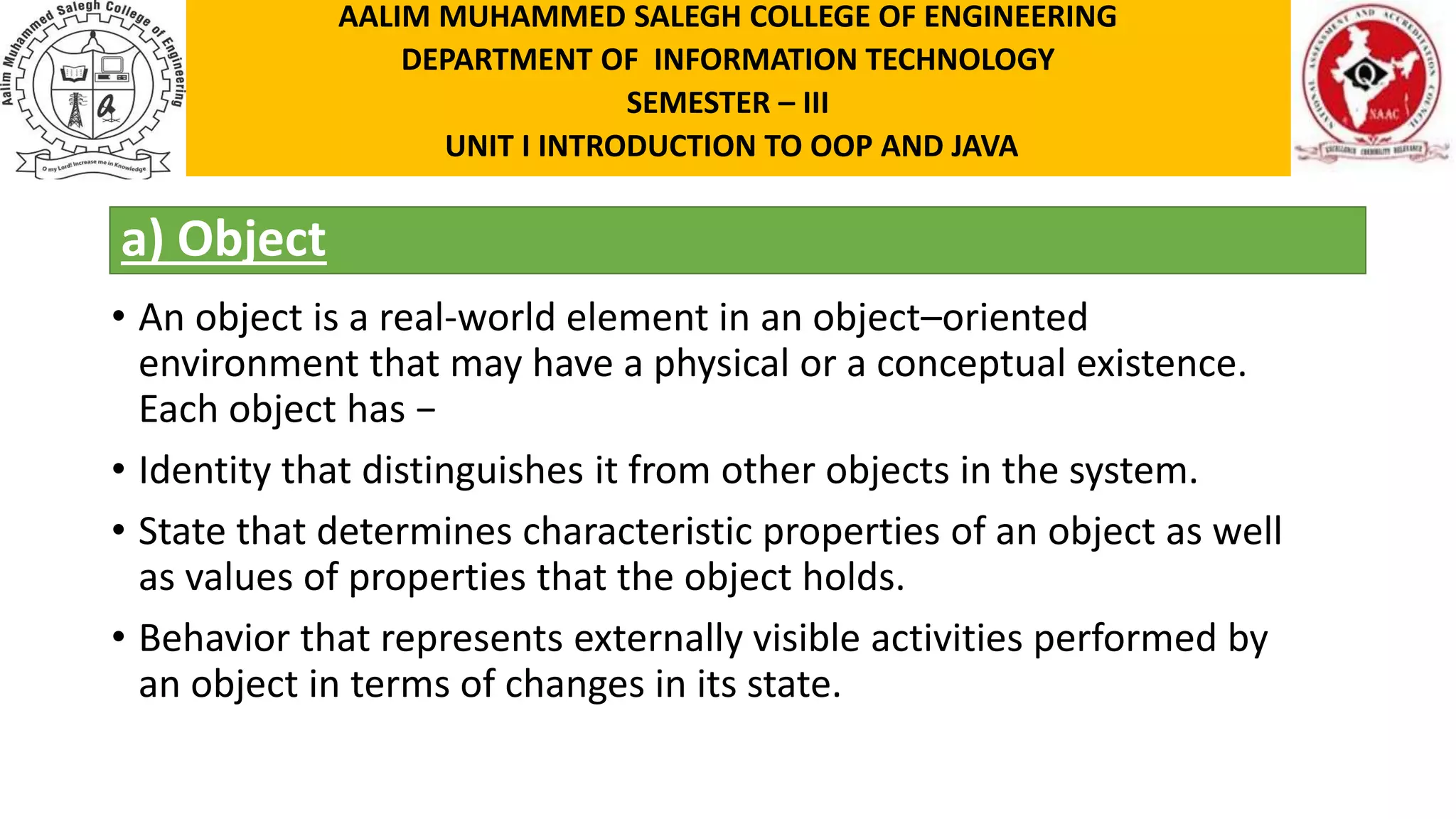
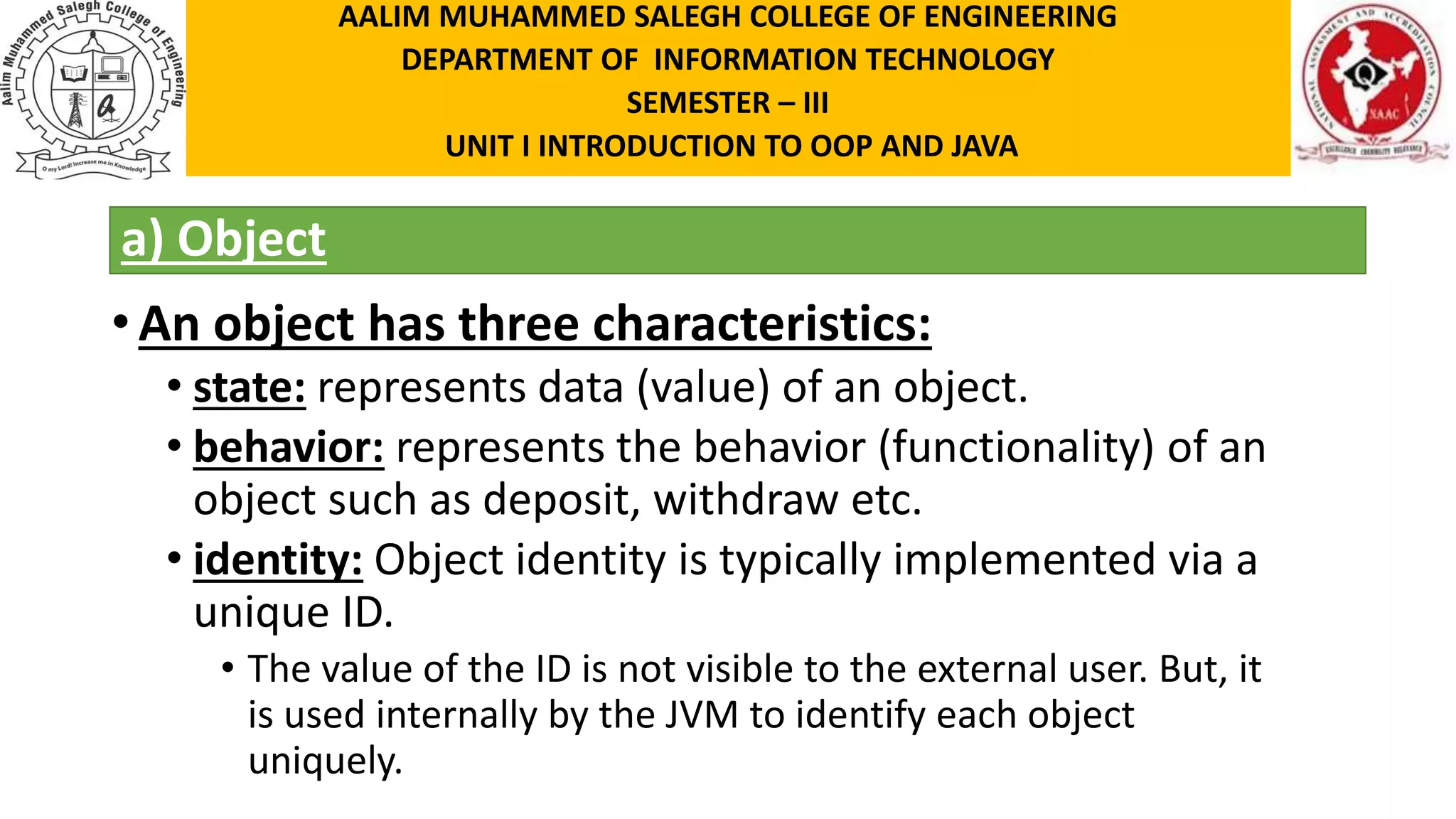
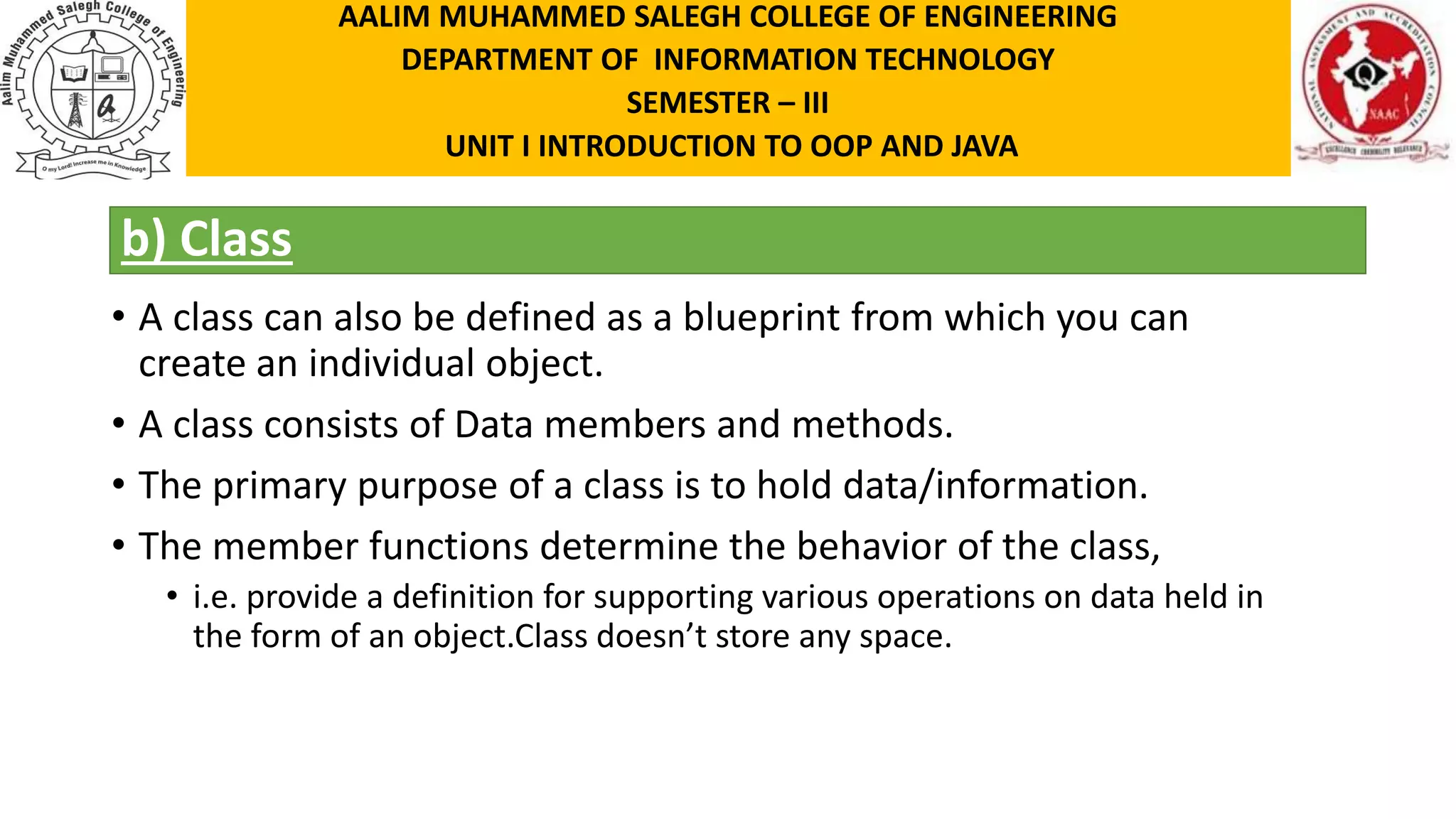
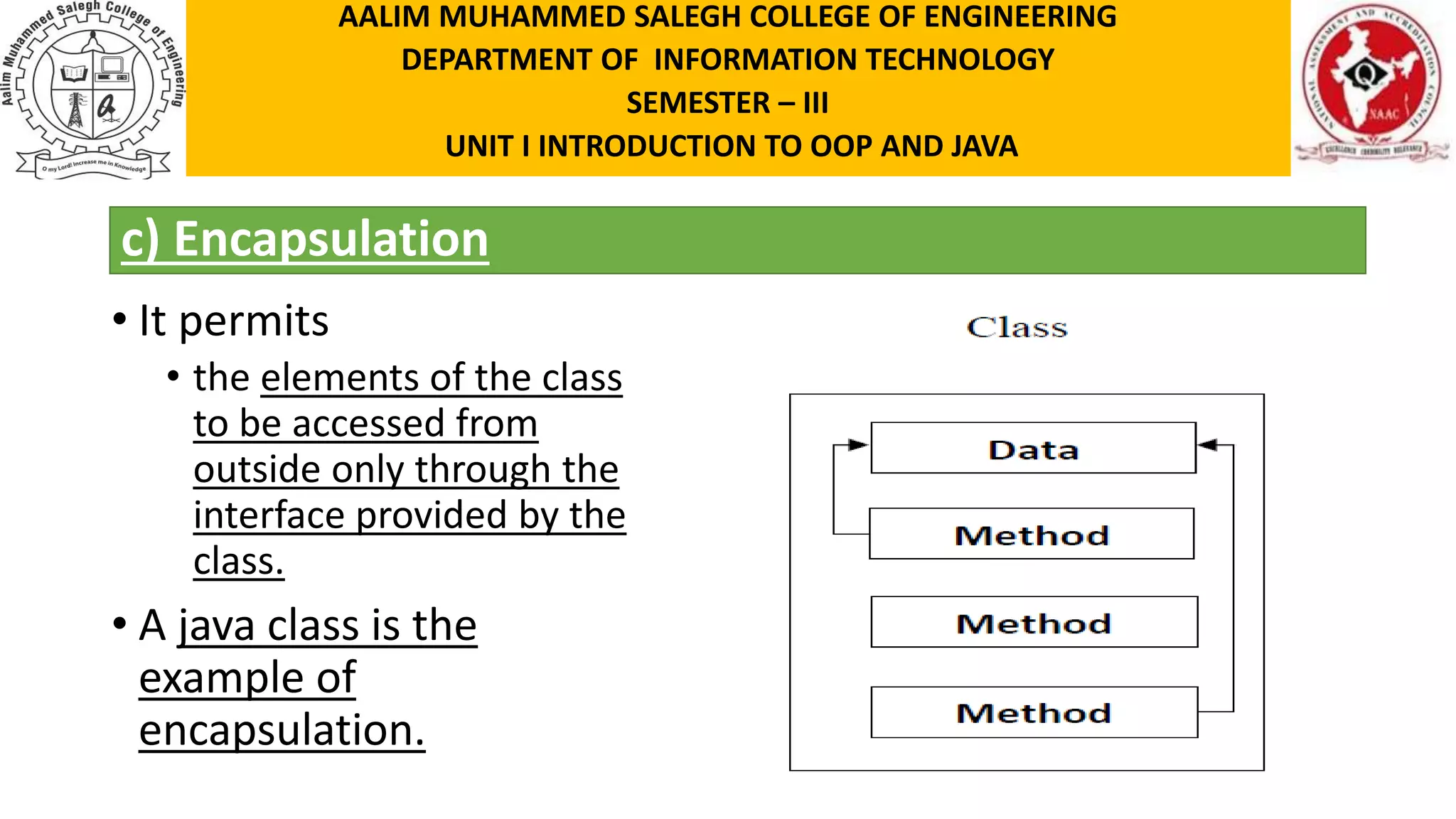
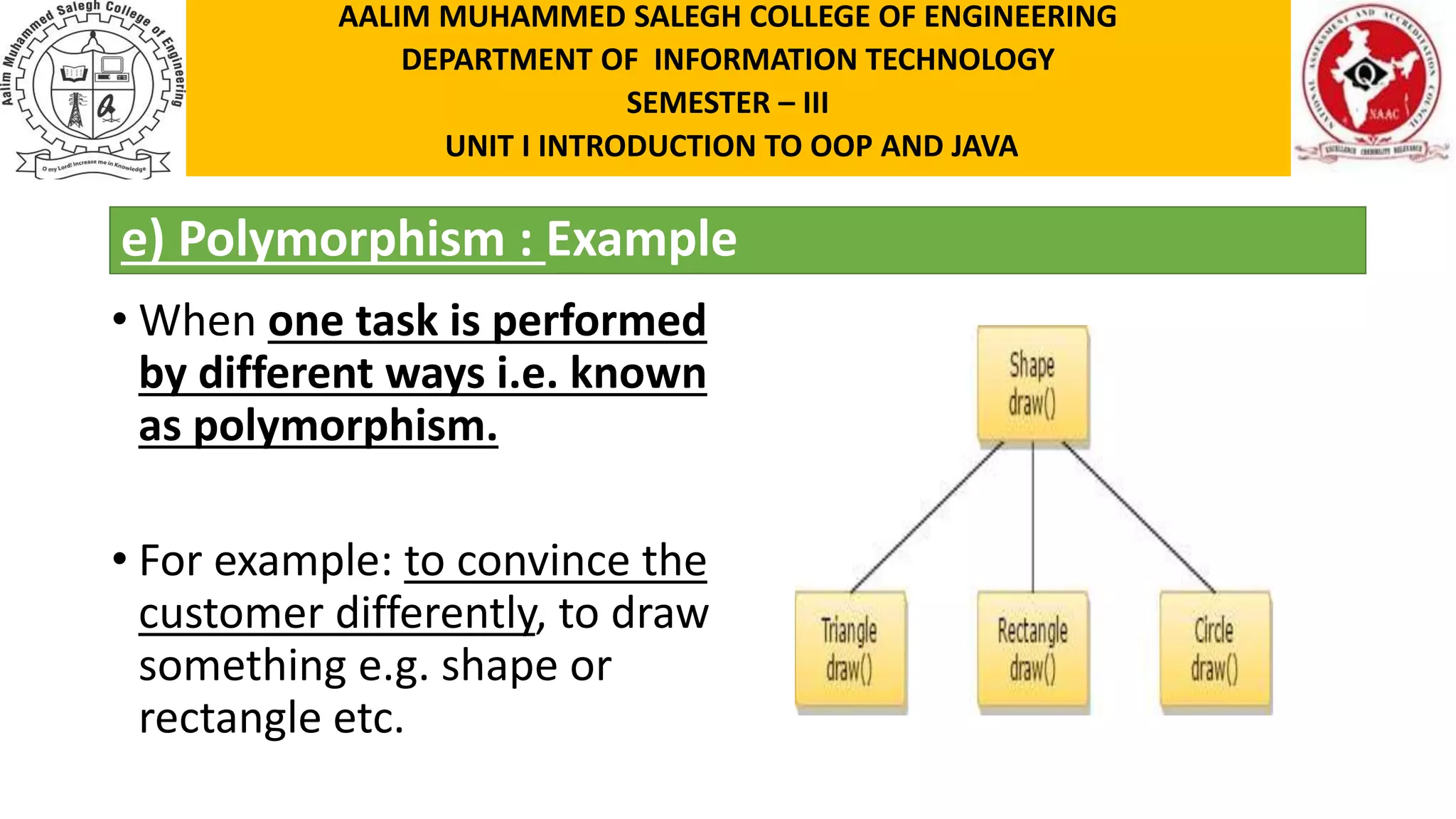
This document discusses the features of object-oriented programming, including objects, classes, encapsulation, abstraction, polymorphism, and inheritance. It provides examples and definitions for each concept. Objects have identity, state, and behavior. Classes provide blueprints for objects and define their attributes and methods. Encapsulation binds data and methods together, and hides implementation details. Abstraction involves hiding details and showing functionality. Polymorphism allows the same method to operate in different ways depending on the object, like calculating area for different shapes. Inheritance allows classes to share structure and behavior with parent classes.