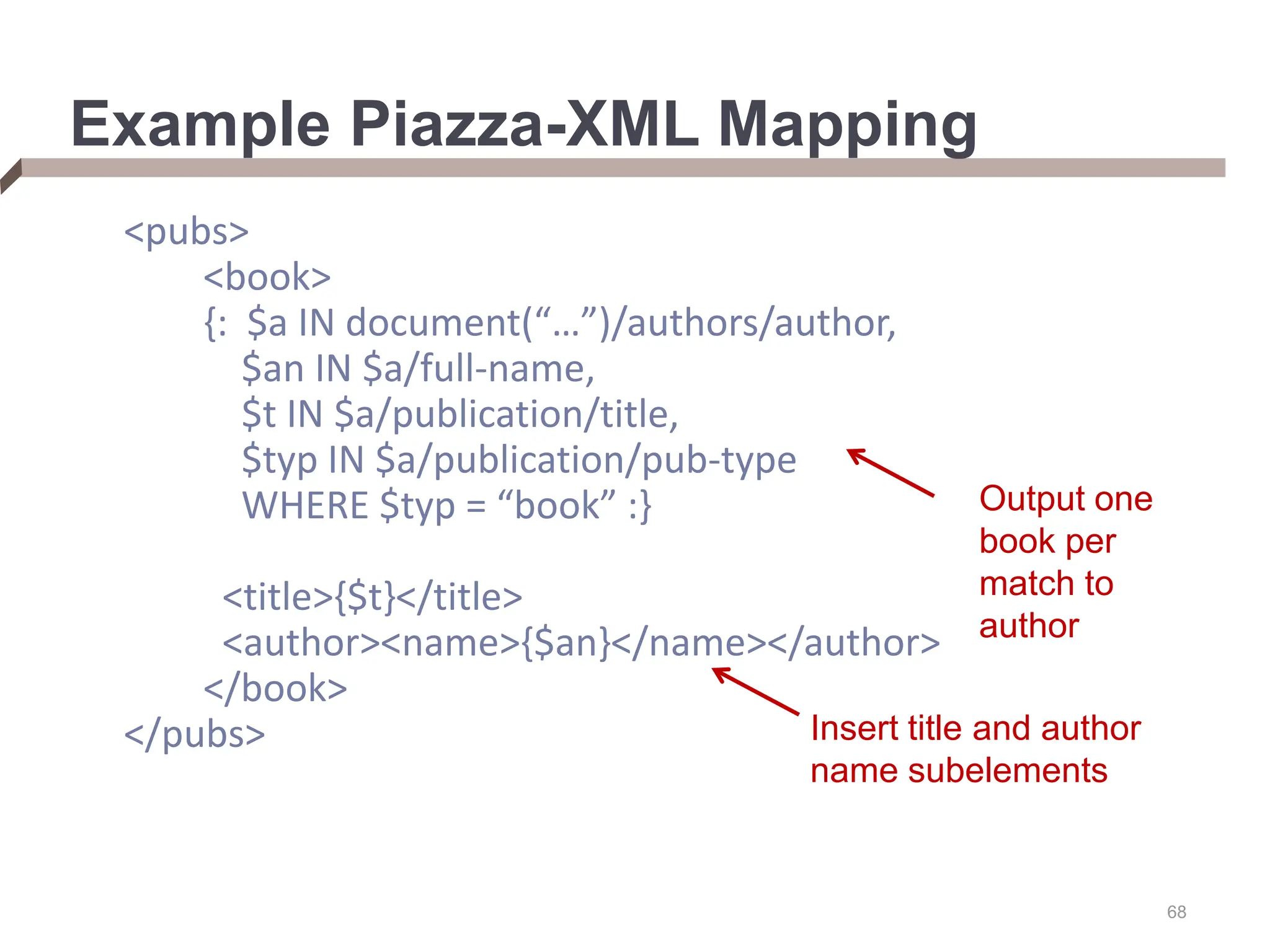
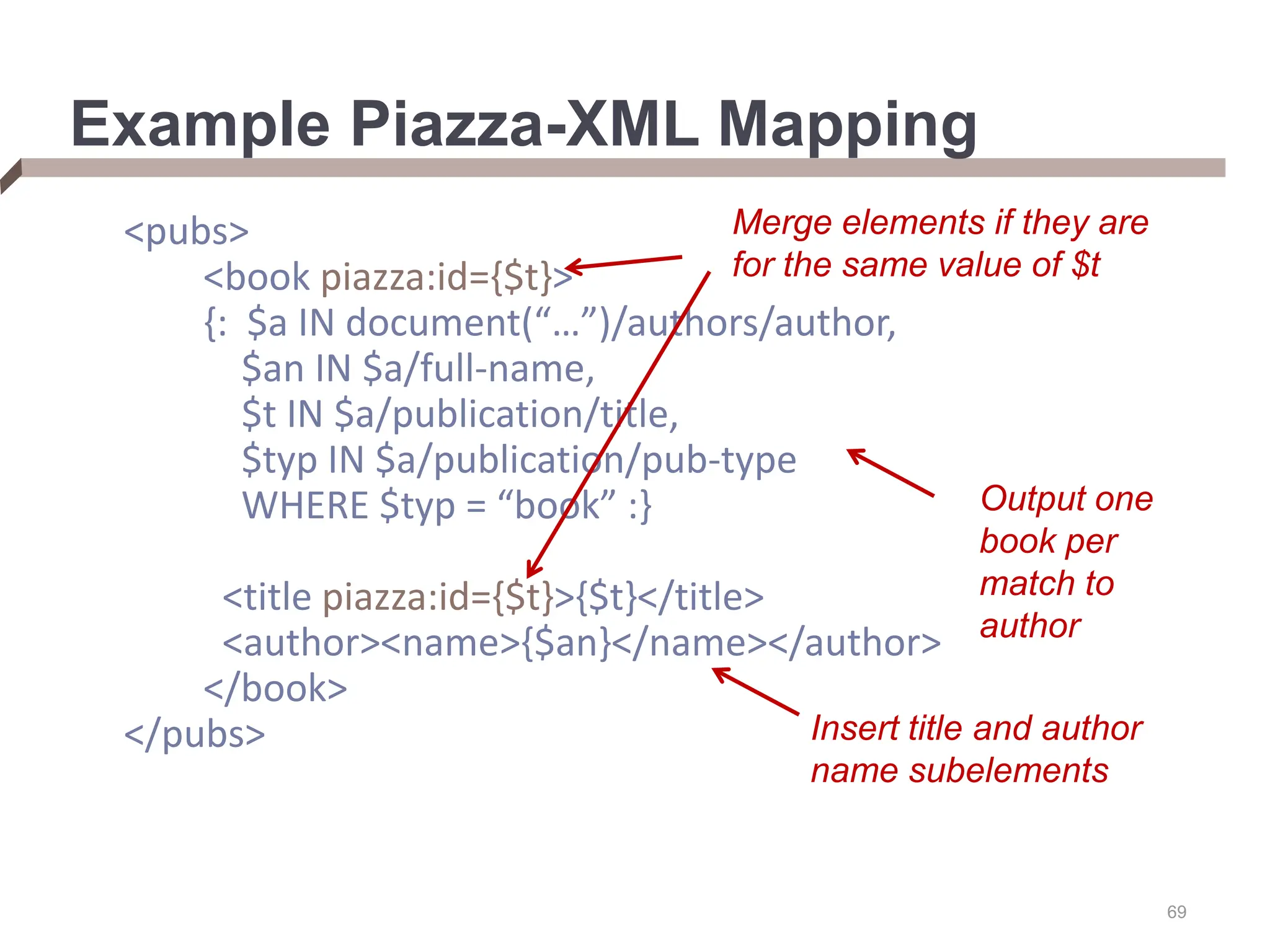
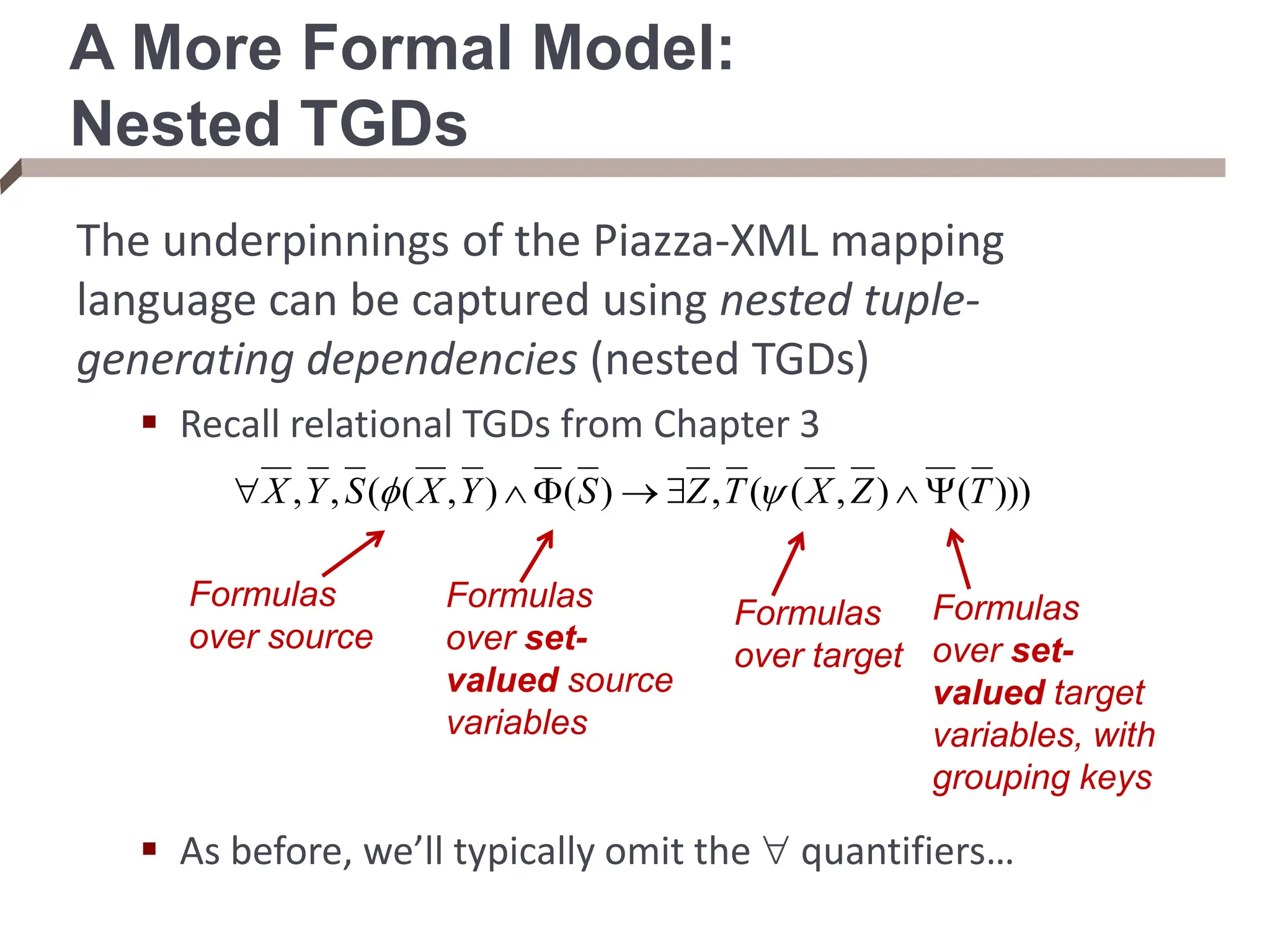
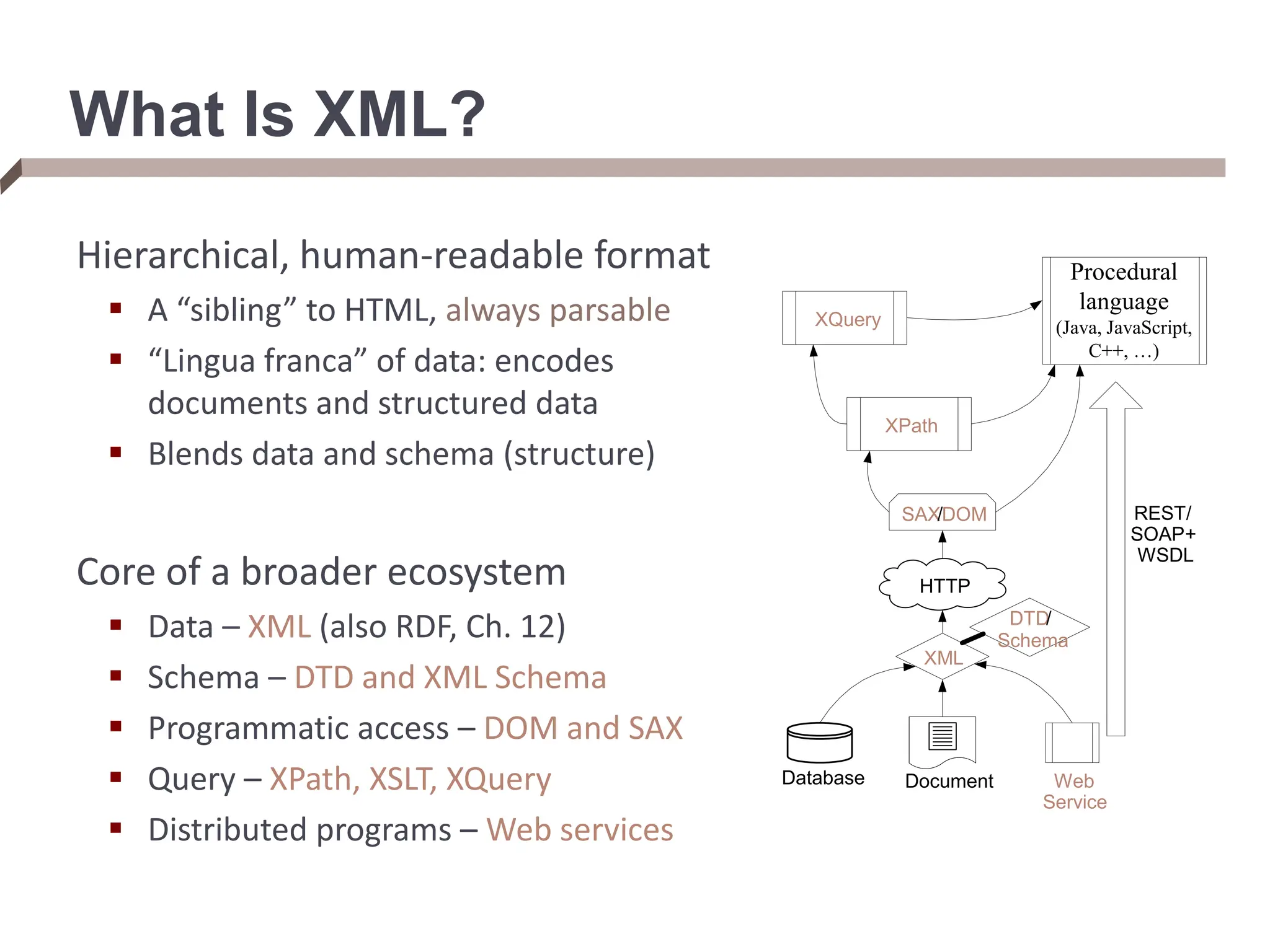
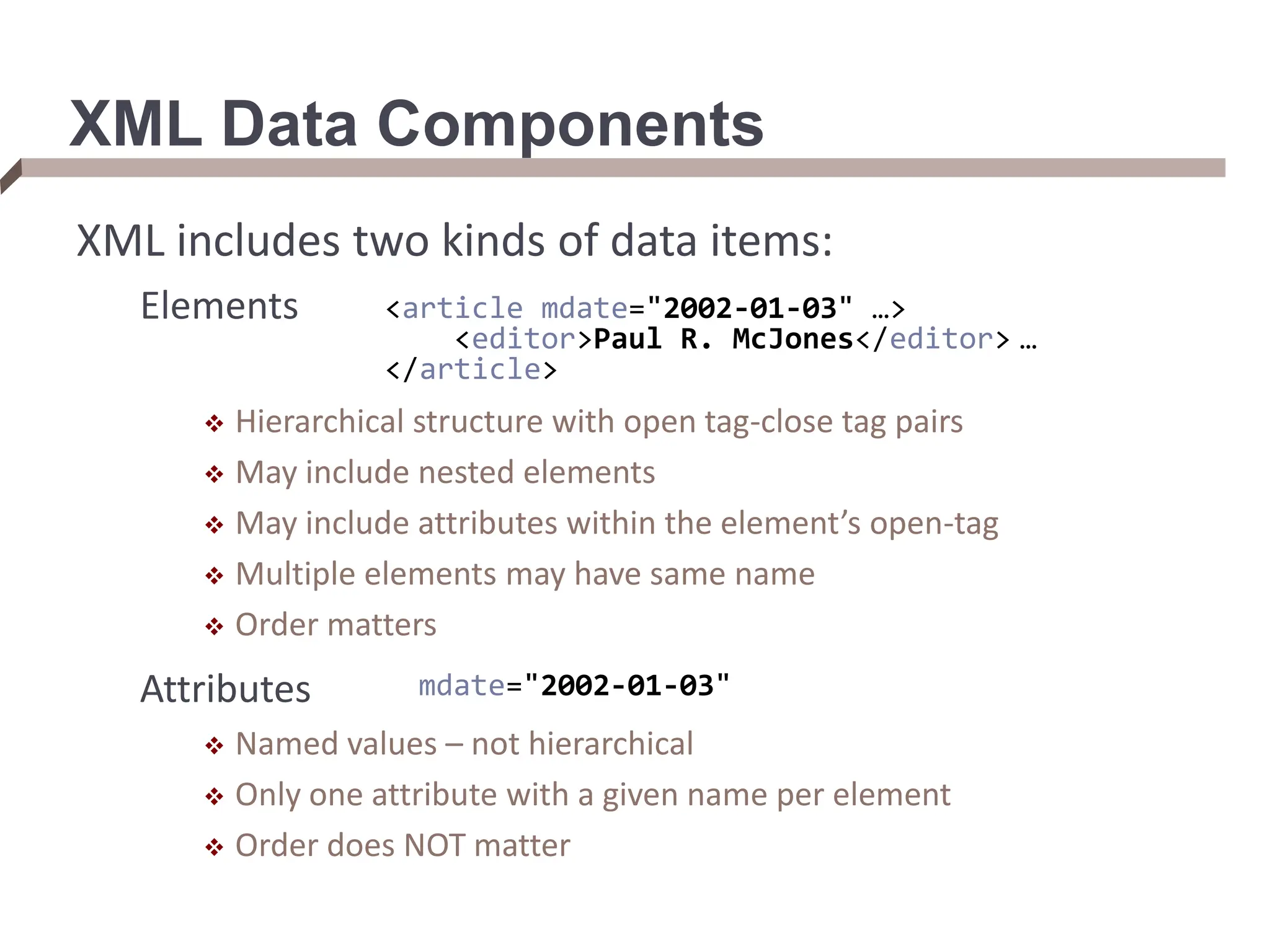
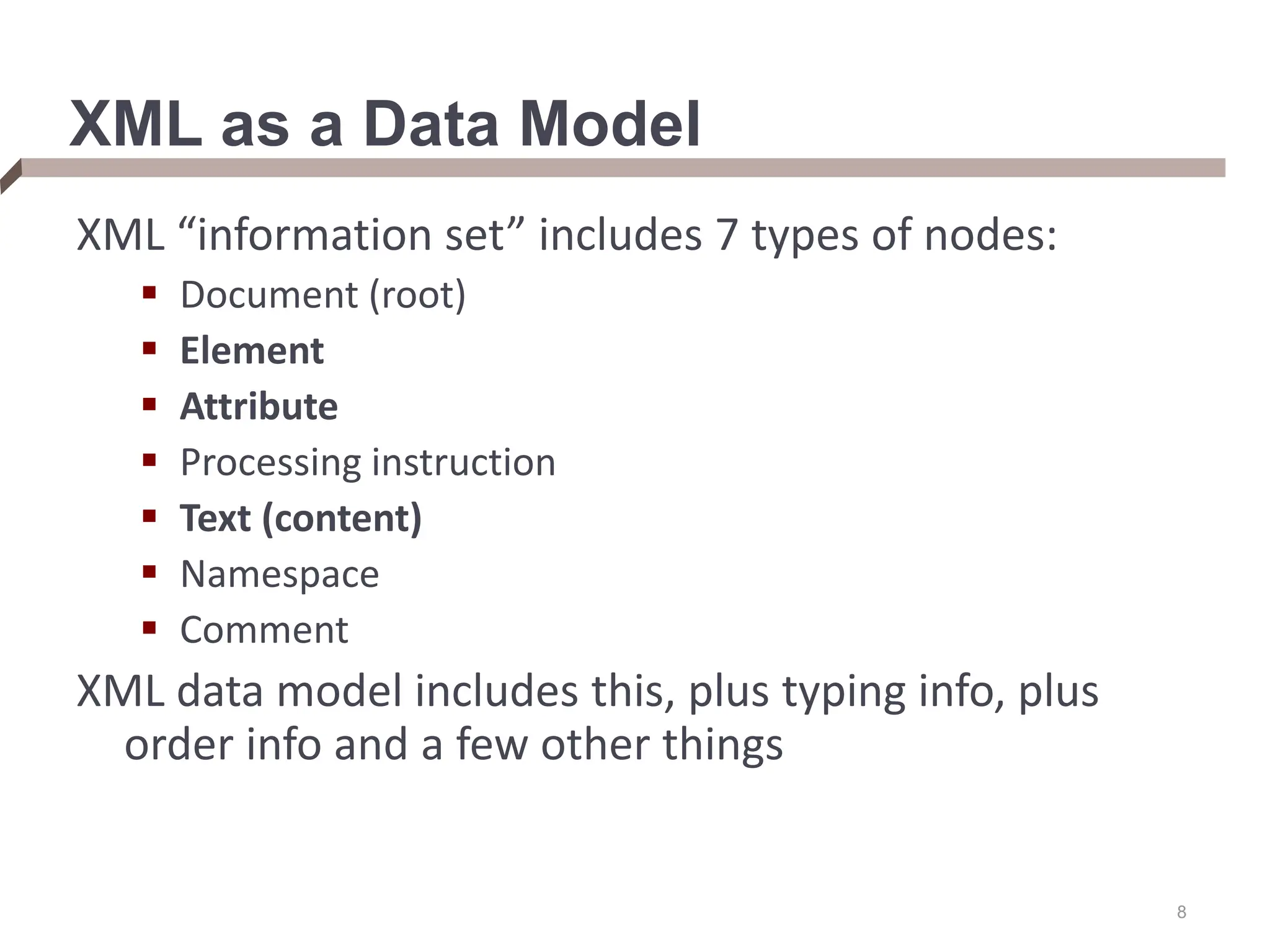
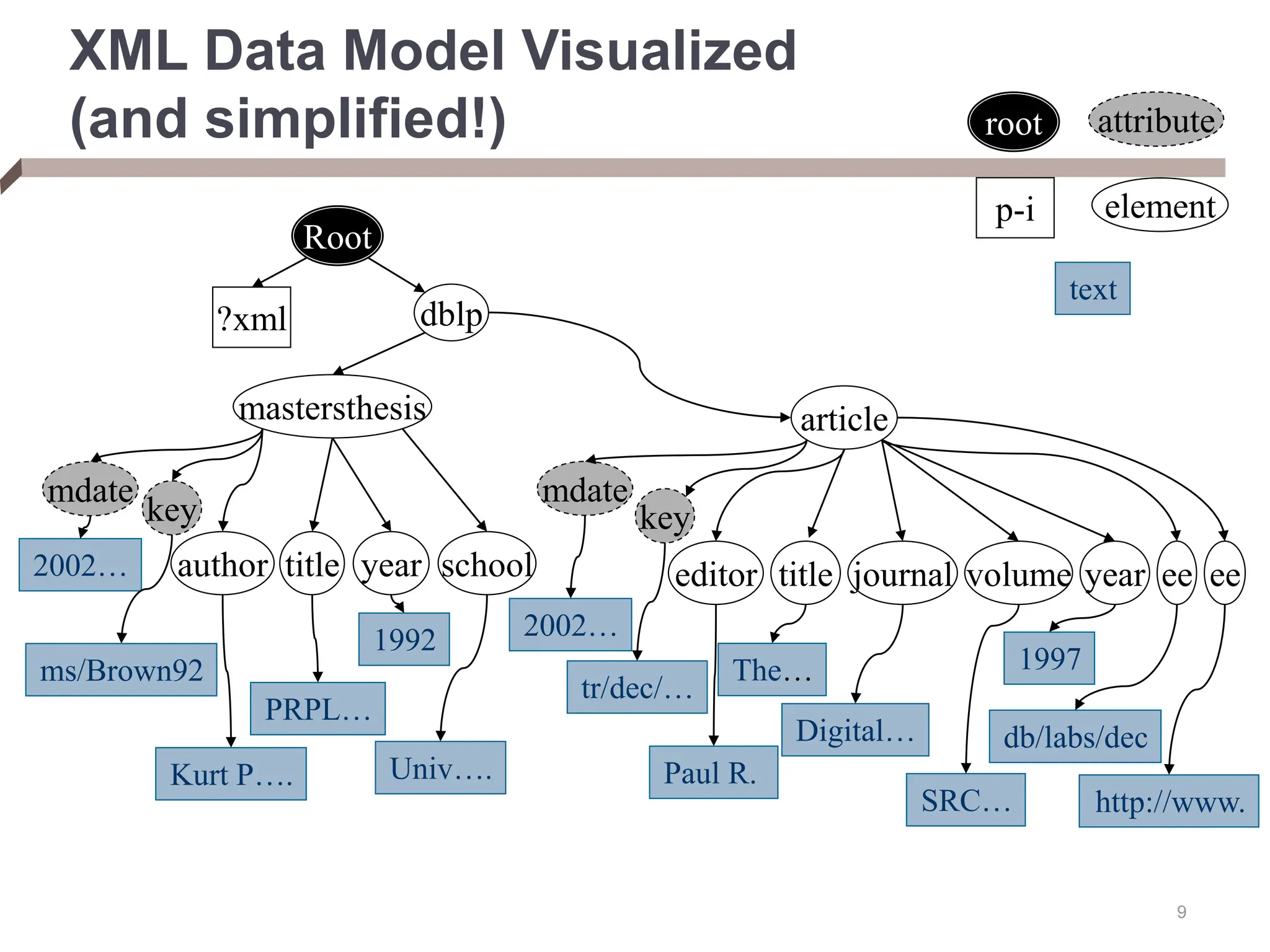
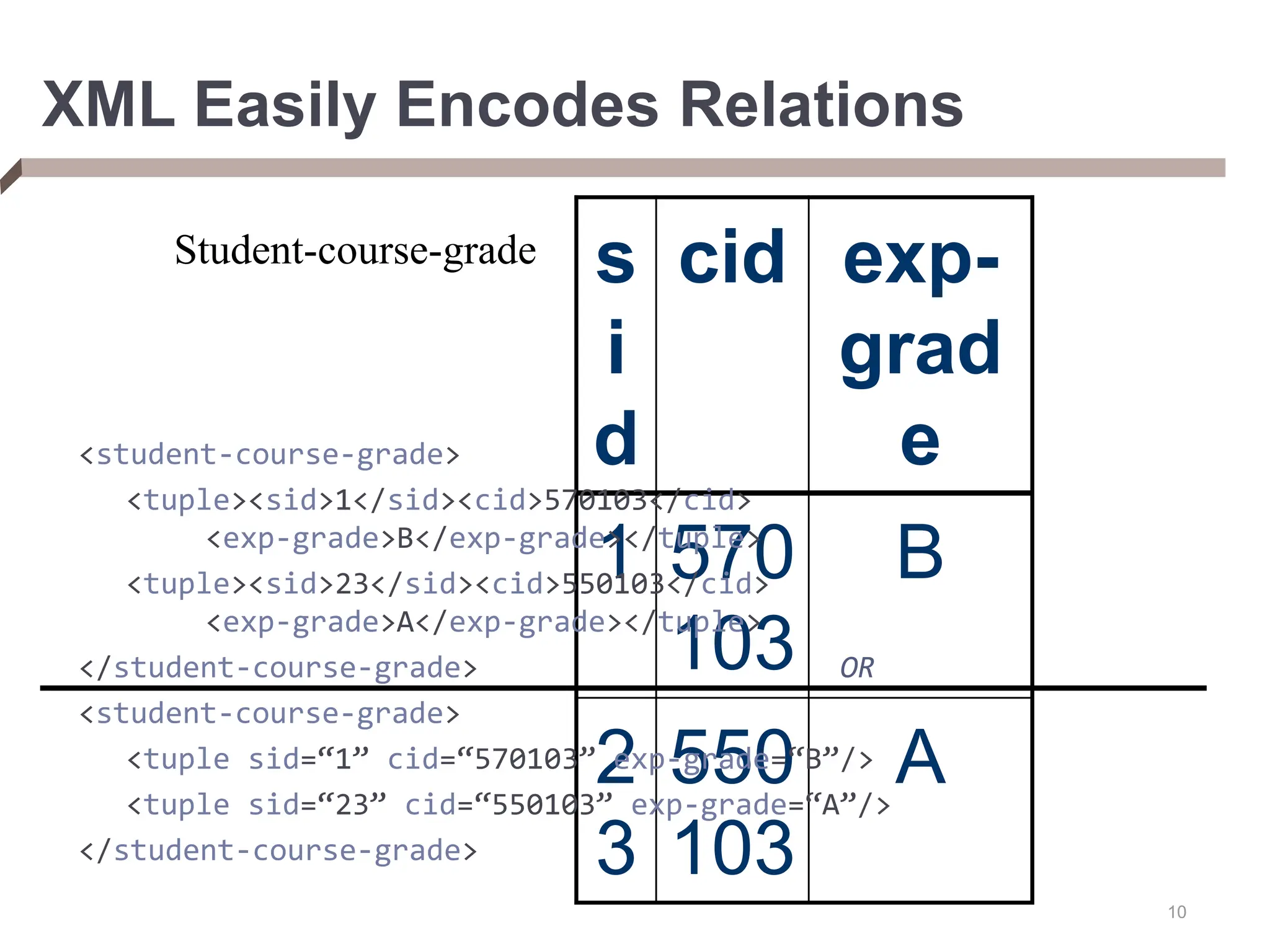
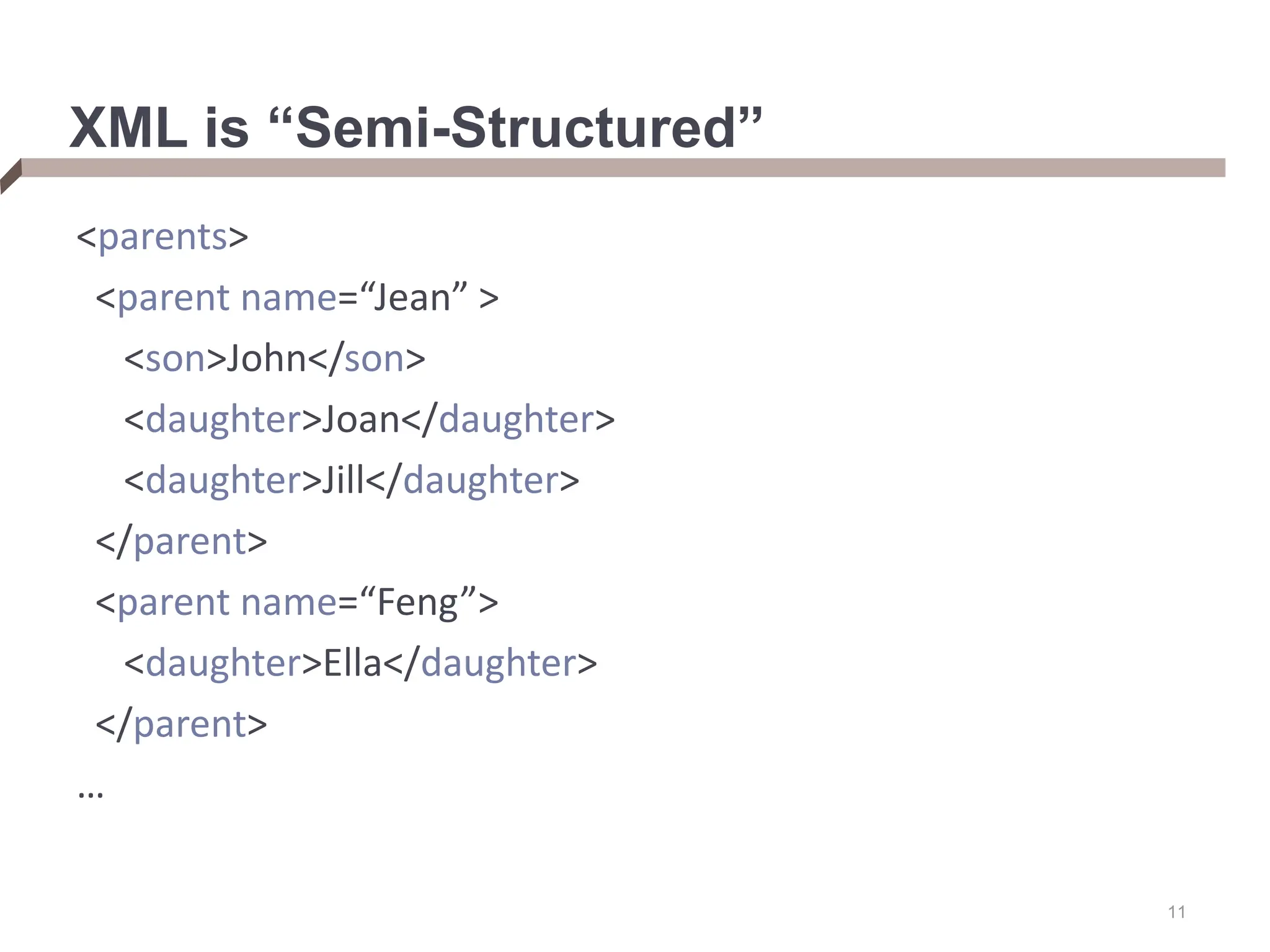
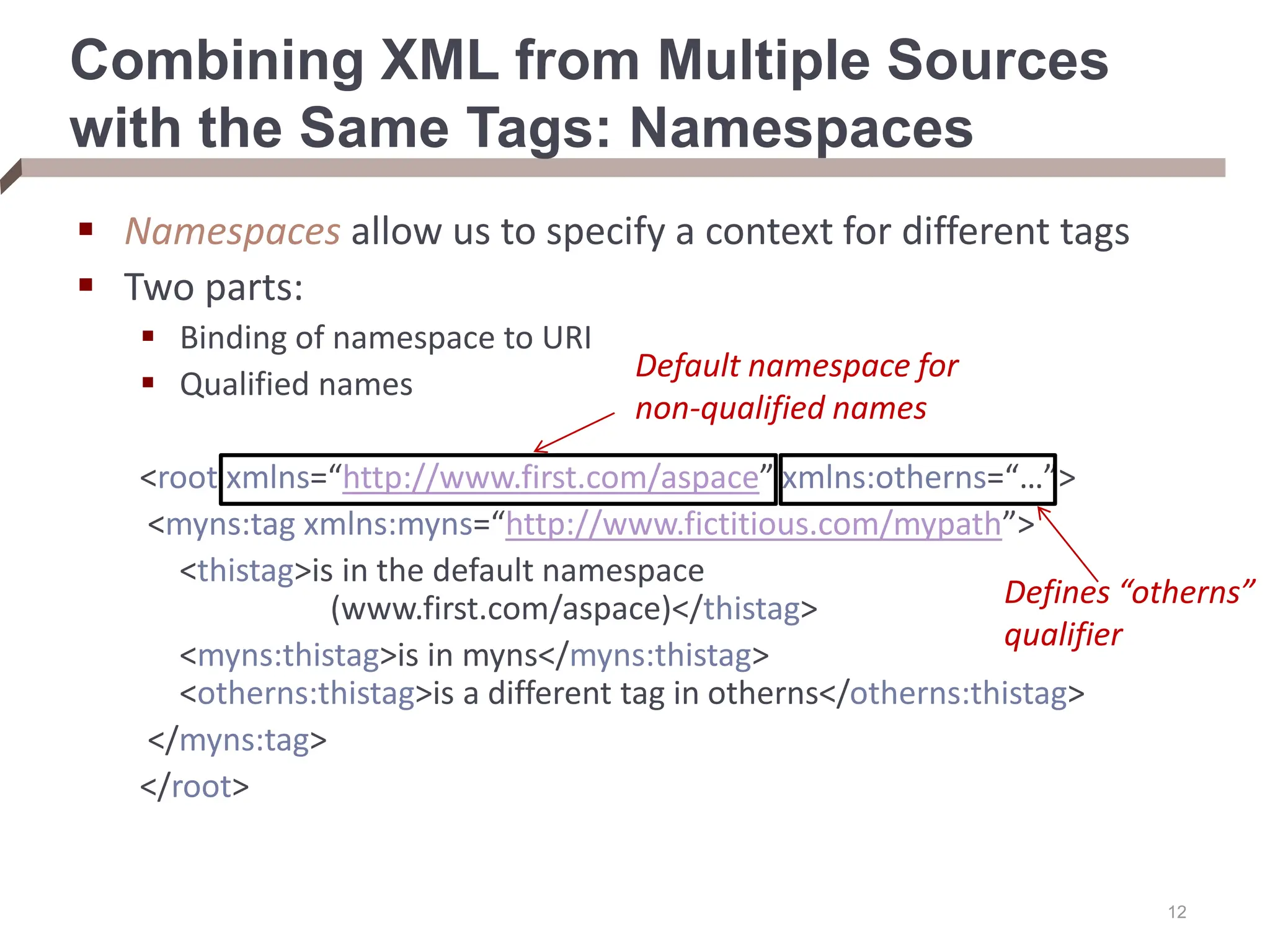
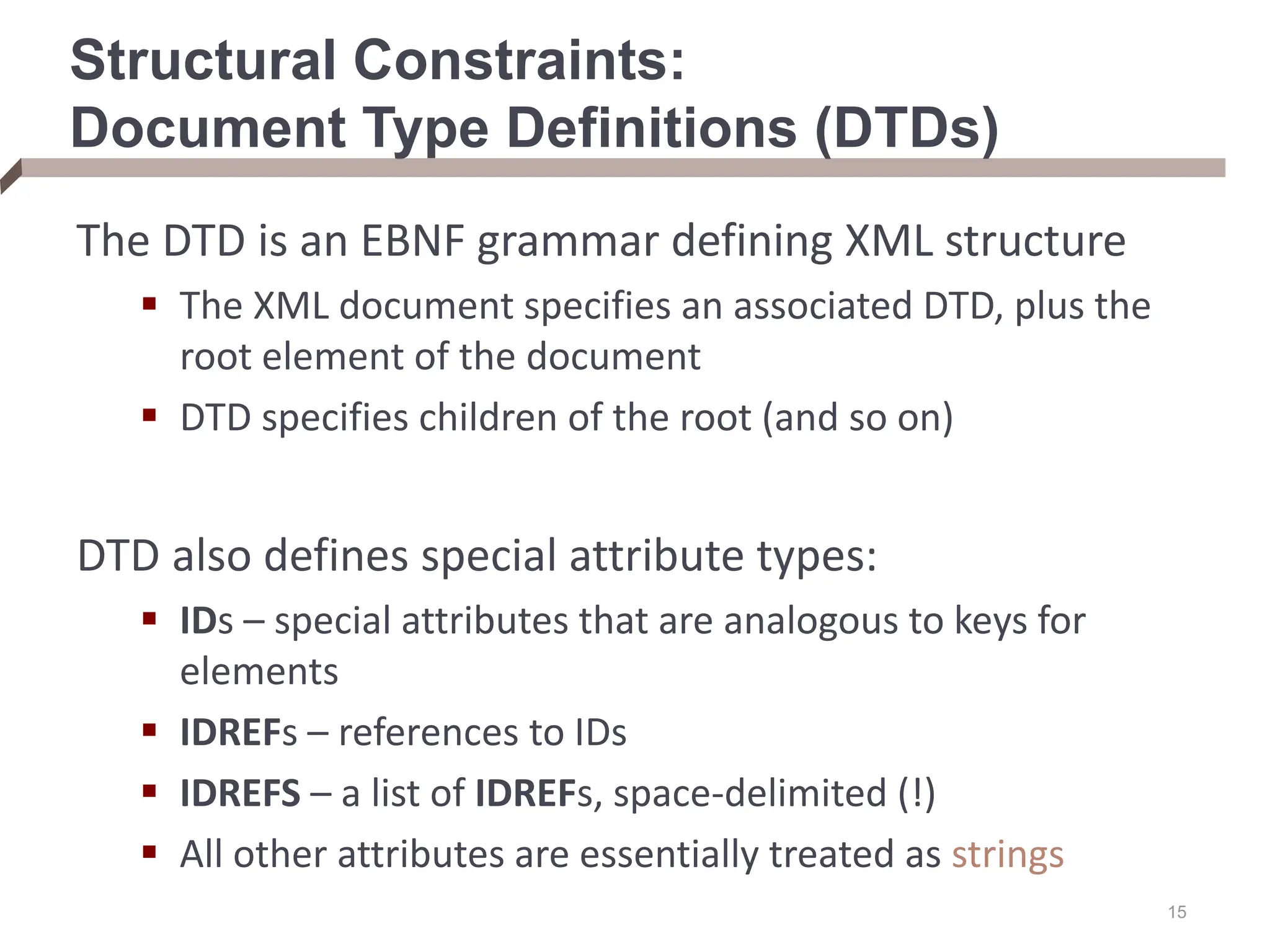
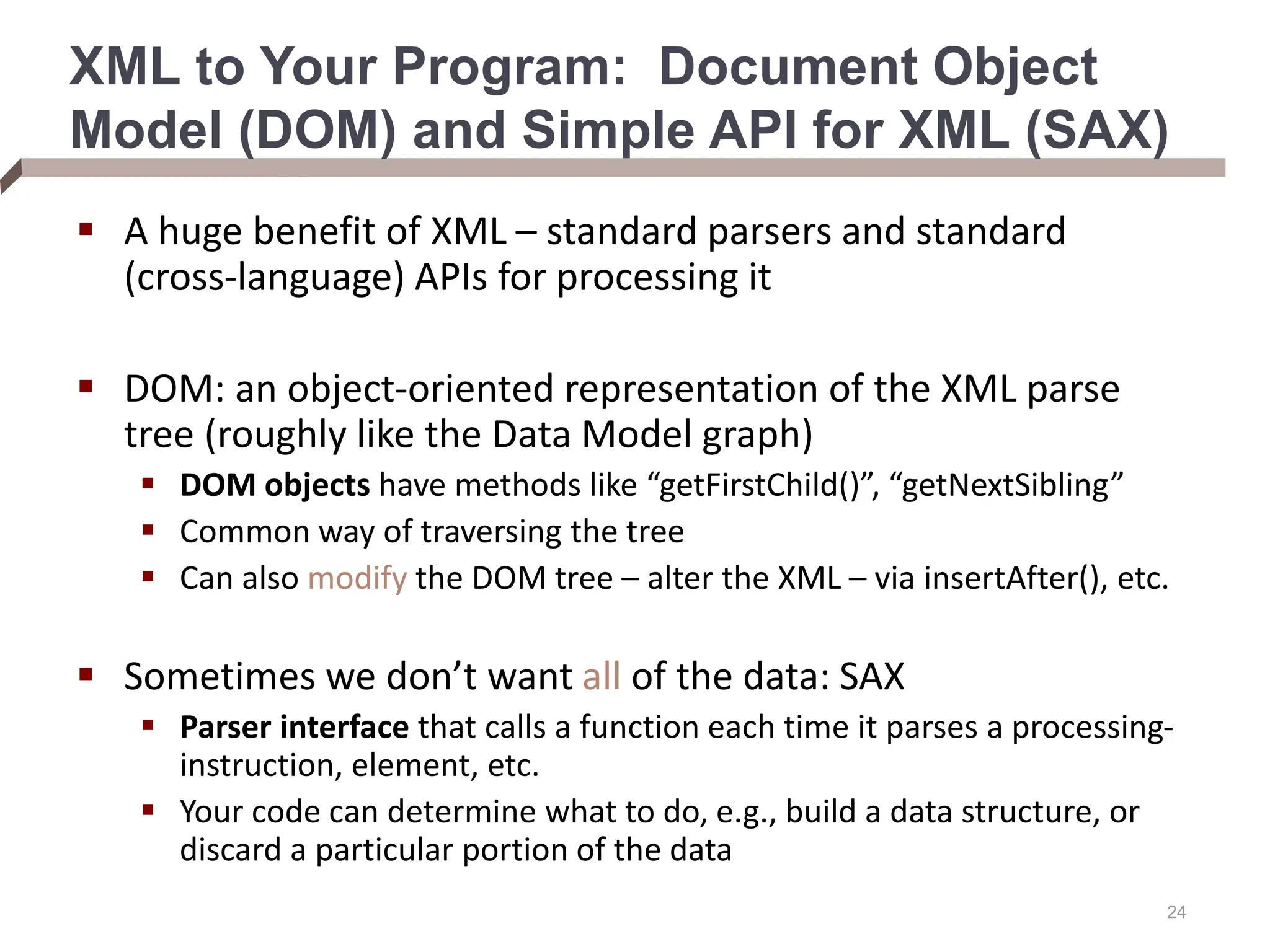
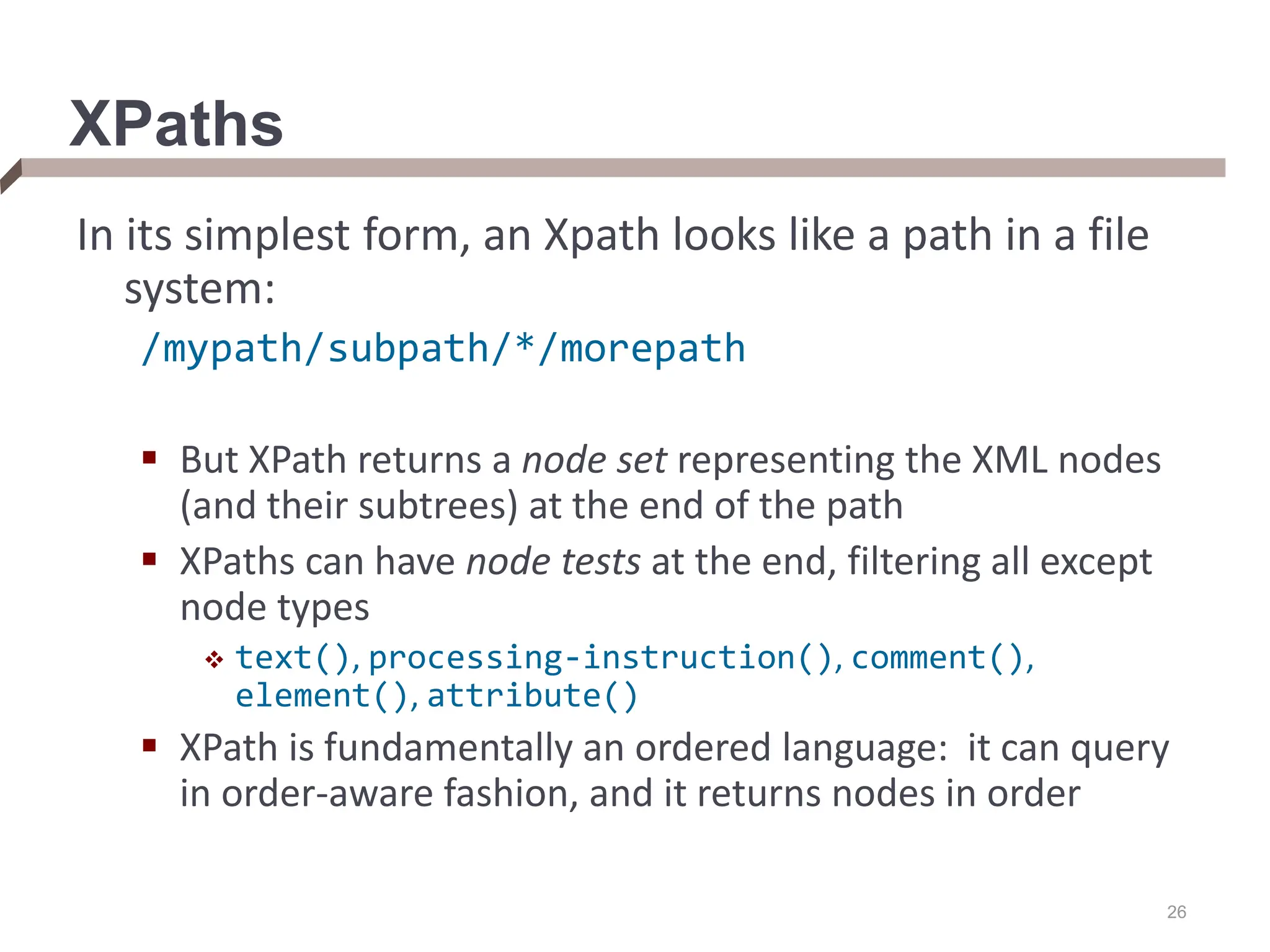
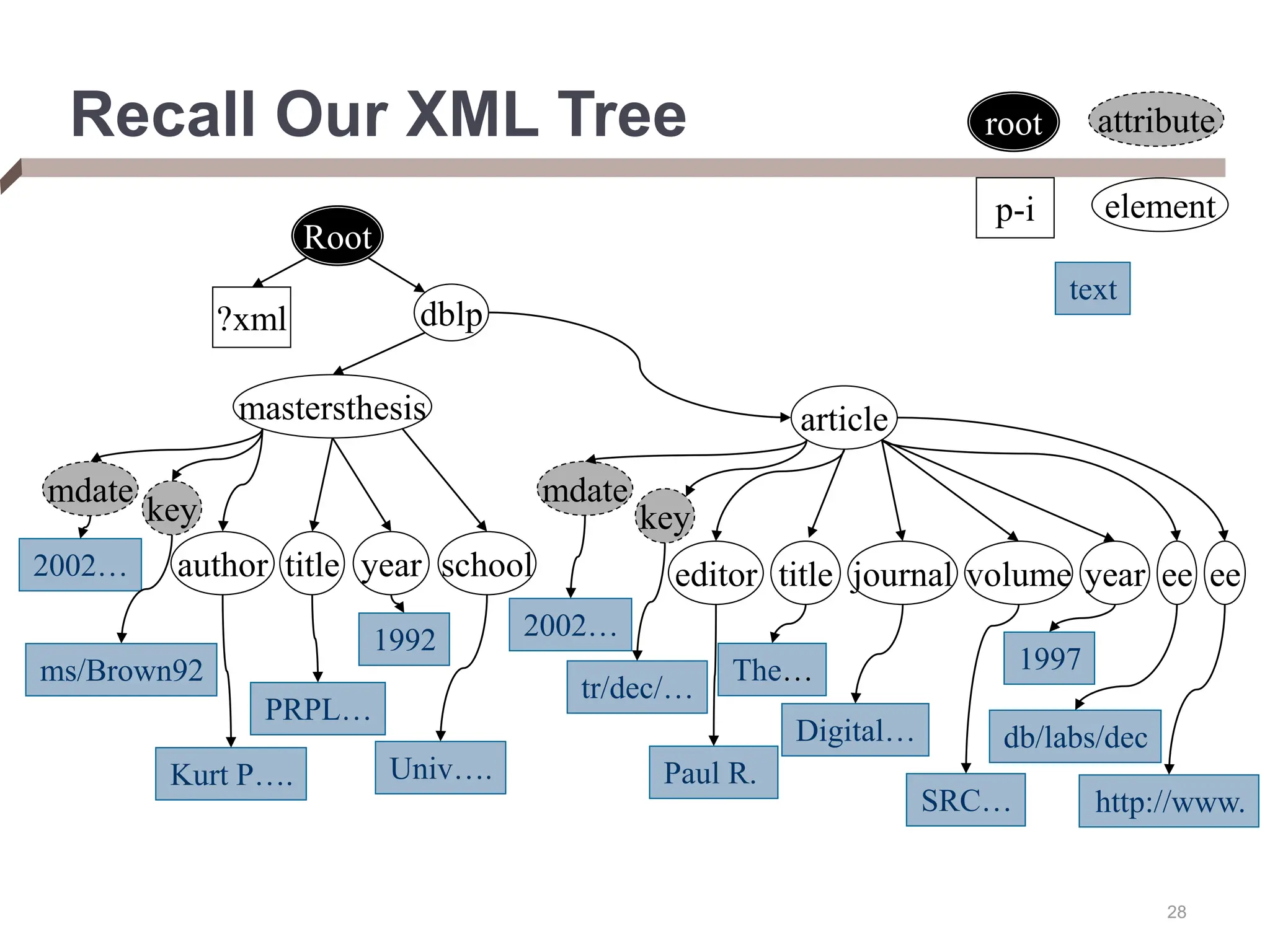
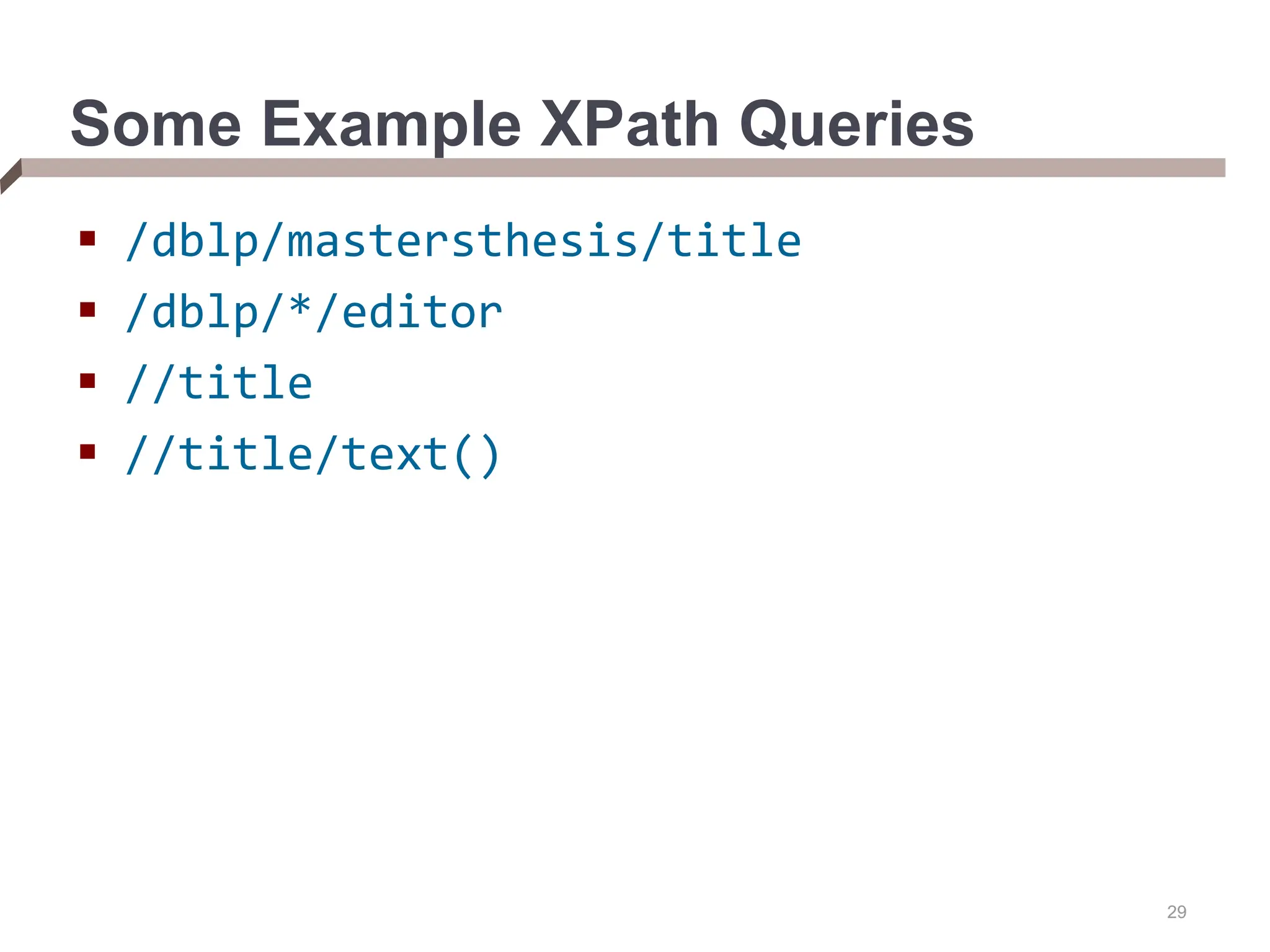
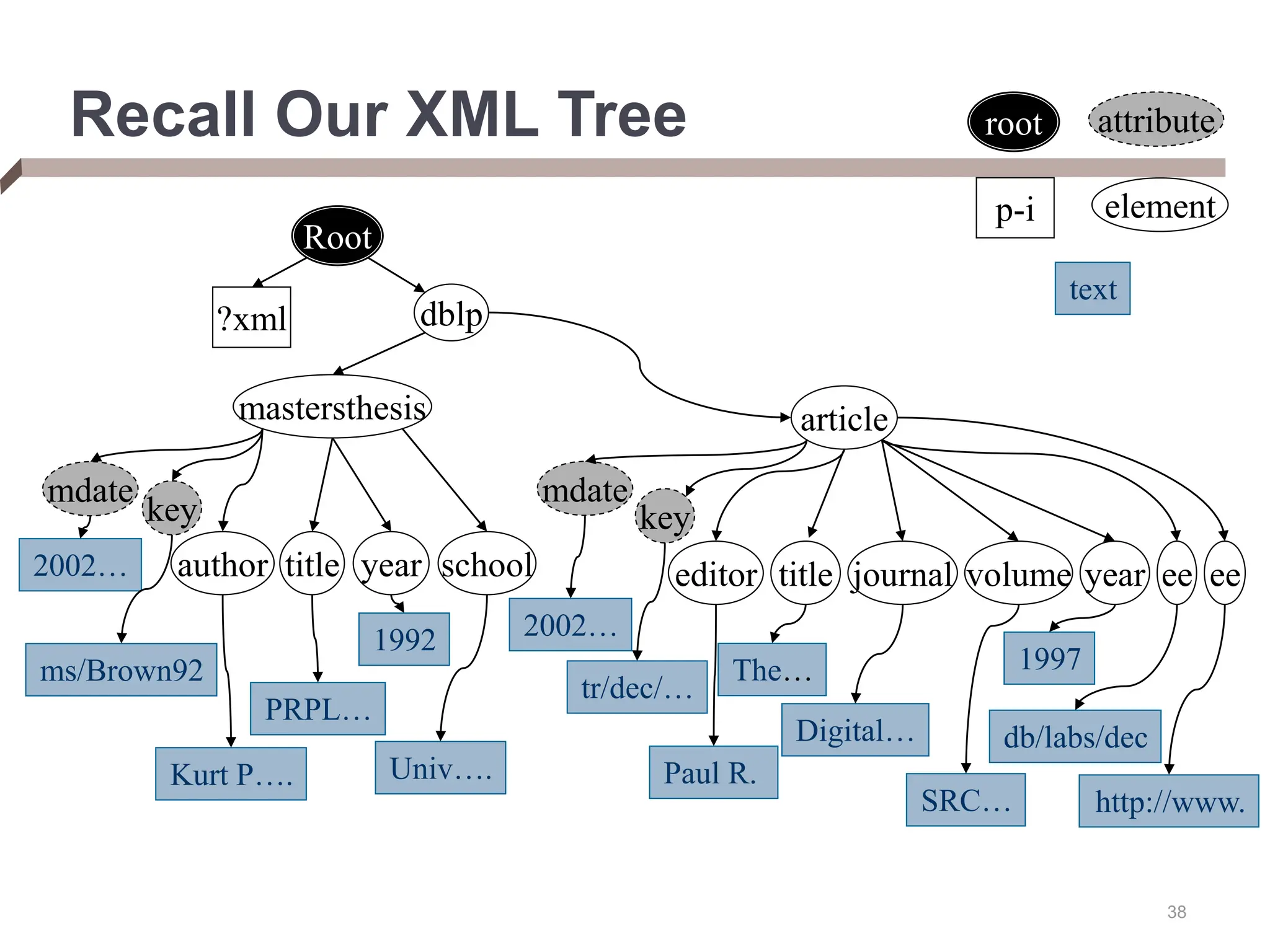
XML provides a standard way to represent and exchange data. It defines elements, which can contain text or other nested elements, and attributes. XML documents can be validated against DTDs or XML schemas, which define allowed structures and datatypes. XML data can be queried using XPath expressions, which select elements or attributes based on their path in the XML tree and optional predicates. XPath allows traversing relationships both vertically and horizontally in the tree structure.









![31 Predicates – Selection Operations A predicate allows us to filter the node set based on selection-like conditions over sub-XPaths: /dblp/article[title = “Paper1”] which is equivalent to: /dblp/article[./title/text() = “Paper1”]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataintegration-240308142430-a5f93f63/75/DATA-INTEGRATION-Gaining-Access-to-Diverse-Data-ppt-31-2048.jpg)

![33 Querying Order We saw in the previous slide that we could query for preceding or following siblings or nodes We can also query a node’s position according to some index: fn::first(), fn::last() index of 0th & last element matching the last step fn::position() relative count of the current node child::article[fn::position() = fn::last()]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataintegration-240308142430-a5f93f63/75/DATA-INTEGRATION-Gaining-Access-to-Diverse-Data-ppt-33-2048.jpg)

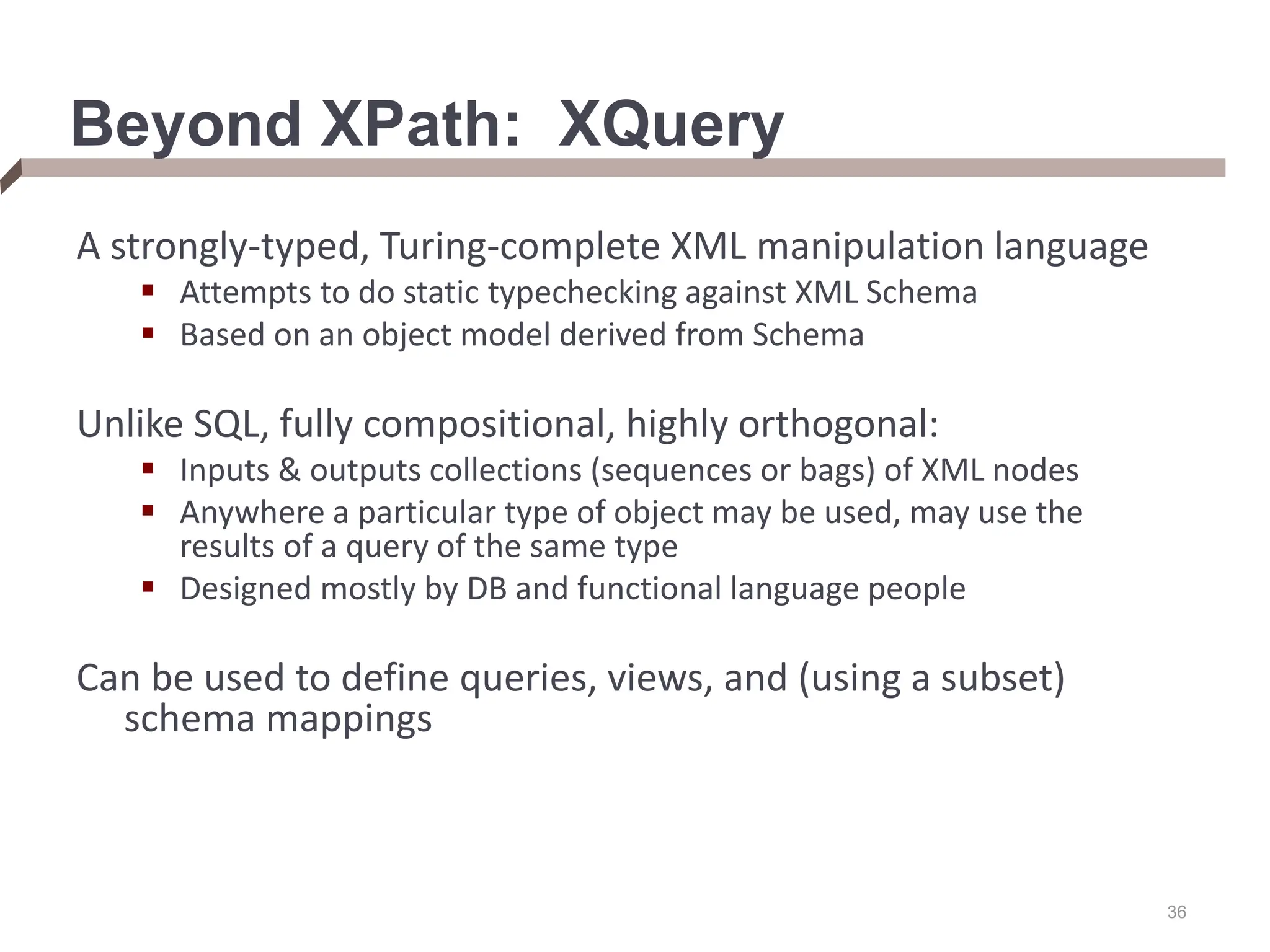
![37 XQuery’s Basic Form Has an analogous form to SQL’s SELECT..FROM..WHERE..GROUP BY..ORDER BY The model: bind nodes (or node sets) to variables; operate over each legal combination of bindings; produce a set of nodes “FLWOR” statement [note case sensitivity!]: for {iterators that bind variables} let {collections} where {conditions} order by {order-paths} return {output constructor} Mixes XML + XQuery syntax; use {} as “escapes”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataintegration-240308142430-a5f93f63/75/DATA-INTEGRATION-Gaining-Access-to-Diverse-Data-ppt-37-2048.jpg)
![40 Two XQuery Examples <root-tag> { for $p in doc (“dblp.xml”)/dblp/article, $yr in $p/yr where $yr = “1997” return <paper> { $p/title } </paper> } </root-tag> for $i in doc (“dblp.xml”)/dblp/article[author/text() = “John Smith”] return <smith-paper> <title>{ $i/title/text() }</title> <key>{ $i/@key }</key> { $i/crossref } </smith-paper>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataintegration-240308142430-a5f93f63/75/DATA-INTEGRATION-Gaining-Access-to-Diverse-Data-ppt-40-2048.jpg)



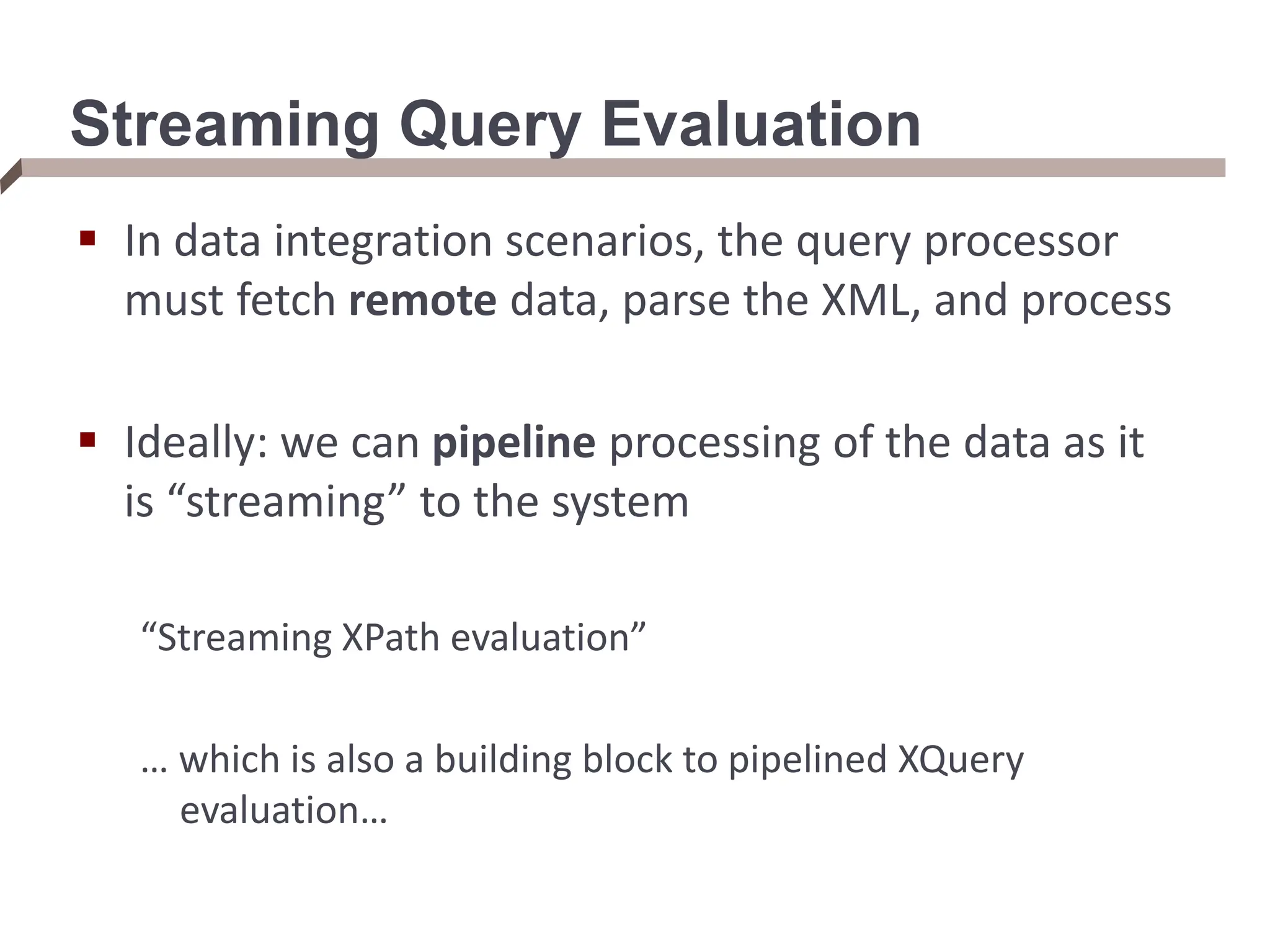


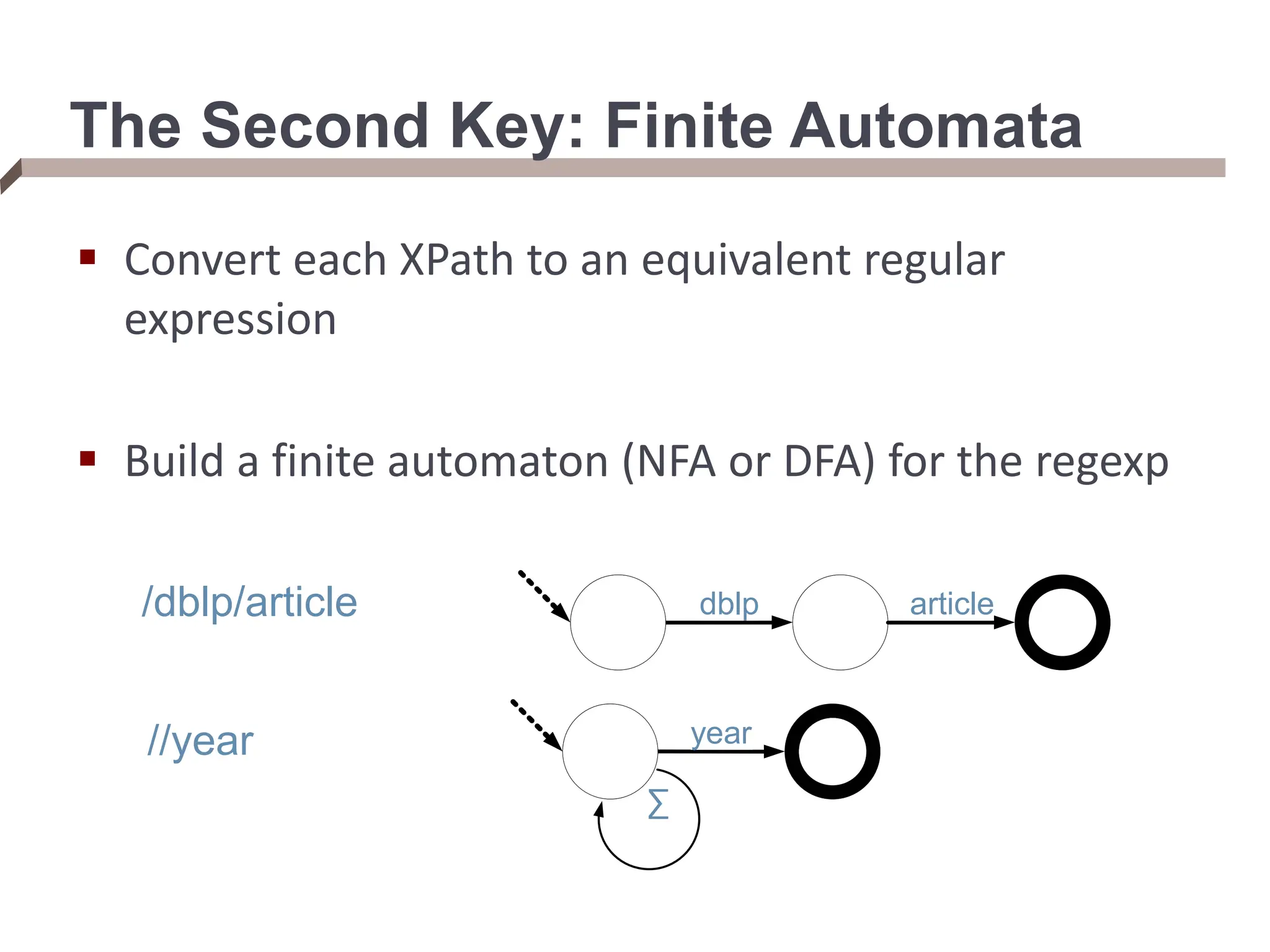
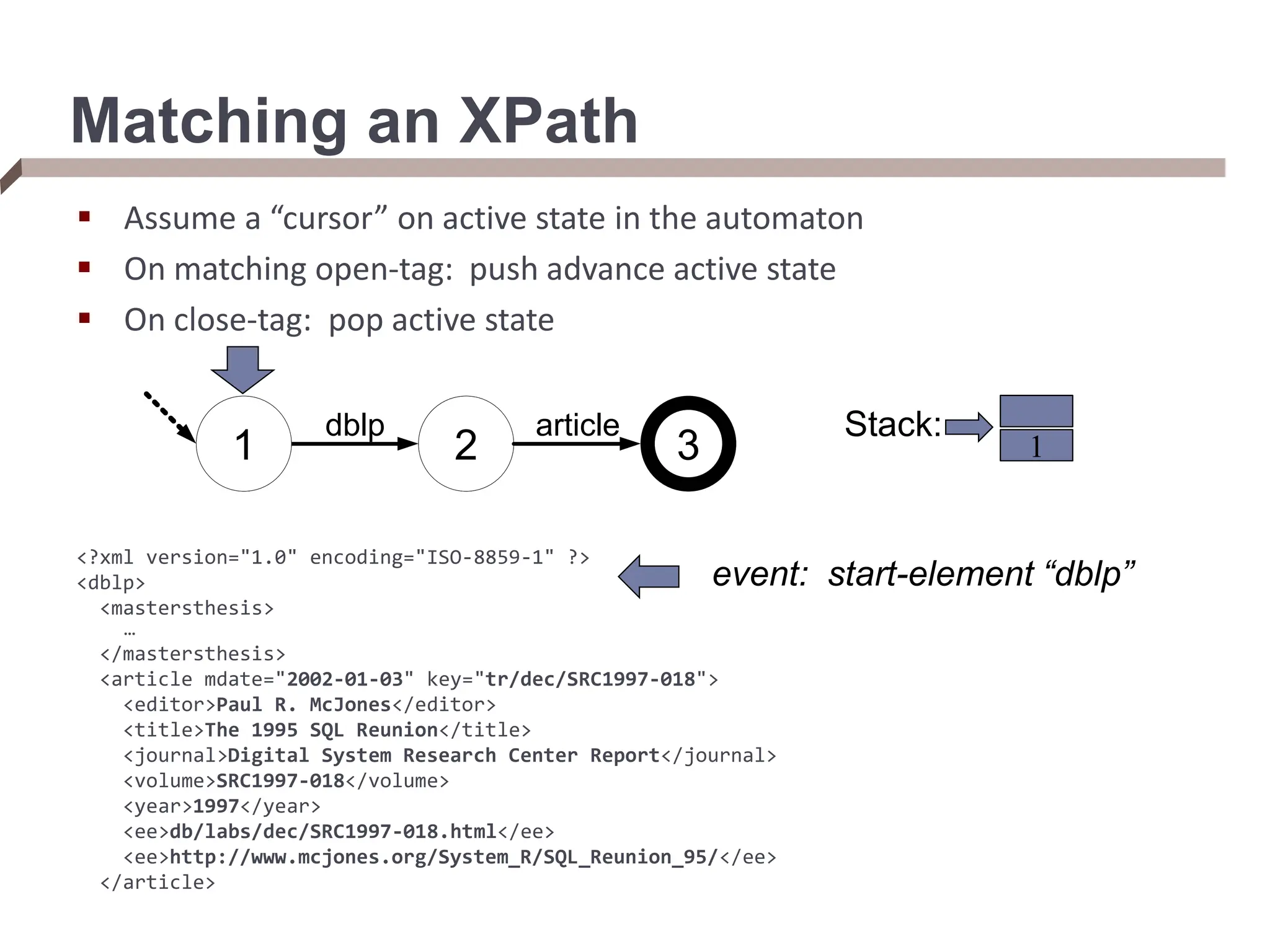
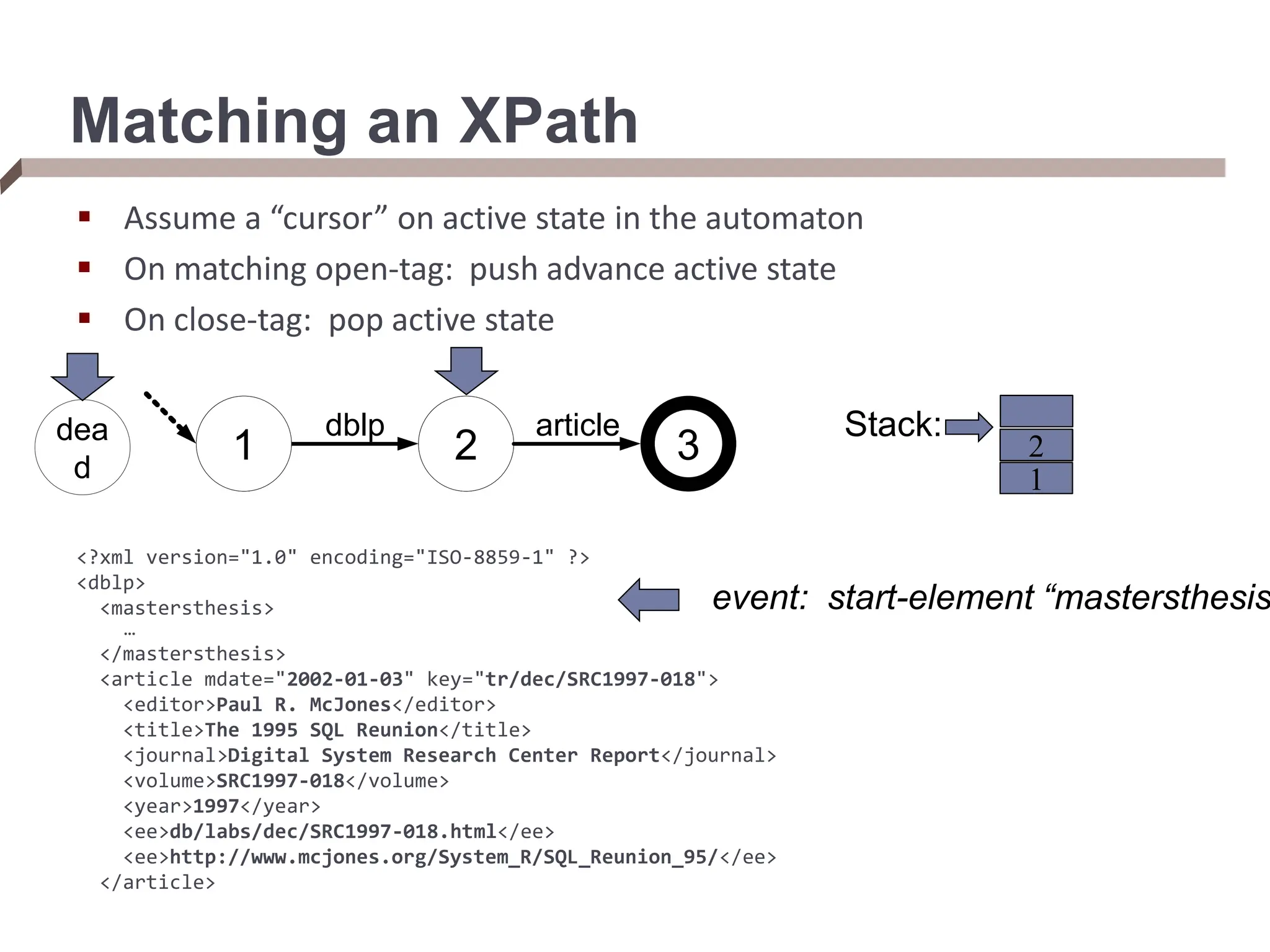
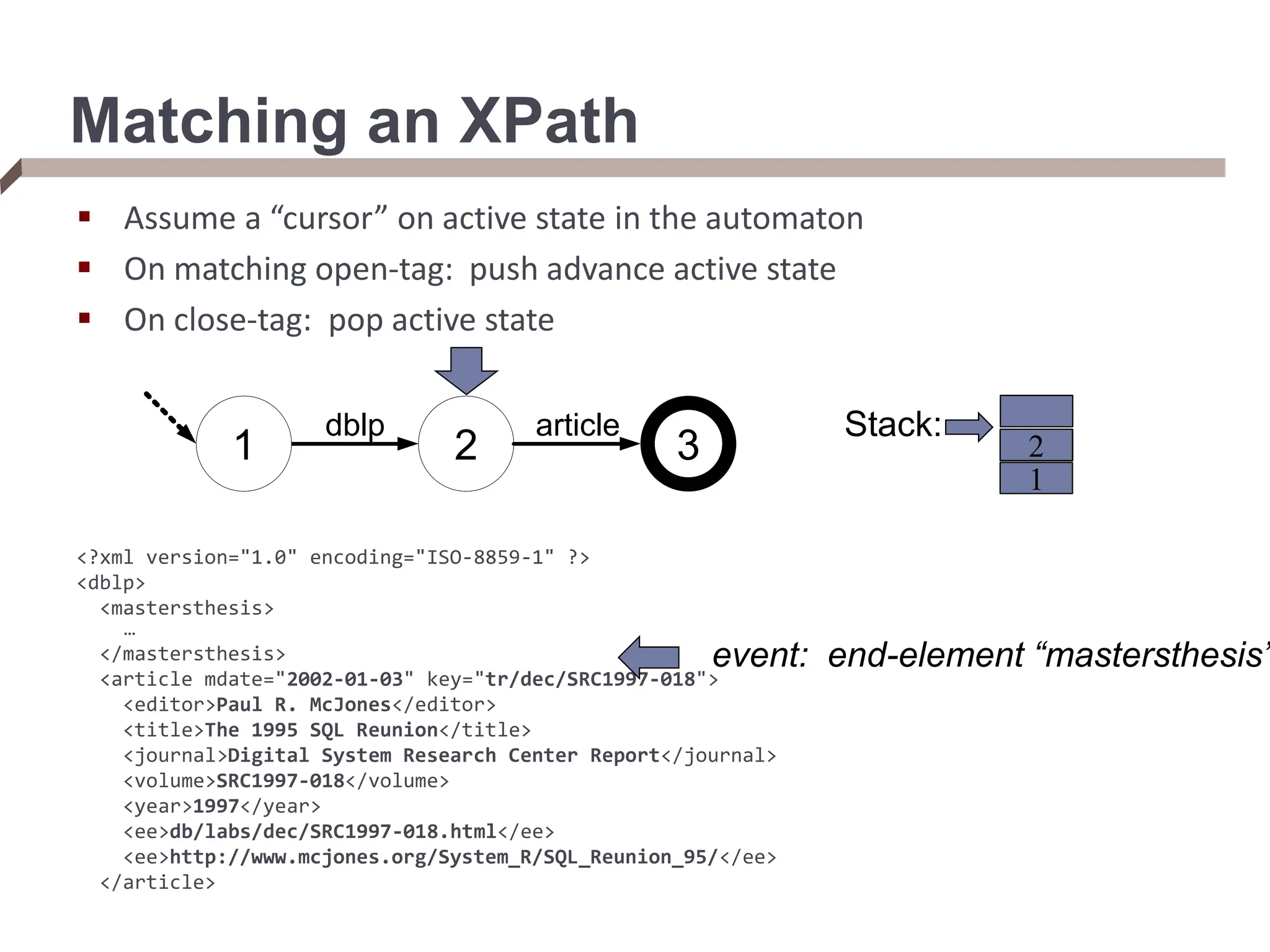
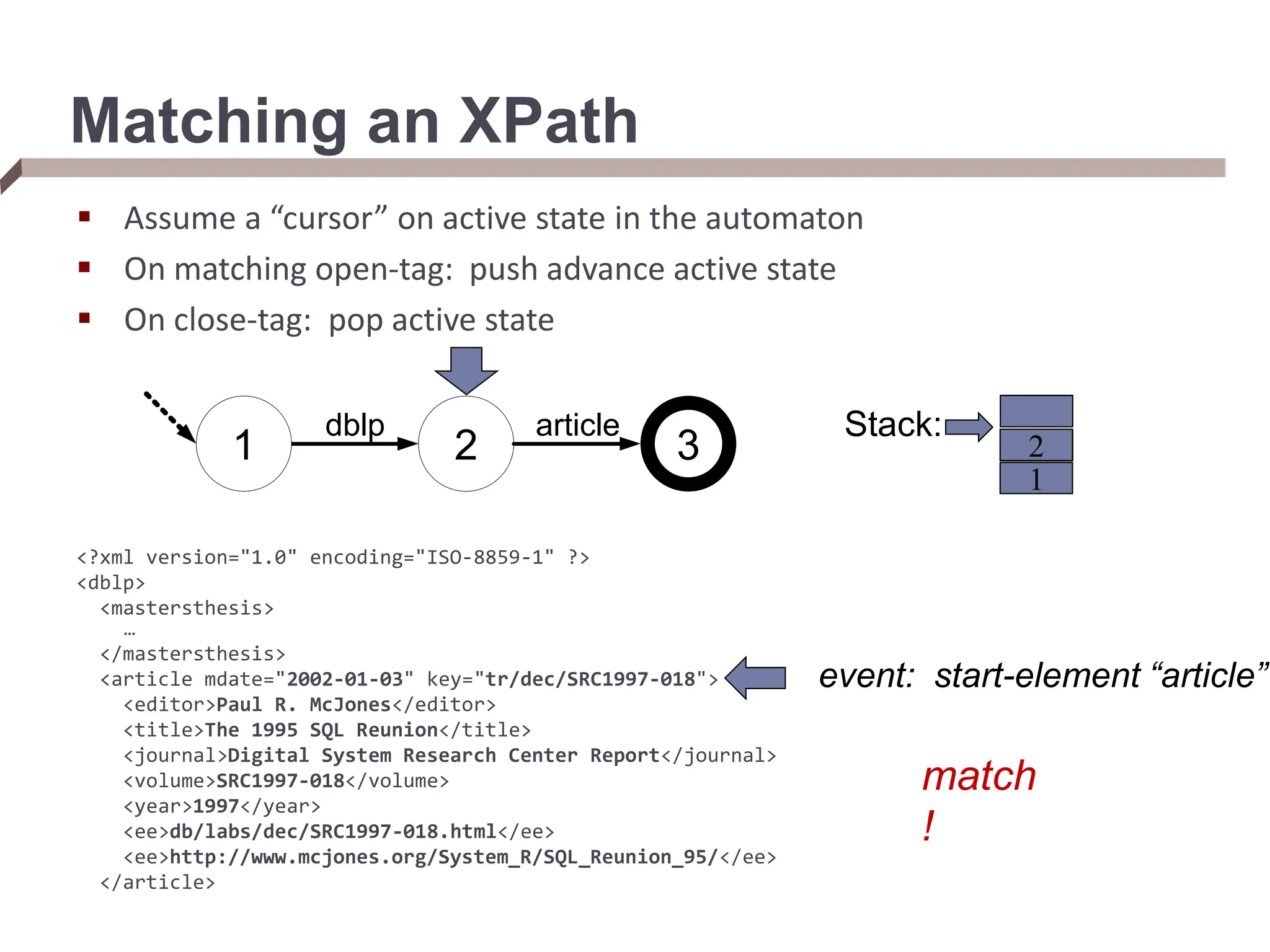
![From XPaths to XQueries An XQuery takes multiple XPaths in the FOR/LET clauses, and iterates over the elements of each XPath (binding the variable to each) FOR $rootElement in doc(“dblp.xml”)/dblp, $rootChild in $rootElement/article[author=“Bob”], $textContent in $rootChild/text() We can think of an XQuery as doing tree matching, which returns tuples ($i, $j) for each tree matching $i and $j in a document Streaming XML path evaluator that supports a hierarchy of matches over an XML document](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataintegration-240308142430-a5f93f63/75/DATA-INTEGRATION-Gaining-Access-to-Diverse-Data-ppt-58-2048.jpg)
![XQuery Path Evaluation Multiple, dependent state machines outputting binding tuples dblp article $ rootElement $ rootChild set text() $ textContent ? = “Bob” author Only activate $rootChild + $textContent on a match to $rootElemen Evaluate a pushed-do selection predicate $rootEle ment $rootC hild $textCon tent FOR $rootElement in doc(“dblp.xml”)/dblp, $rootChild in $rootElement/article[author=“Bob”], $textContent in $rootChild/text()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataintegration-240308142430-a5f93f63/75/DATA-INTEGRATION-Gaining-Access-to-Diverse-Data-ppt-59-2048.jpg)

![An Example XQuery Plan dblp.xml Streaming XPath <dblp>... (<dblp>…</dblp>, <article>…</article>, [“Paul R. McJones”,”The 1995…”, …]) ... dblp article $ rootElement $ rootChild set text() $ textContent Σ = “B ob” author dblp.xml (<dblp>…</dblp>, <article>…</article>, [“Paul R. McJones”,”The 1995…”, …]) ... ⊐ ⋈ XPath matcher $textContent XML tagging $ txt (“Paul R. McJones”) (“The 1995…”) XML grouping (<text>Paul R. McJones</text>) (<text>The 1995…</text>) (<text>Paul R. McJones</text><text>The 1995…</text>) XML tagging (<editor>Paul R. McJones</editor>, <title>The 1995…</title>, <text>Paul R. McJones</text><text>The 1995…</text>) Π (<article>…</article>, [“Paul R. McJones”,”The 1995…”, …]) ... (<article>…</article>, [“Paul R. McJones”,”The 1995…”, …], <editor>Paul R. McJones</editor>, <title>The 1995…</title>, <text>Paul R. McJones</text><text>The 1995…</text>) Π (<BobResult><editor>Paul R. McJones</editor> <title>The 1995…</title><text>Paul R. McJones</text> <text>The 1995…</text></BobResult>) XPath matcher editor $ editor set title $ title $rootChild Streaming XPath evaluation Relational-style query operators (outerjoin) XPath evaluation against a binding XML output operator](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataintegration-240308142430-a5f93f63/75/DATA-INTEGRATION-Gaining-Access-to-Diverse-Data-ppt-62-2048.jpg)