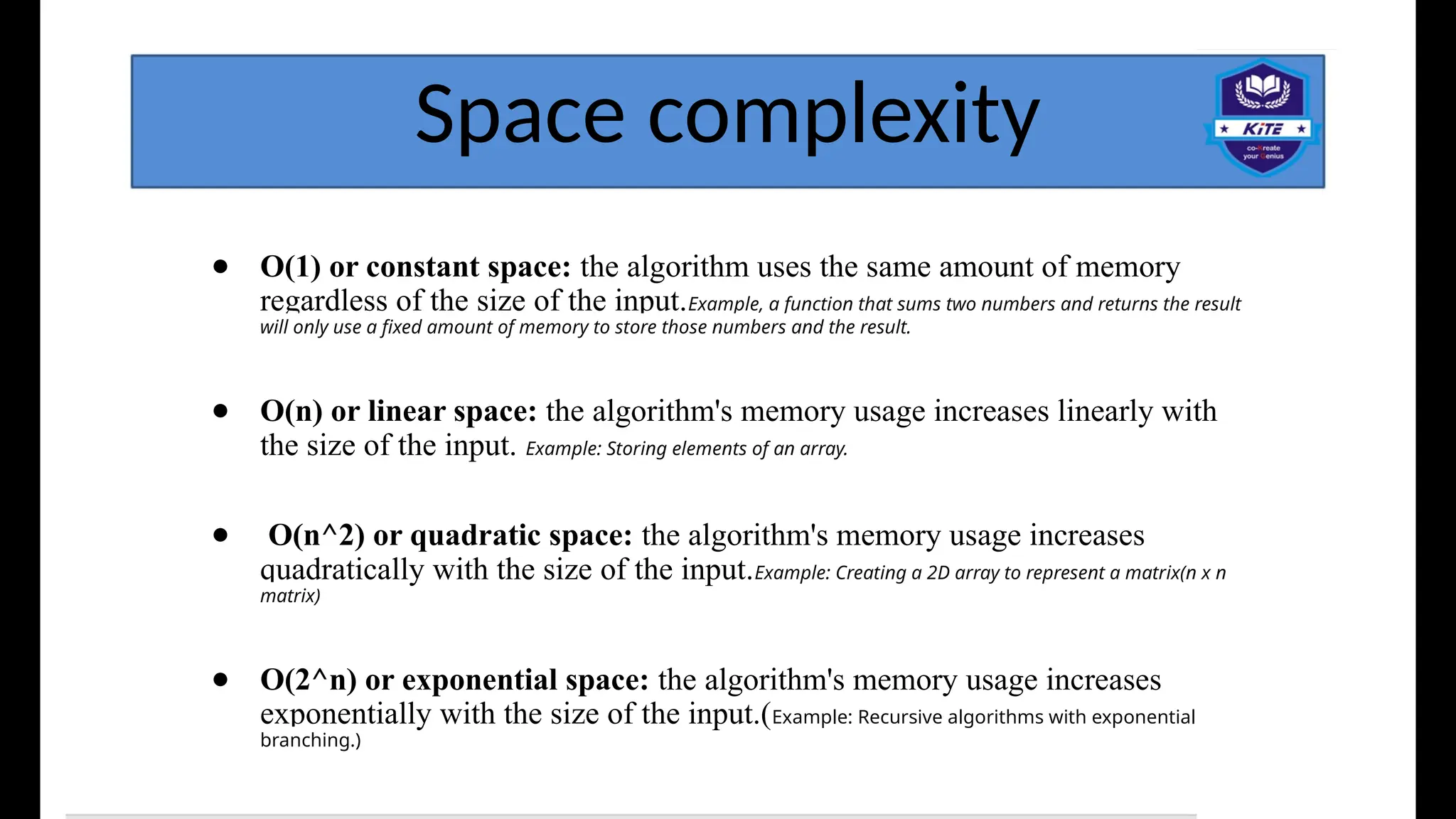
Data structures and algorithms (DSA) are foundational concepts in computer science that address the efficient organization and processing of data. Data Structures: Data structures are methods for organizing and storing data in a computer's memory to facilitate efficient access and modification. They provide a logical arrangement of data, allowing for optimized operations. Common data structures include: Arrays: Contiguous blocks of memory storing elements of the same data type. Linked Lists: Collections of nodes where each node contains data and a reference (or link) to the next node. Stacks: Linear data structures following a Last-In, First-Out (LIFO) principle. Queues: Linear data structures following a First-In, First-Out (FIFO) principle. Trees: Hierarchical data structures where each node can have child nodes. Examples include binary trees and binary search trees. Graphs: Non-linear data structures consisting of nodes (vertices) and connections (edges) between them. Hash Tables: Data structures that map keys to values using a hash function for efficient lookups.




![program Input: Here our input is an integer array of size "n" and we have one integer "k" that we need to search for in that array. Output: If the element "k" is found in the array, then we have return 1, otherwise we have return 0/ for-loop to iterate with each element in the array for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { // check if ith element is equal to "k" or not if (arr[i] == k) return 1; // return 1, if you find "k" } return 0; // return 0, if you didn't find "k" }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-lm1-introduction-250811081848-67cebf77/75/Data-structures-and-ALGORITHMS-methd-binary-SEARCH-20-2048.jpg)
![∙ Best case: This is the lower bound on running time of an algorithm. We must knowthecause that causes the minimum number of operations to be executed. In the above example, our array was [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] and we are finding if "1" is present in the array or not. So here, after only one comparison, we will get that element is present in the array. So, this is the best case of our algorithm. Average case: We calculate the running time for all possible inputs, sum all the calculated values and divide the sum by the total number of inputs. We must know(or predict) distribution of cases. ∙ Worst case: This is the upper bound on running time of an algorithm. We must knowthecause that causes the maximum number of operations to be executed. In our example, the worst case can be if the given array is [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] and we try to find if element "6"ispresent in the array or not. Here, the if-condition of our loop will be executed 5 times and then the algorithm will give "0" as output.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit1-lm1-introduction-250811081848-67cebf77/75/Data-structures-and-ALGORITHMS-methd-binary-SEARCH-21-2048.jpg)