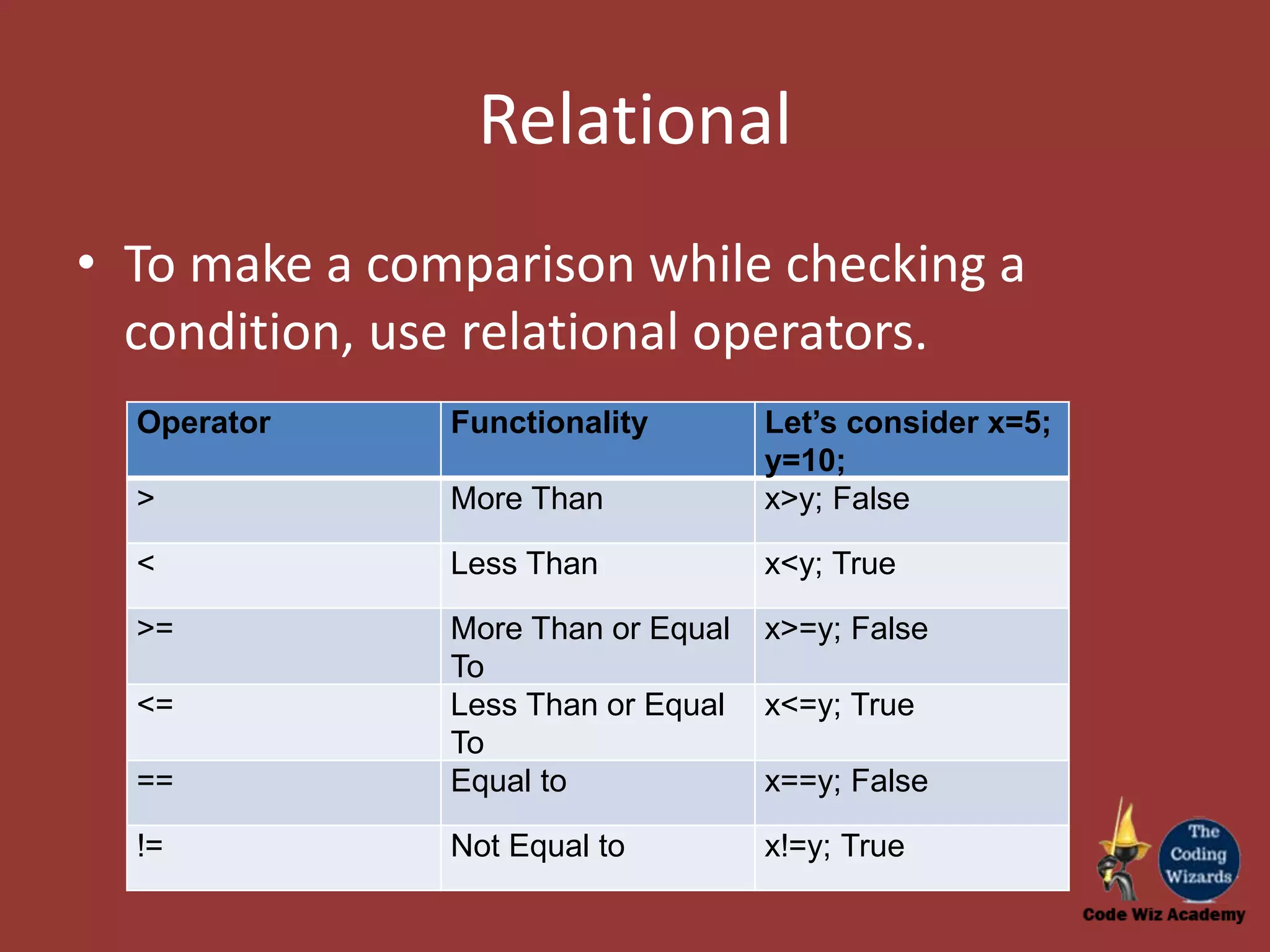
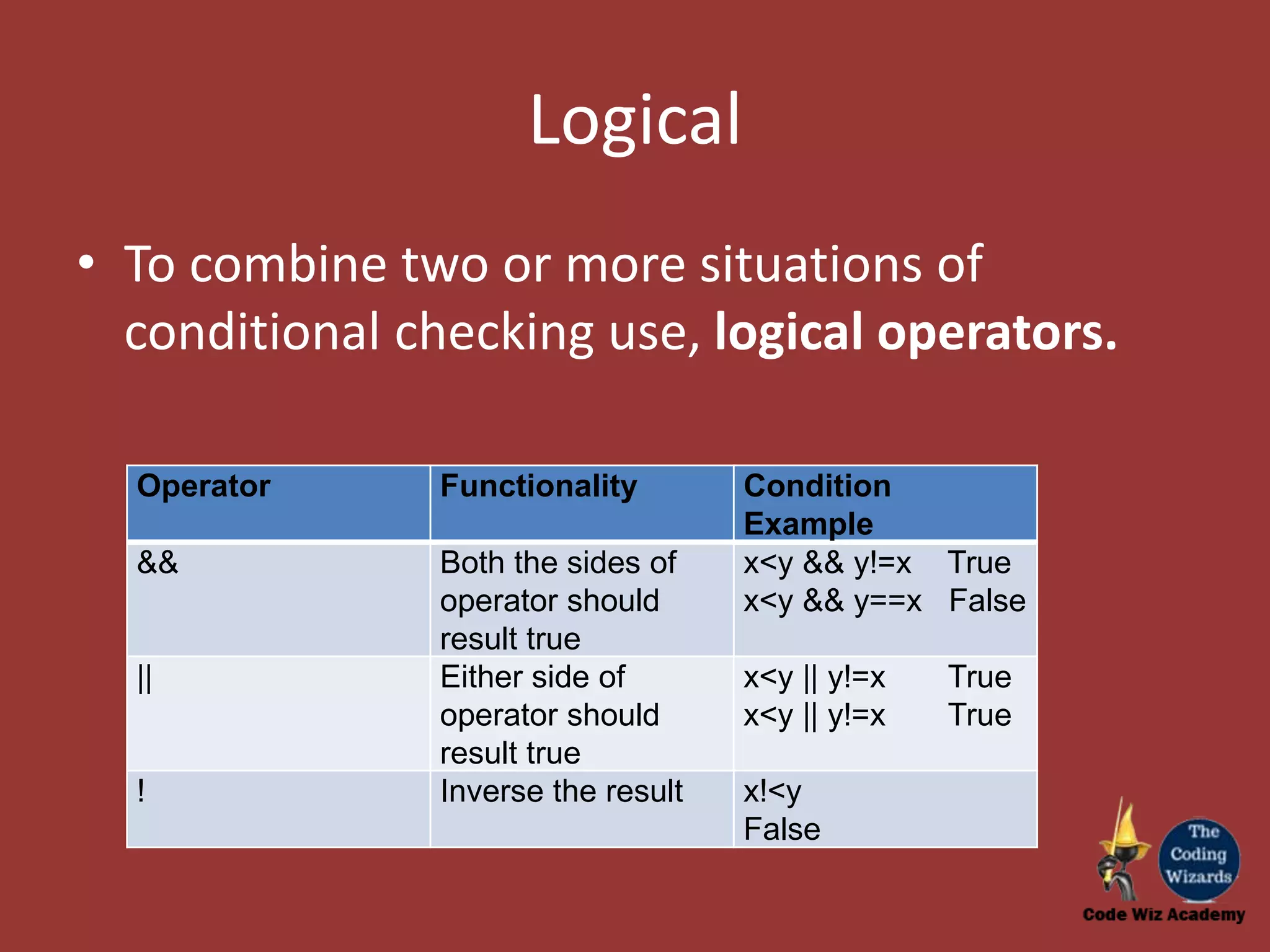
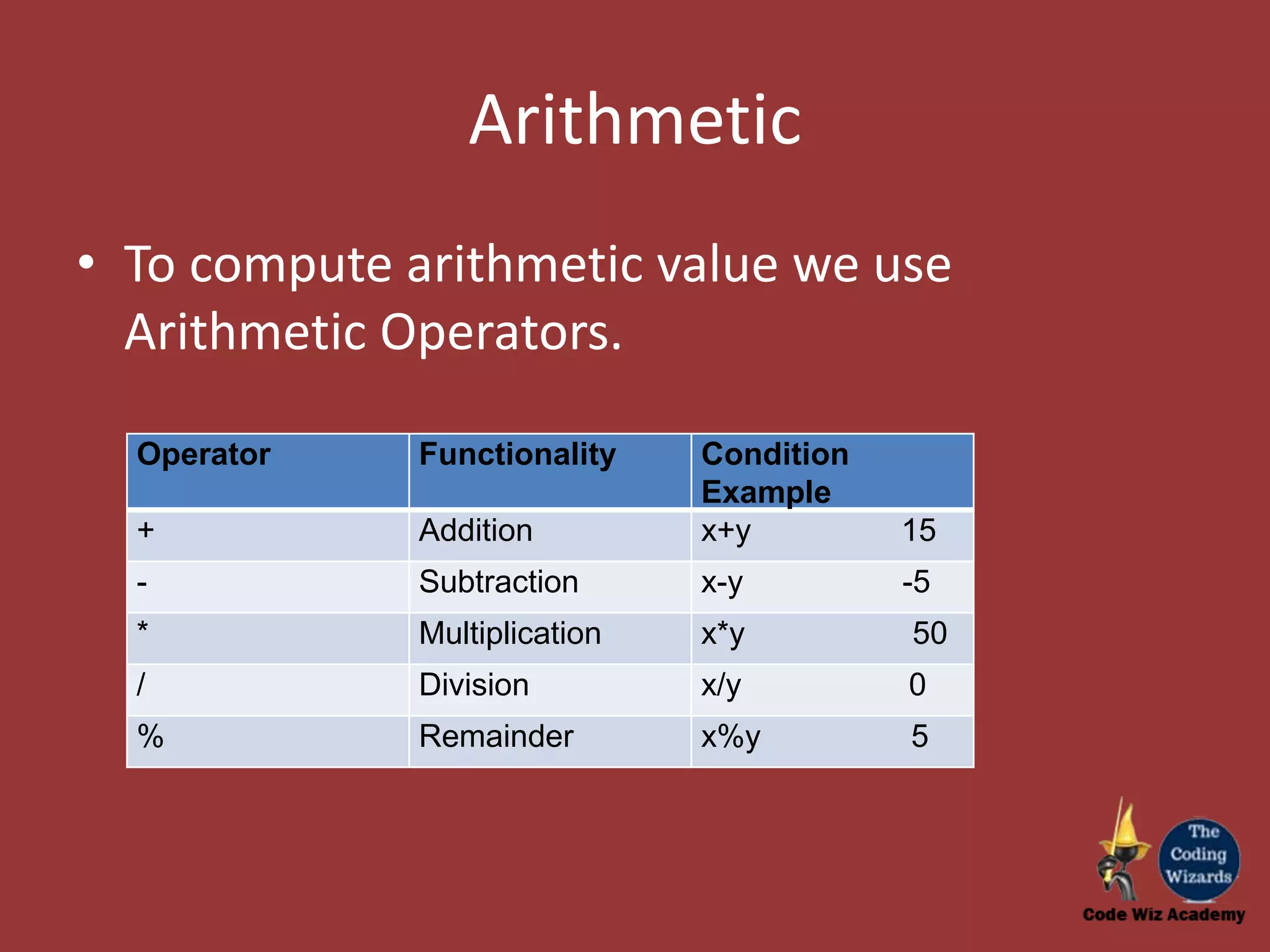
The document provides an overview of conditional constructs such as if, if-else, and if-elseif-else in programming, specifically using JavaScript. It explains the use of various operators including relational, logical, arithmetic, and unary operators to evaluate conditions and perform specific actions based on those evaluations. Additionally, it illustrates examples of coding constructs and their functionality for solving complex problems.