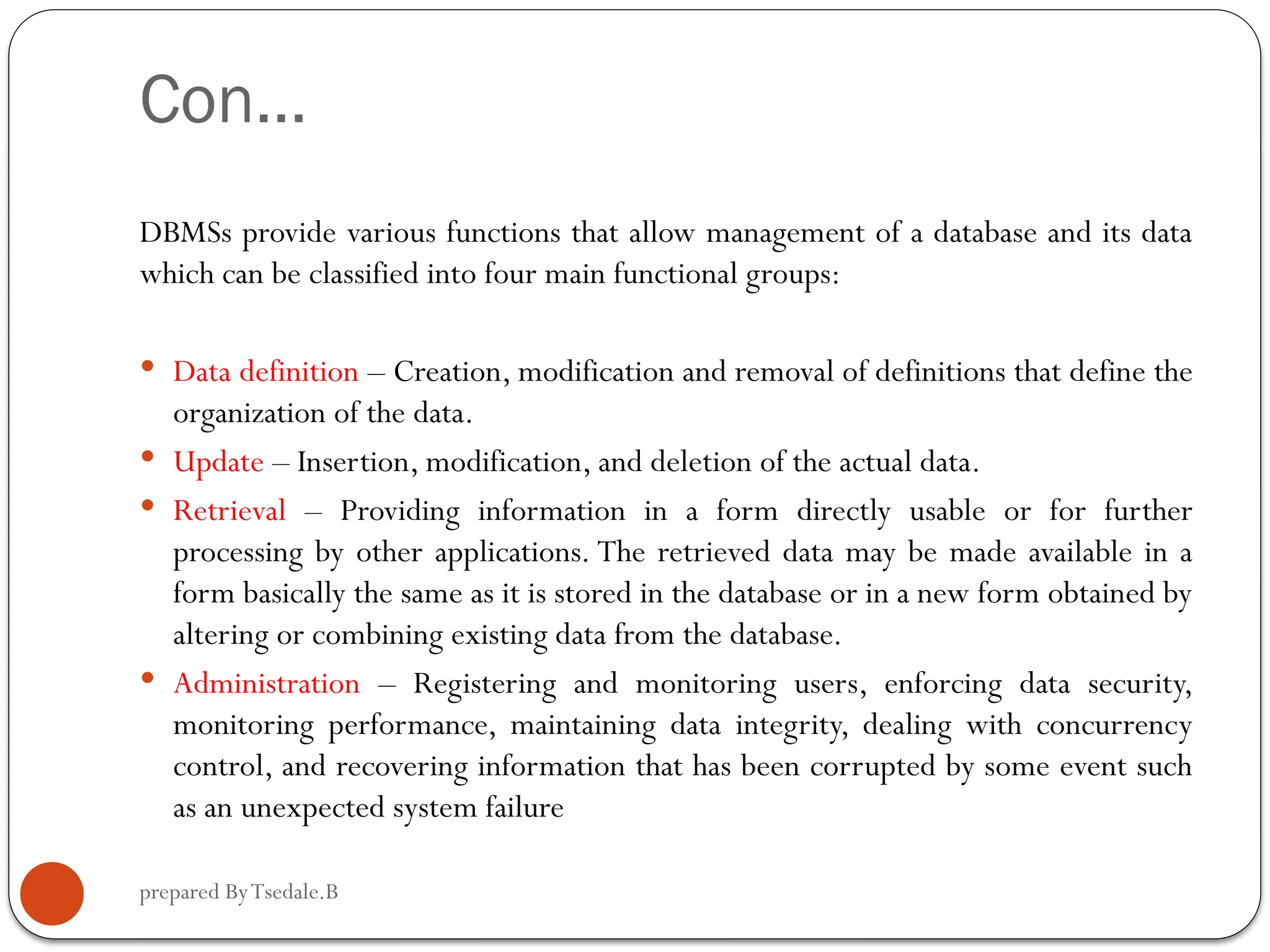
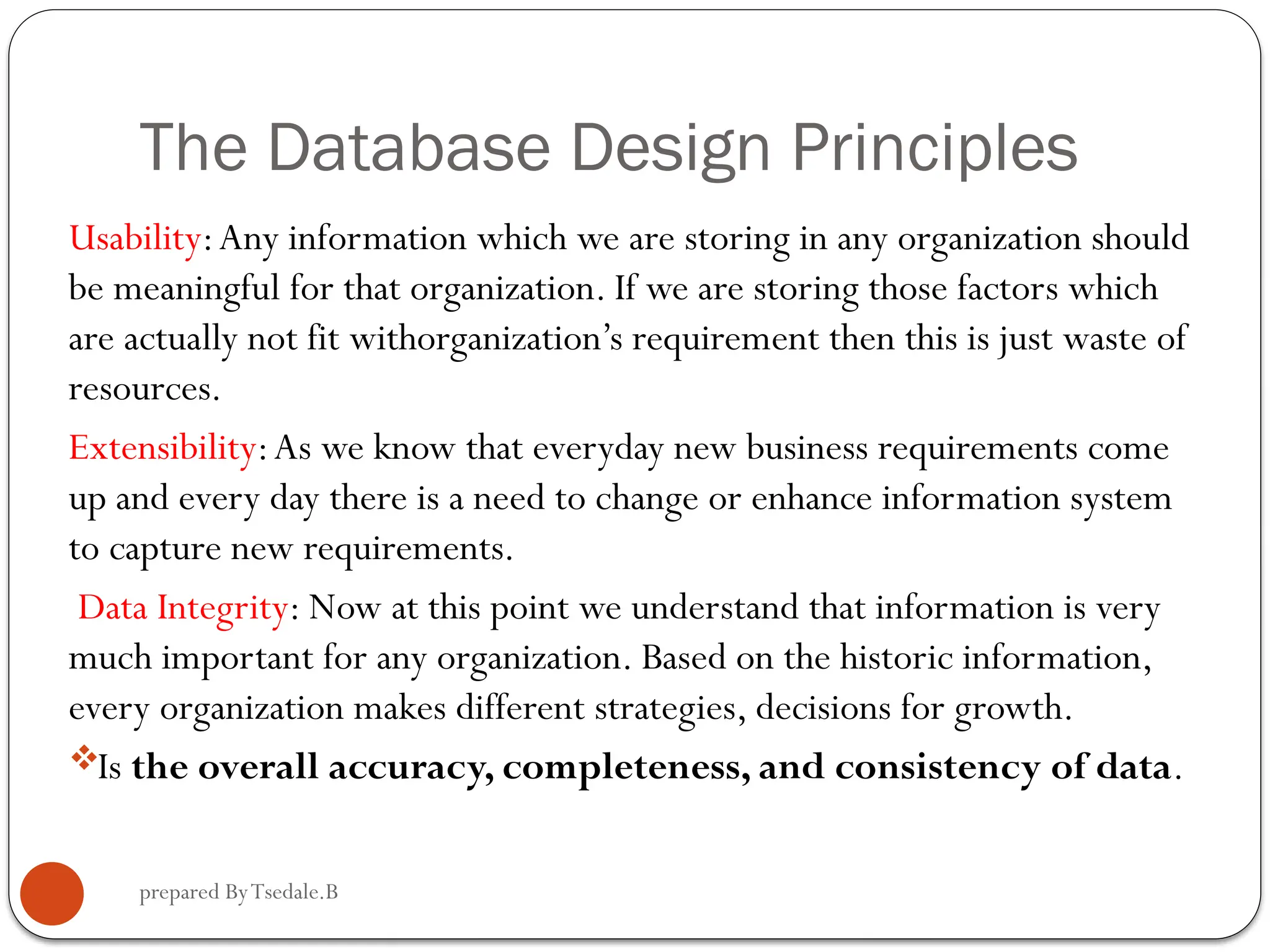
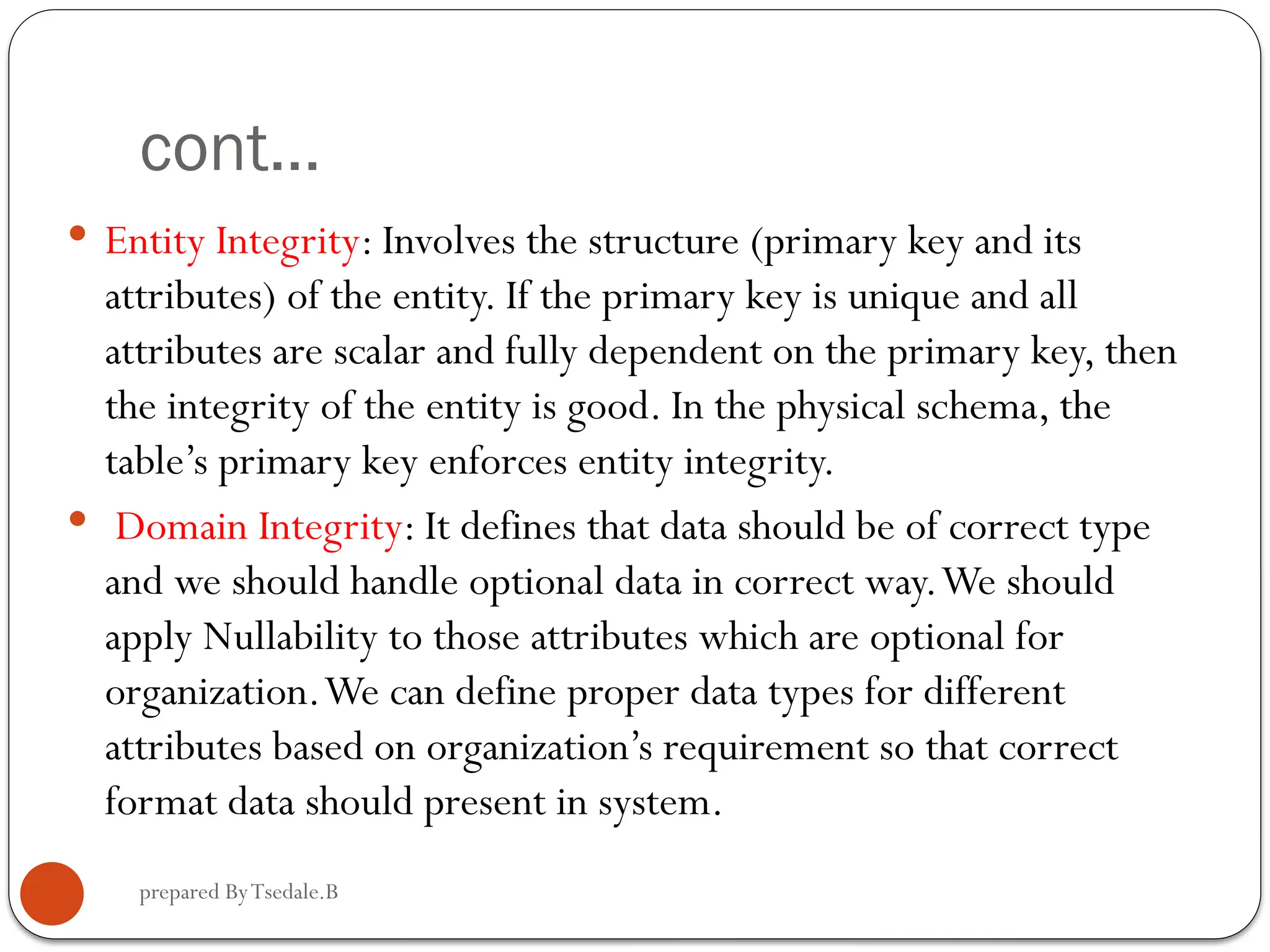
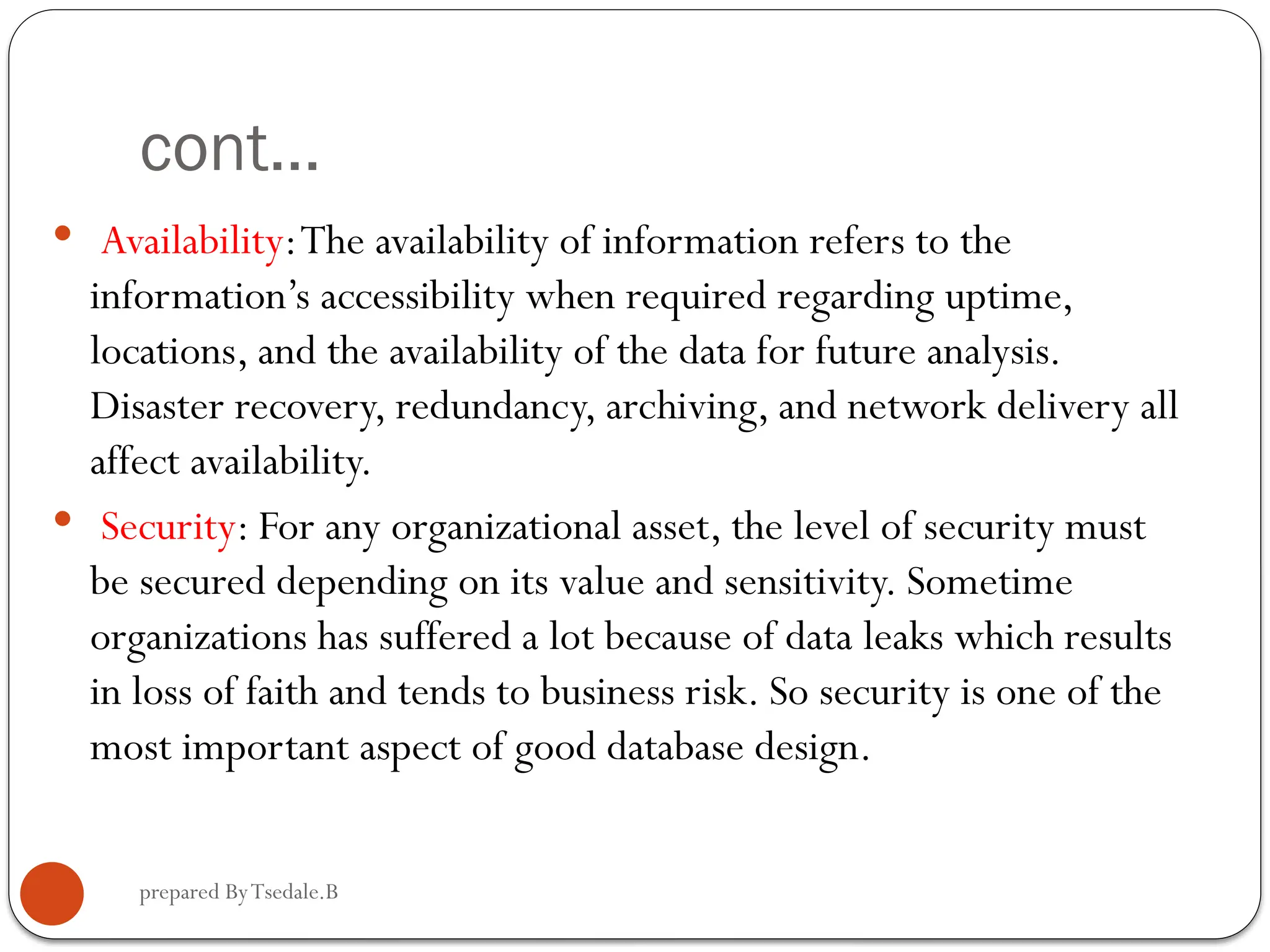
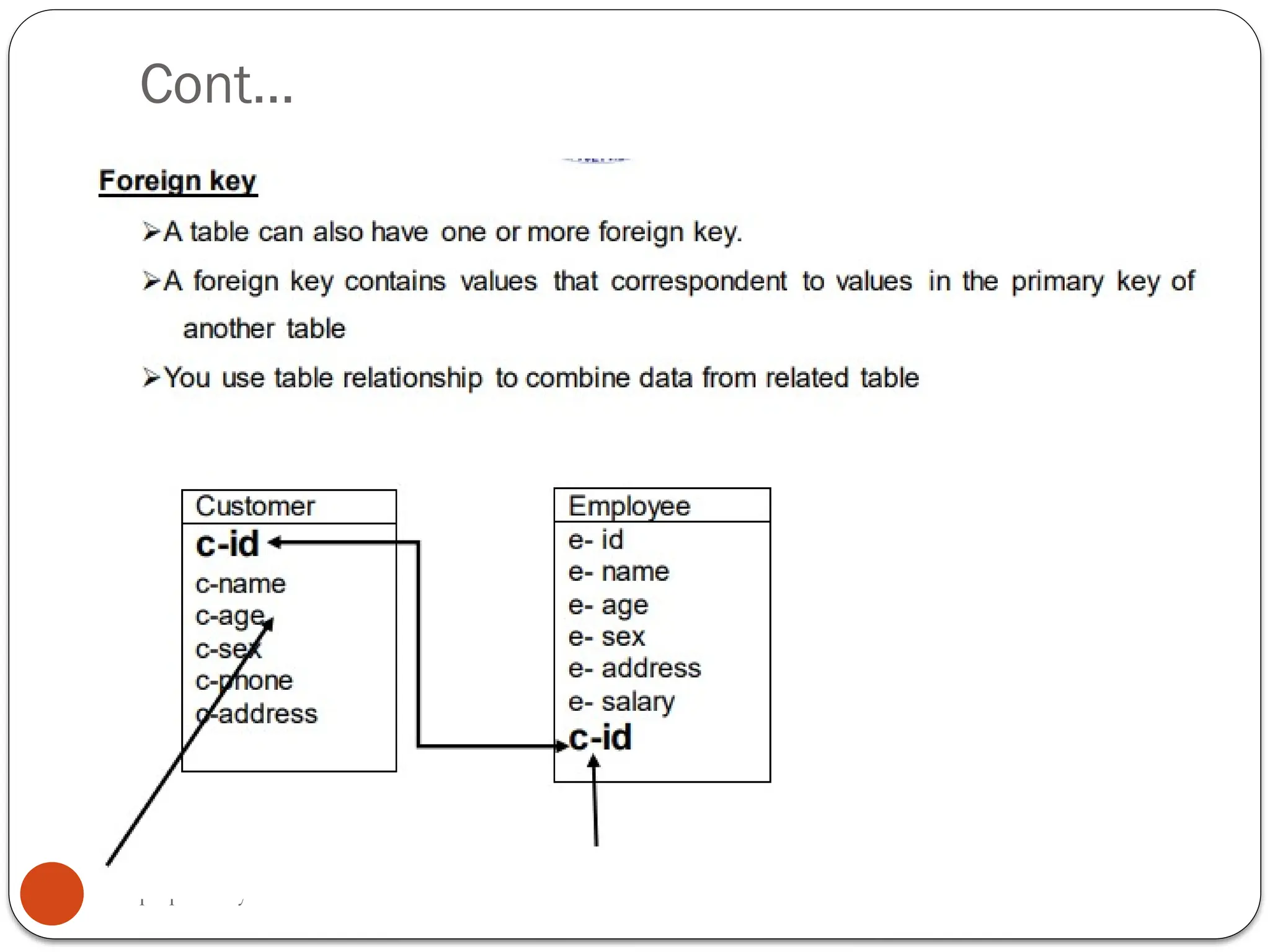
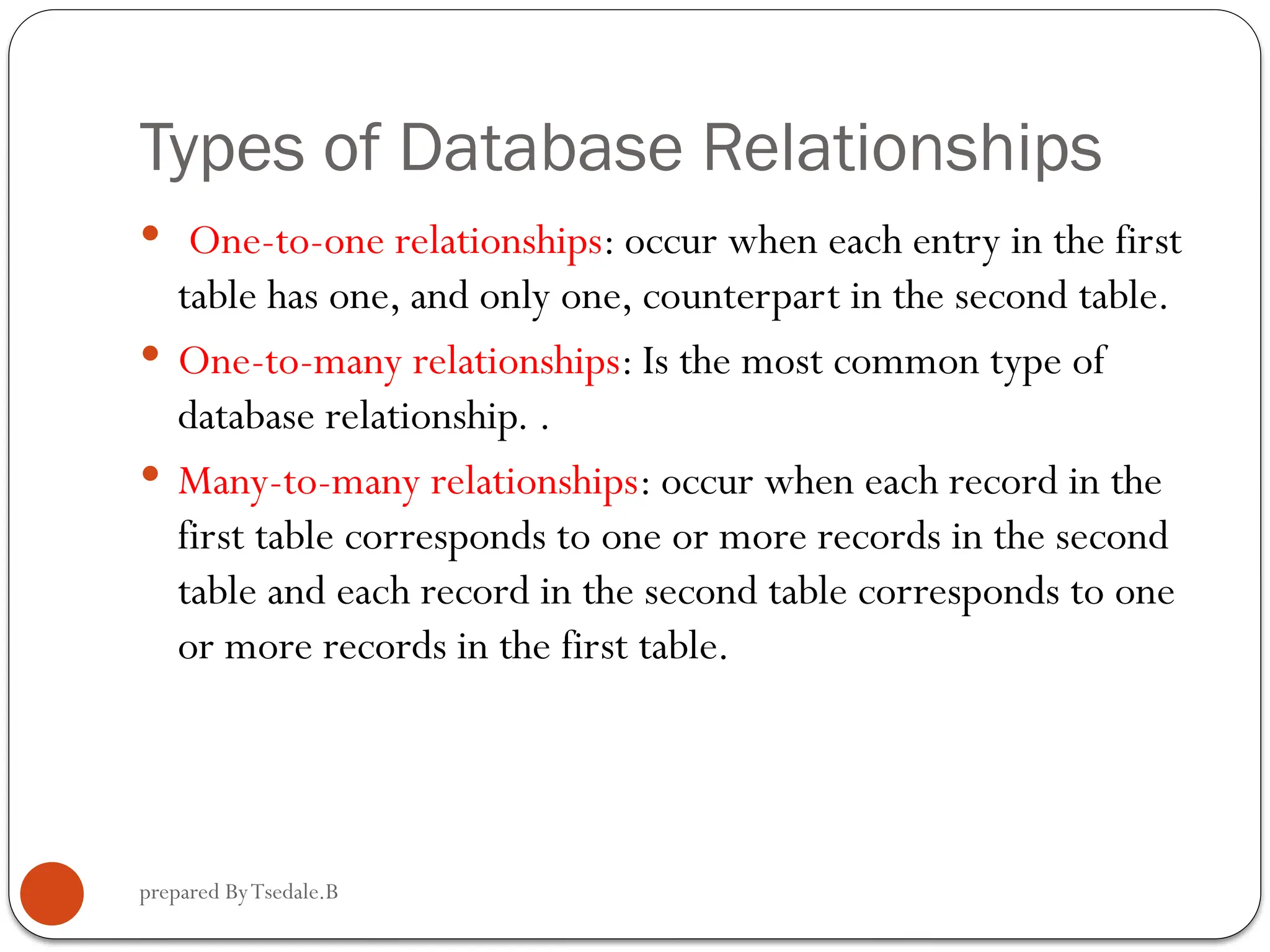
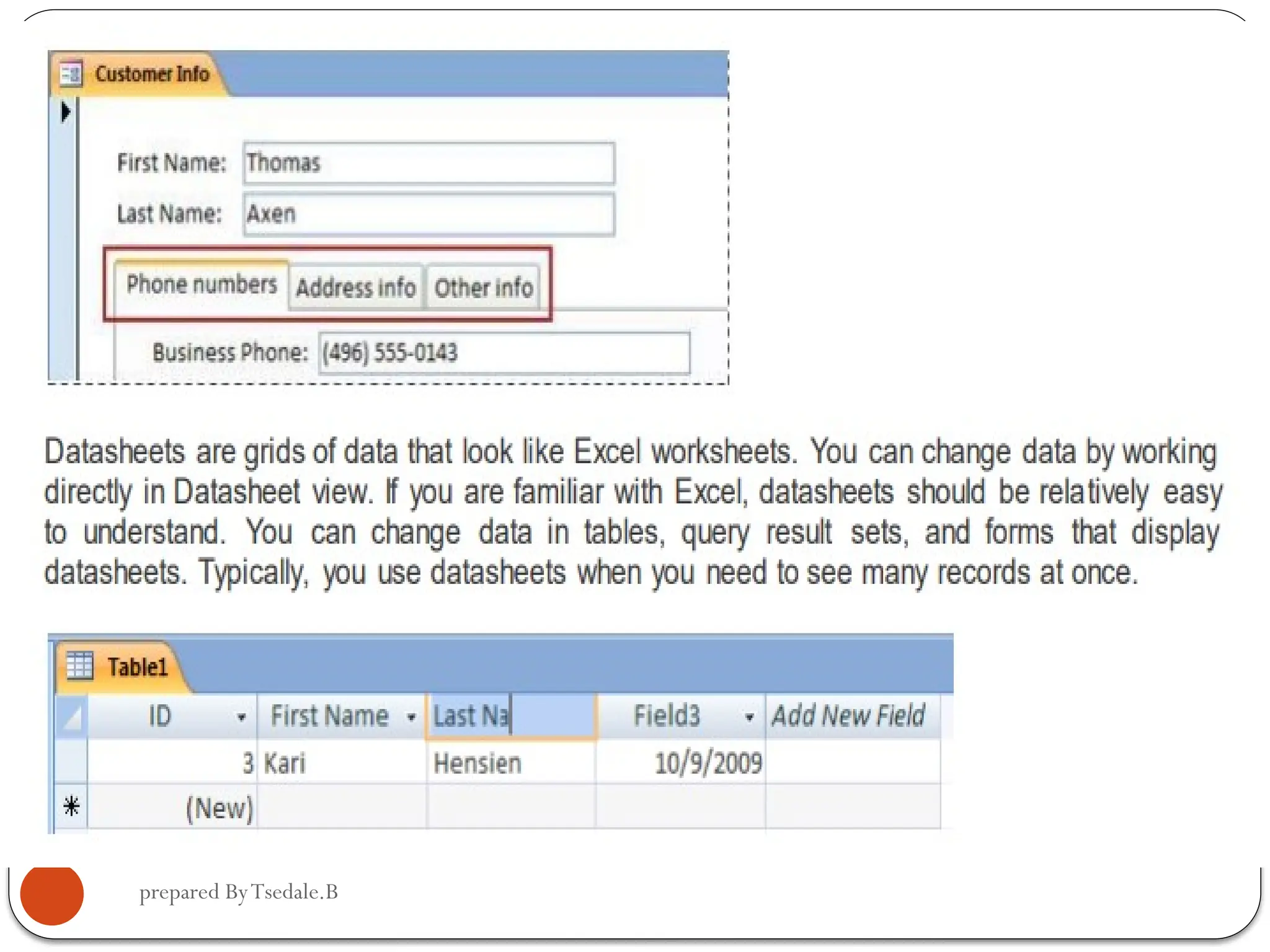
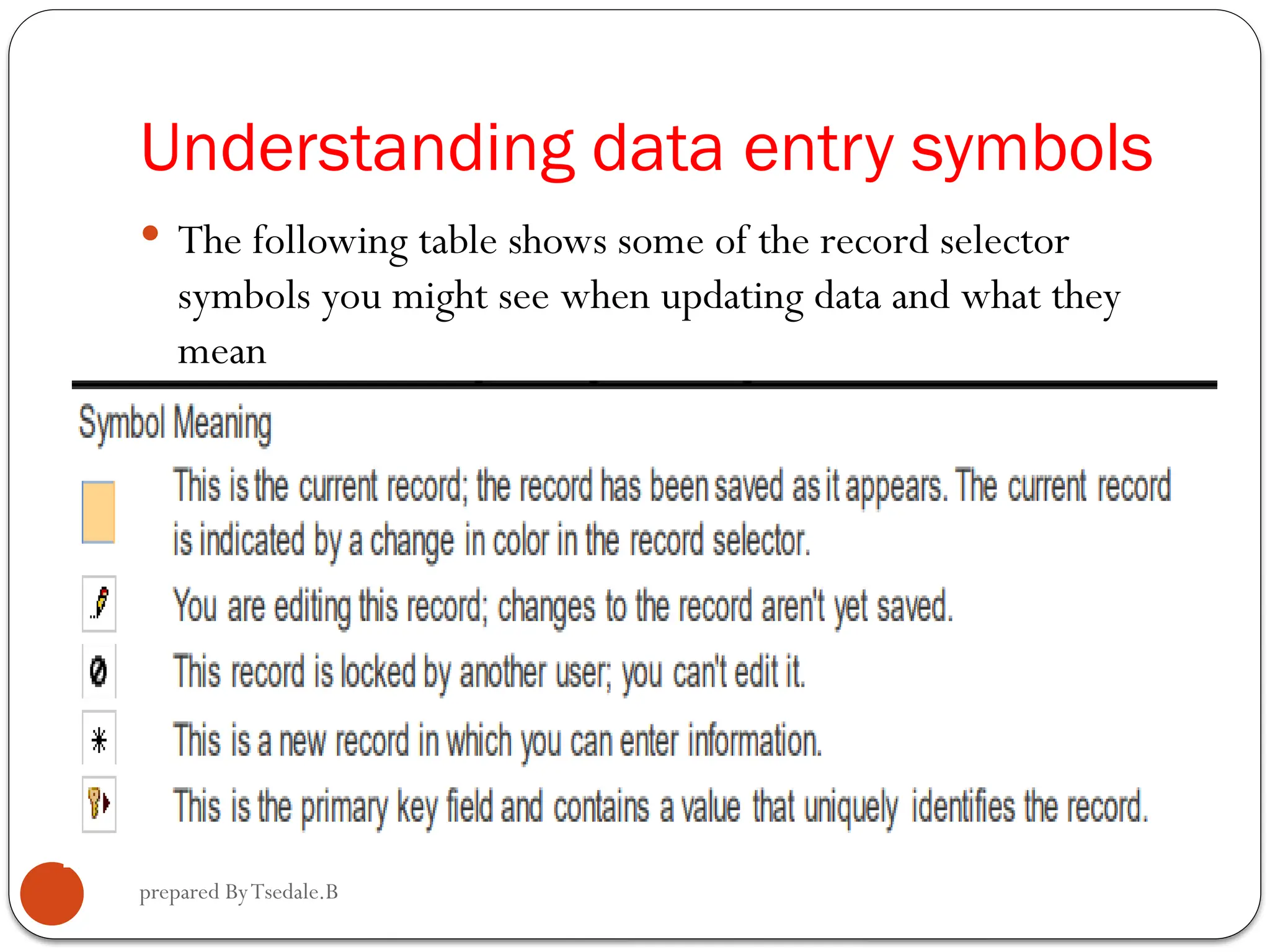
The document outlines a module for operating database applications, defining competencies and learning outcomes such as creating database objects, customizing settings, and generating reports. It discusses Microsoft Access as a database management tool, covering topics like data organization, database relationships, design principles, and the importance of data integrity and security. The guide also provides information on data types, naming conventions, and ways to add, edit, and delete records within a database.