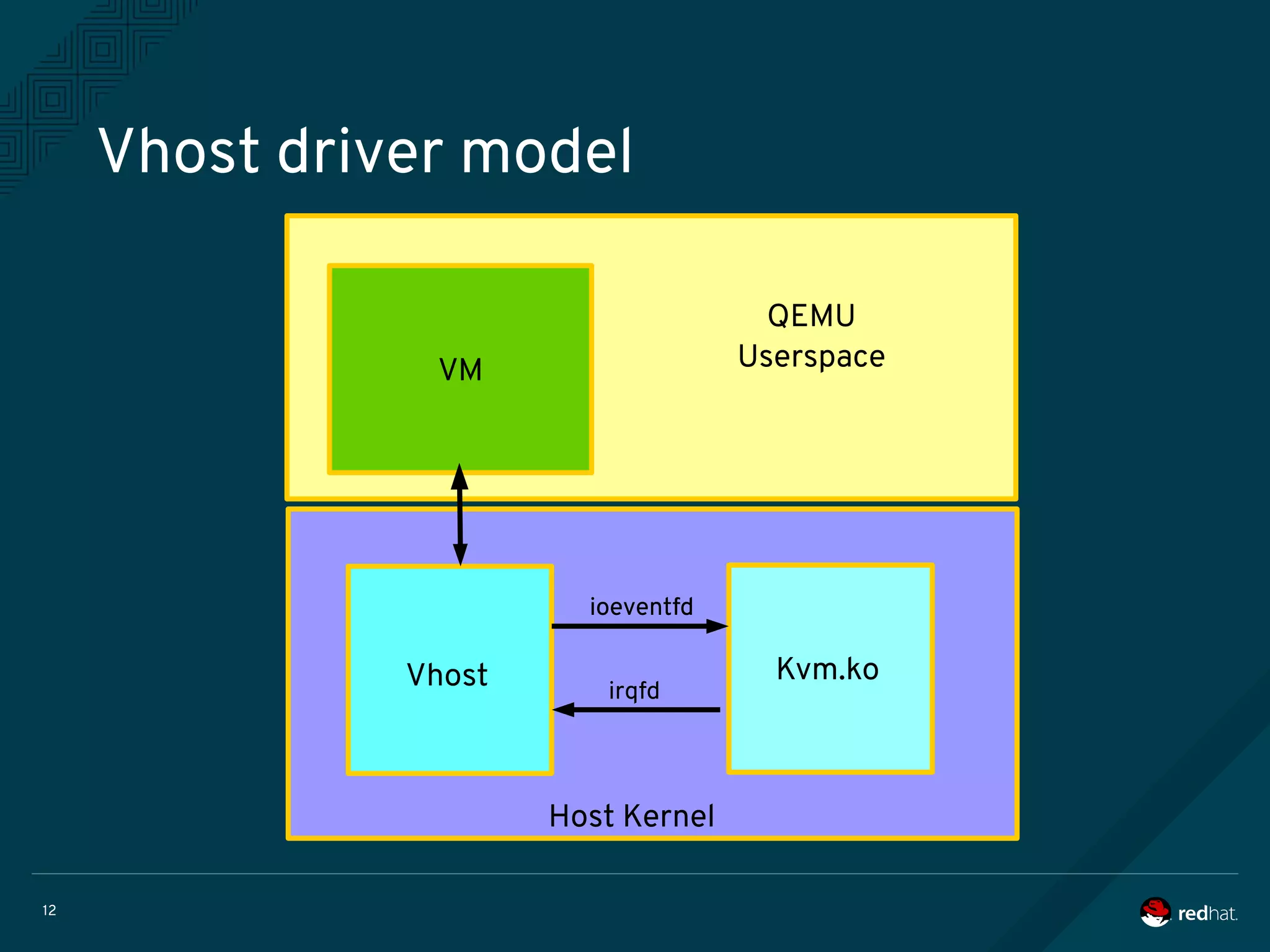
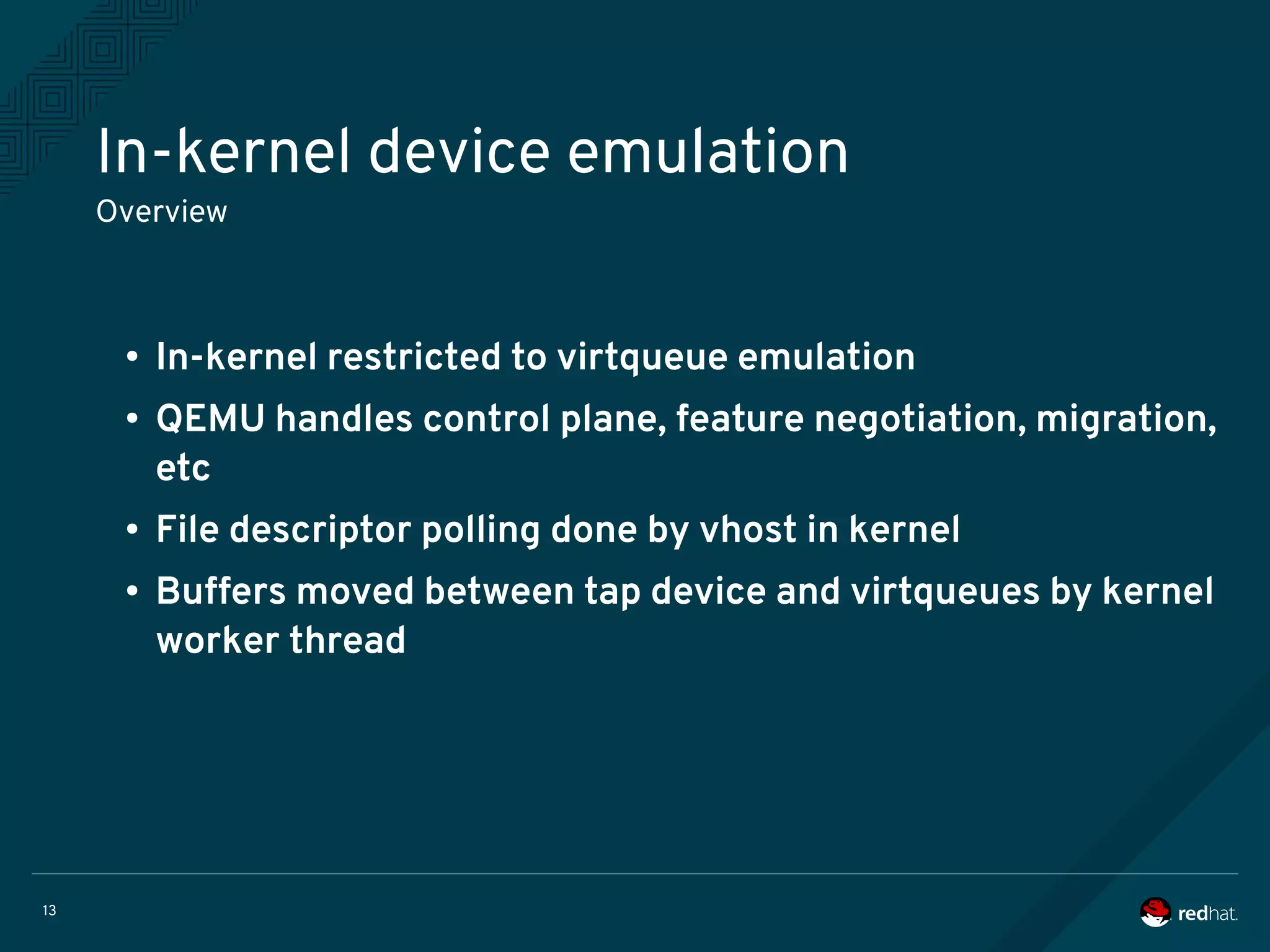
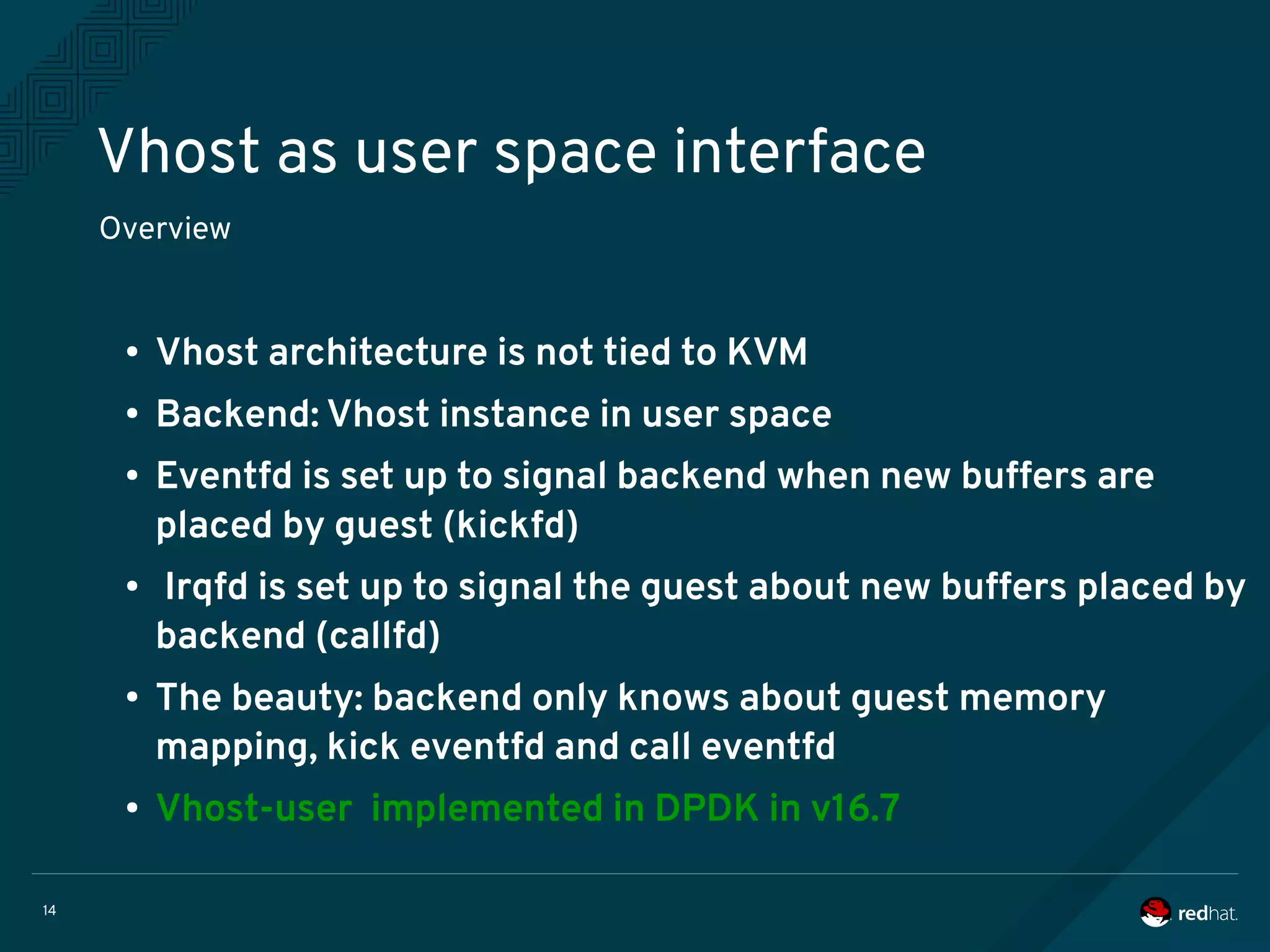
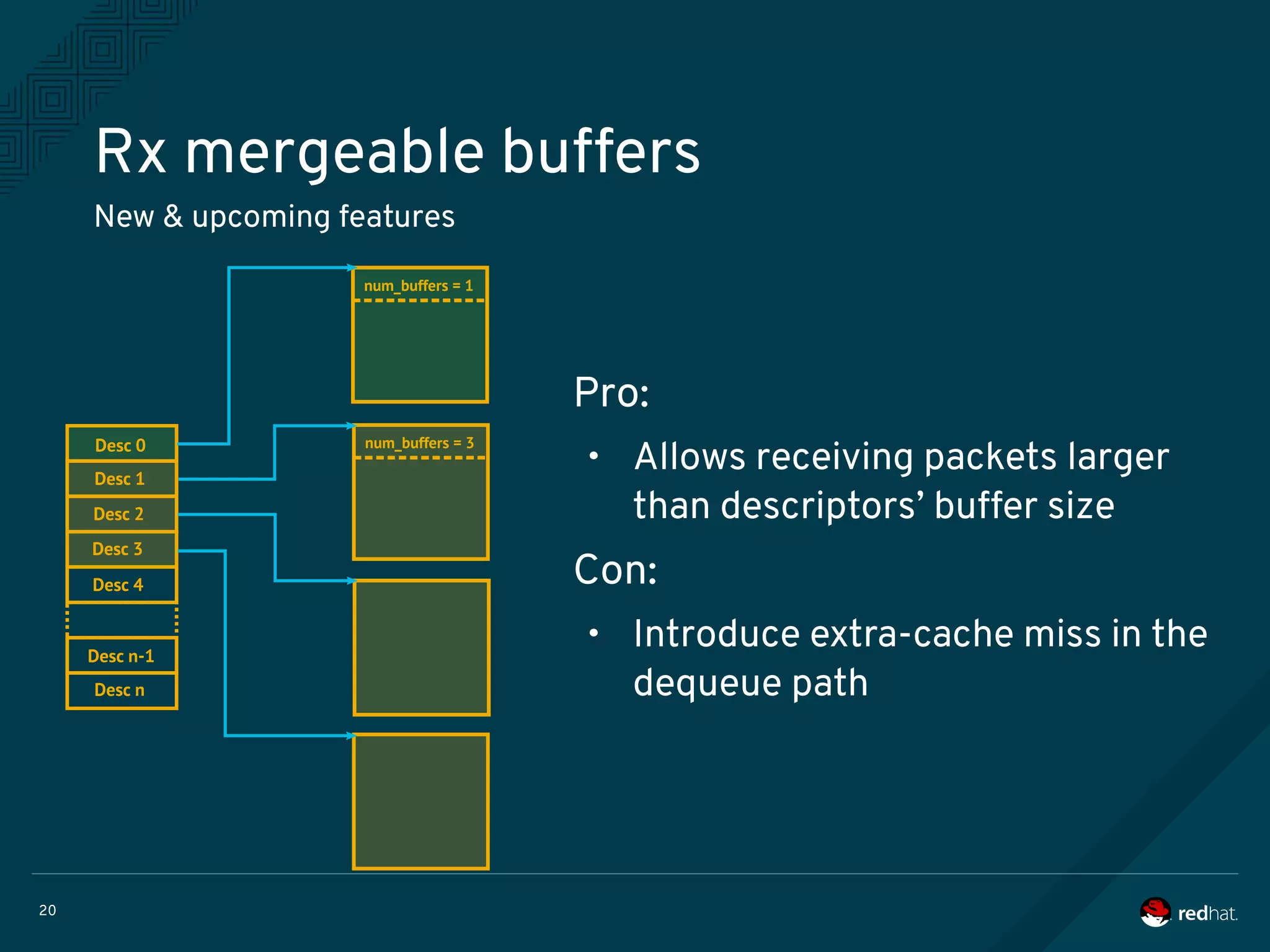
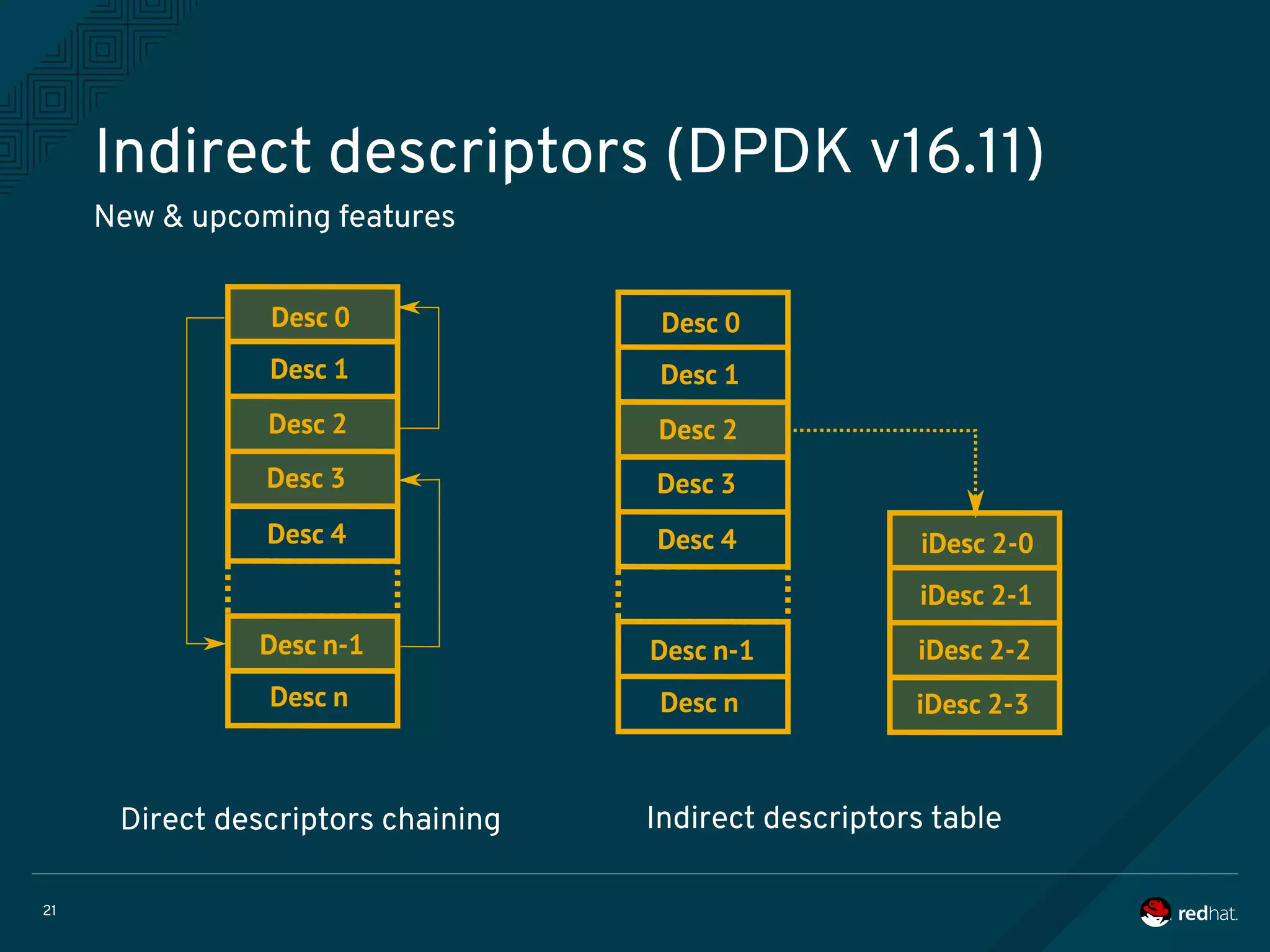
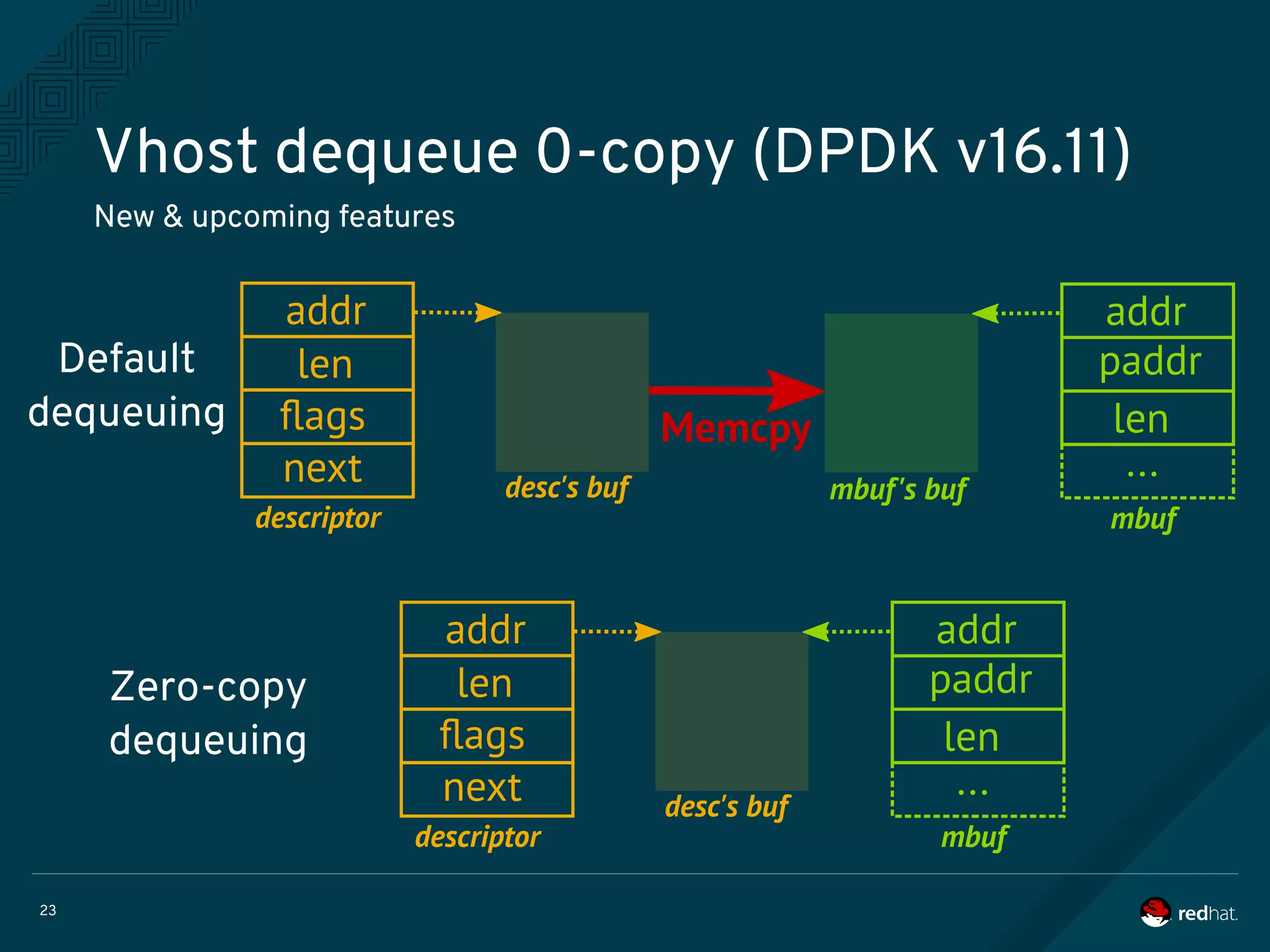
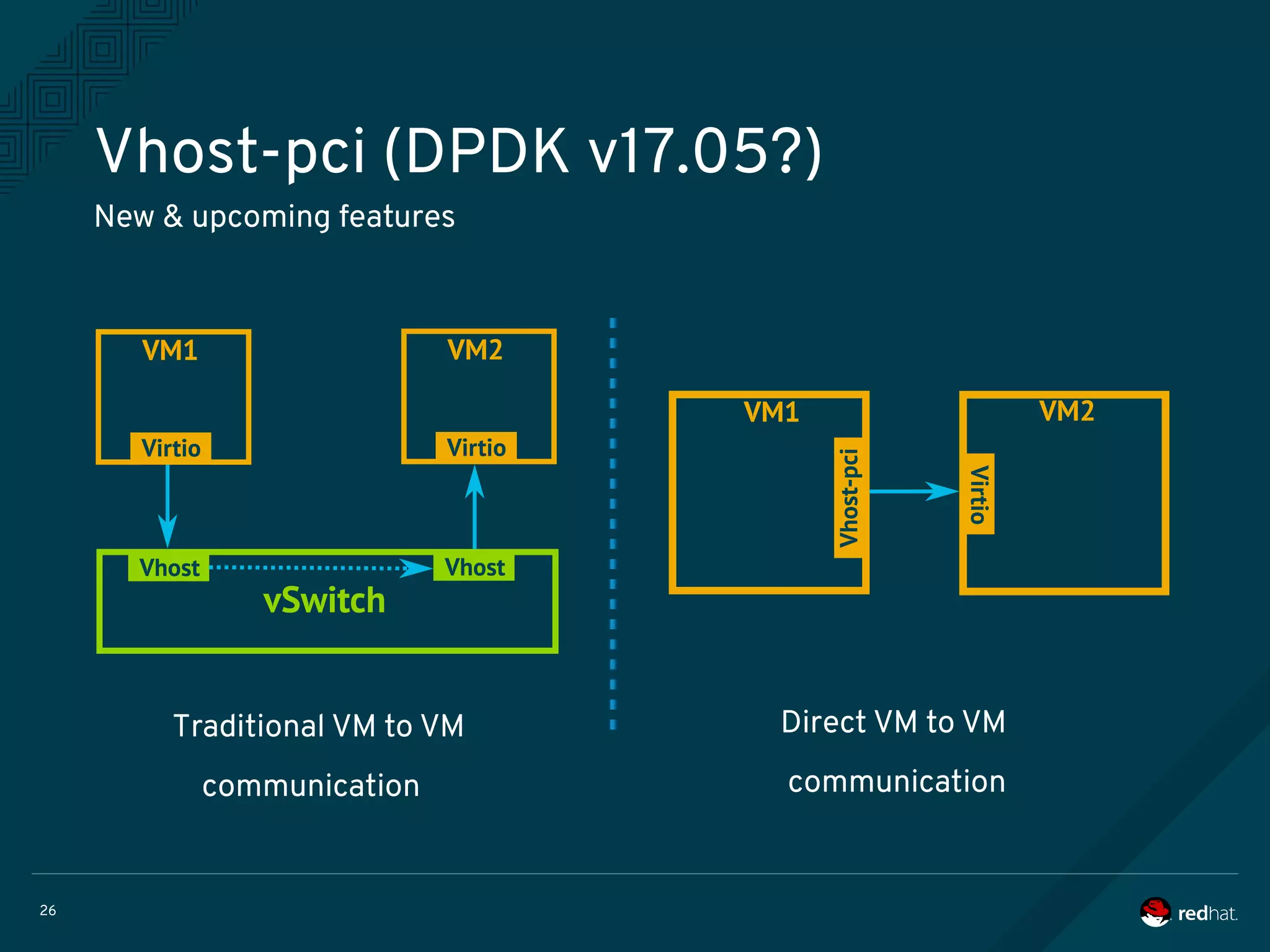
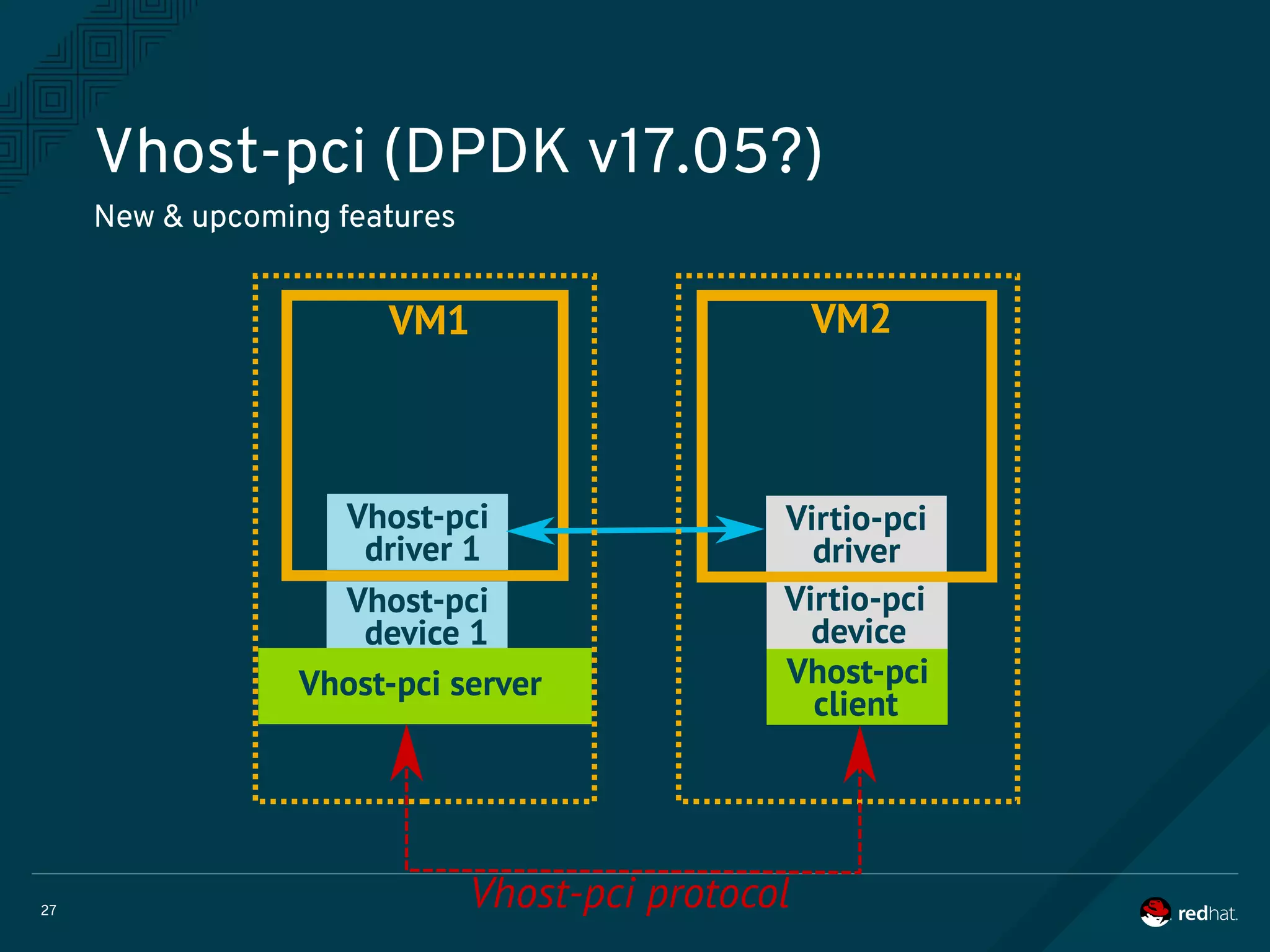
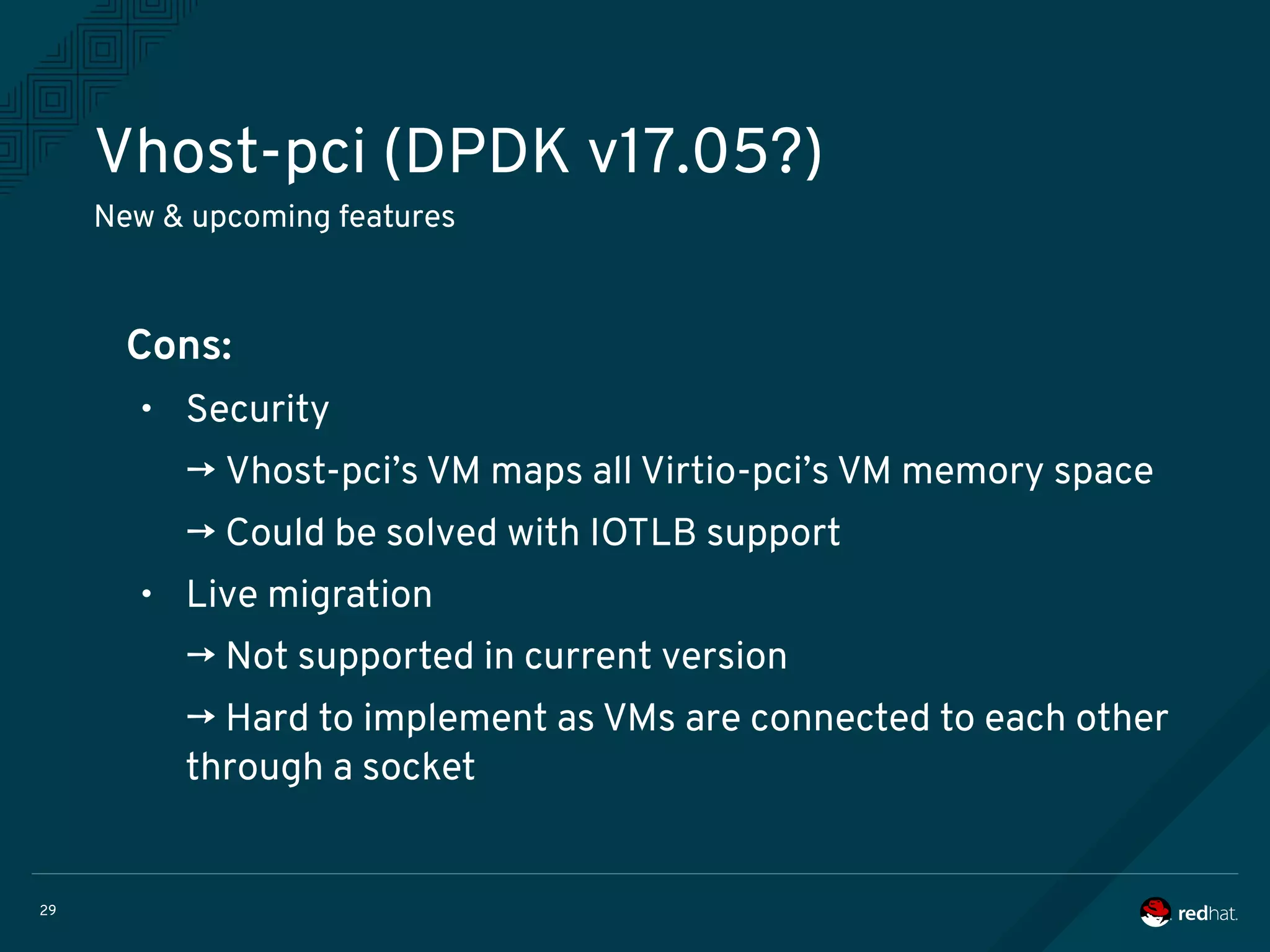
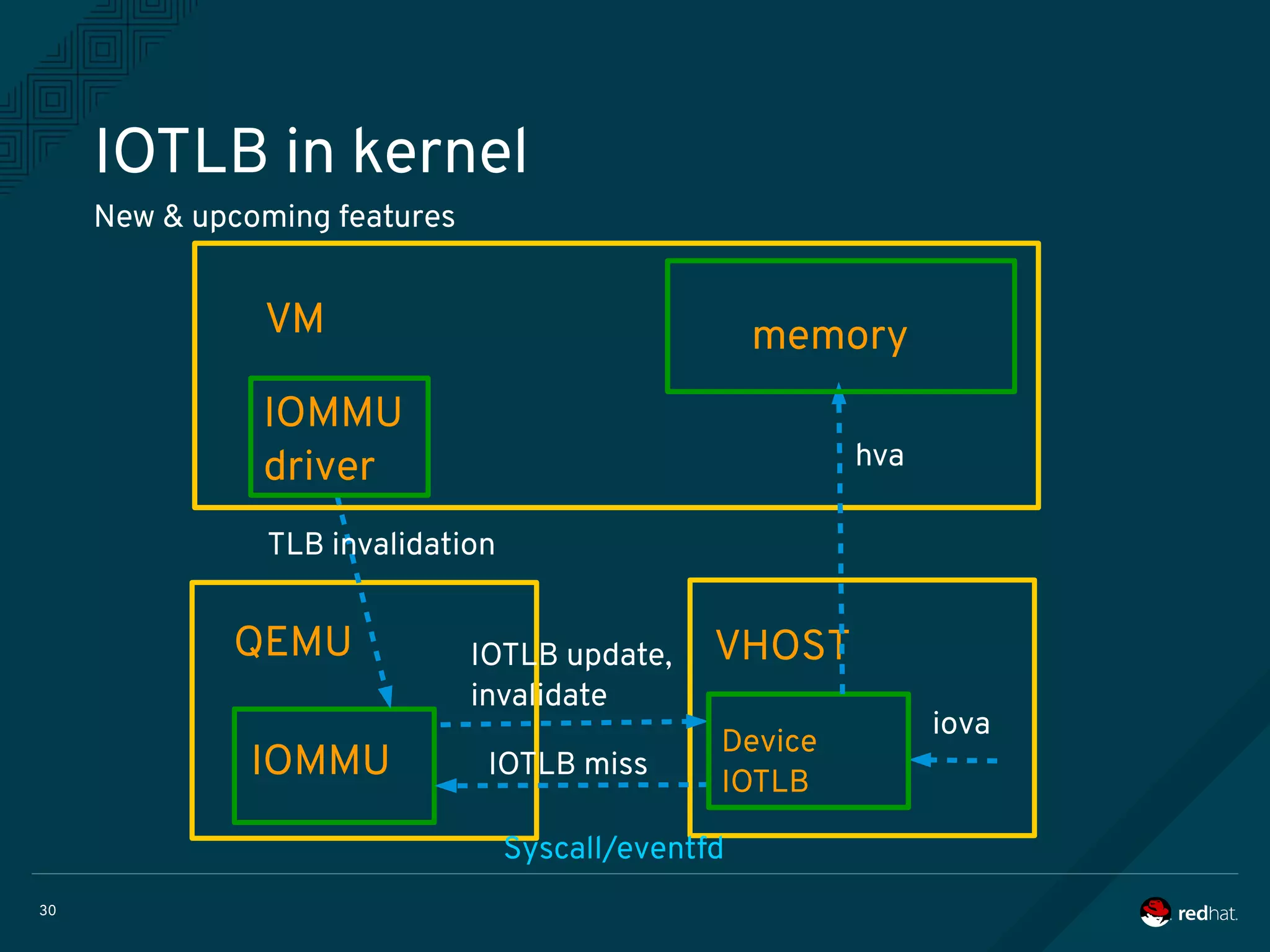
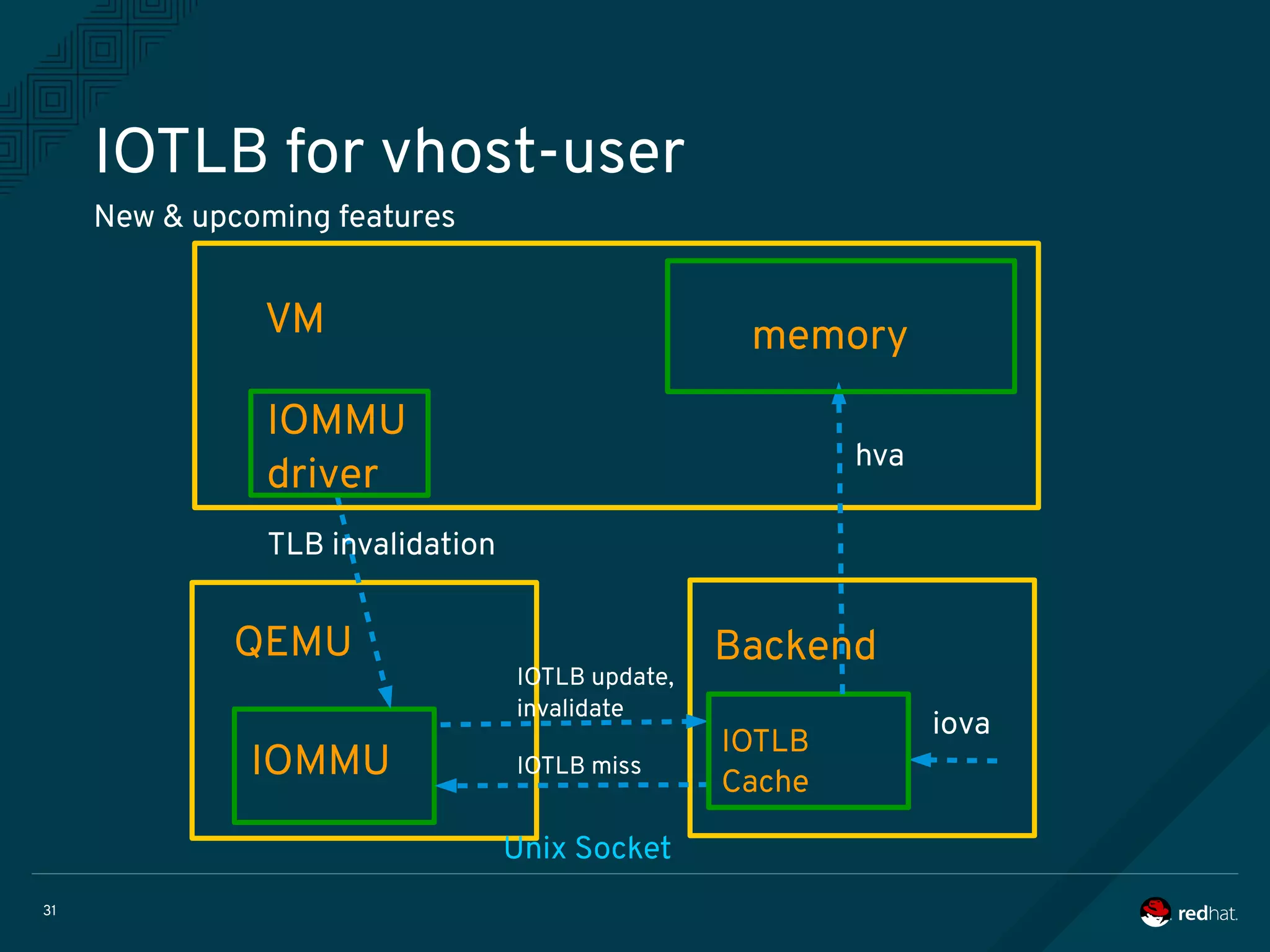
The document discusses the potential benefits of using DPDK (Data Plane Development Kit) for virtual machine (VM) networking, highlighting its focus on fast packet processing and flexibility. Key challenges include performance trade-offs, reliability during migration, and security considerations with untrusted guests. Upcoming features and enhancements aim to improve performance metrics such as packet loss and memory efficiency in VM networking contexts.