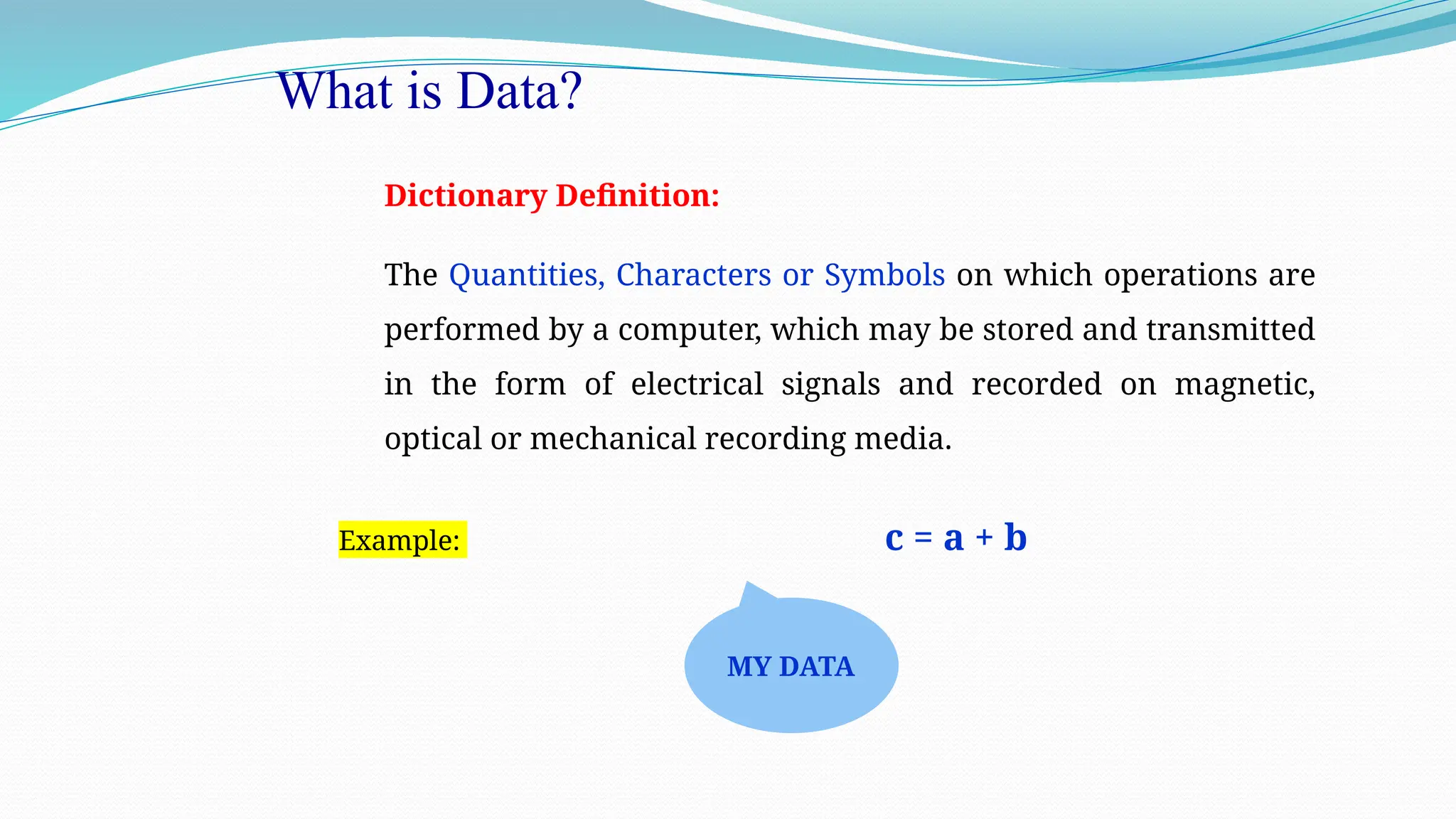
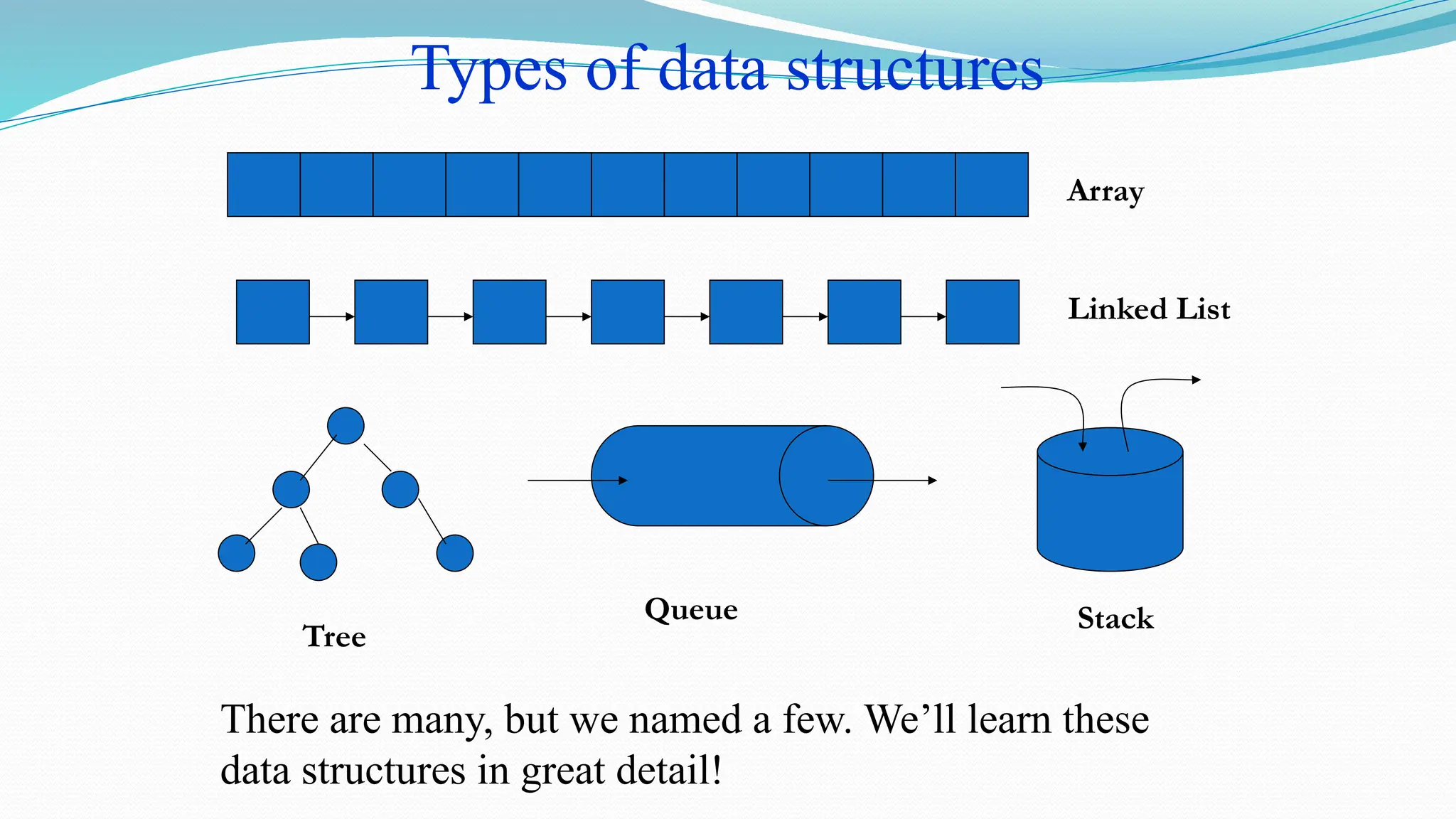
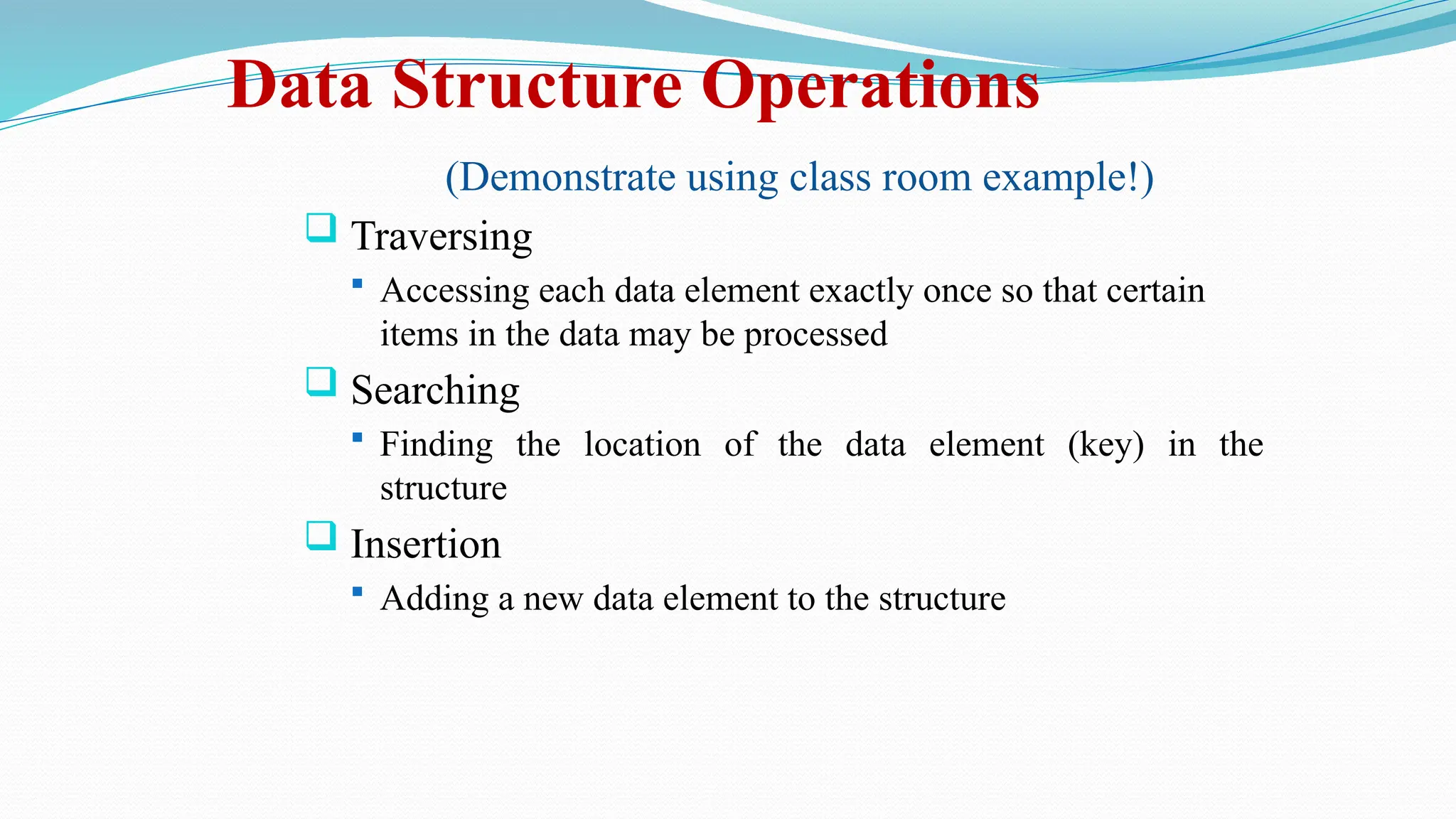
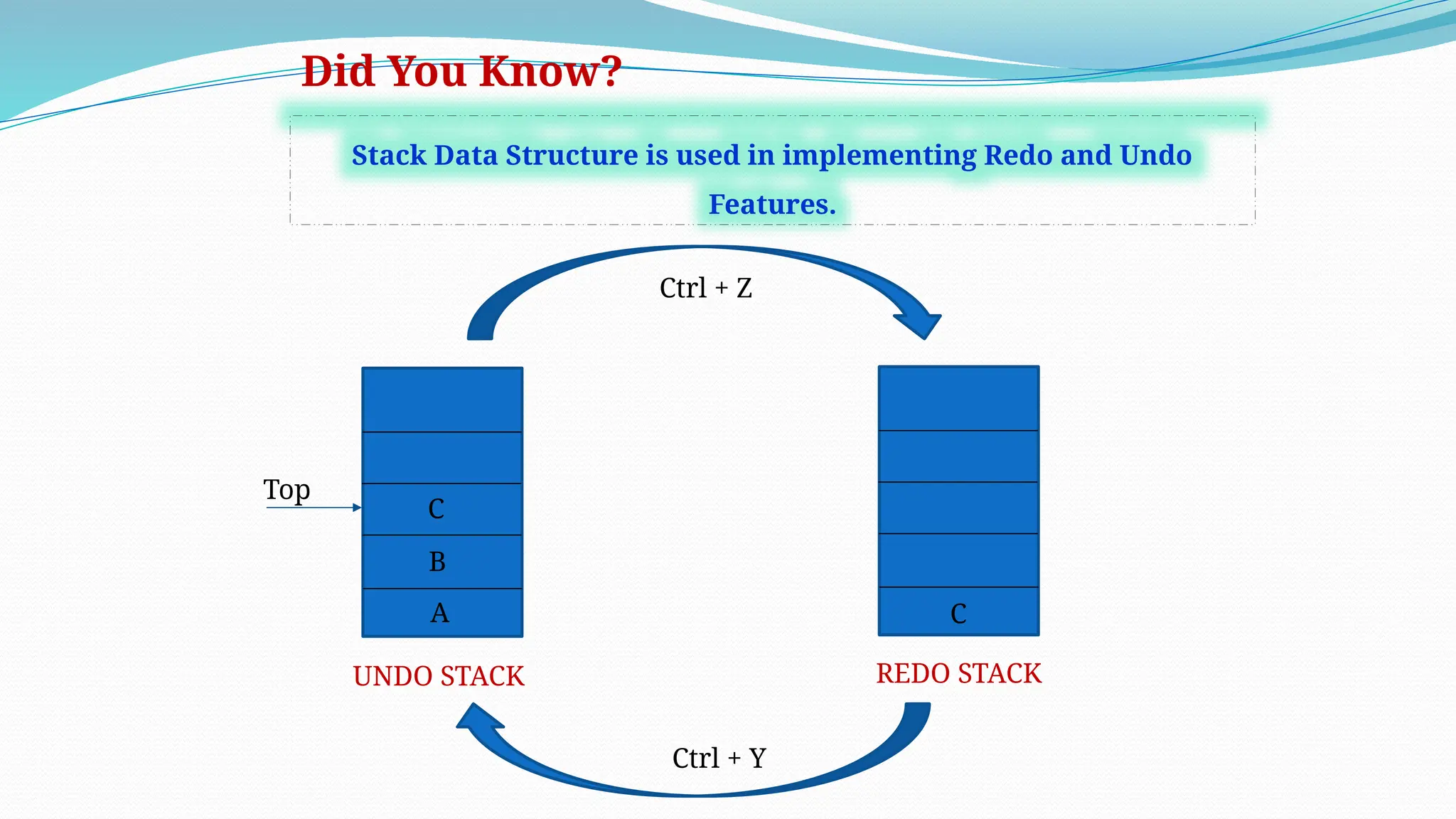
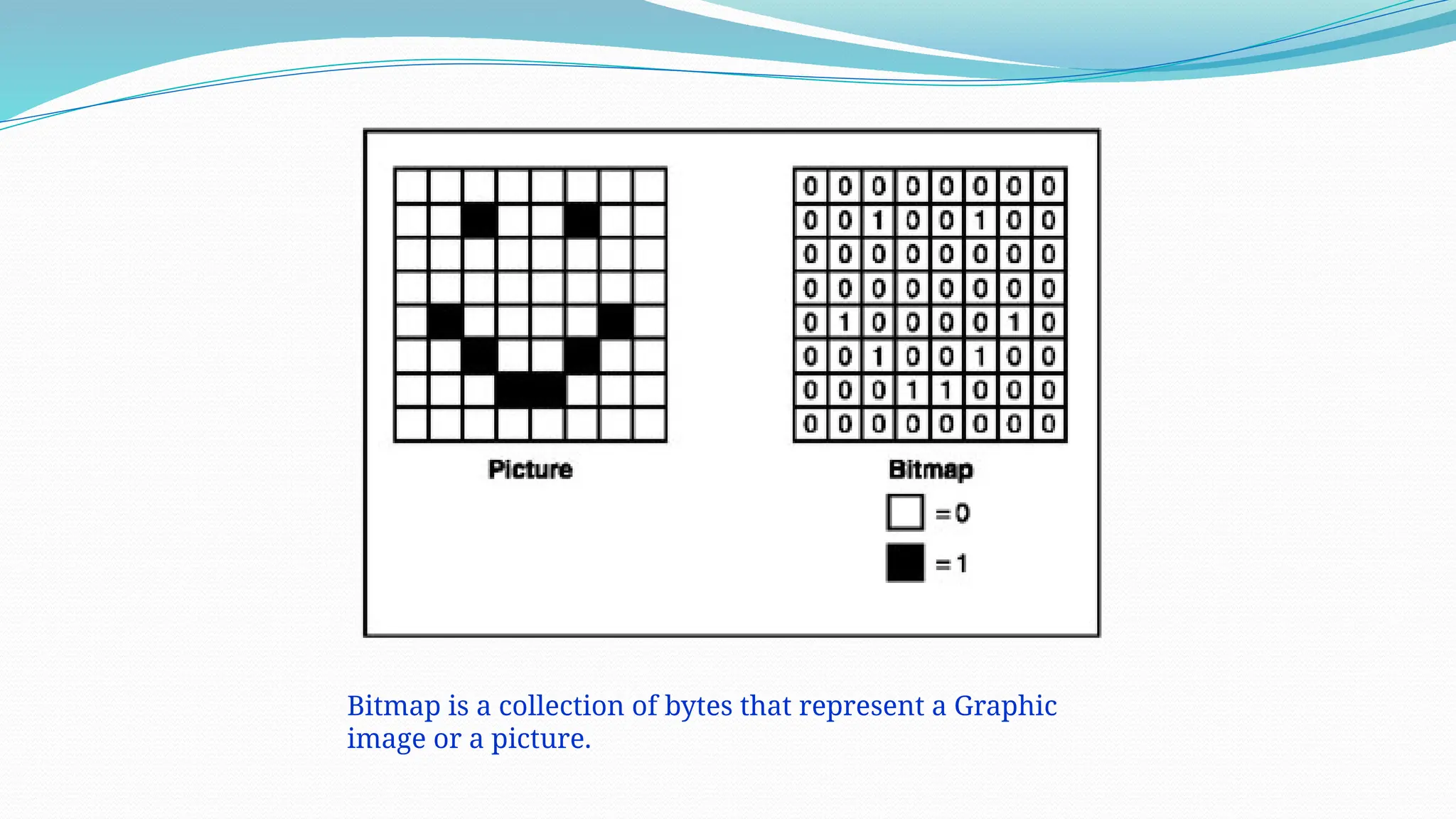
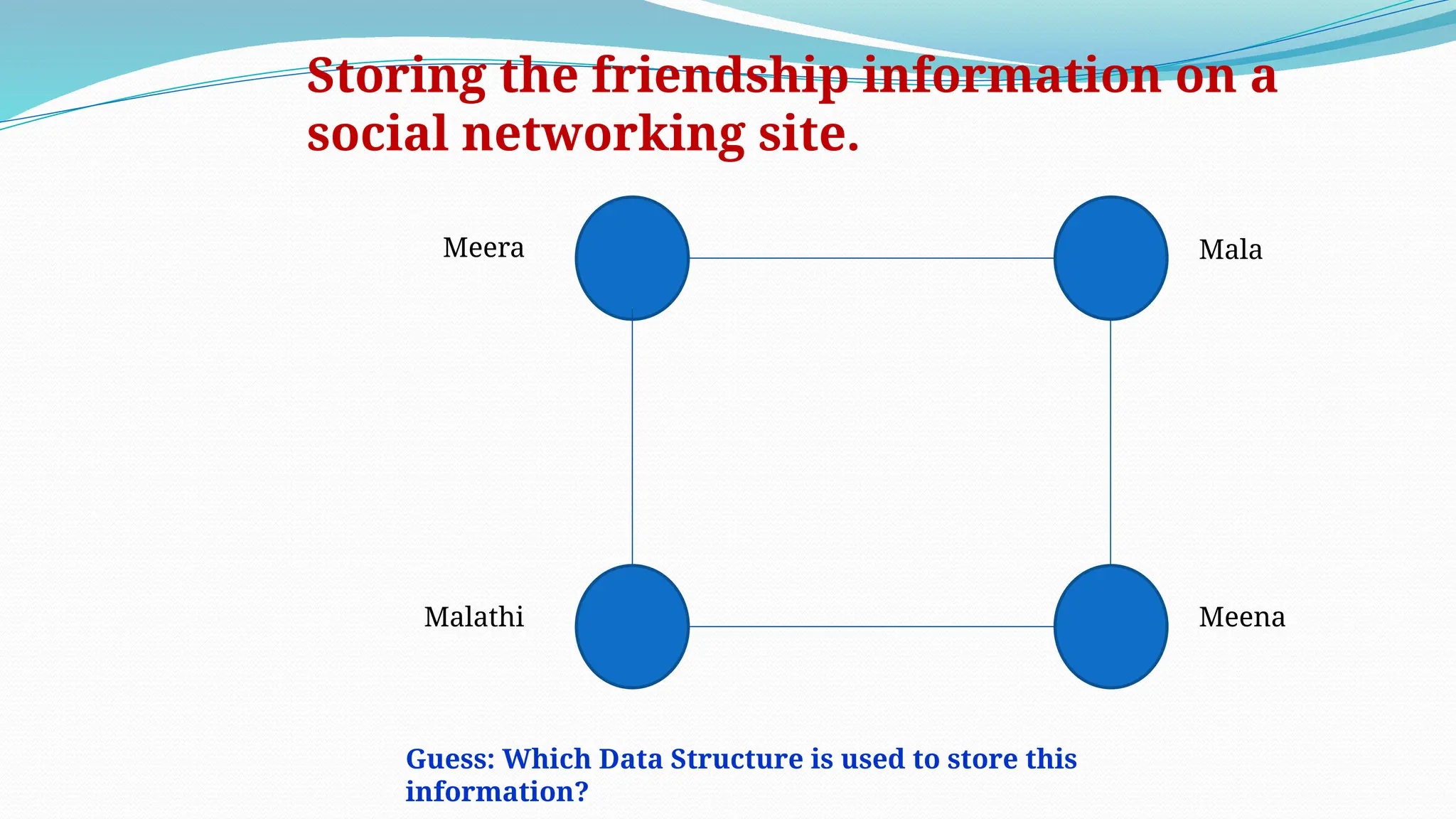
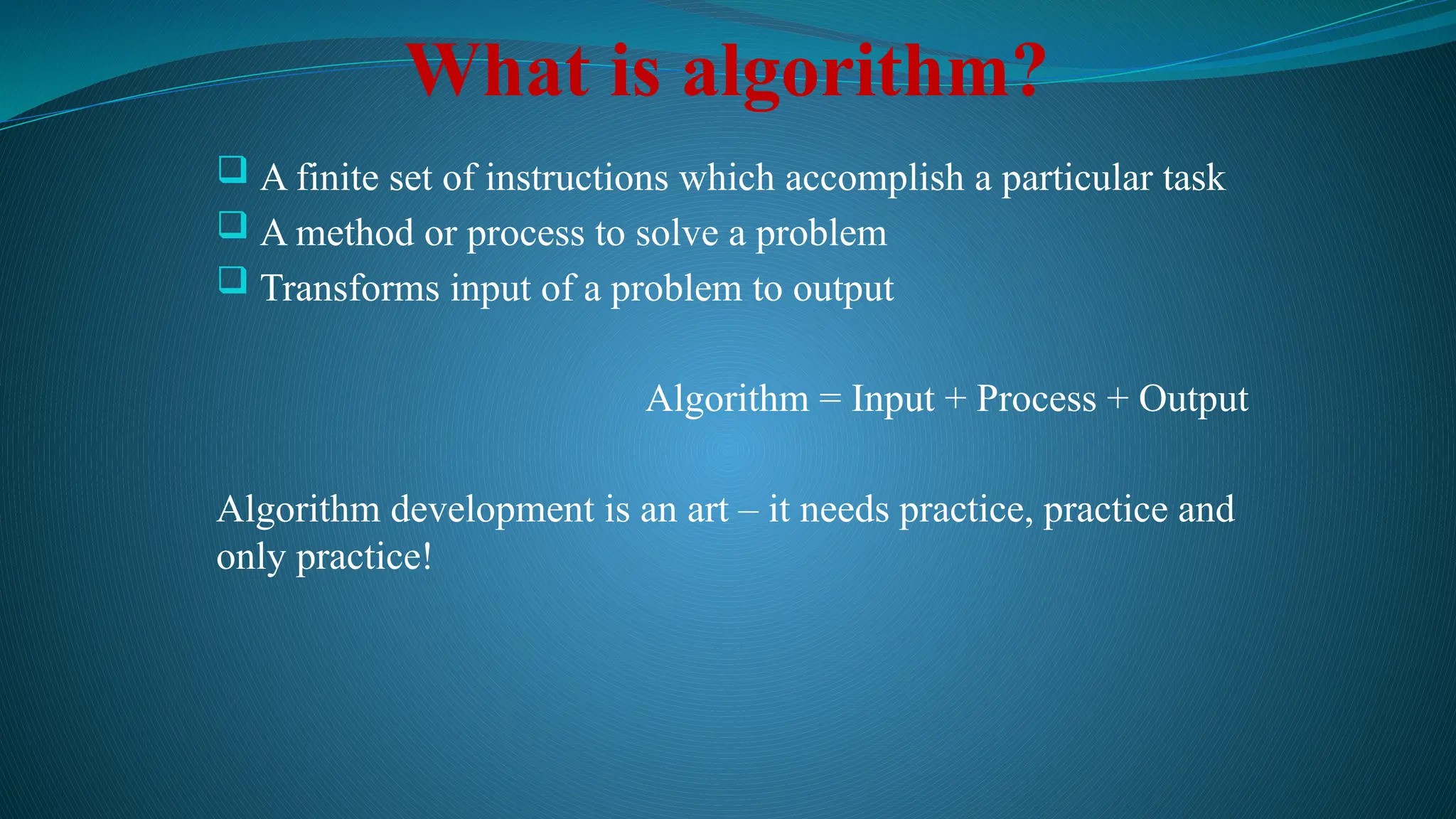
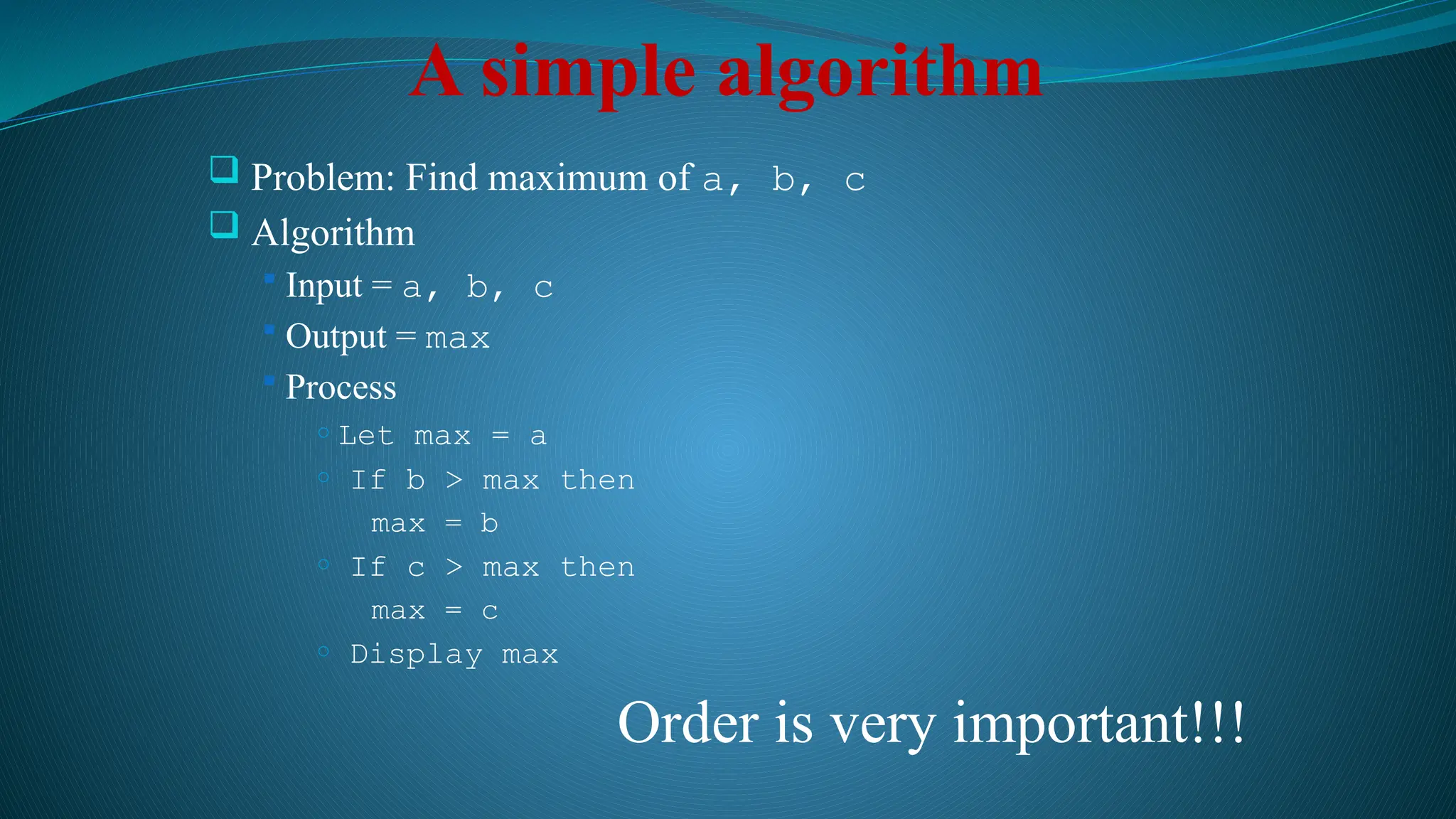
The document defines data as quantities or symbols processed by computers, detailing various types of data such as textual, numeric, audio, and video. It explains data structures as systematic ways to organize data for efficient storage and retrieval, and introduces concepts like arrays, linked lists, and the operations performed on data structures, such as searching, sorting, and merging. Additionally, it outlines algorithms as finite instructions for solving problems, emphasizing the importance of efficiency and optimization in algorithm development.