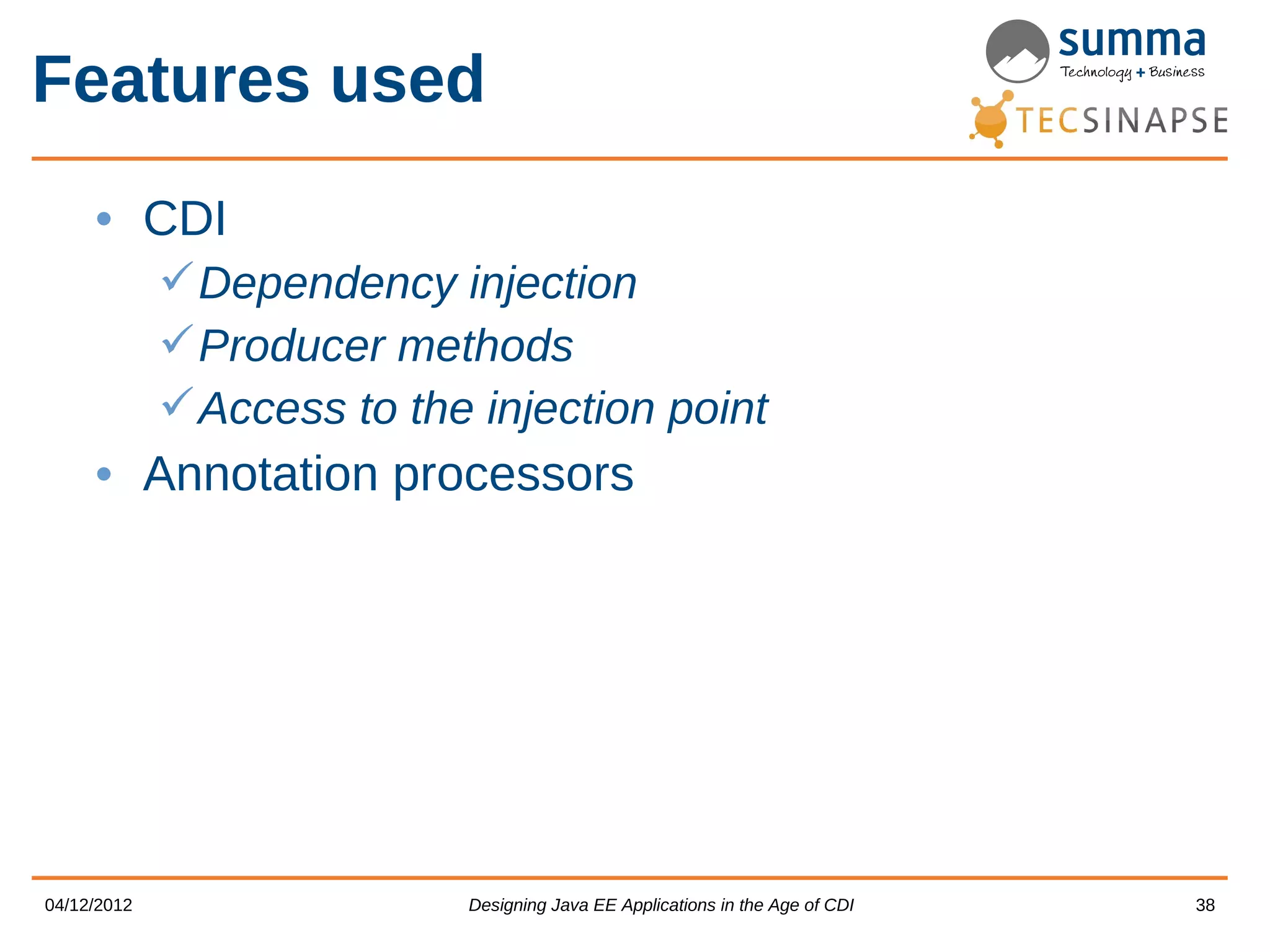
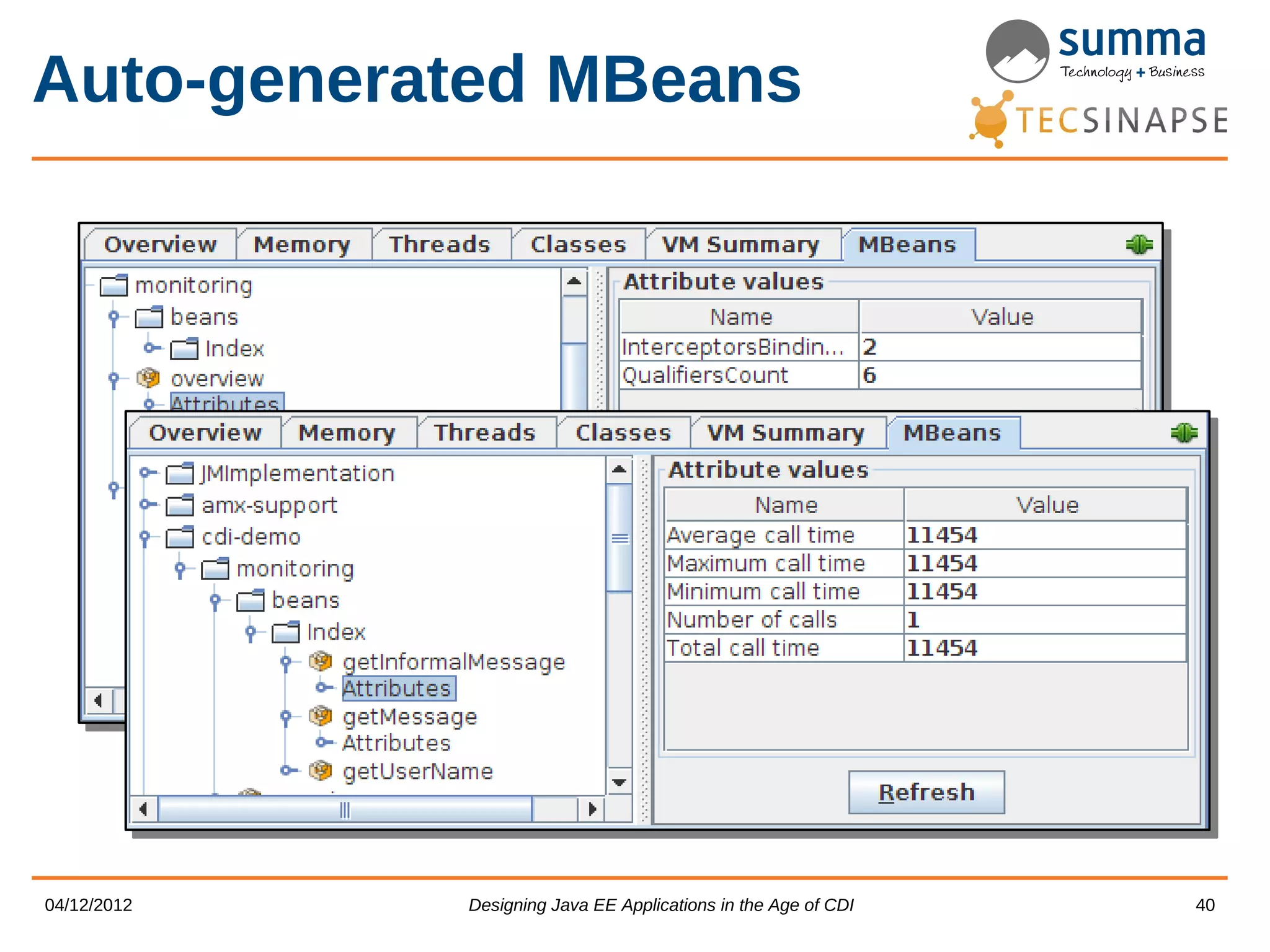
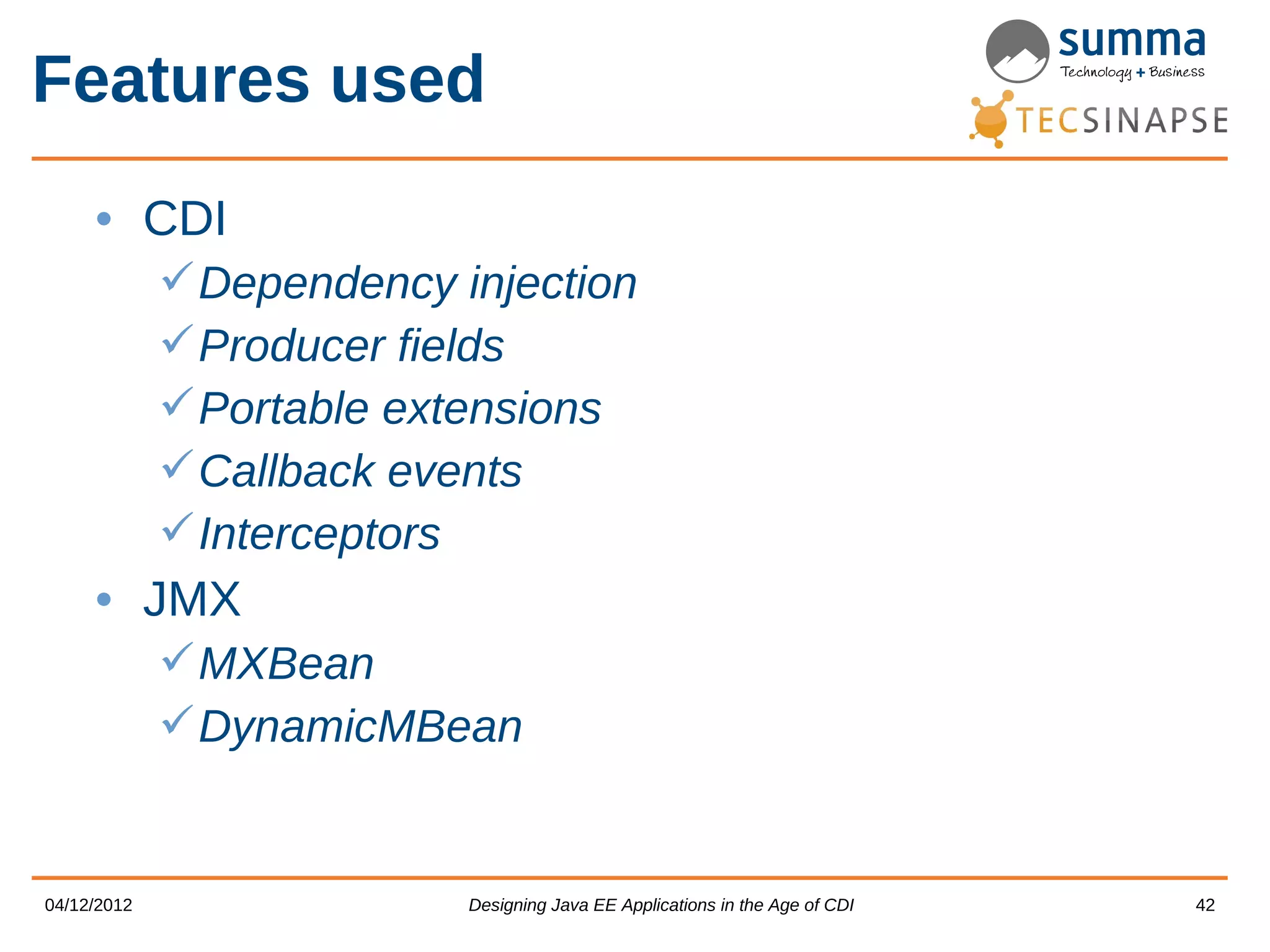
CDI provides features for dependency injection, events, interceptors, and extensions in Java EE applications. The presentation discusses CDI scopes, qualifiers, producers, events, interceptors, decorators, access to injection points, and portable extensions. It demonstrates how to generate JMX MBeans from CDI metadata and use CDI with JMX. The presenters encourage designing new Java EE applications using CDI's unique capabilities.










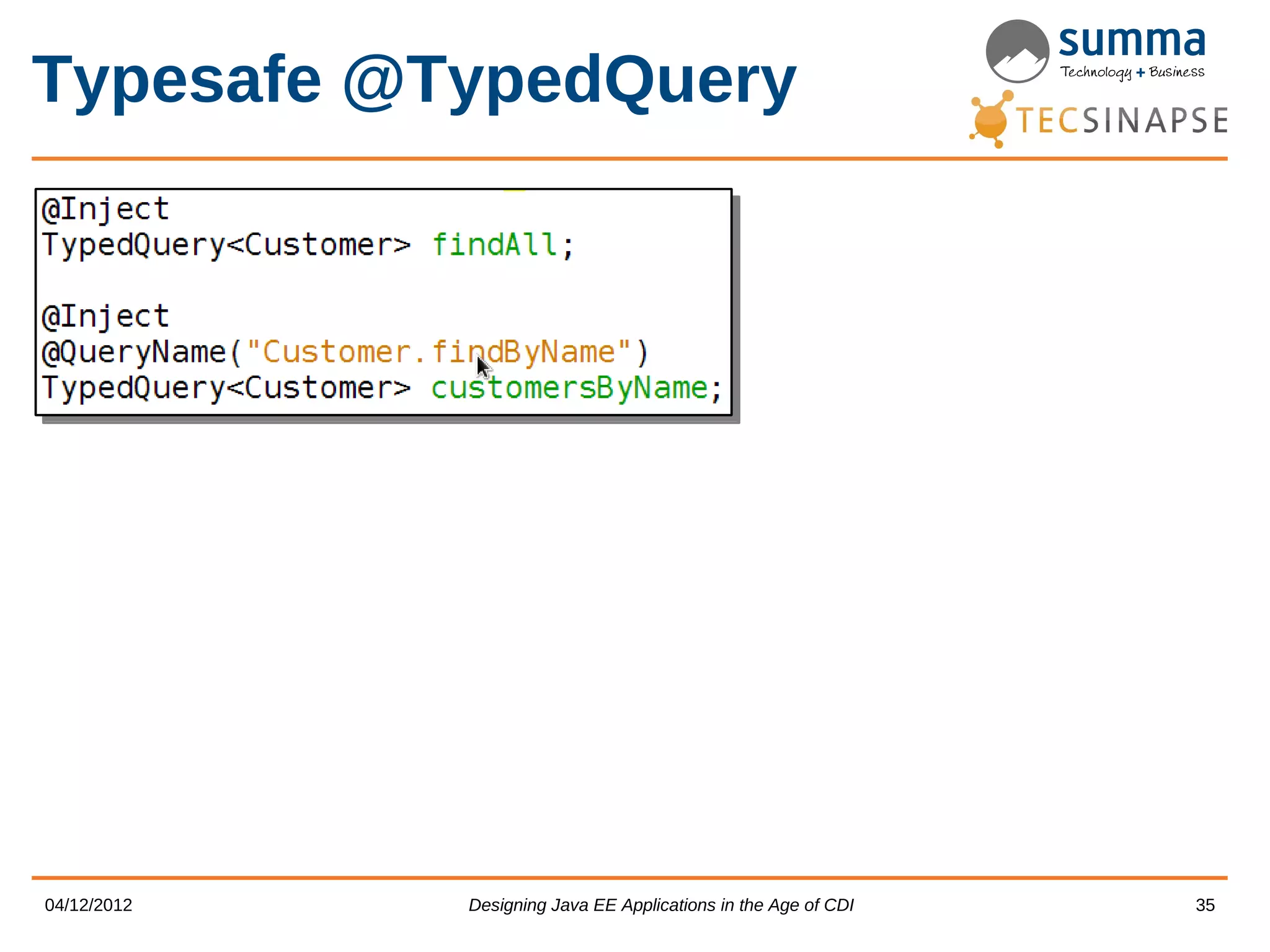
![Typesafe @TypedQuery ------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------------------------------------- COMPILATION ERROR :: COMPILATION ERROR ------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------------------------------------- and returns false. and returns false. model/CustomerModel.java:[47,25] error: Named query 'Customer.findByNme' not defined yet. model/CustomerModel.java:[47,25] error: Named query 'Customer.findByNme' not defined yet. model/CustomerModel.java:[43,25] error: Named query 'Customer.findAl' not defined yet. model/CustomerModel.java:[43,25] error: Named query 'Customer.findAl' not defined yet. 2 errors 2 errors ------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------------------------------------- 04/12/2012 Designing Java EE Applications in the Age of CDI 36](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/con21001pdf-121211052218-phpapp01/75/Designing-Java-EE-Applications-in-the-Age-of-CDI-36-2048.jpg)