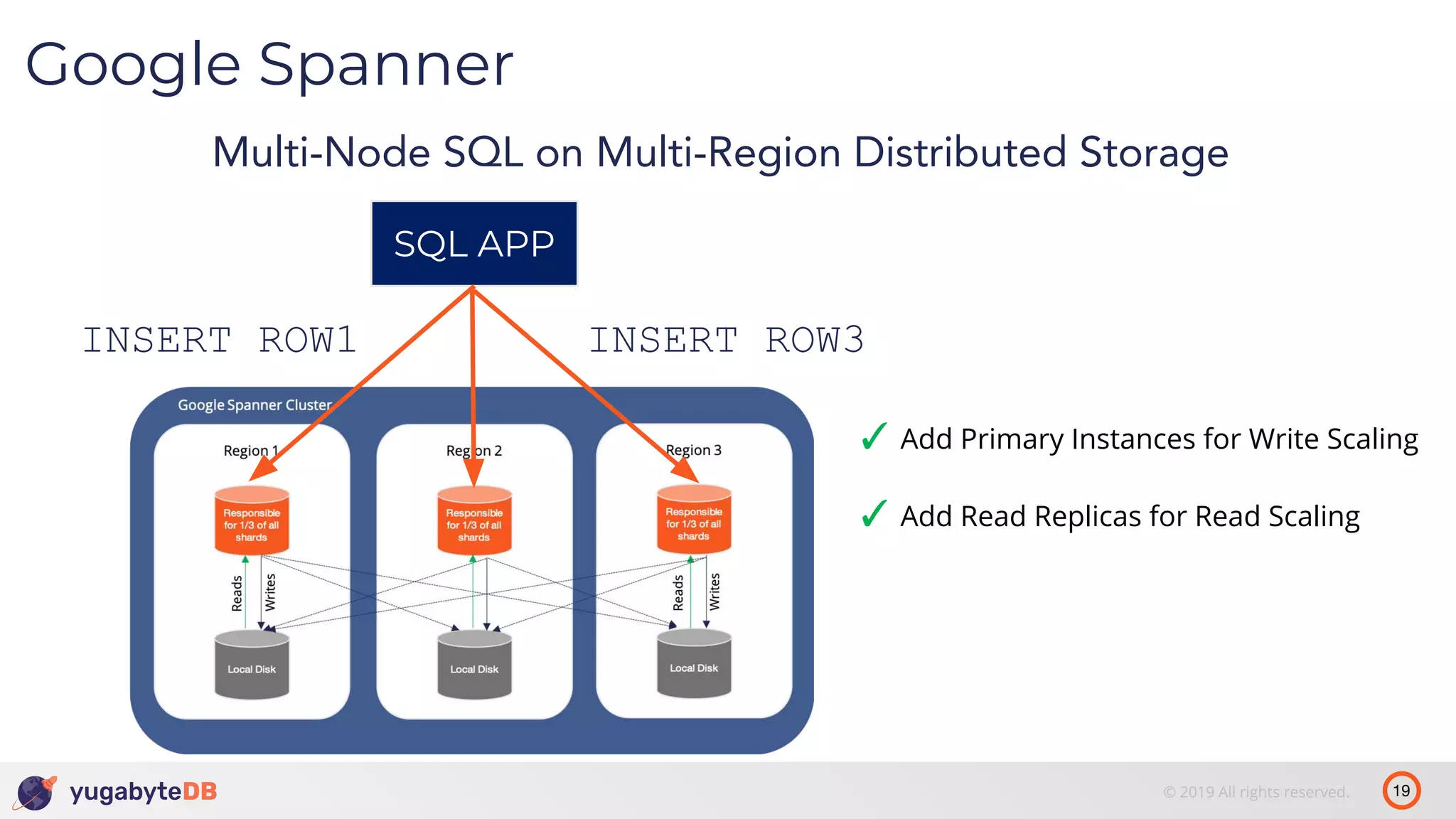
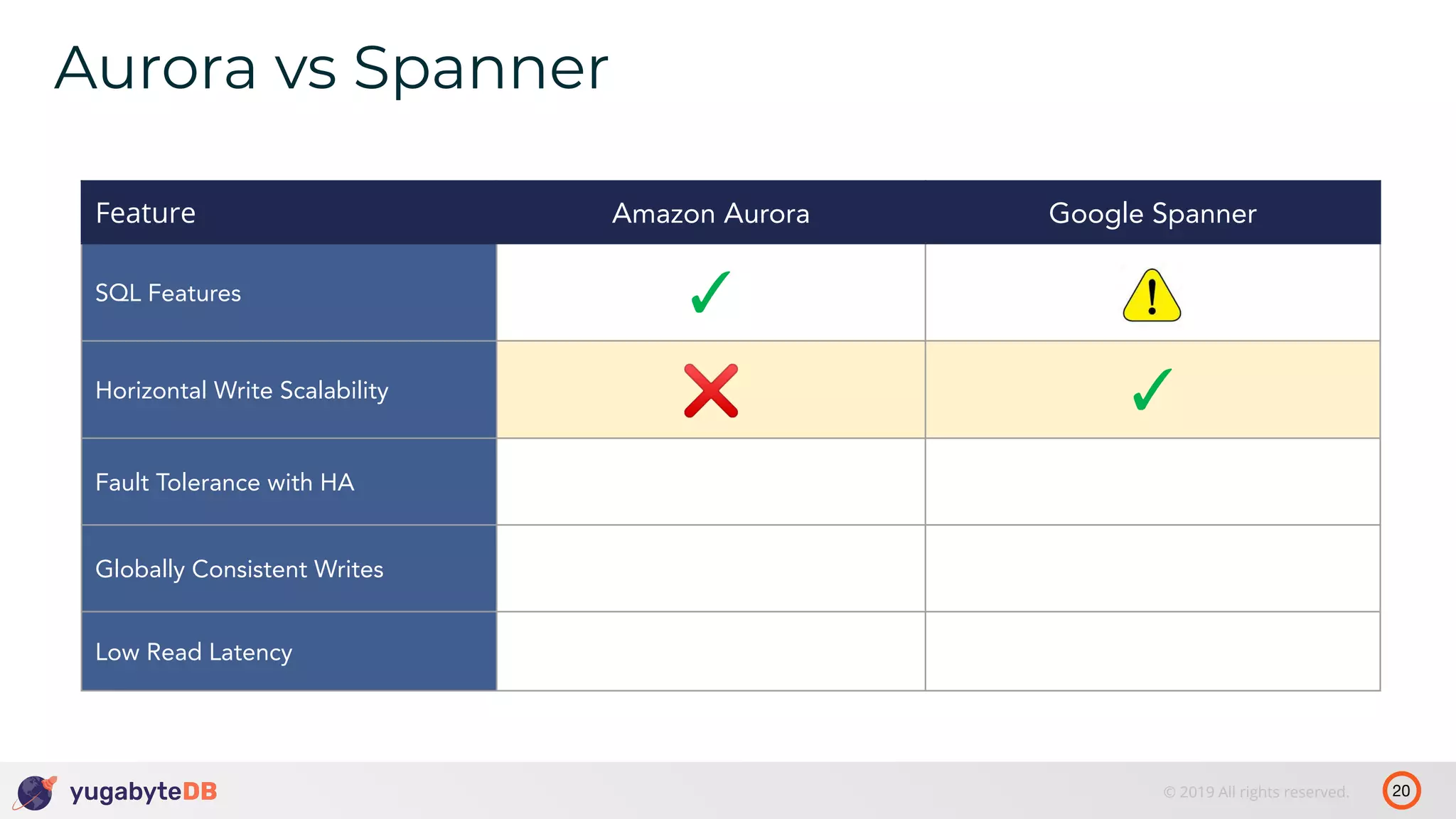
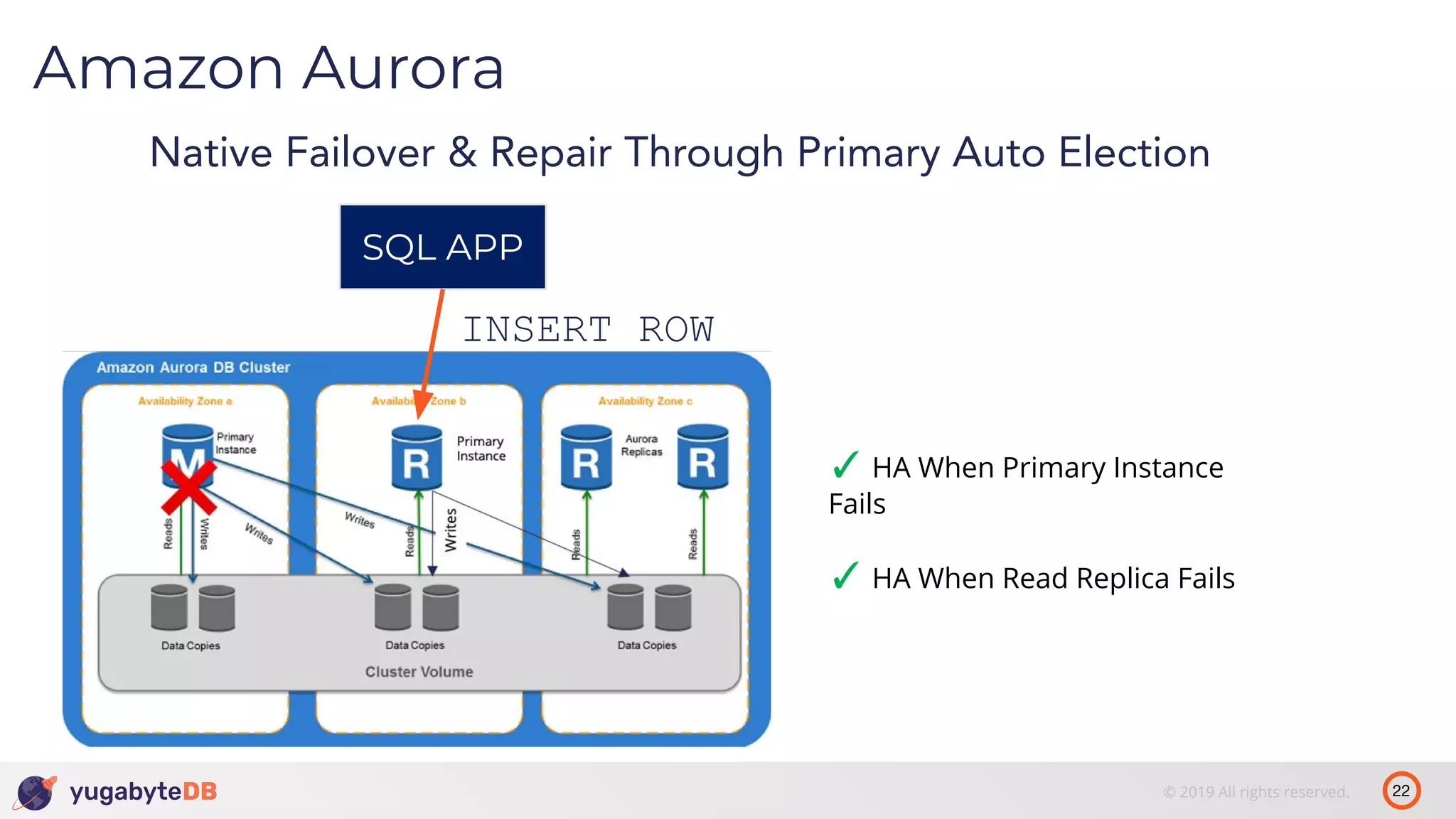
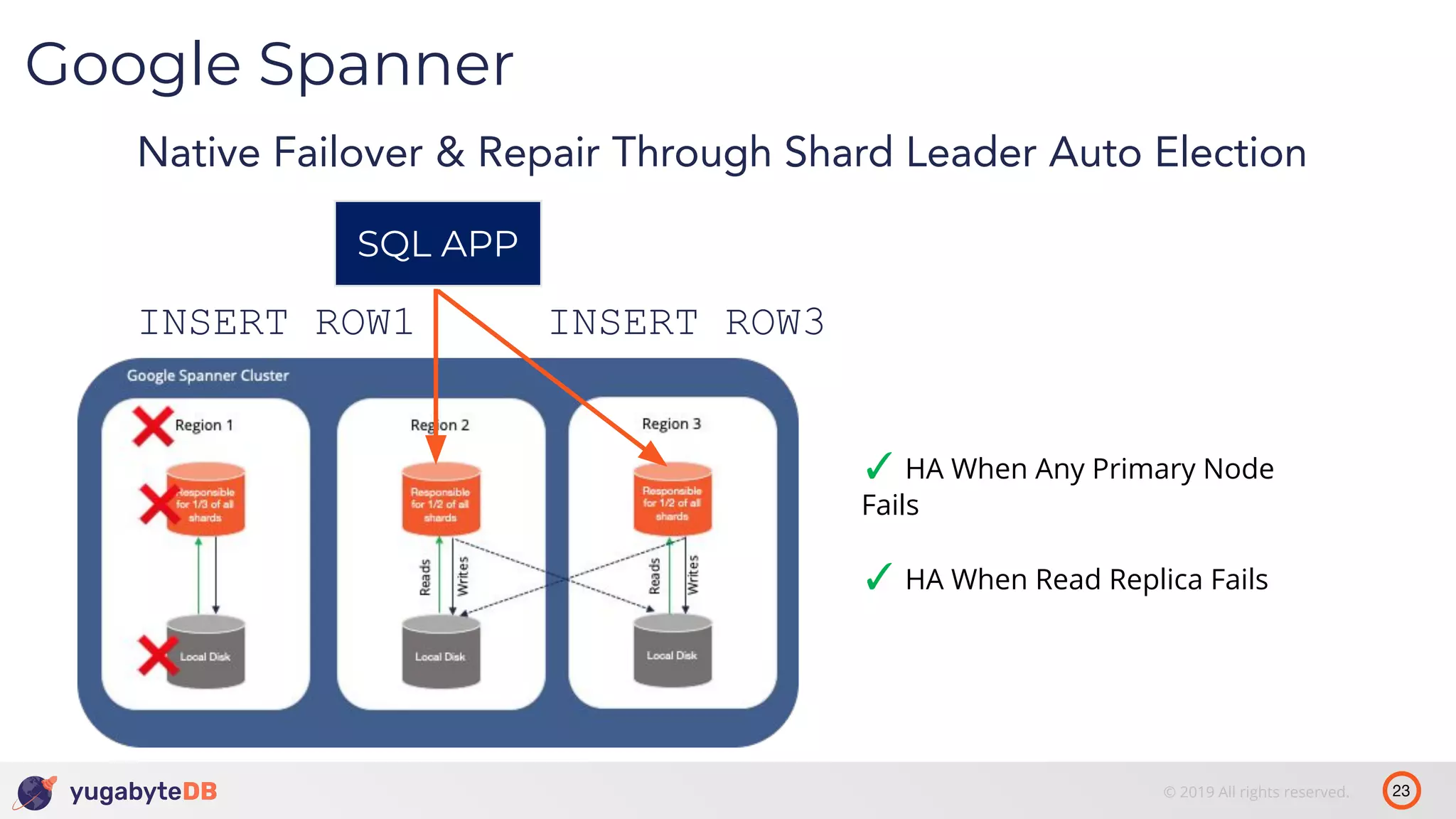
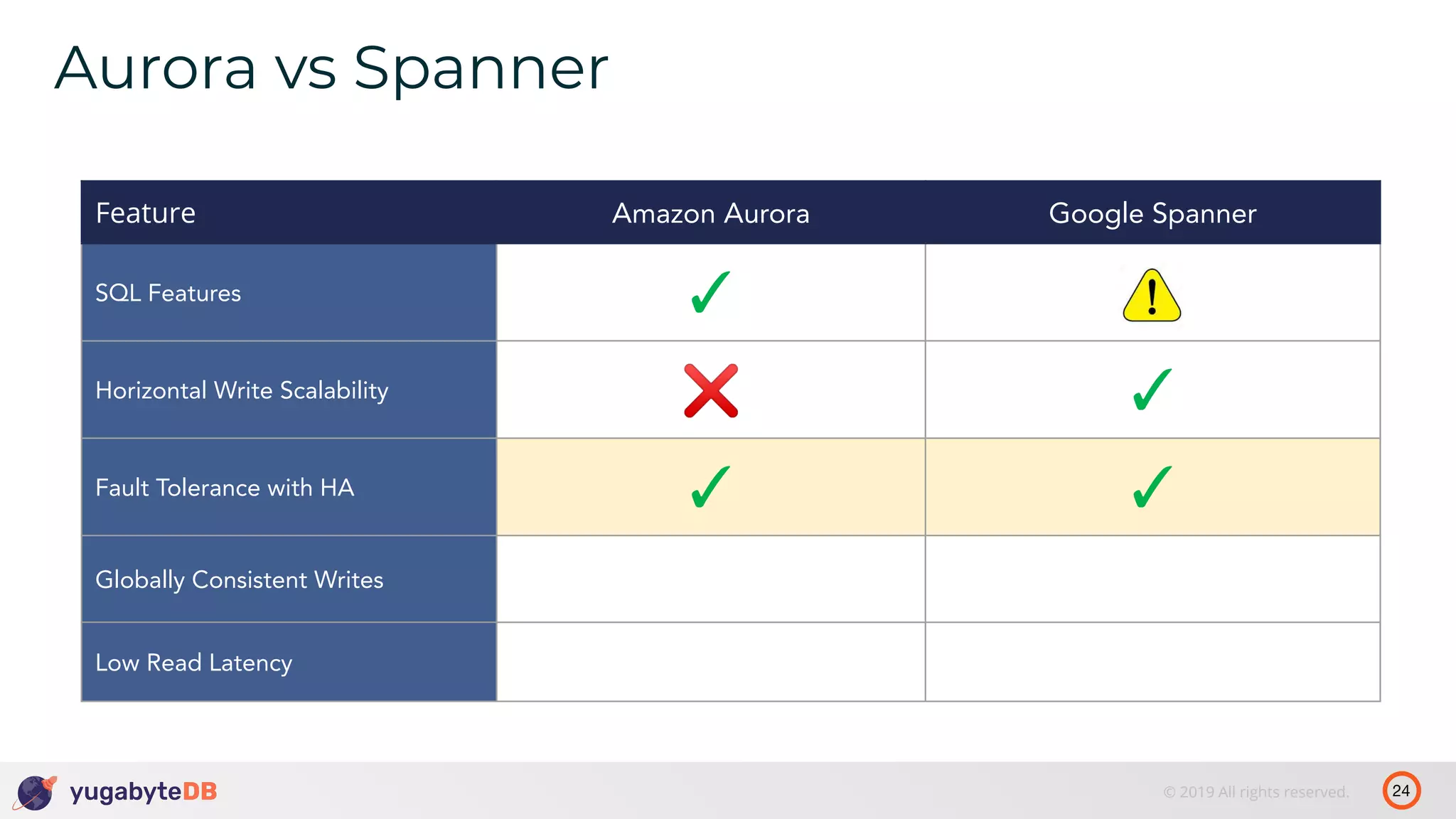
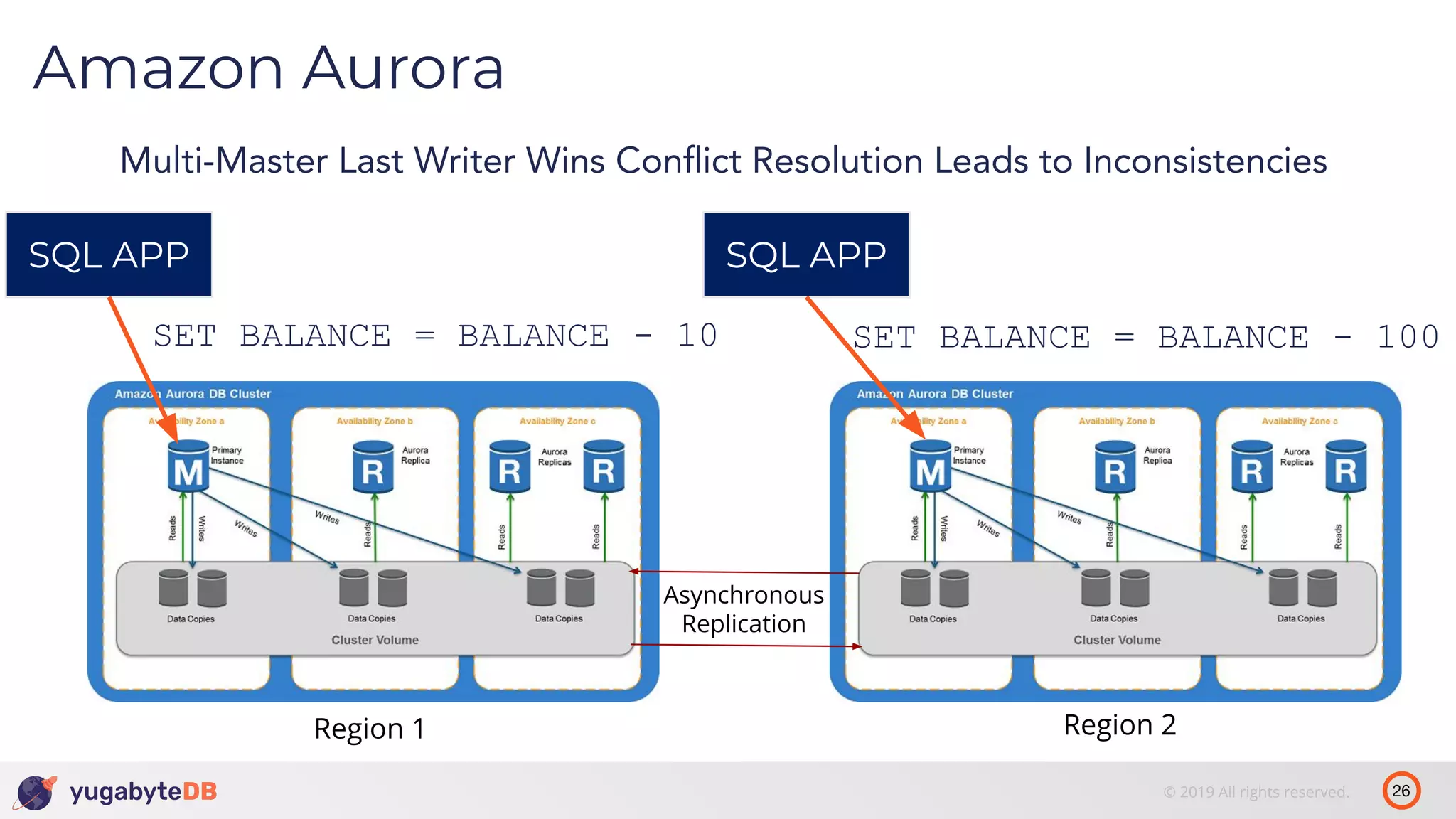
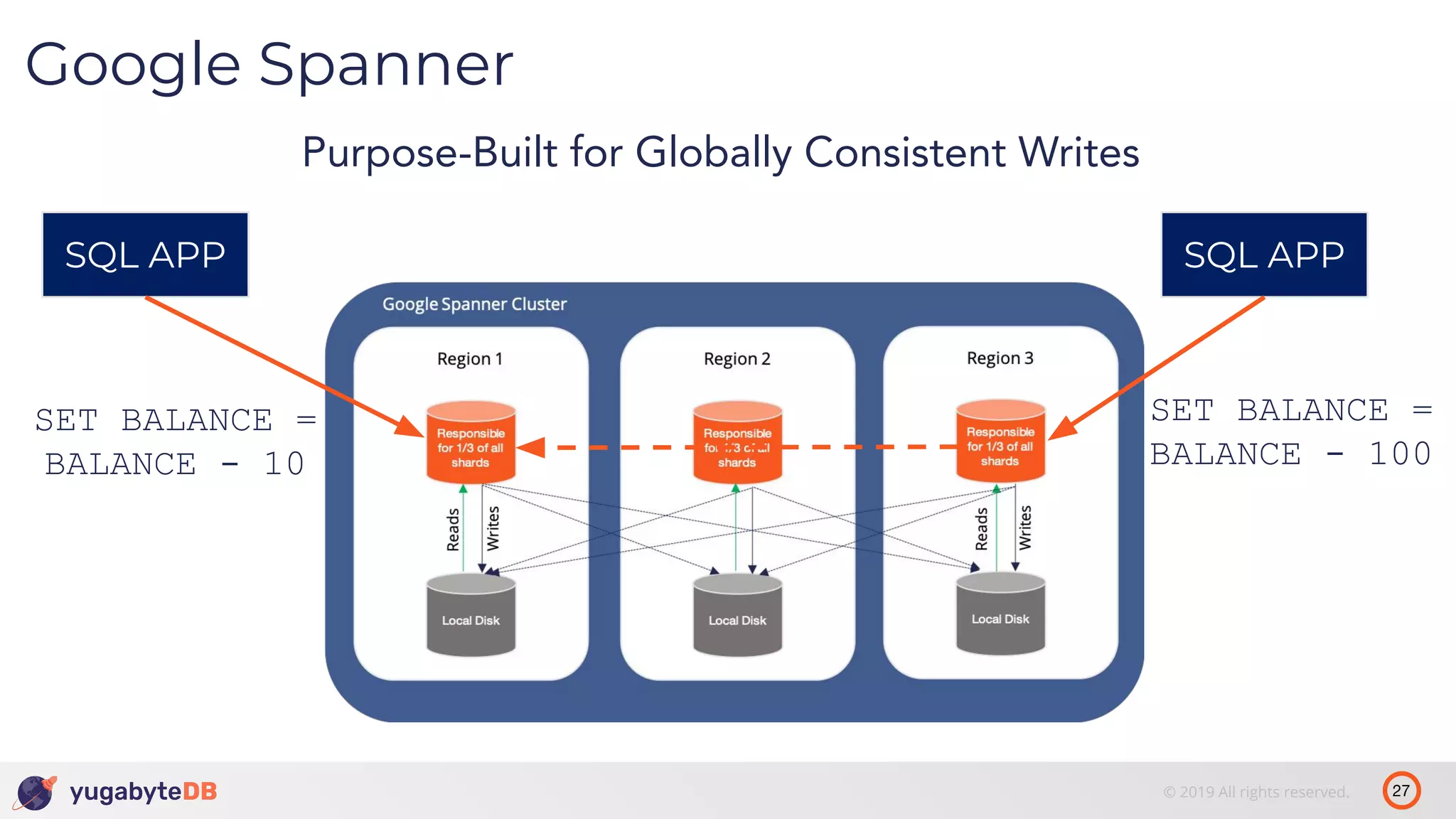
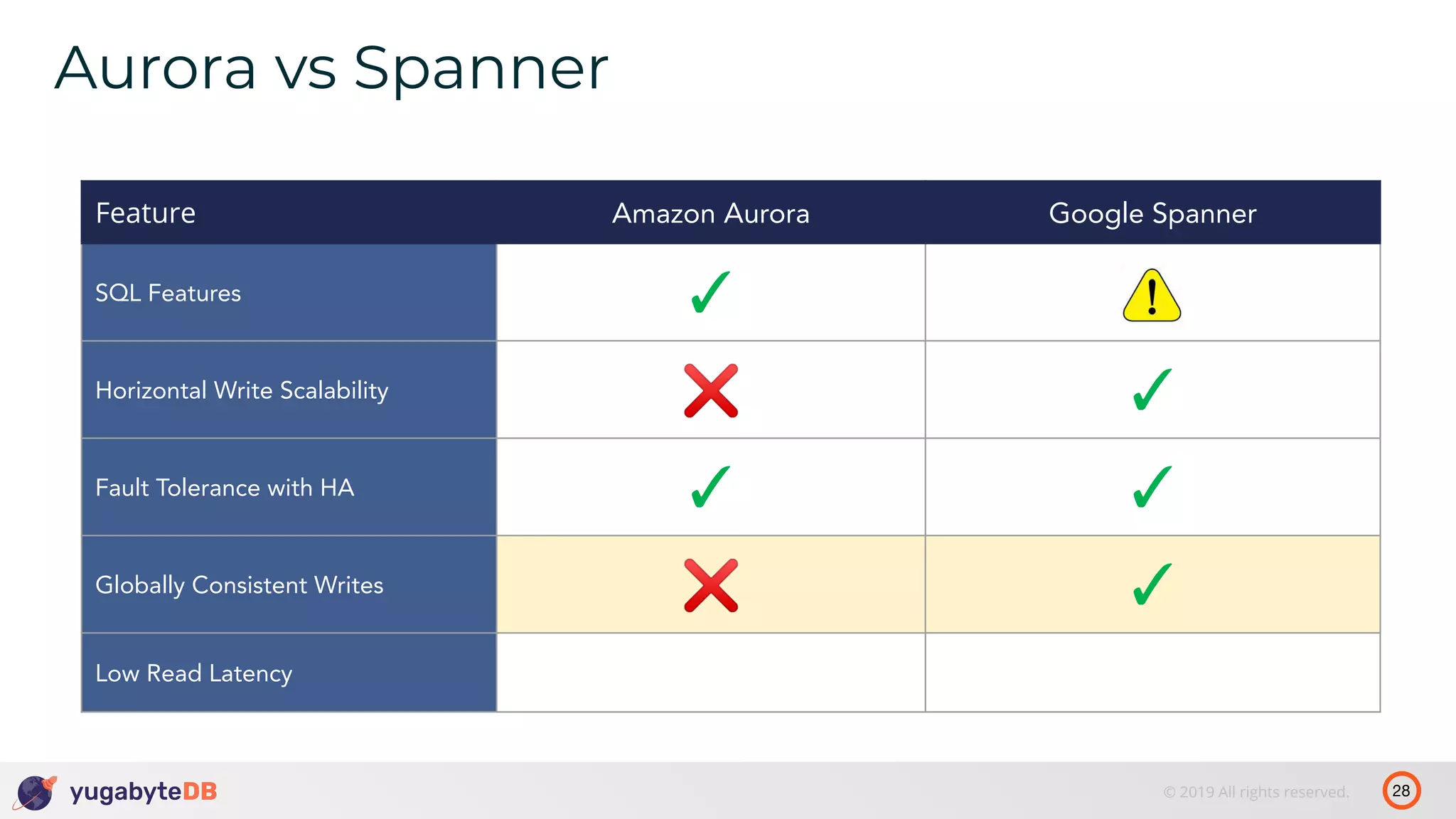
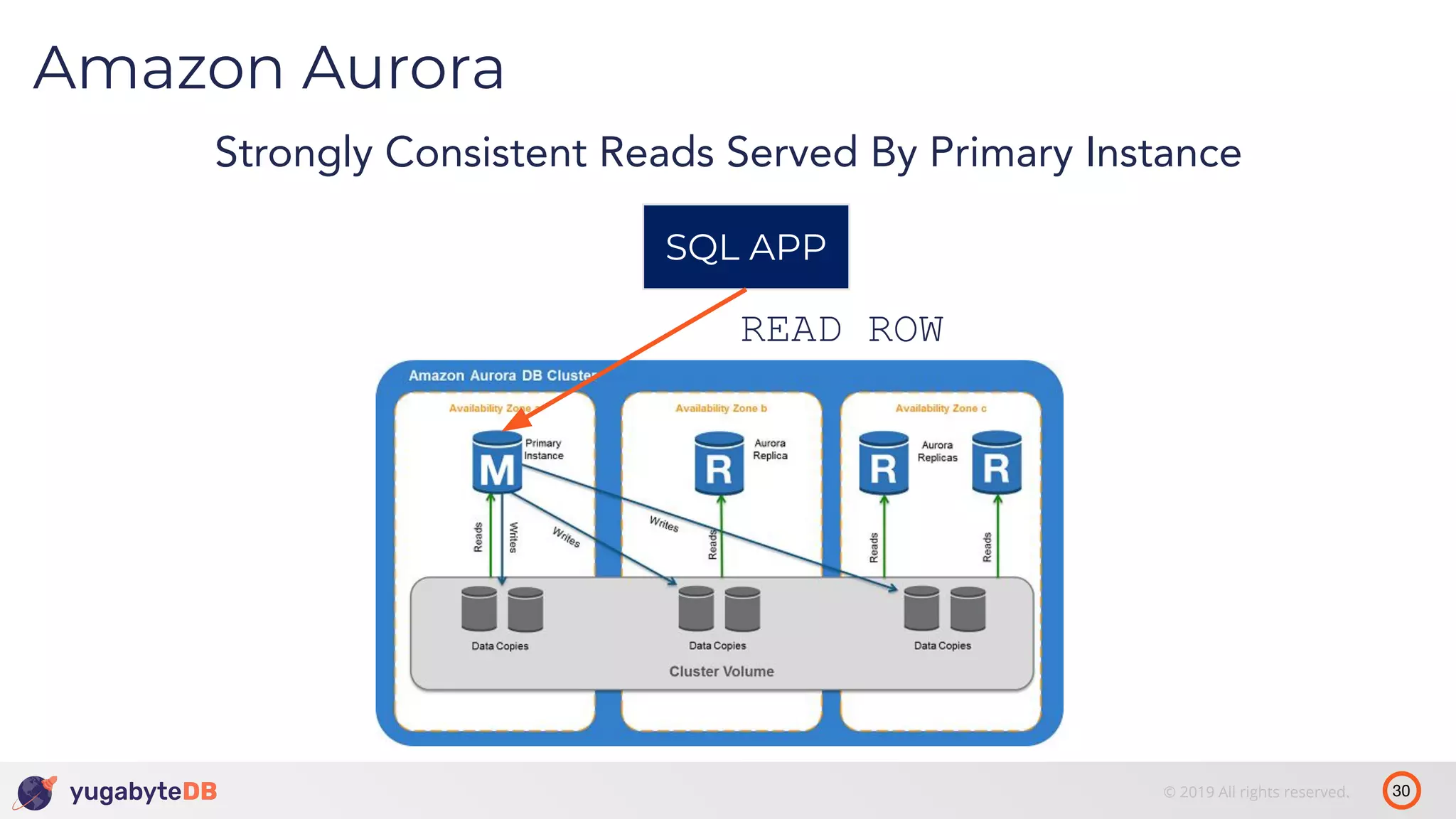
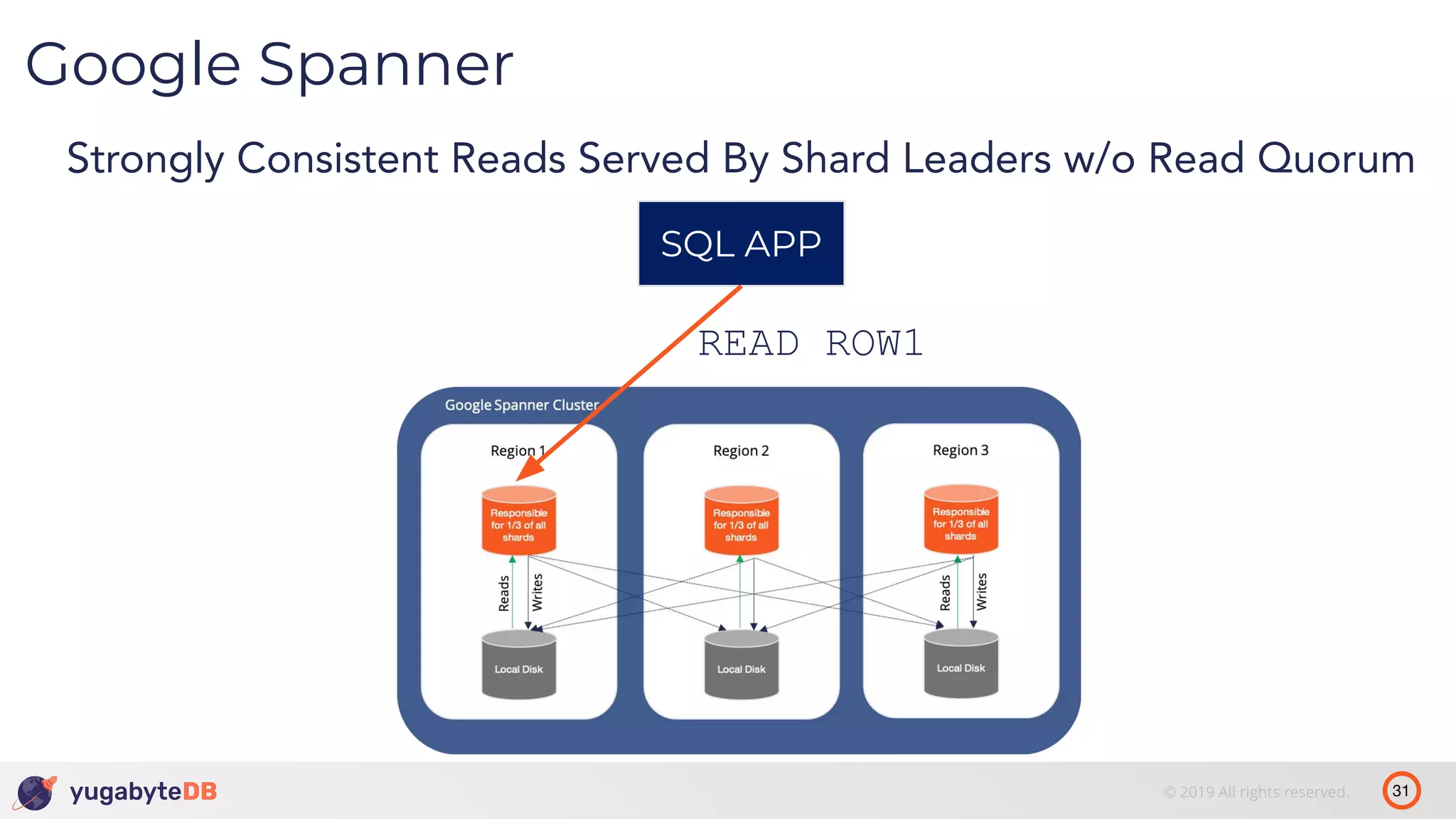
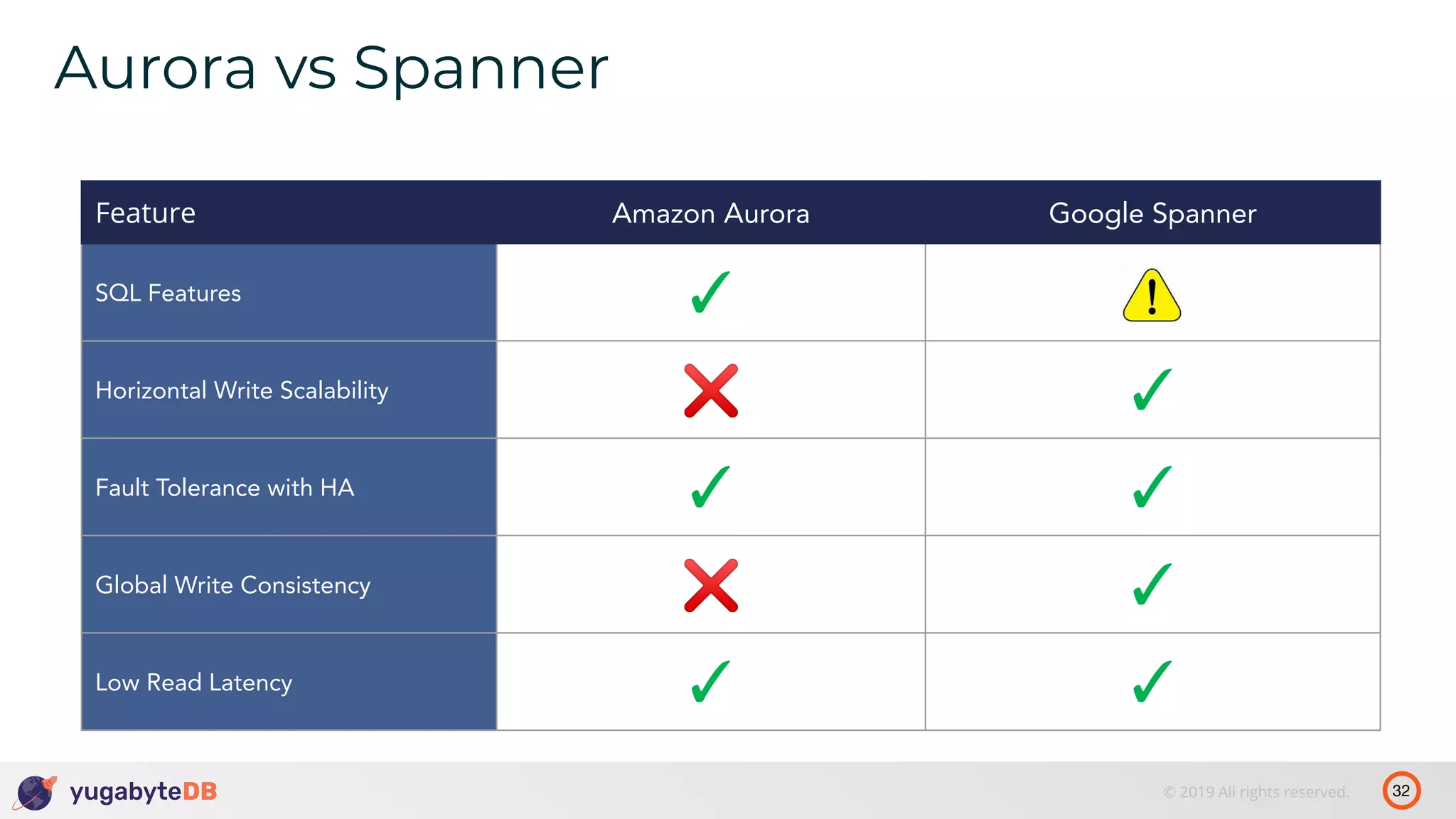
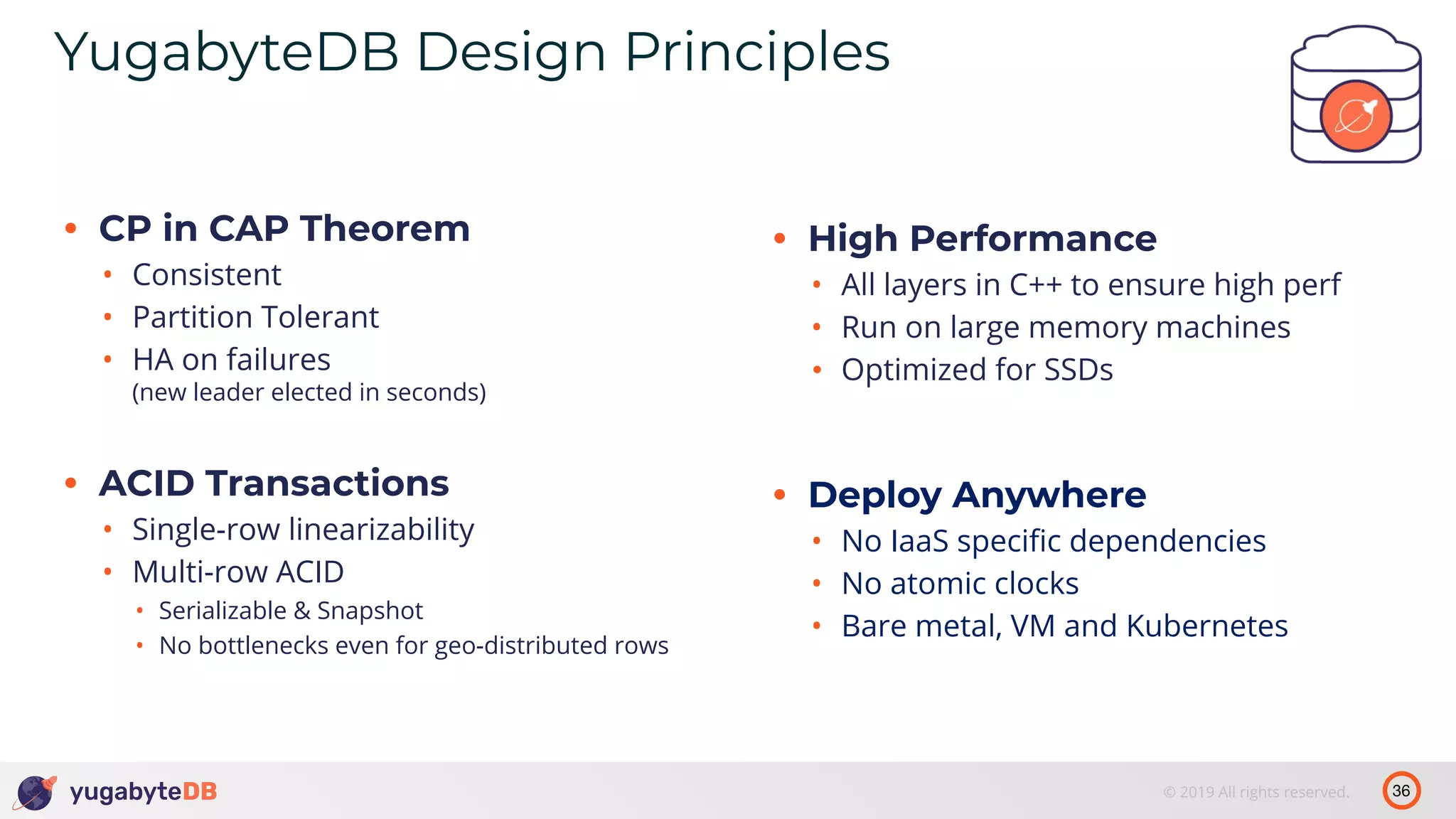
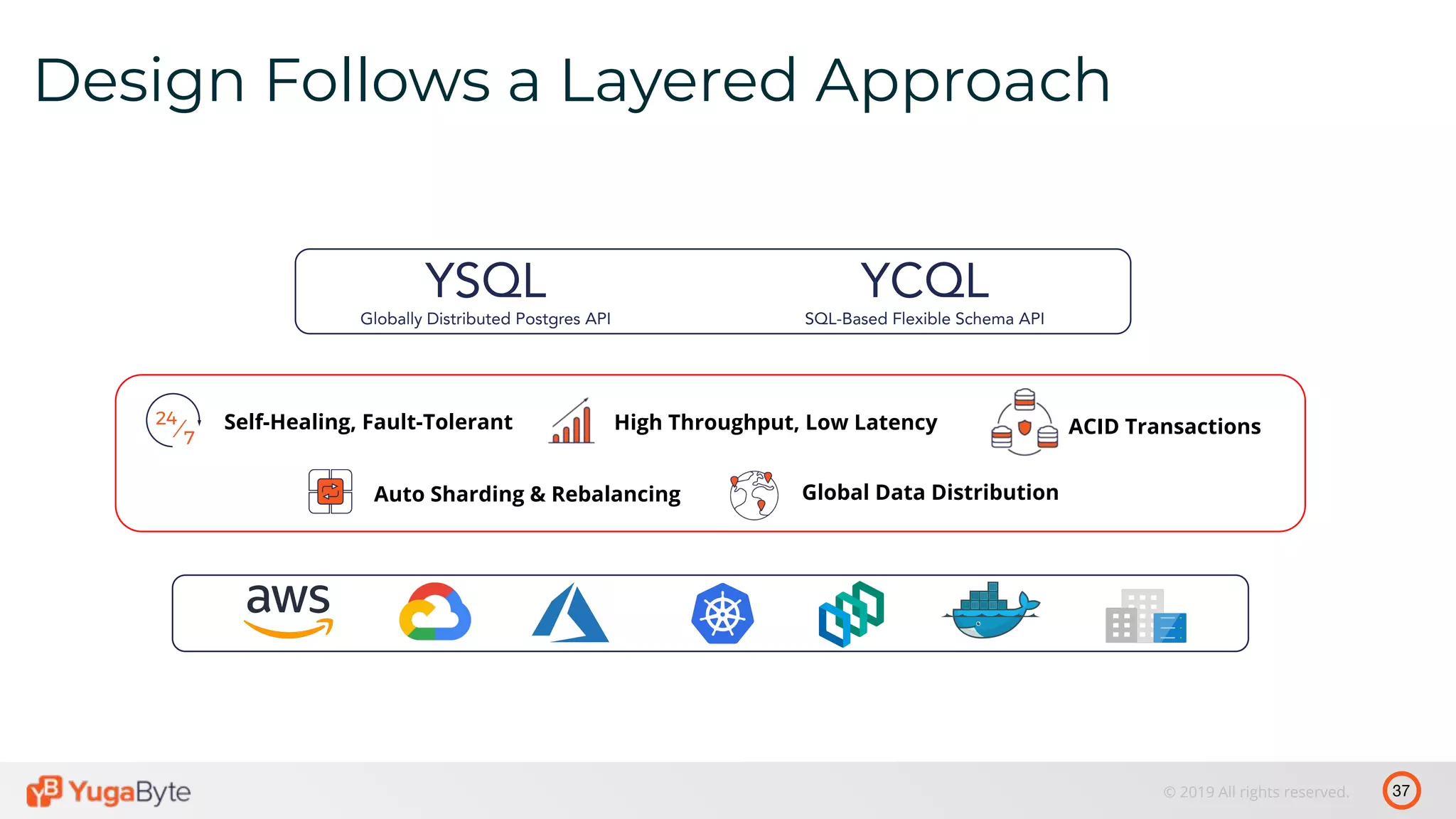
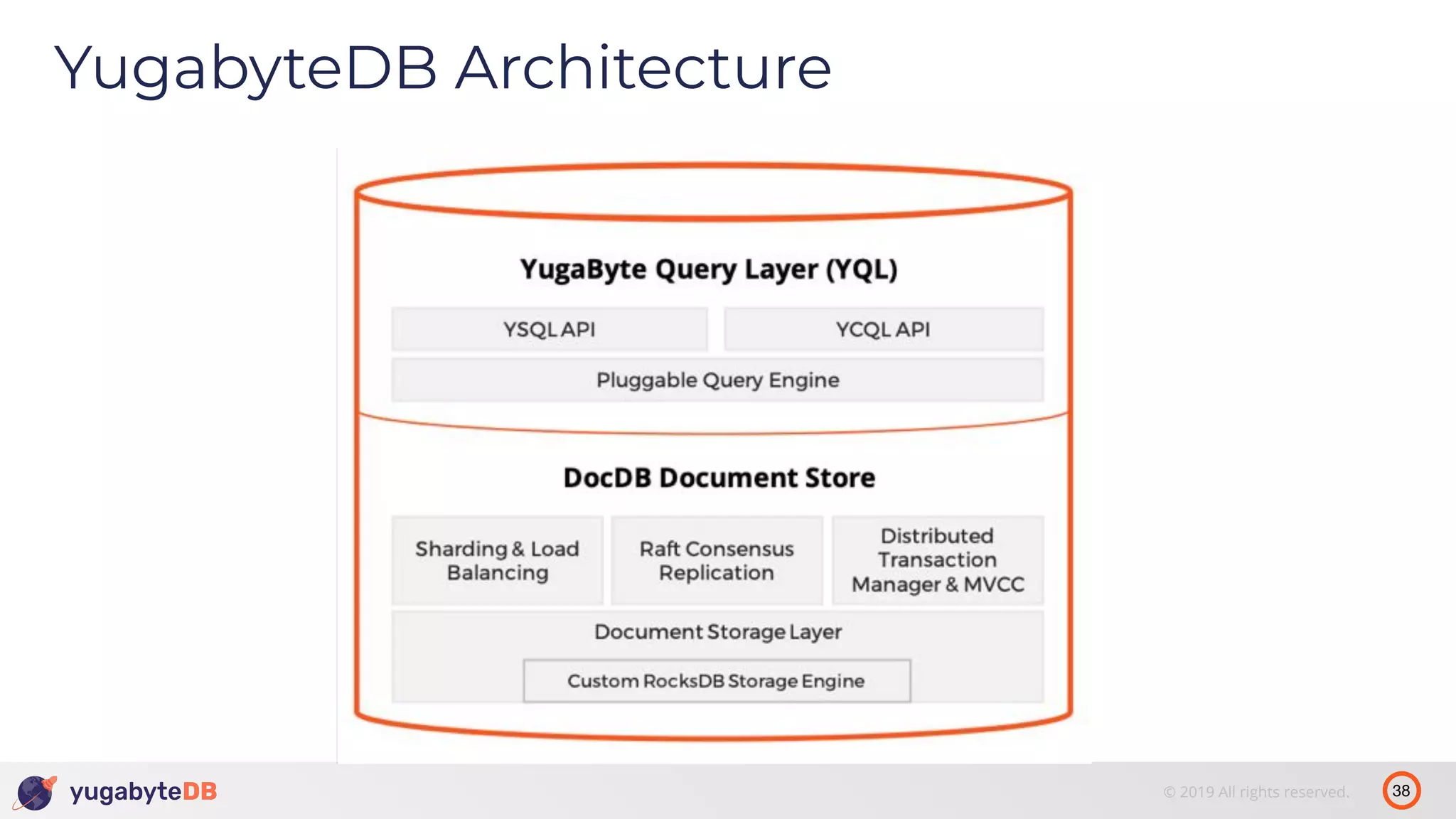
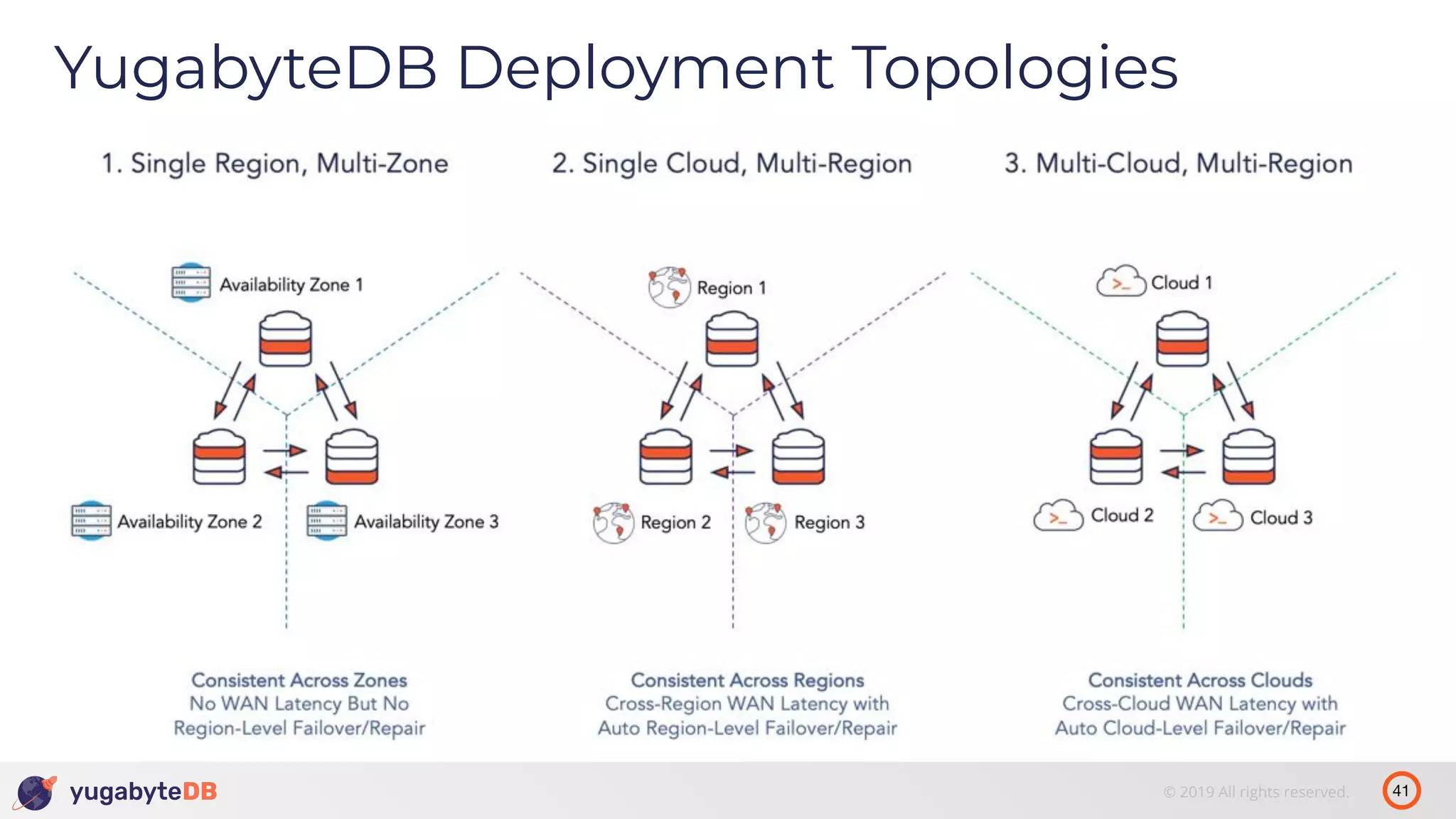
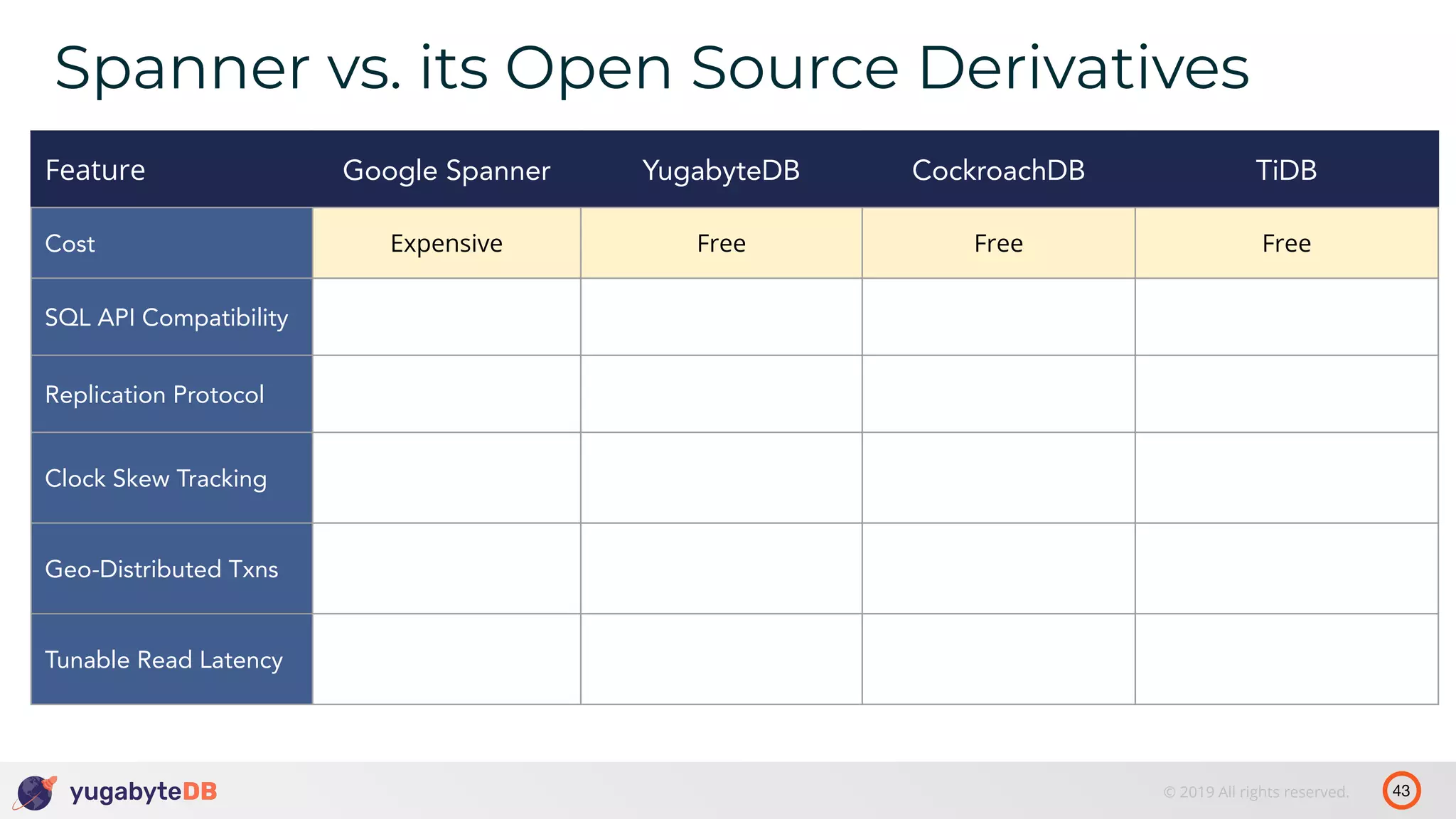
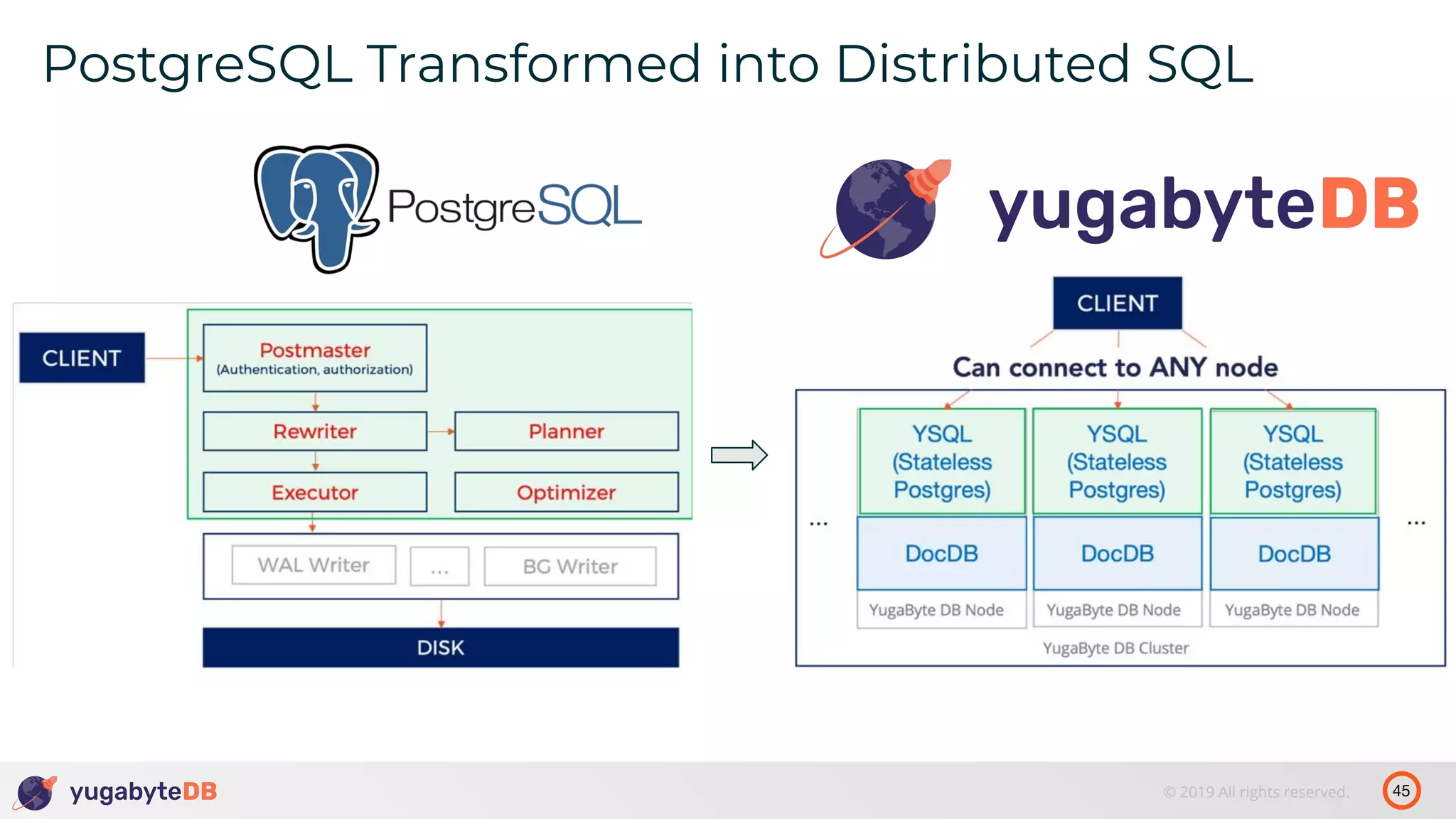
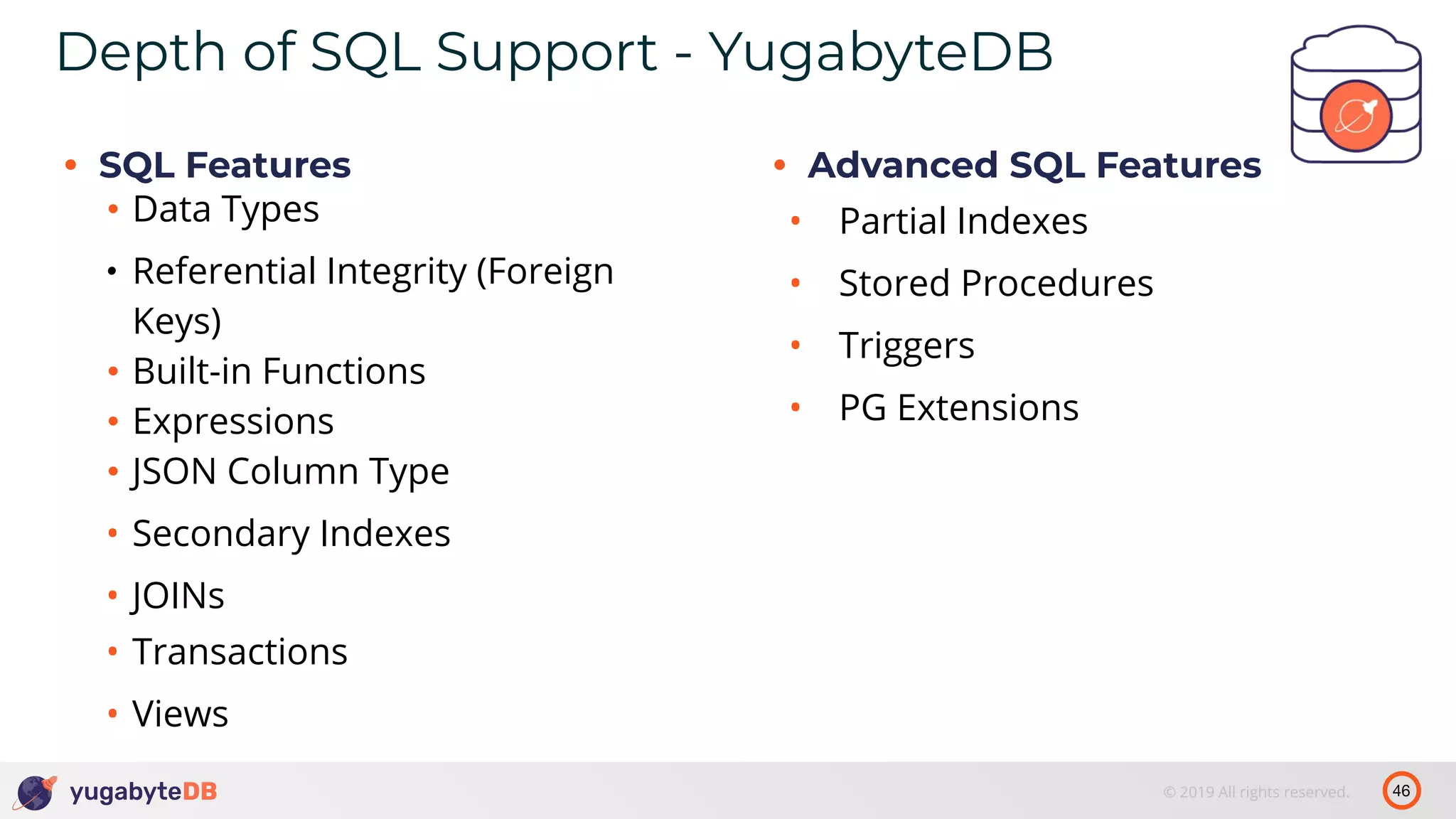
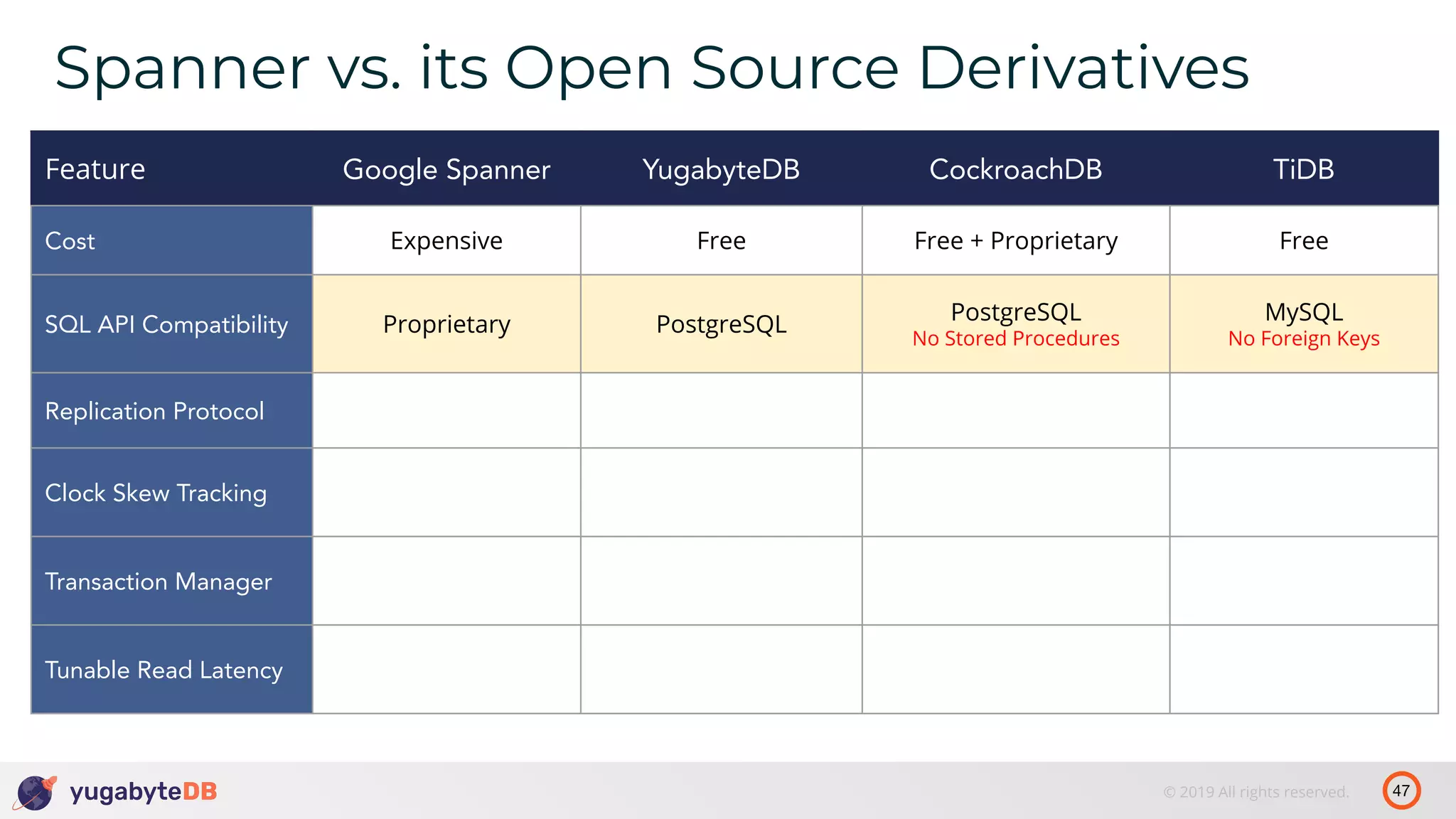
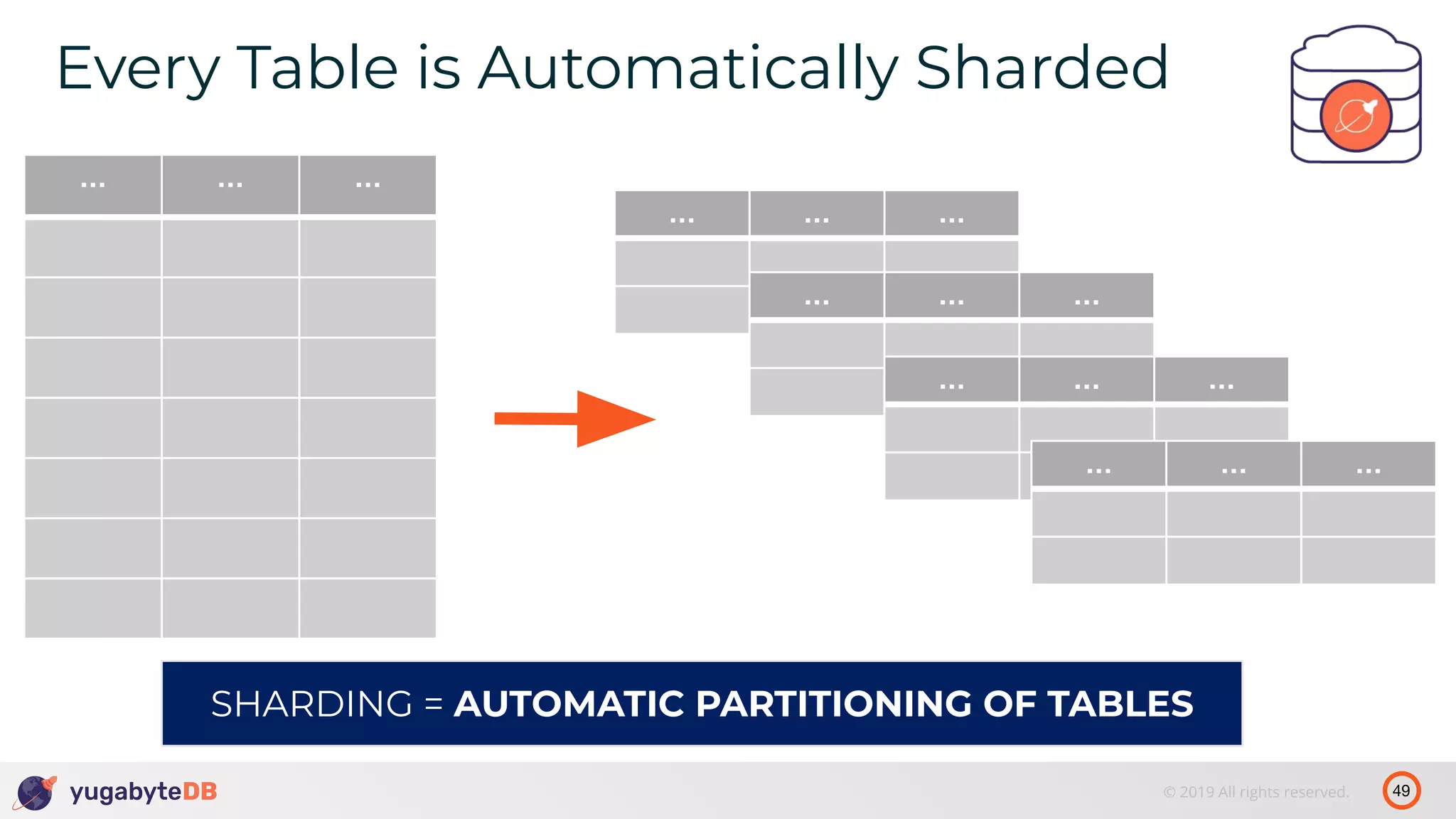
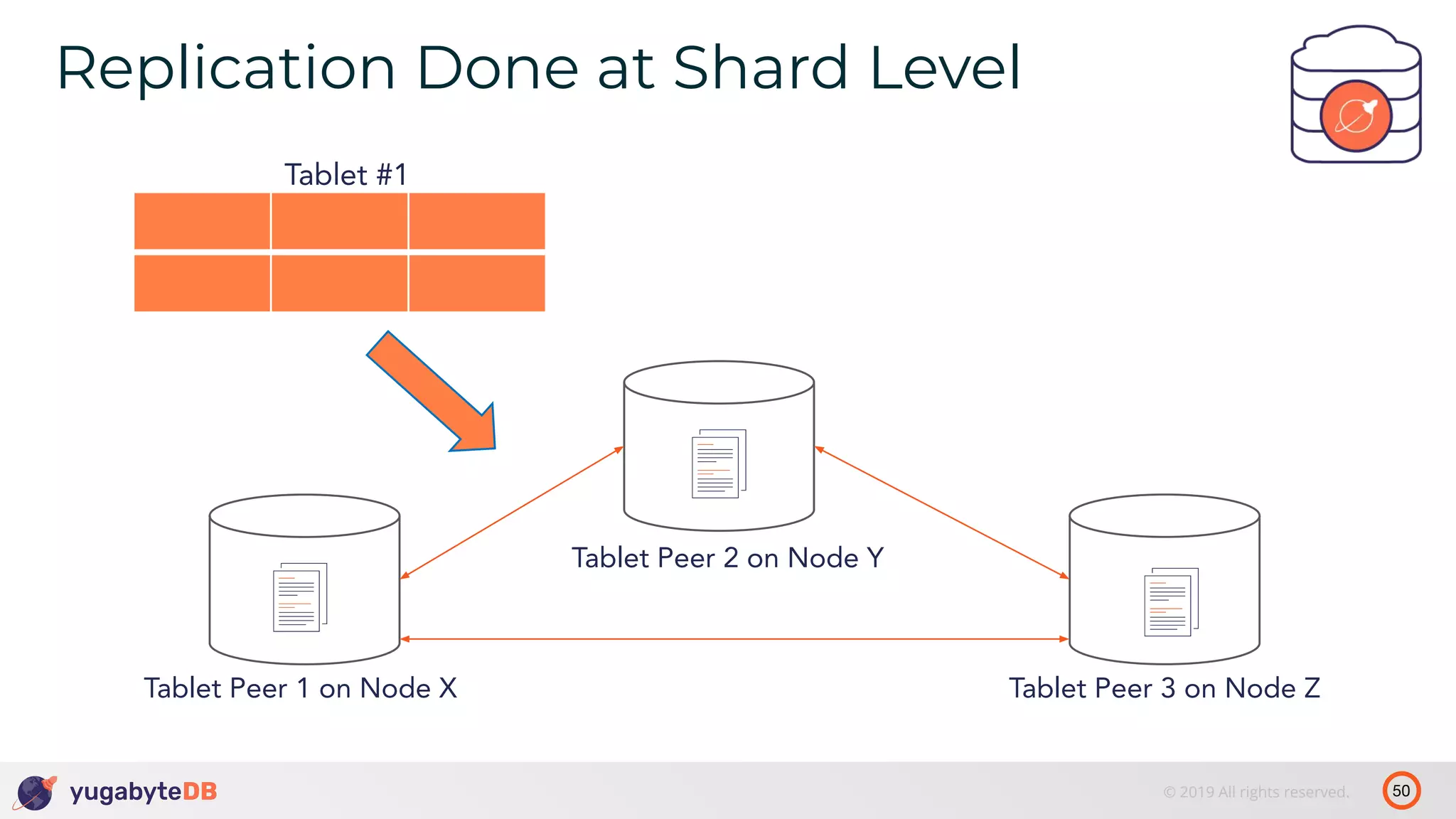
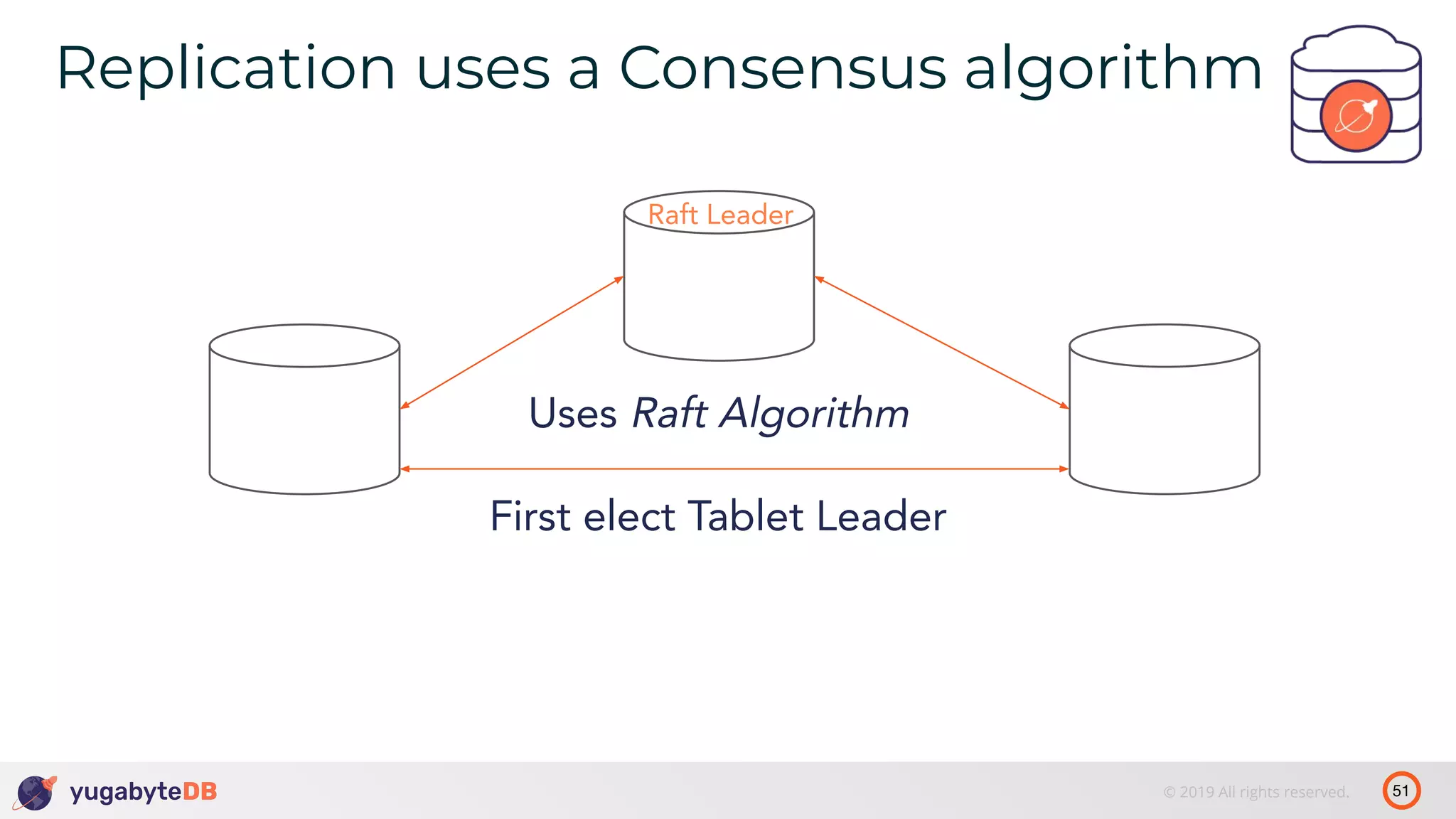
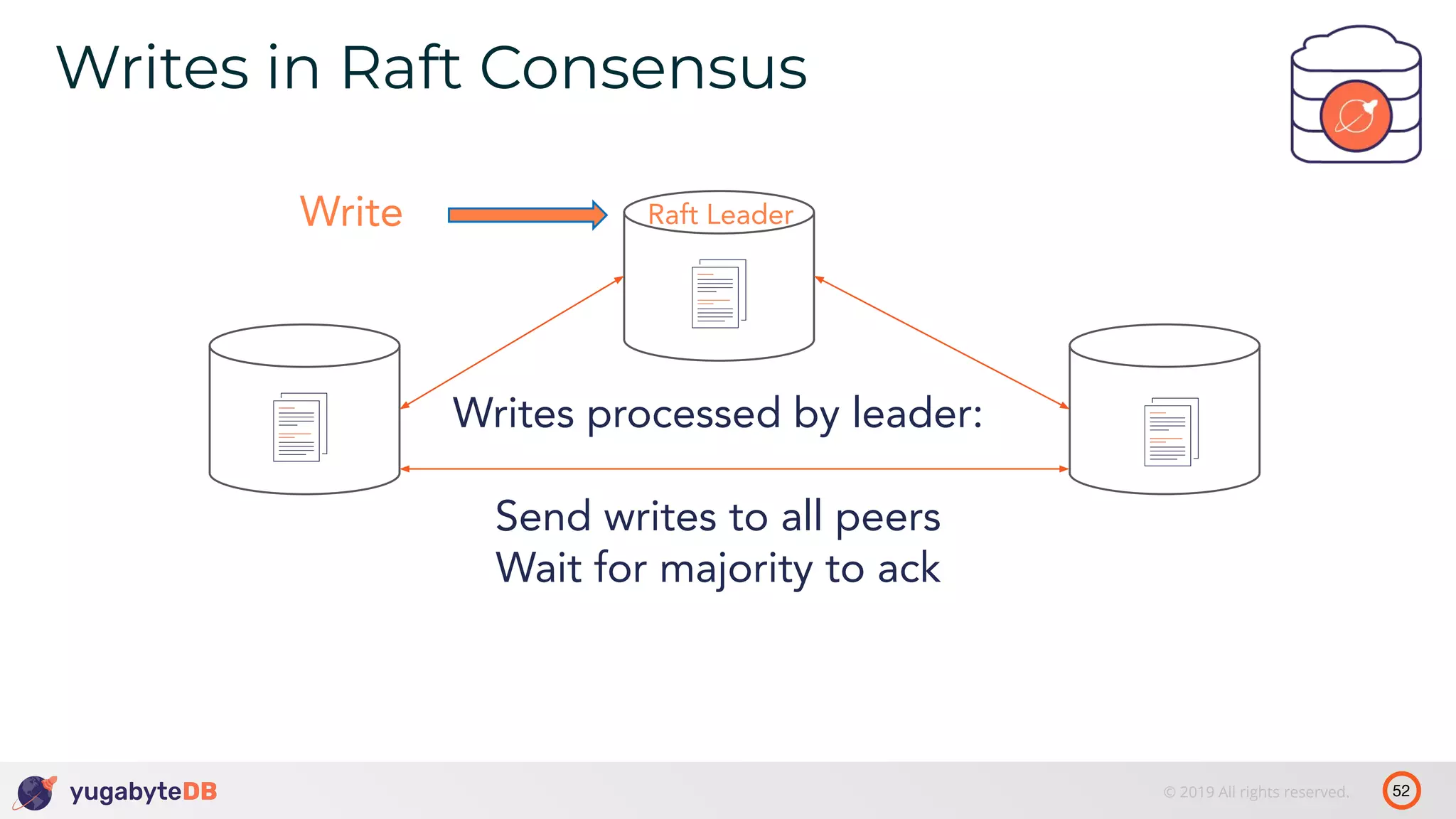
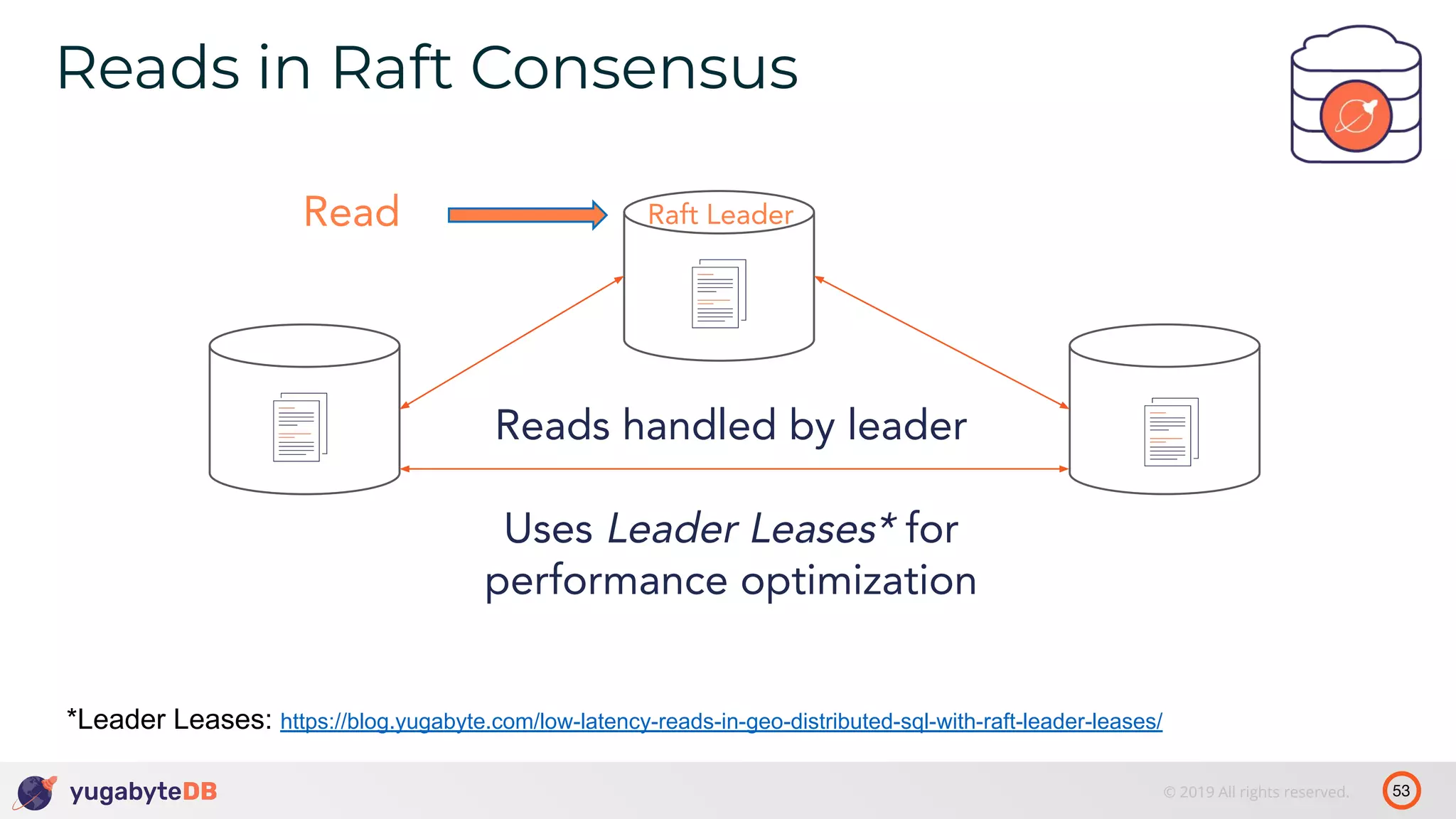
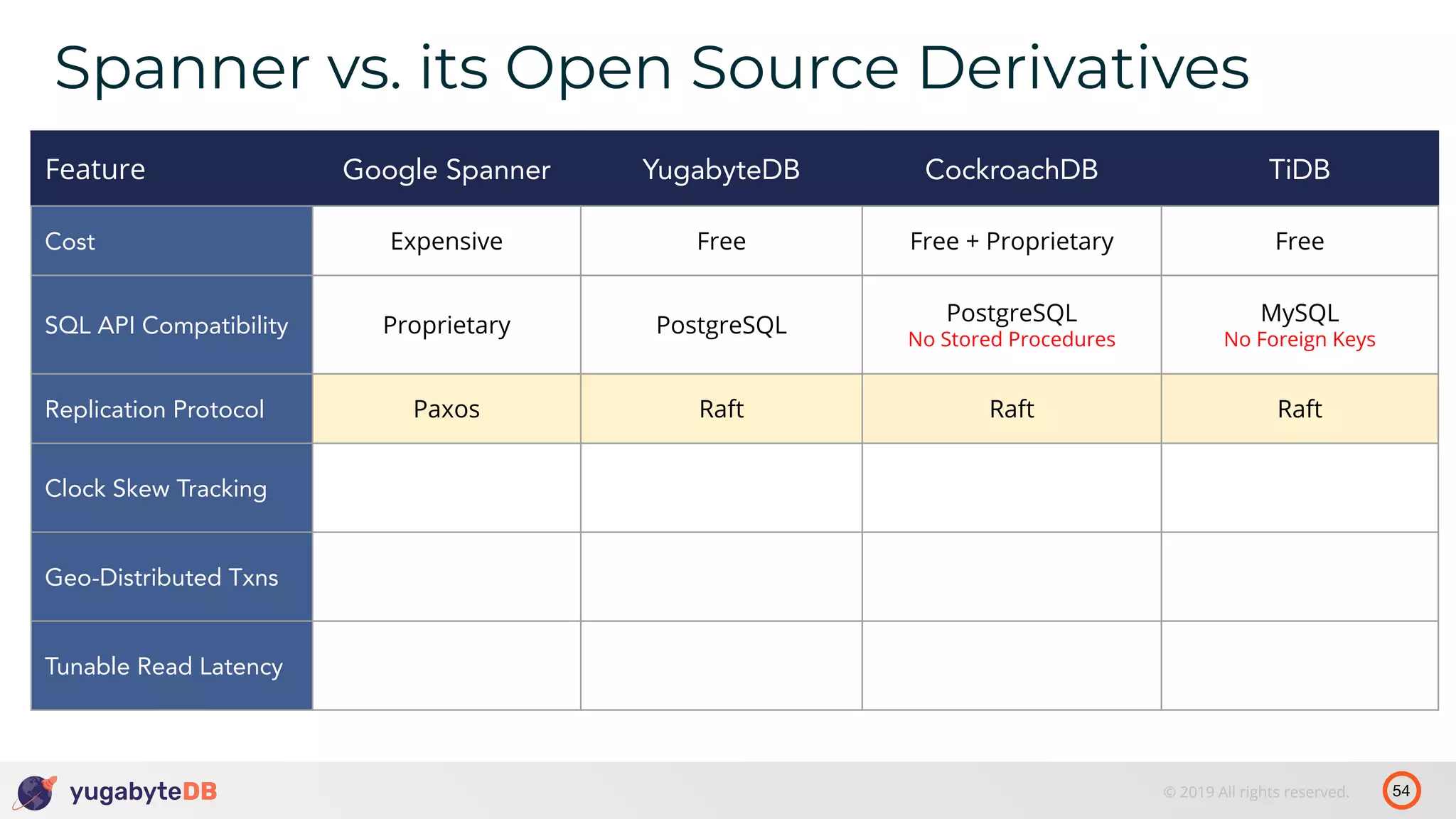
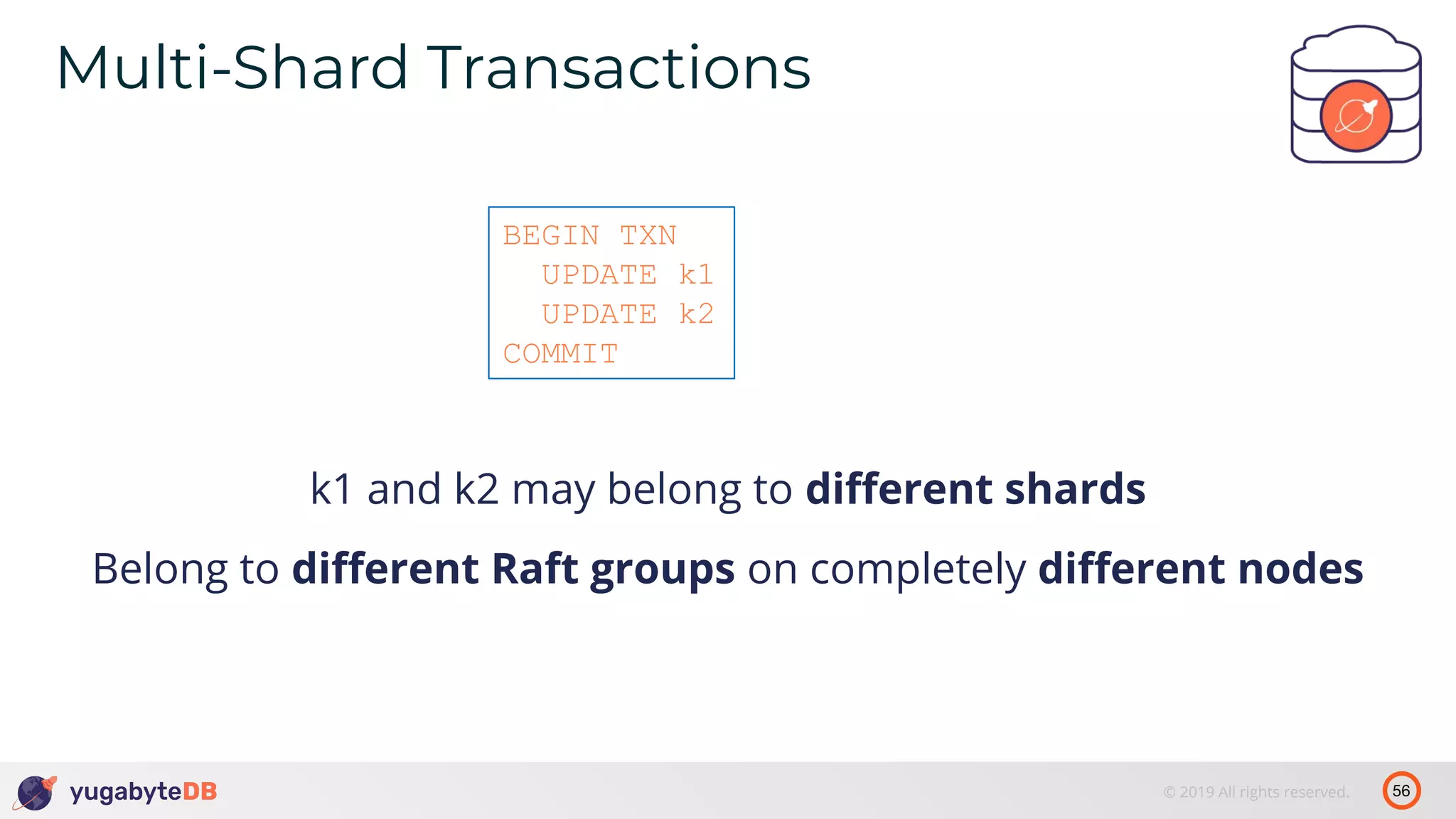
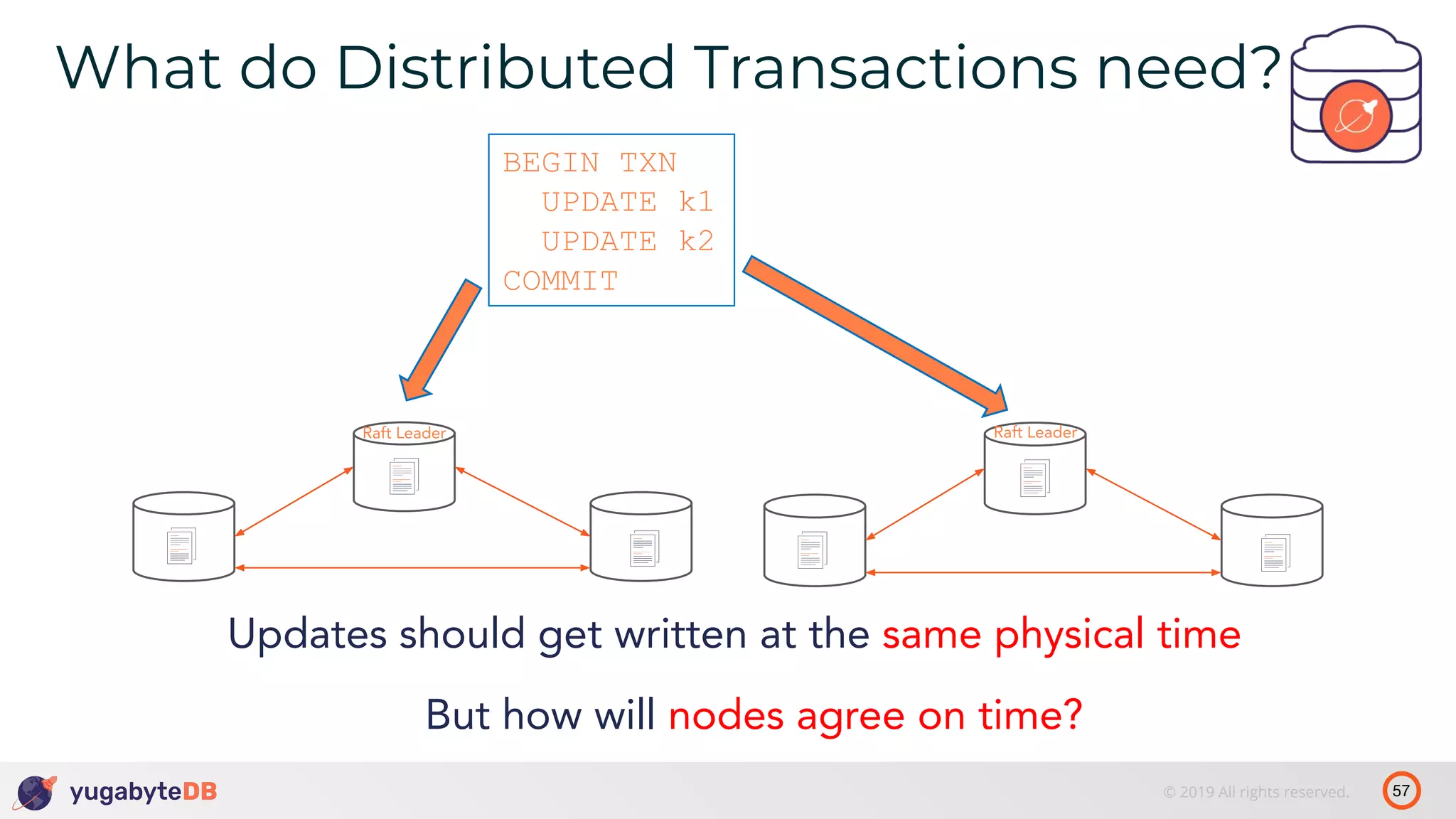
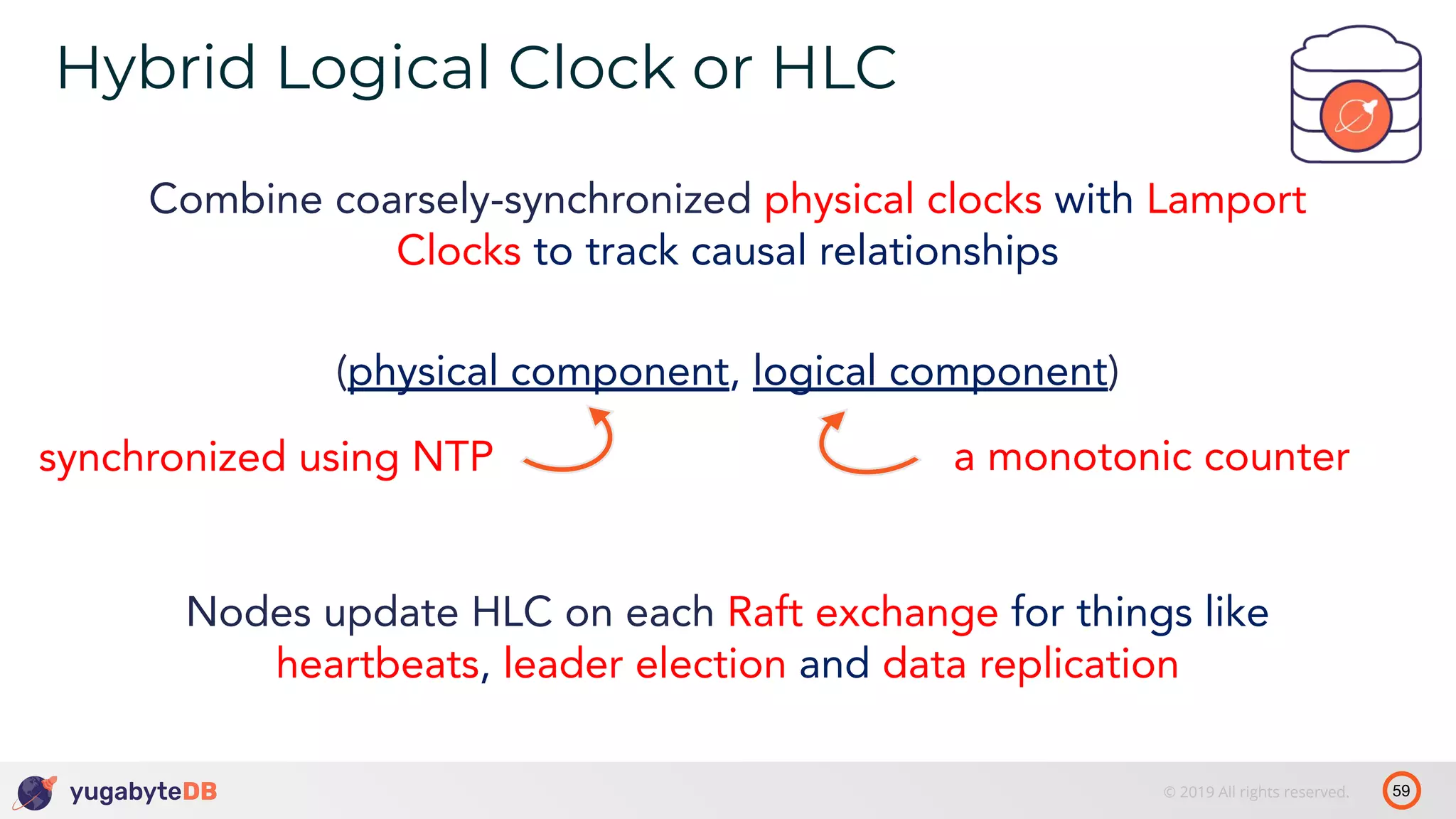
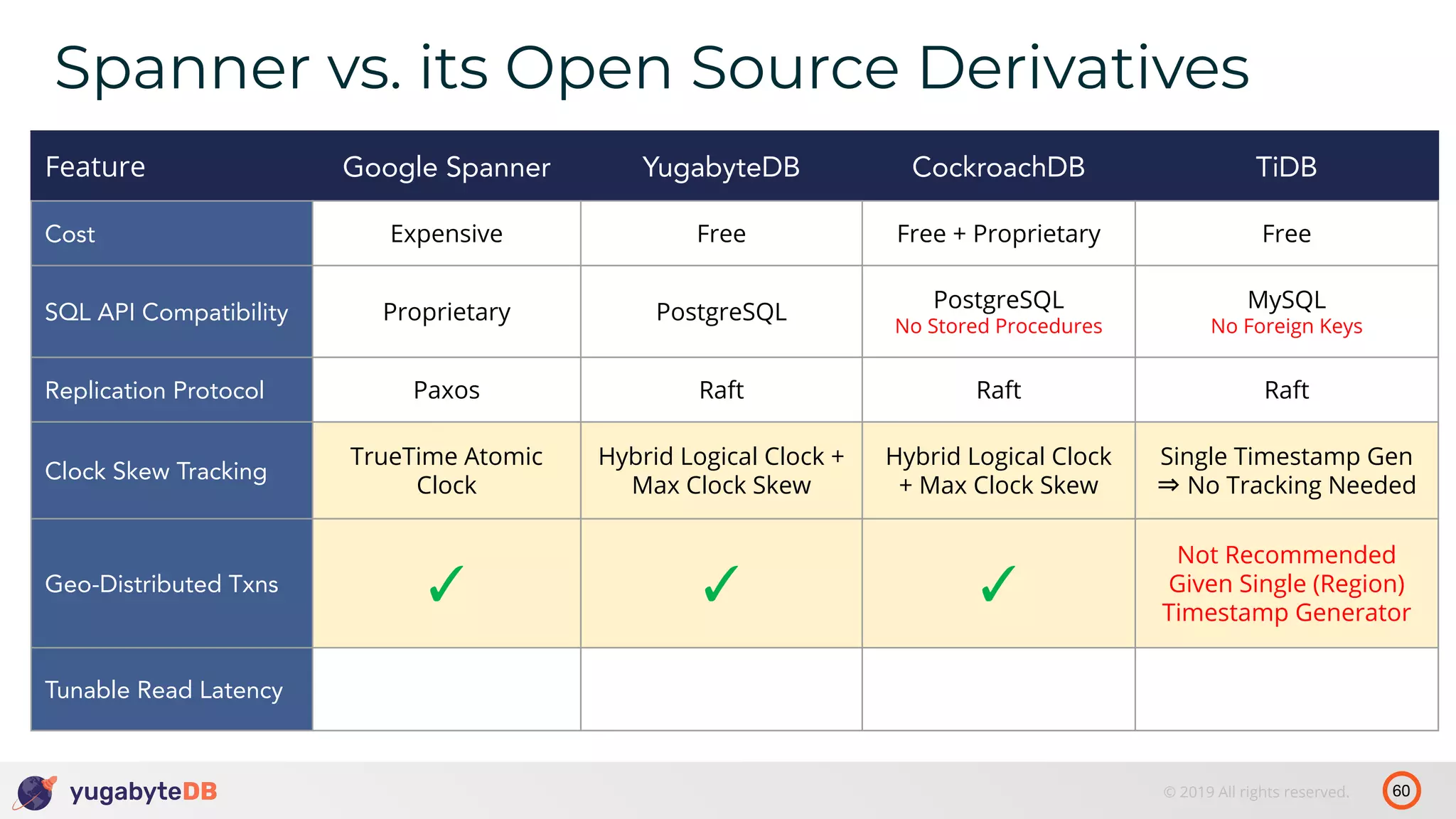
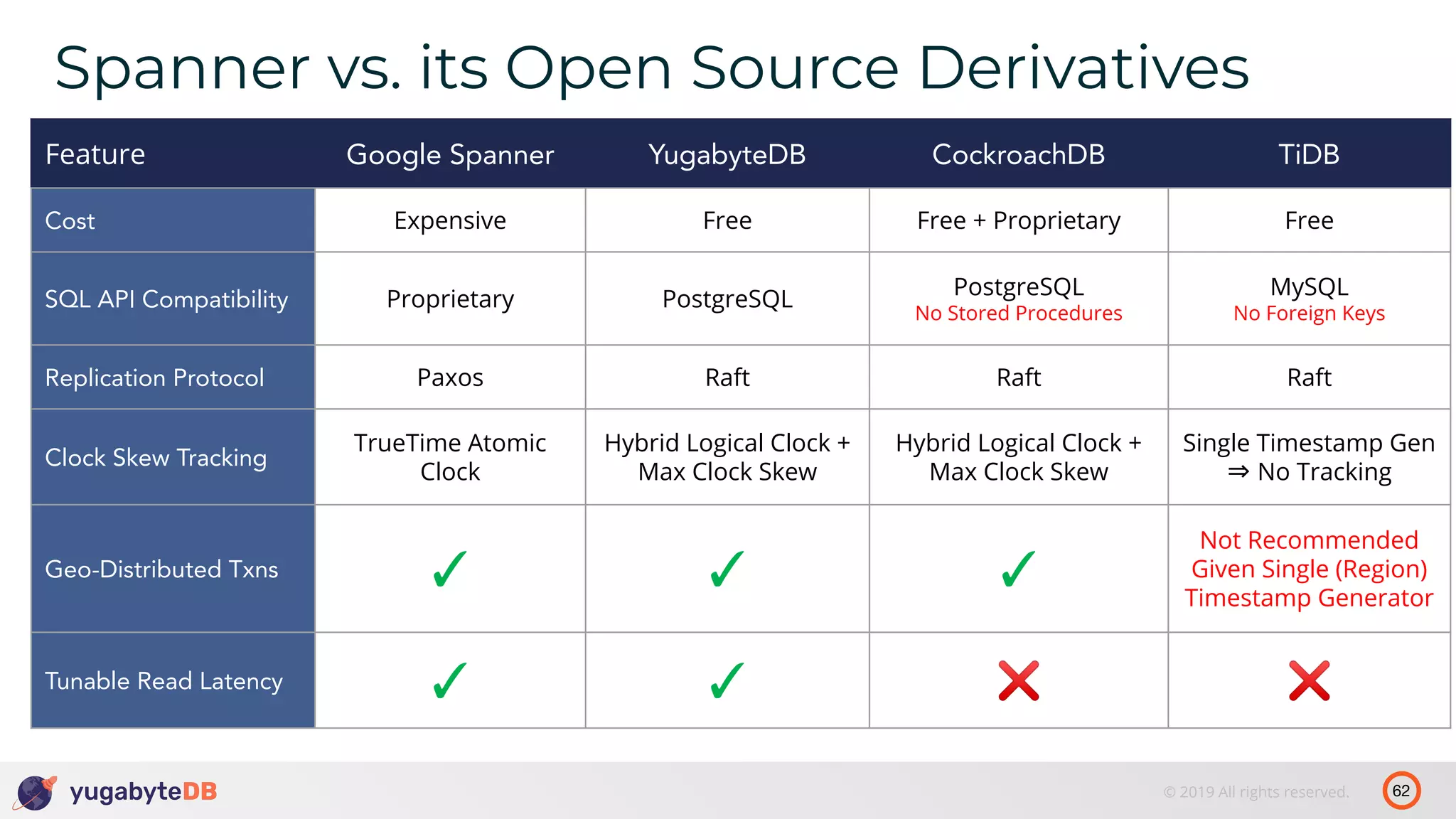
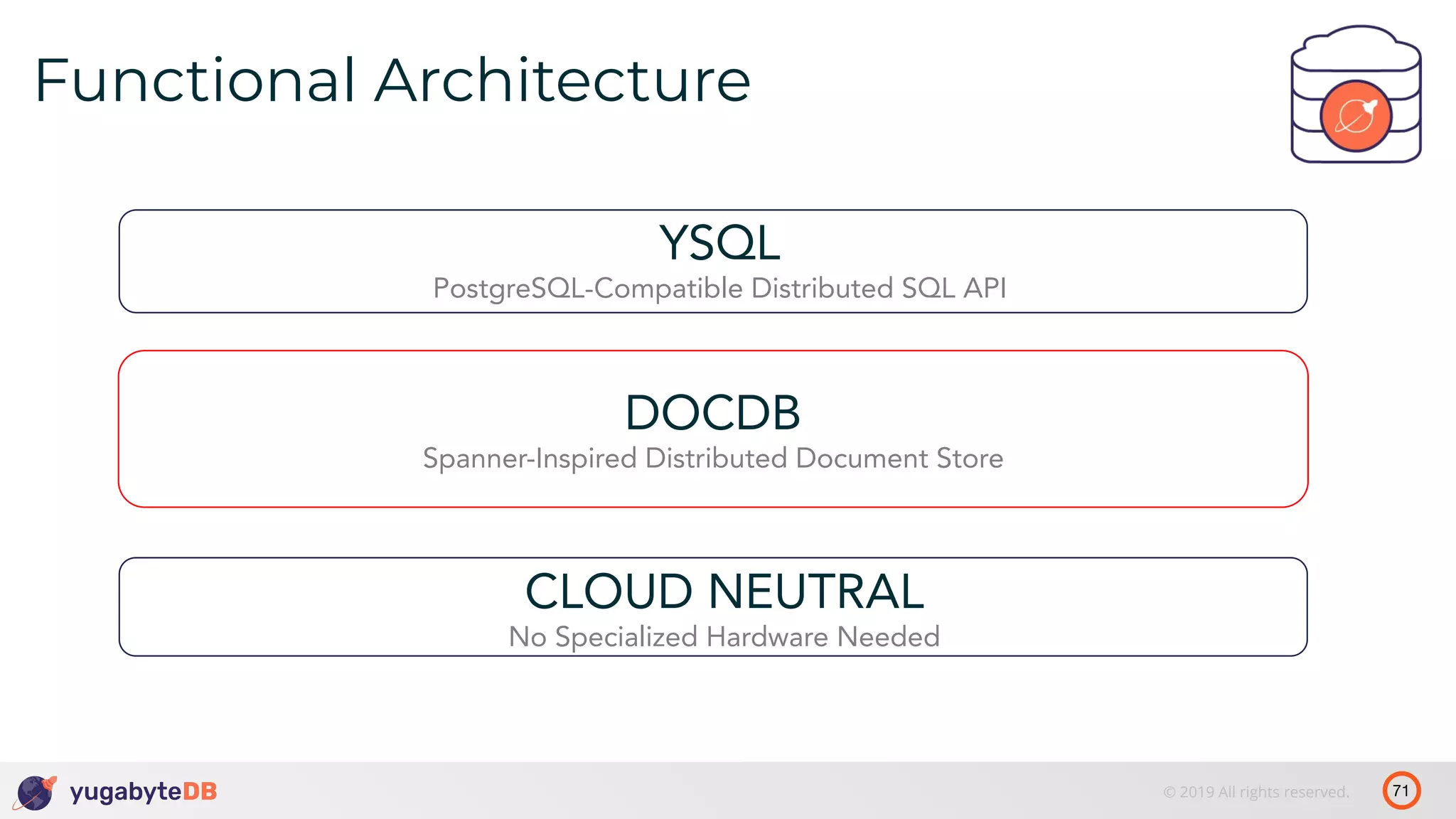
The document discusses distributed SQL databases, particularly focusing on Amazon Aurora and Google Spanner, comparing their architectures and features. It highlights the advantages of distributed SQL in terms of scalability, fault tolerance, and globally consistent writes while addressing common issues associated with traditional SQL databases. Additionally, it introduces YugabyteDB, an open-source alternative inspired by Spanner, and its design principles aimed at achieving high performance and consistency in distributed environments.