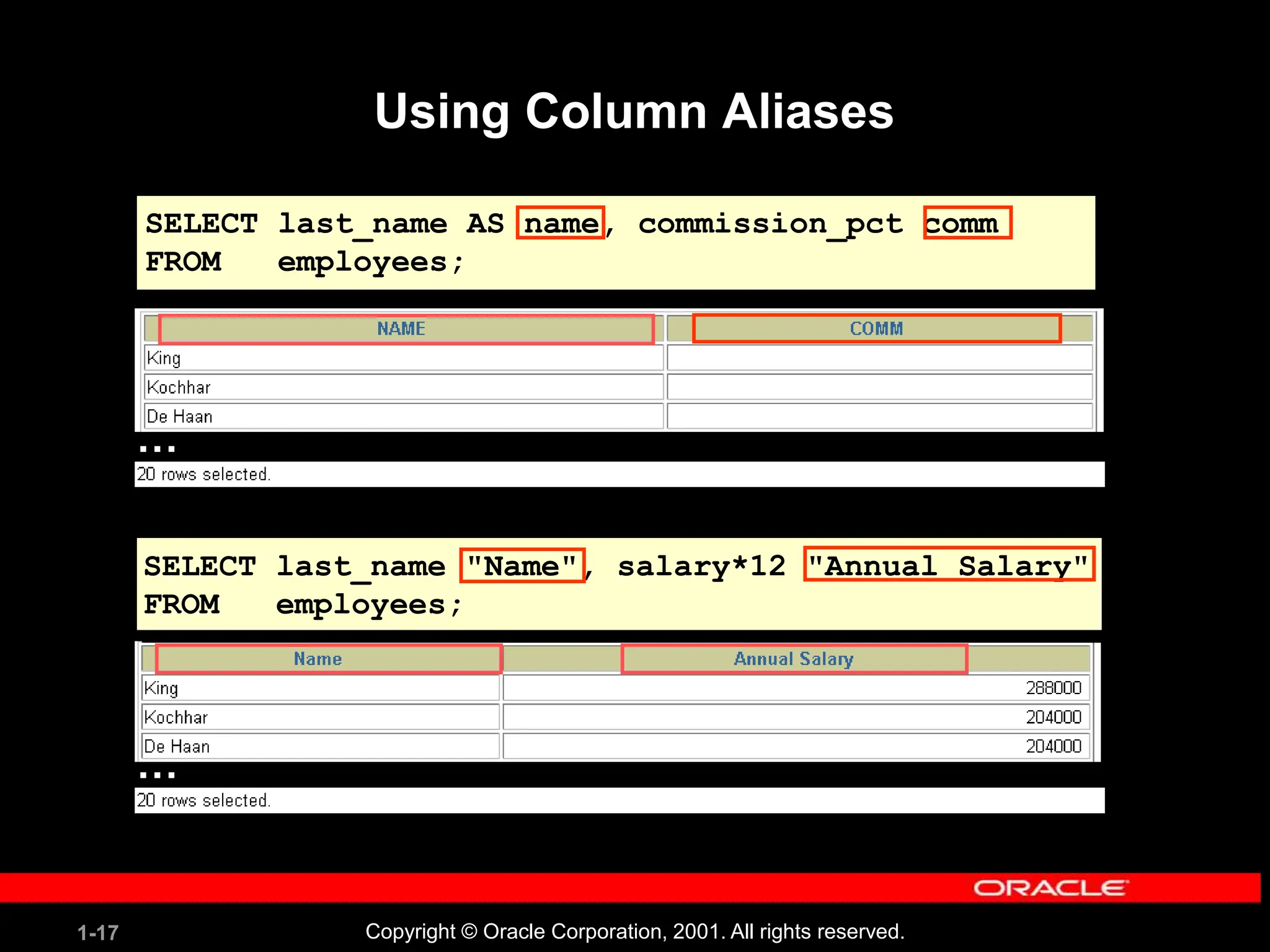
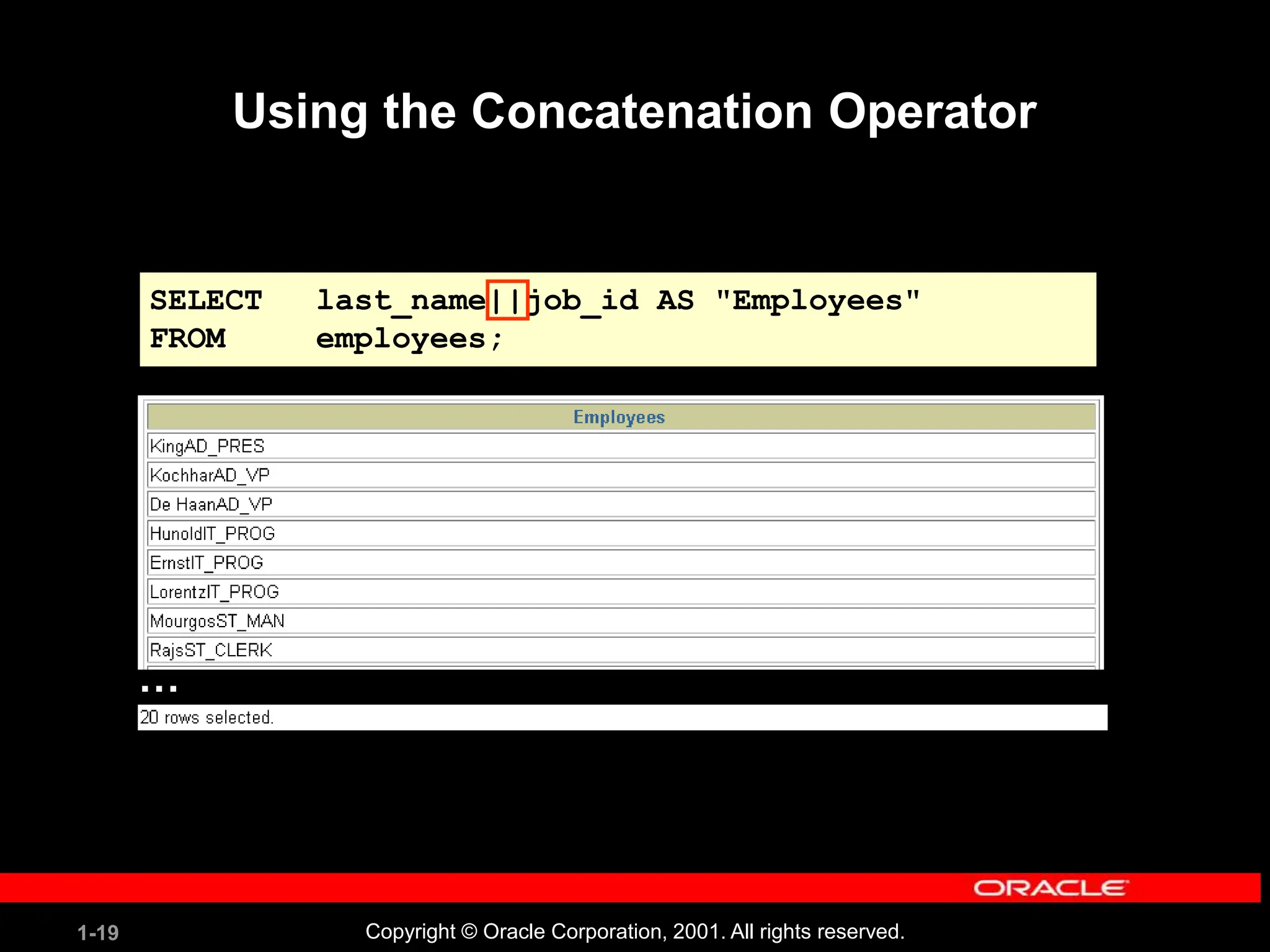
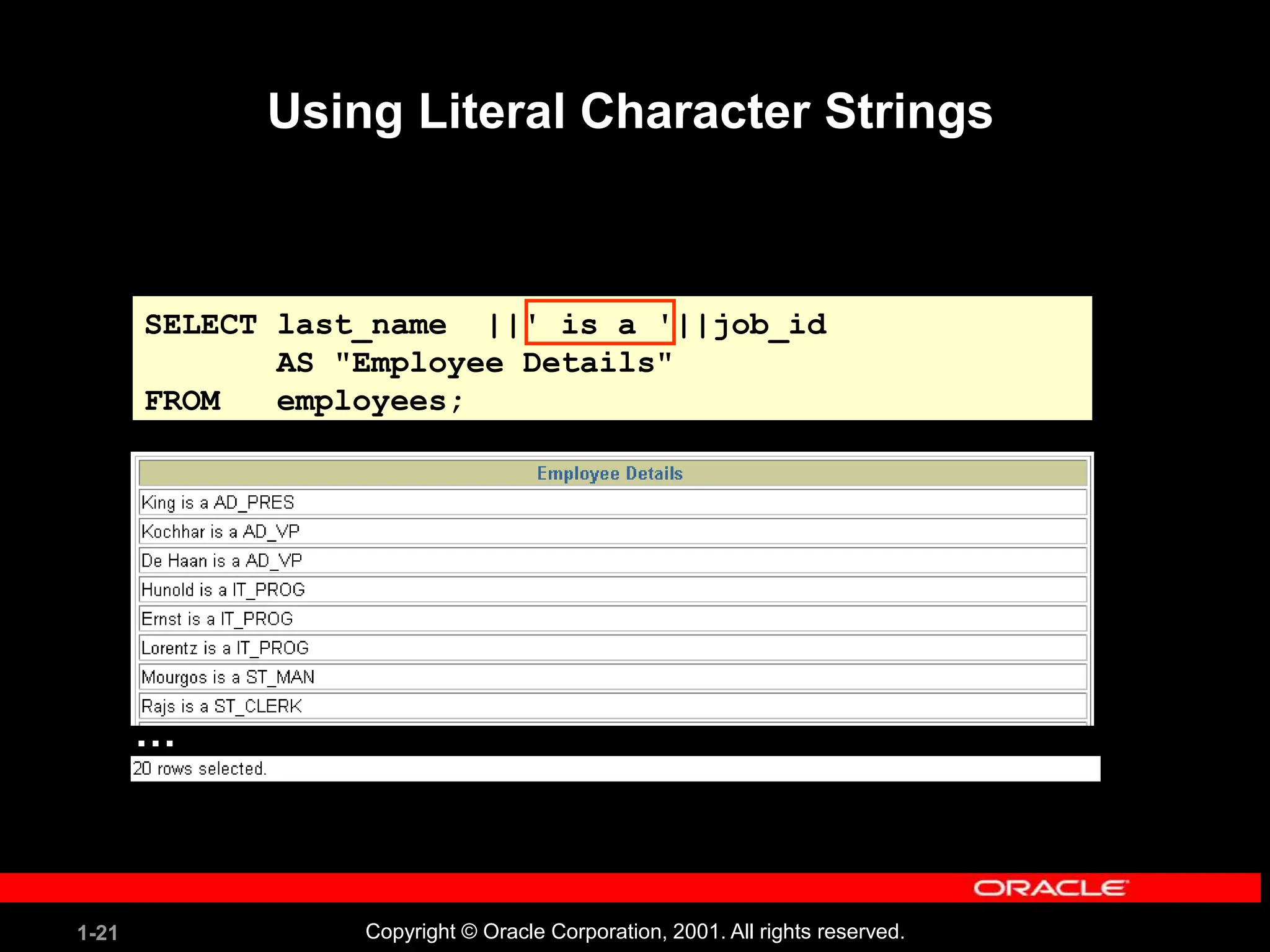
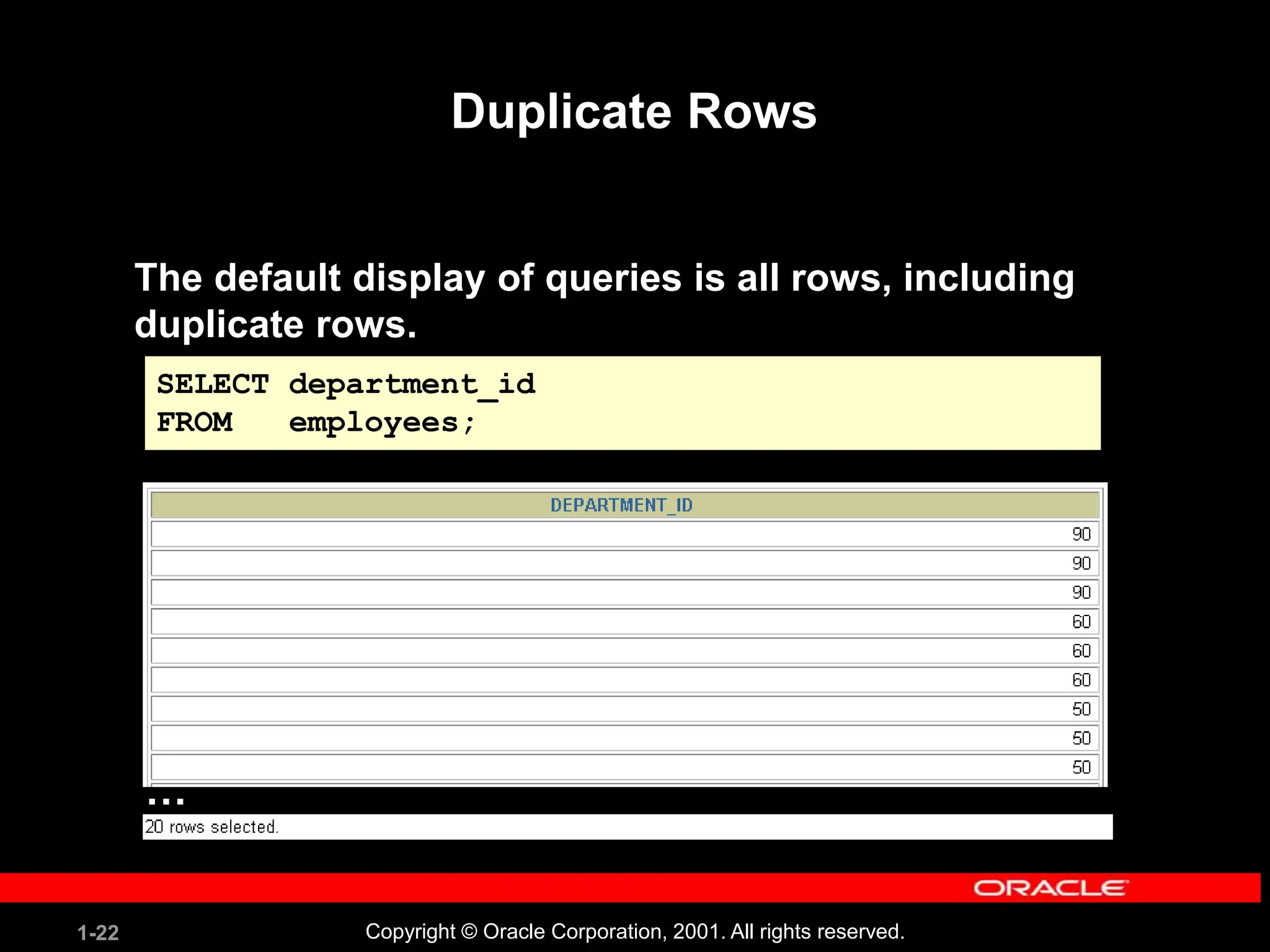
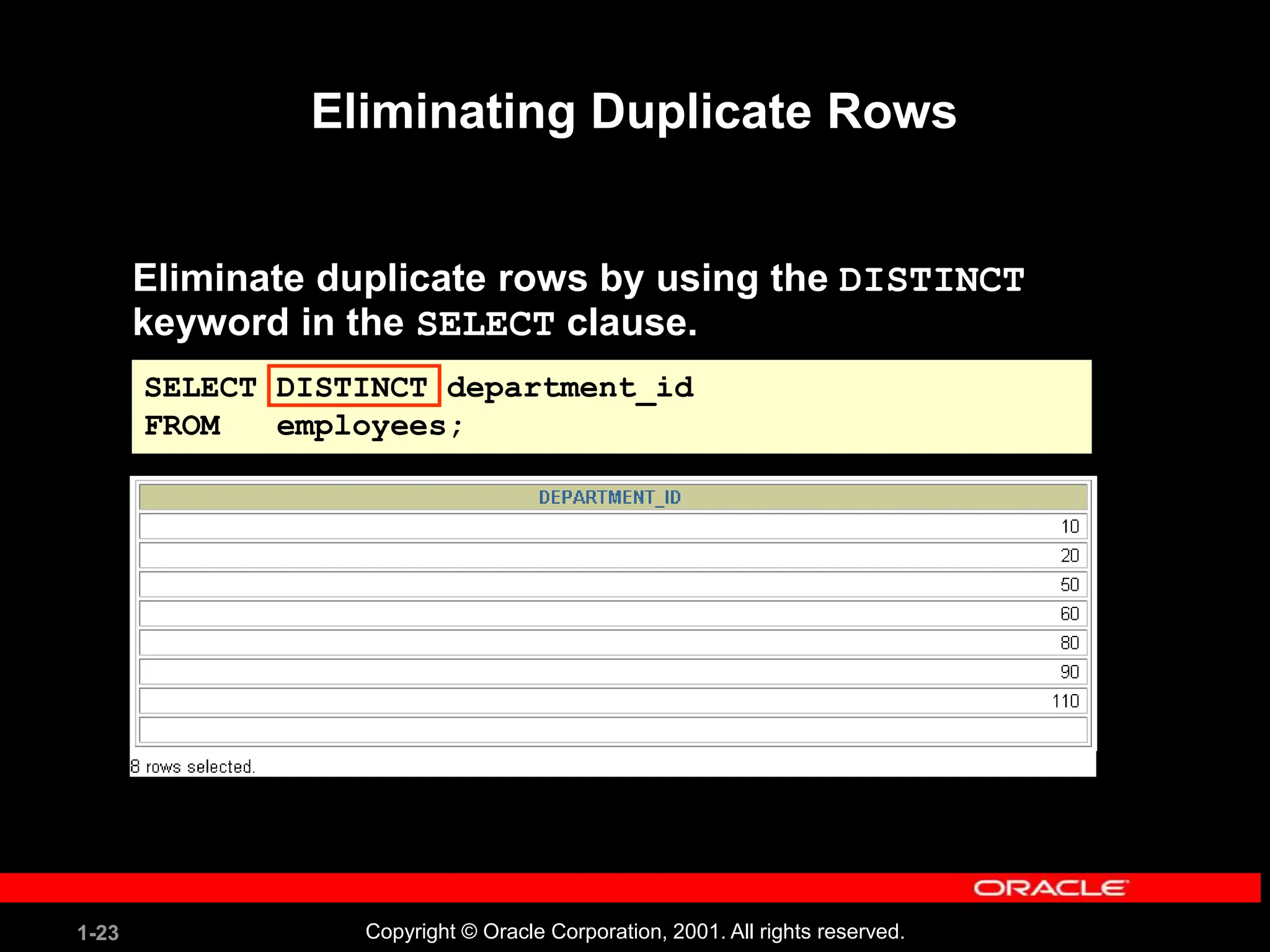
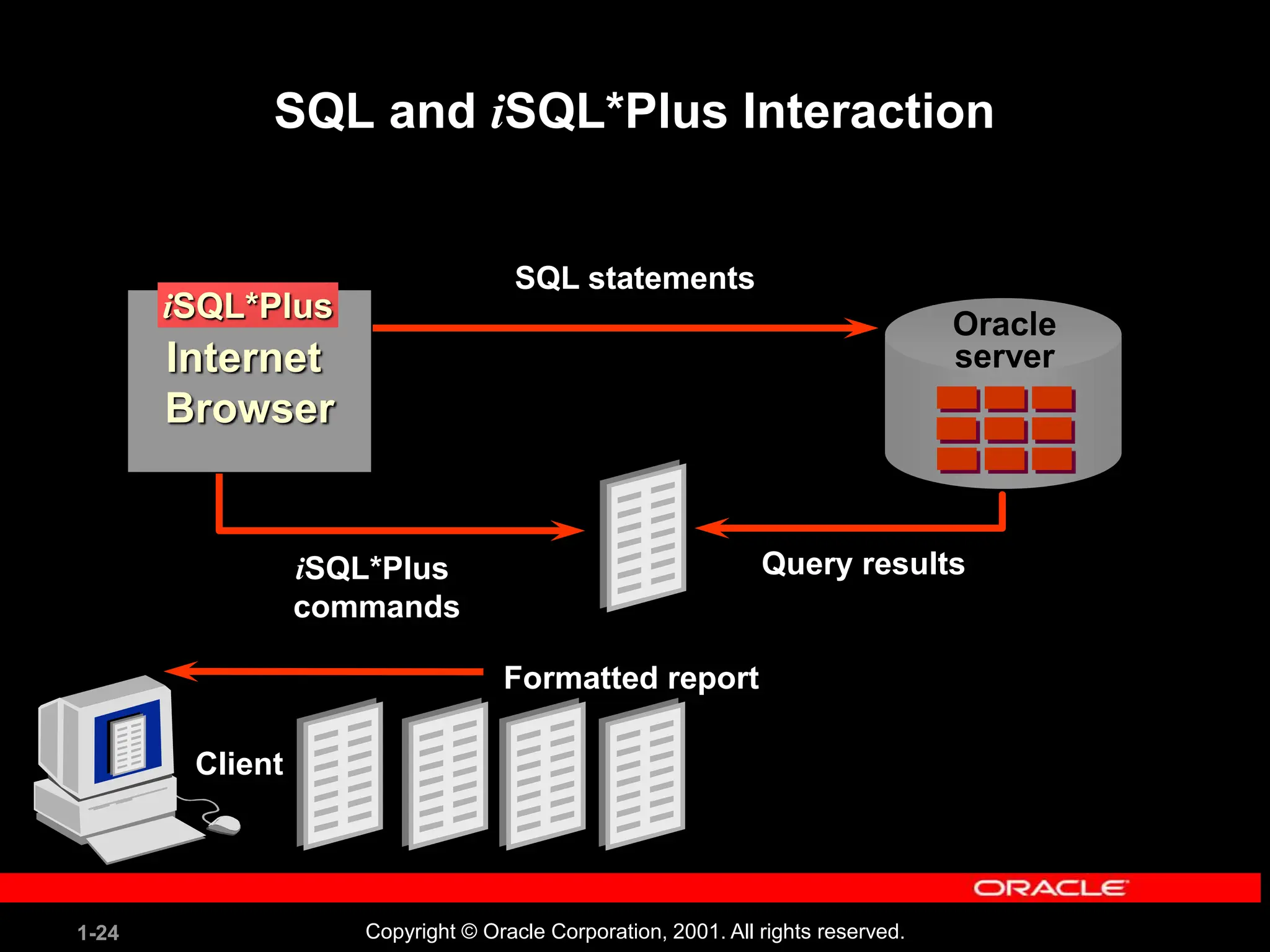
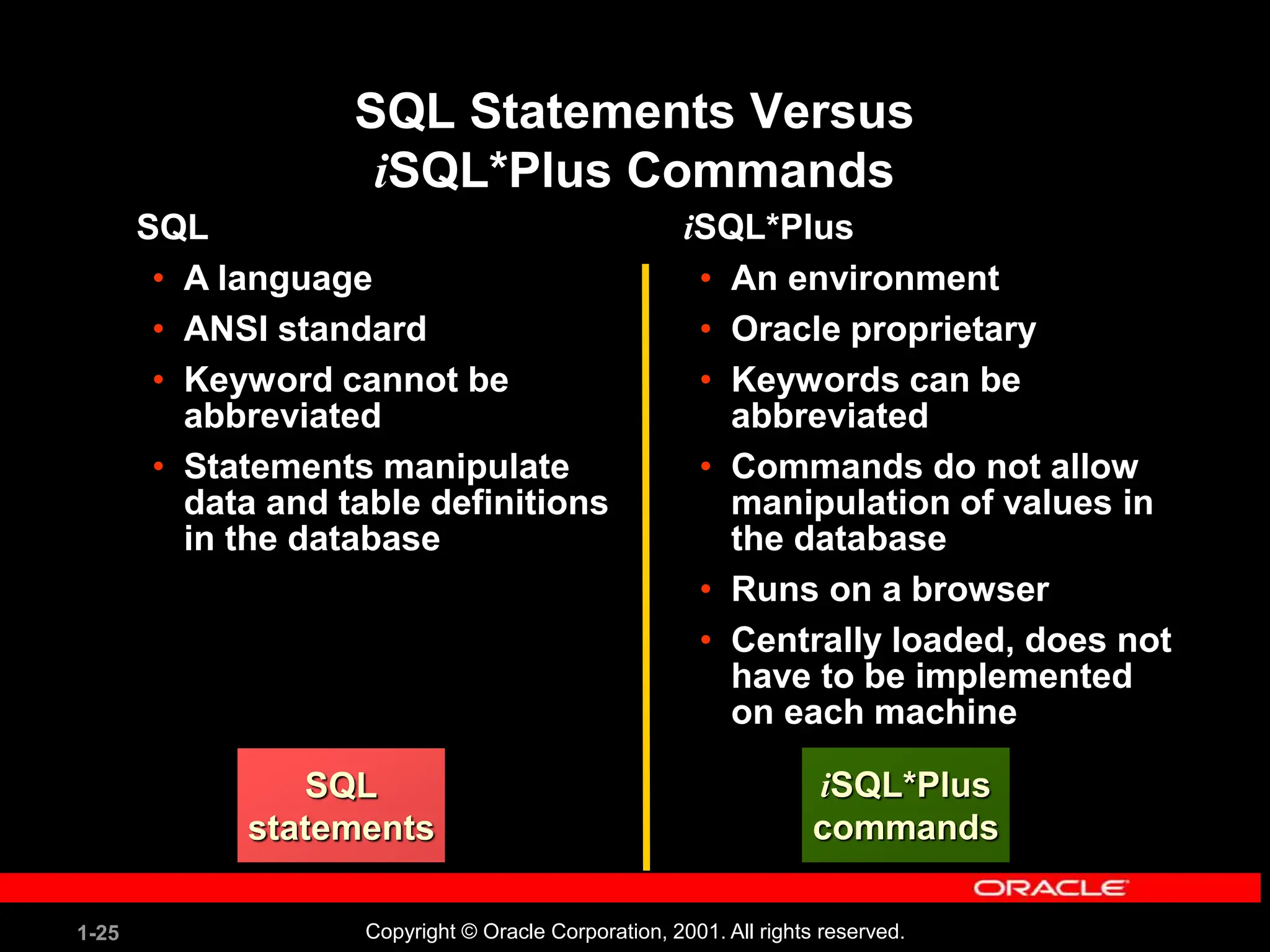
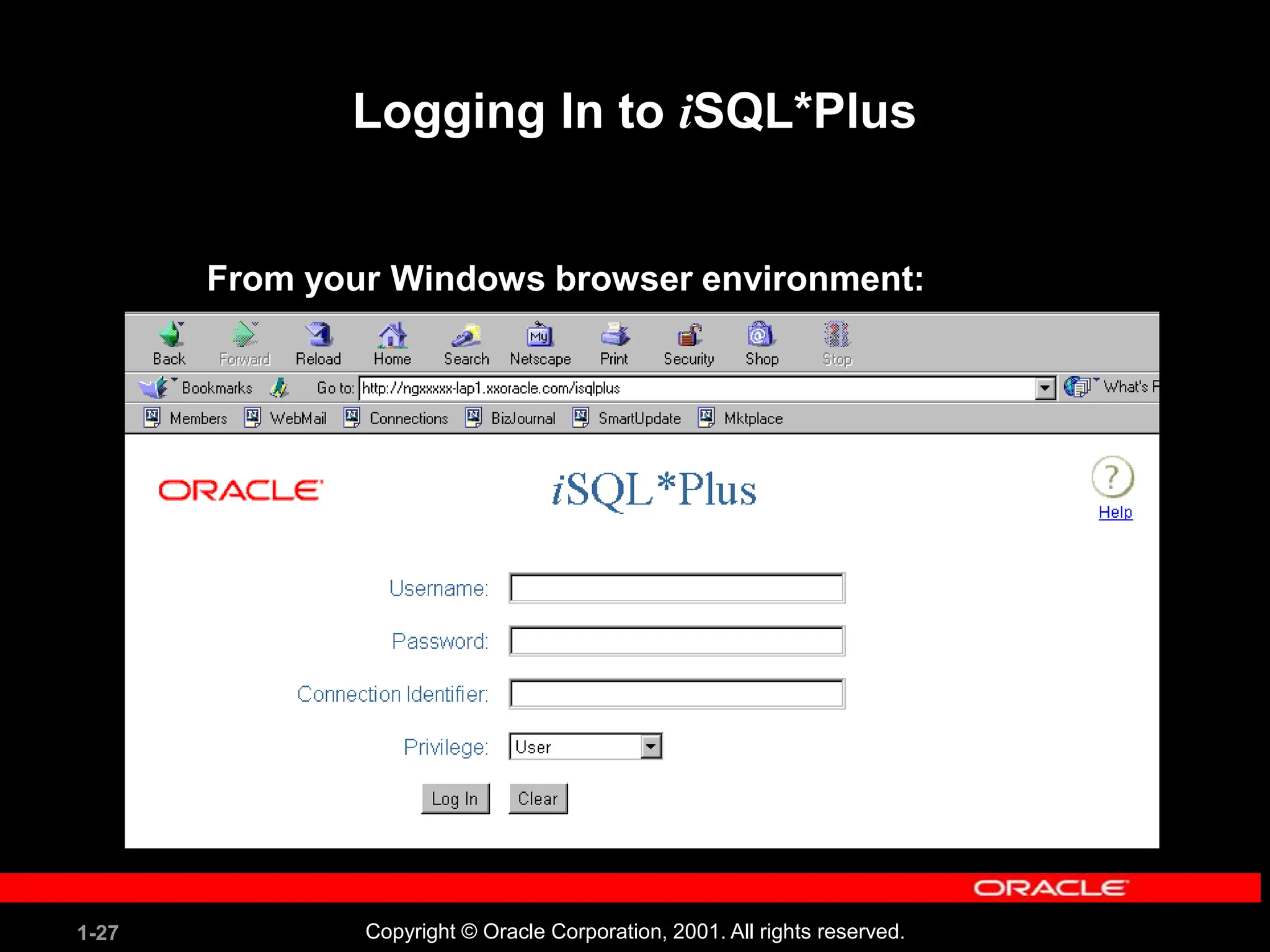
This document covers the basics of writing SQL select statements, including execution, column selection, and the use of various SQL commands and clauses. It explains the structure of SQL statements, how to handle null values, create column aliases, and utilize the isql*plus environment for executing SQL commands. Key learning objectives include the construction of select statements, output manipulation, and interaction with tables.


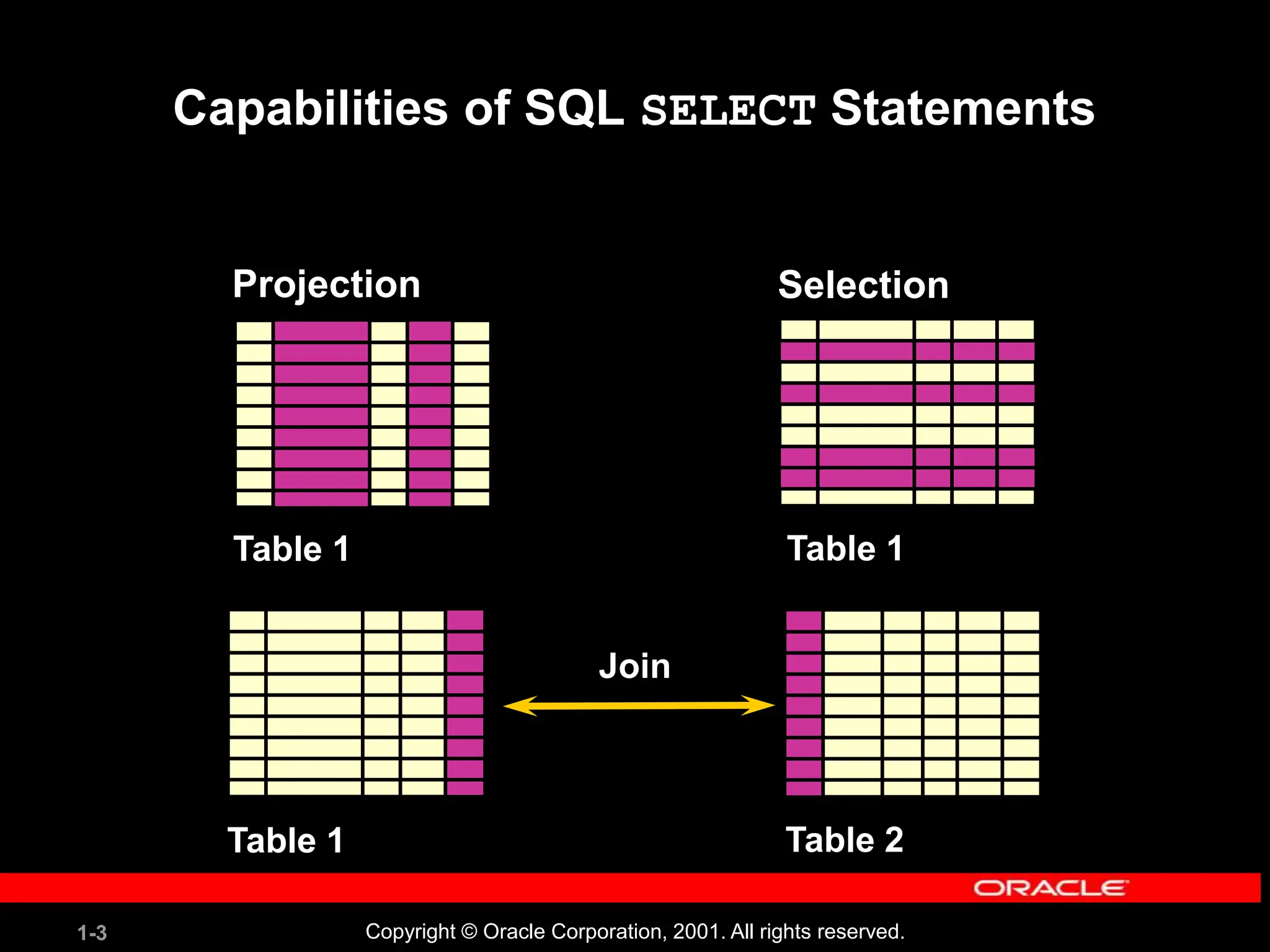
![1-4 Copyright © Oracle Corporation, 2001. All rights reserved. Basic SELECT Statement SELECT *|{[DISTINCT] column|expression [alias],...} FROM table; • SELECT identifies what columns • FROM identifies which table](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les01-240424185627-6f2cc032/75/Database-Management-Systems-SQL-And-DDL-language-4-2048.jpg)
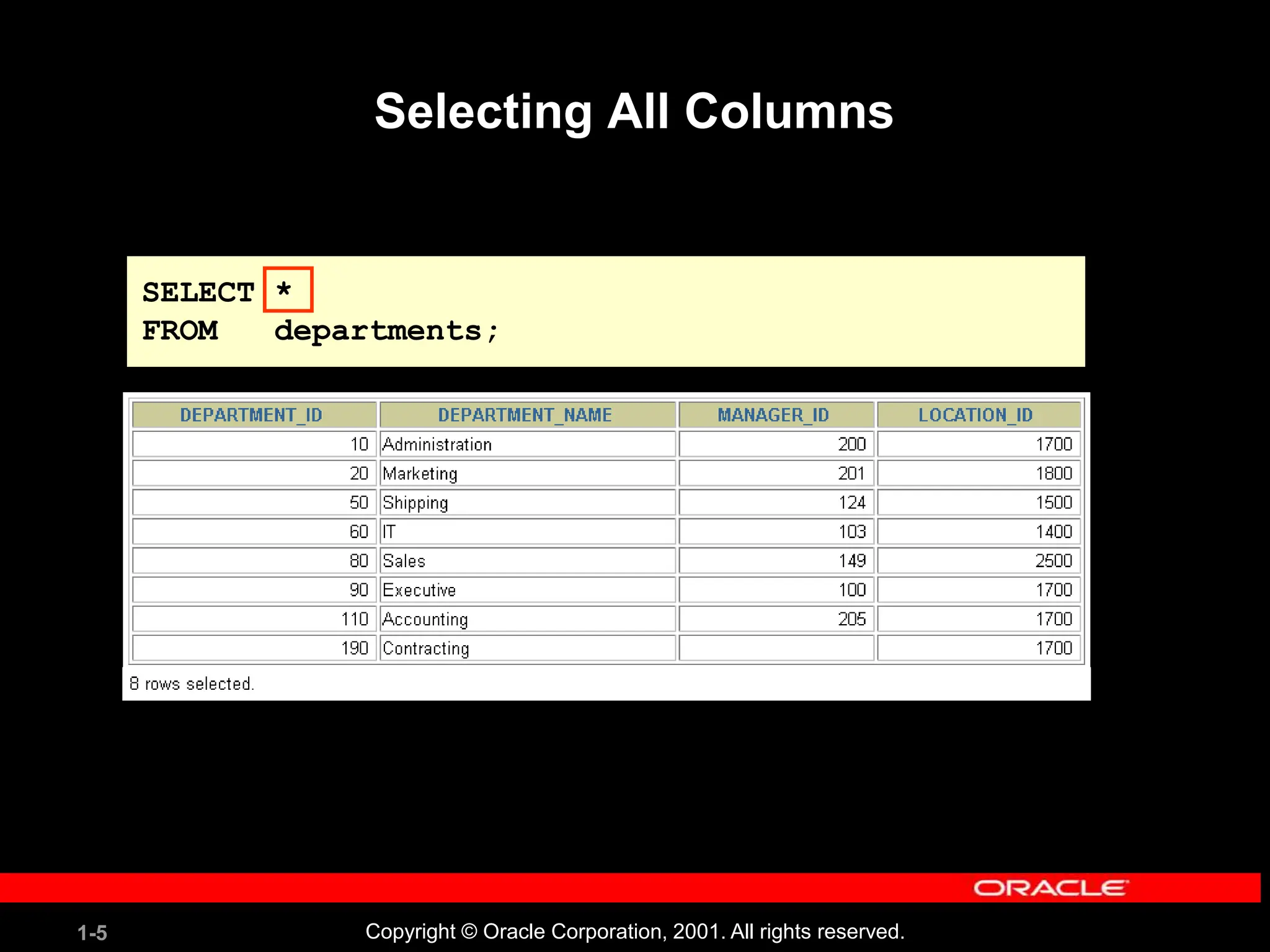
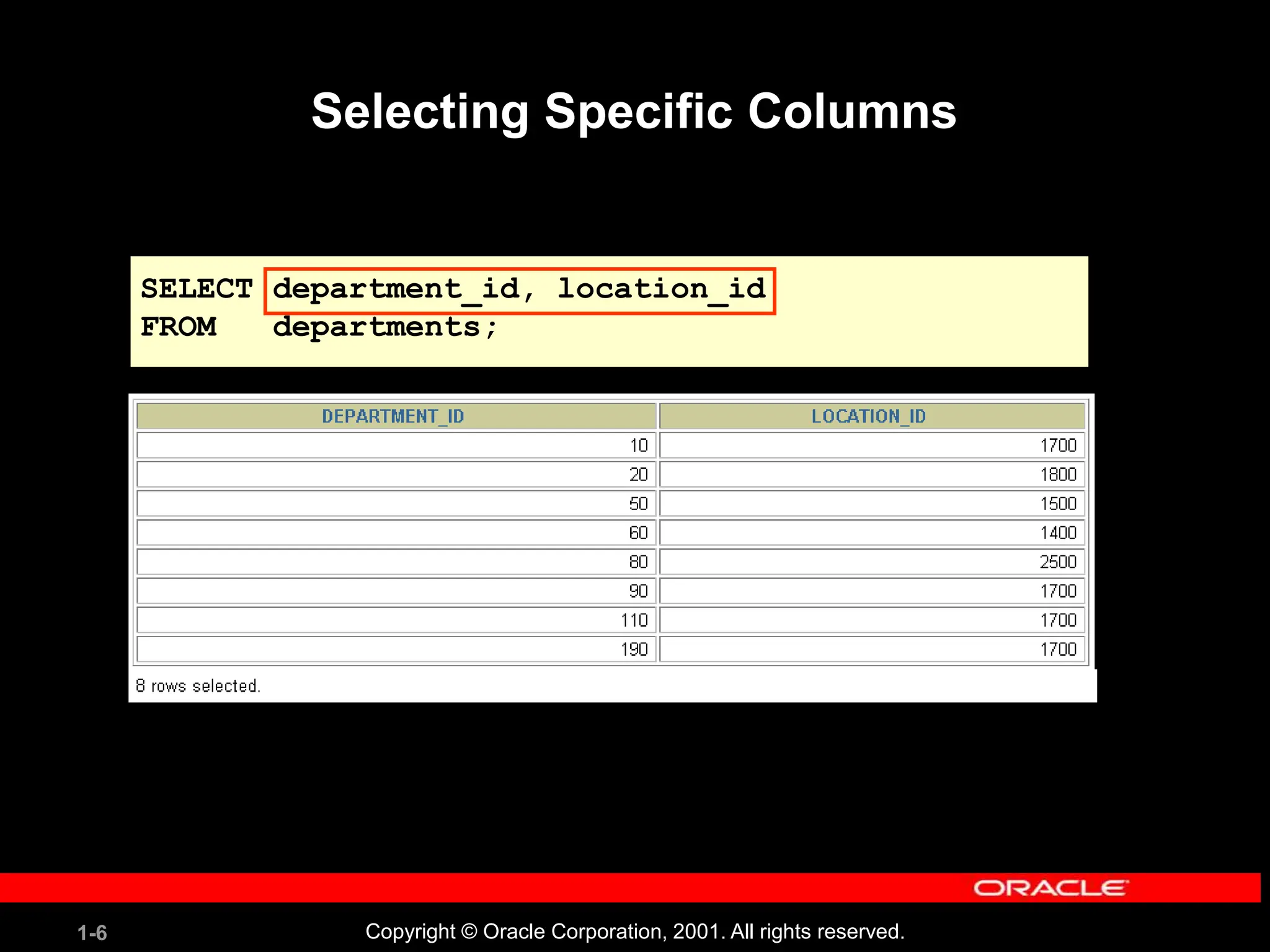






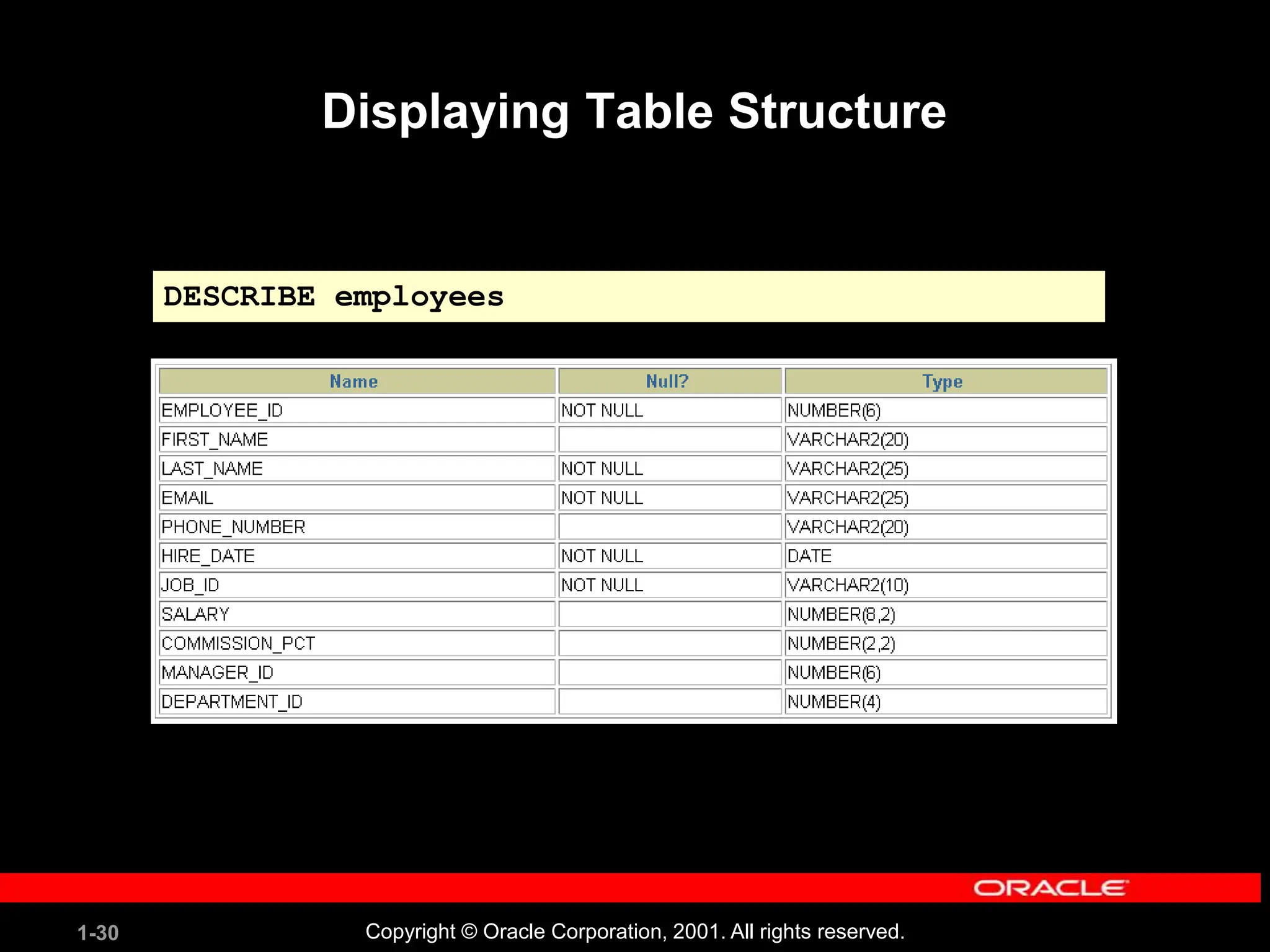
![1-29 Copyright © Oracle Corporation, 2001. All rights reserved. Displaying Table Structure Use the iSQL*Plus DESCRIBE command to display the structure of a table. DESC[RIBE] tablename](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les01-240424185627-6f2cc032/75/Database-Management-Systems-SQL-And-DDL-language-29-2048.jpg)
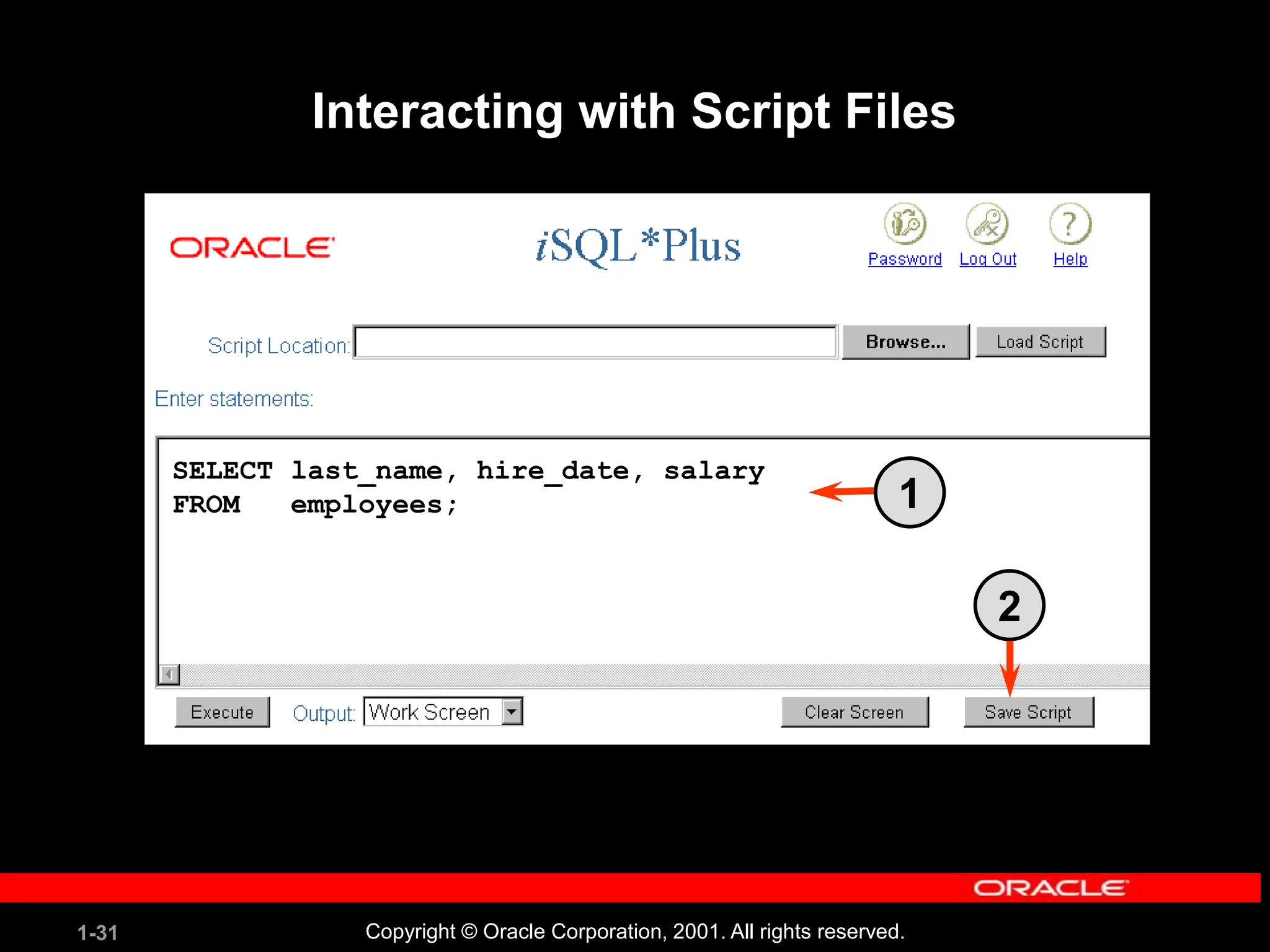
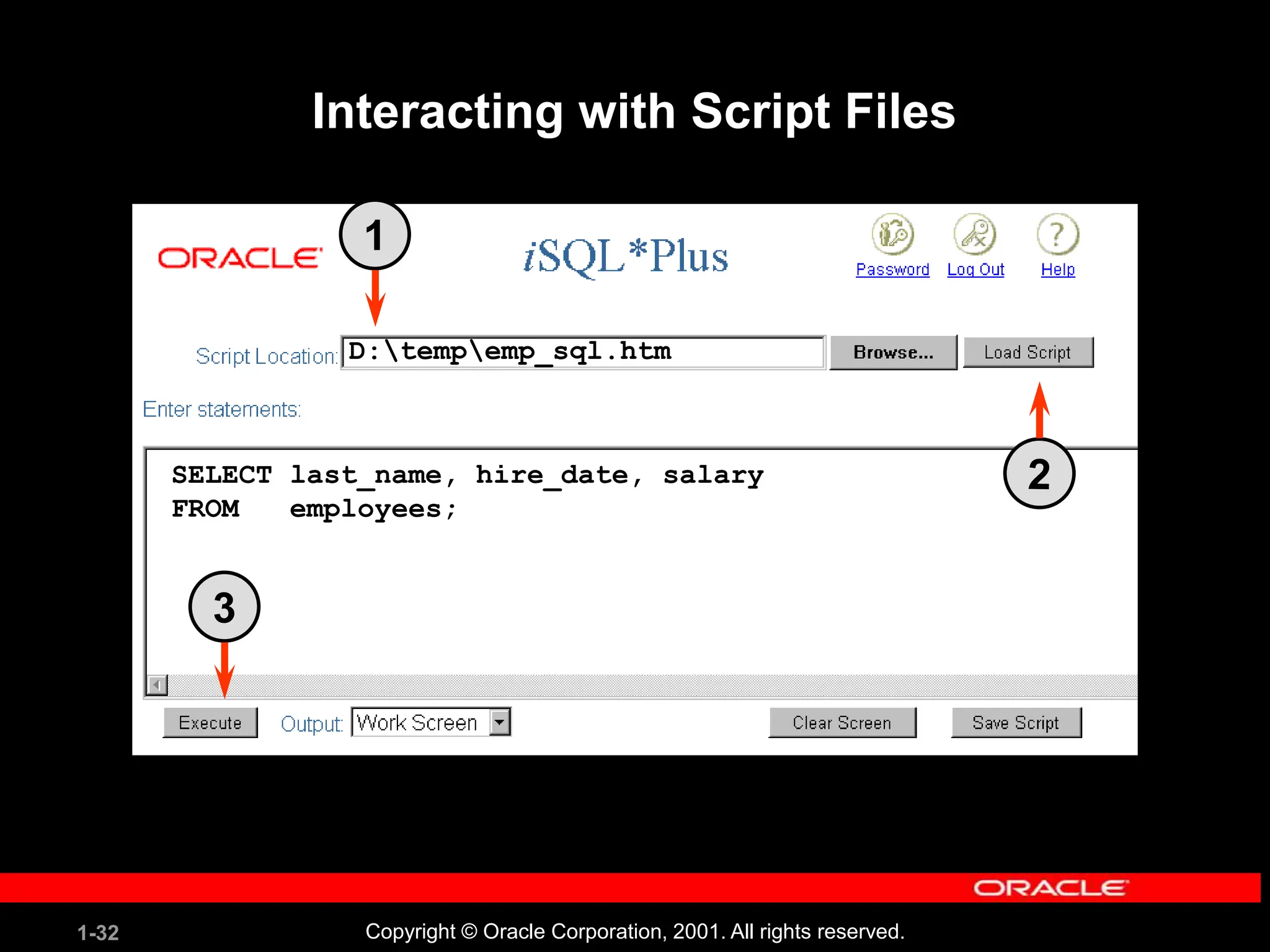
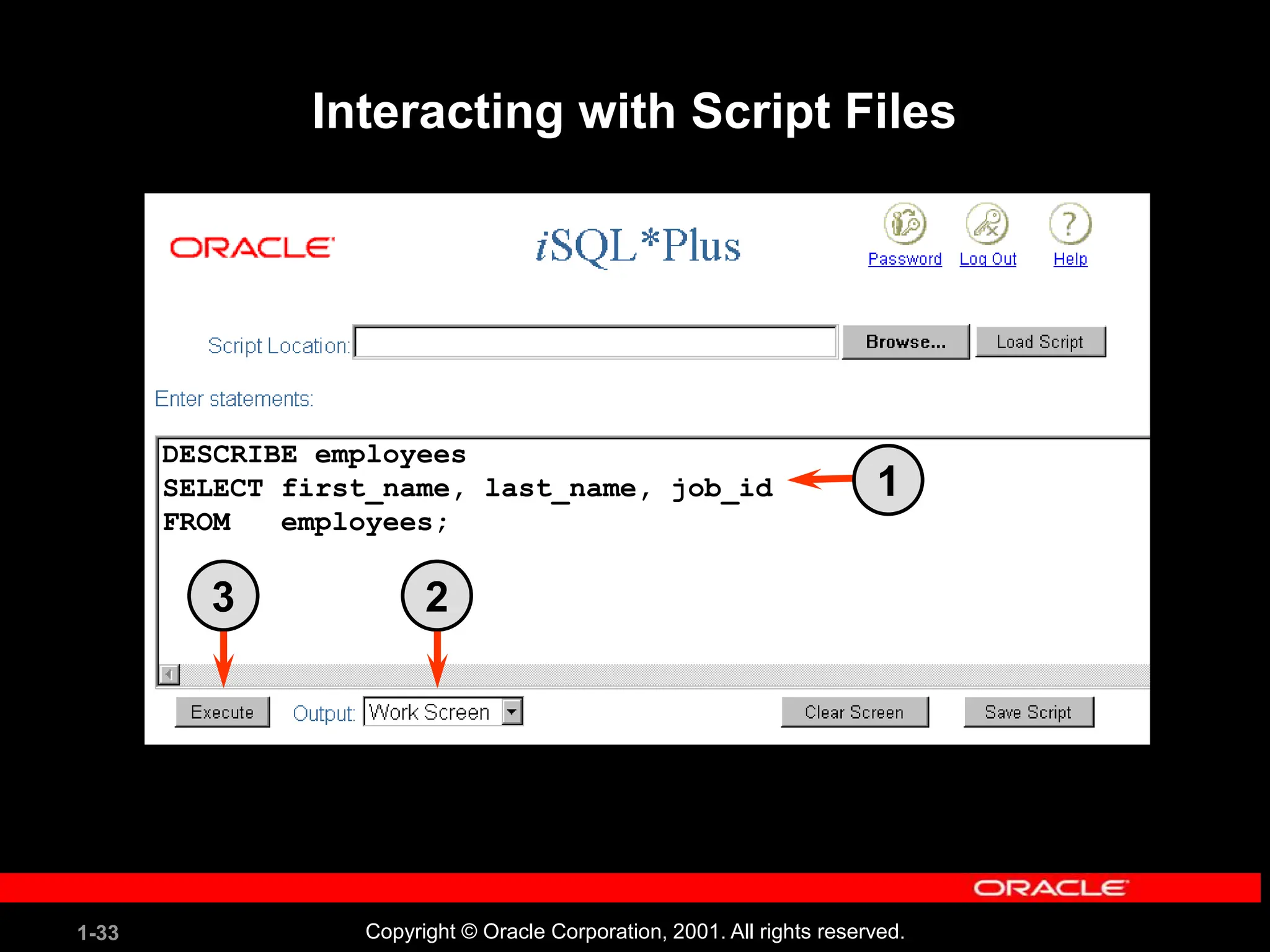
![1-34 Copyright © Oracle Corporation, 2001. All rights reserved. Summary SELECT *|{[DISTINCT] column|expression [alias],...} FROM table; In this lesson, you should have learned how to: • Write a SELECT statement that: – Returns all rows and columns from a table – Returns specified columns from a table – Uses column aliases to give descriptive column headings • Use the iSQL*Plus environment to write, save, and execute SQL statements and iSQL*Plus commands.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/les01-240424185627-6f2cc032/75/Database-Management-Systems-SQL-And-DDL-language-34-2048.jpg)