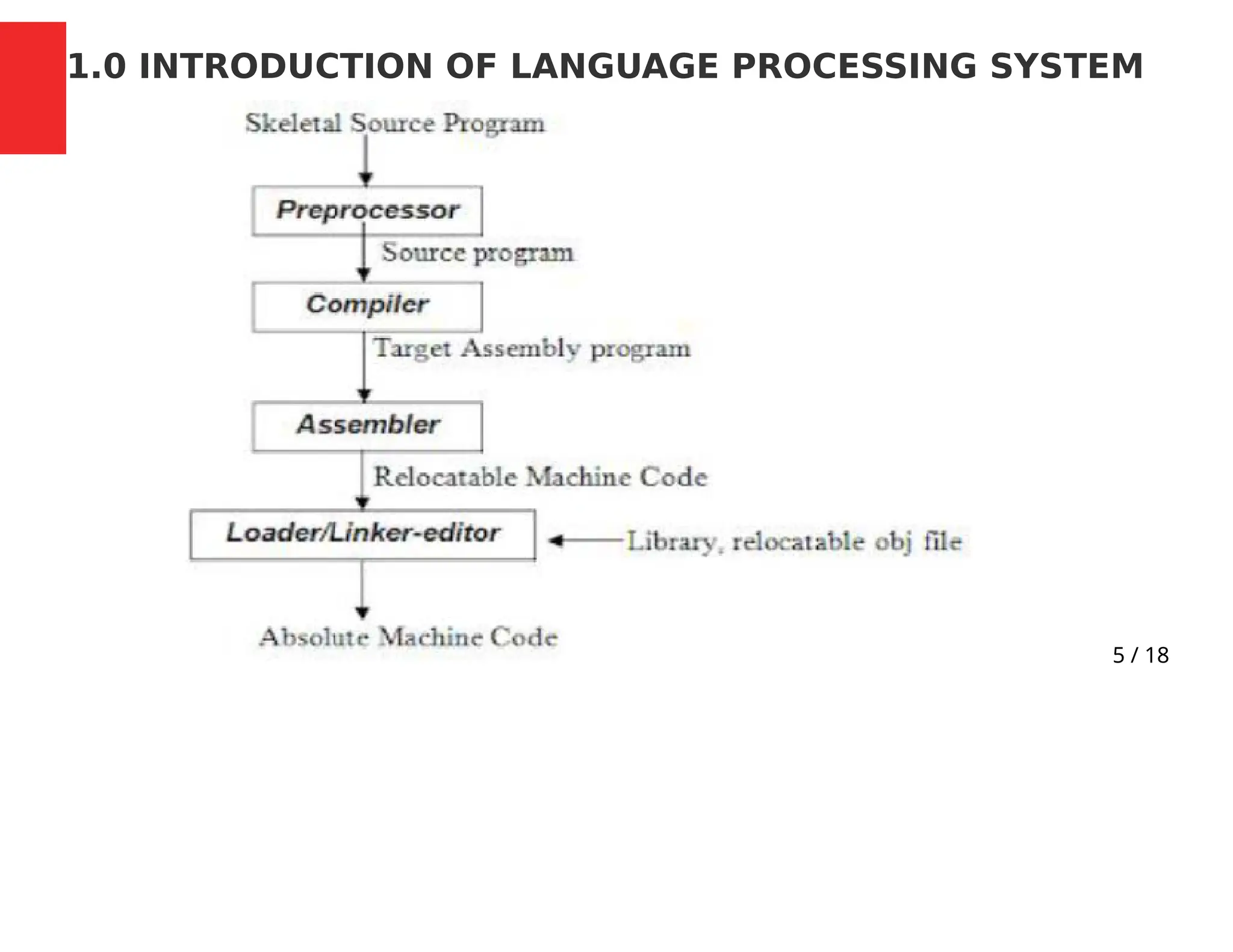
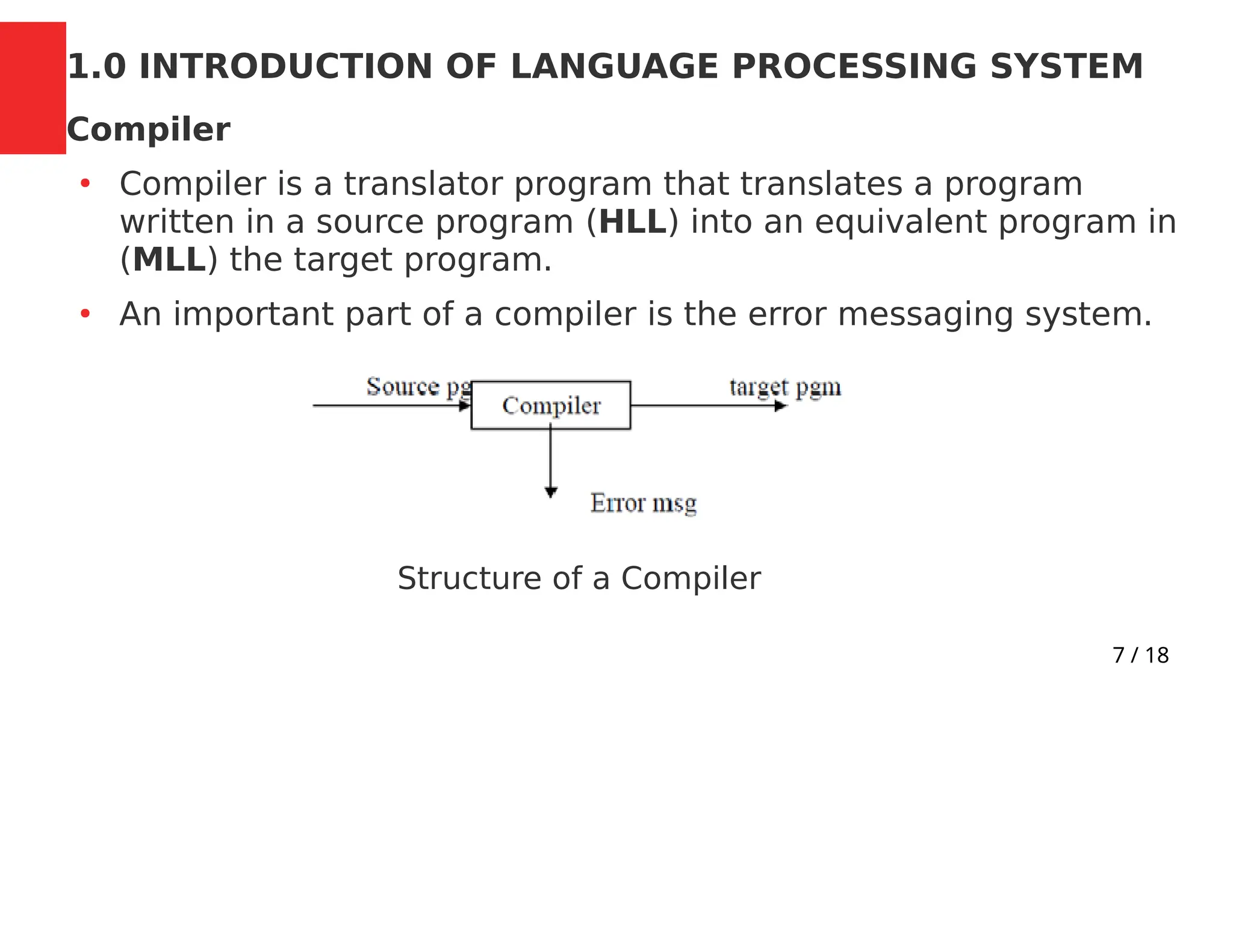
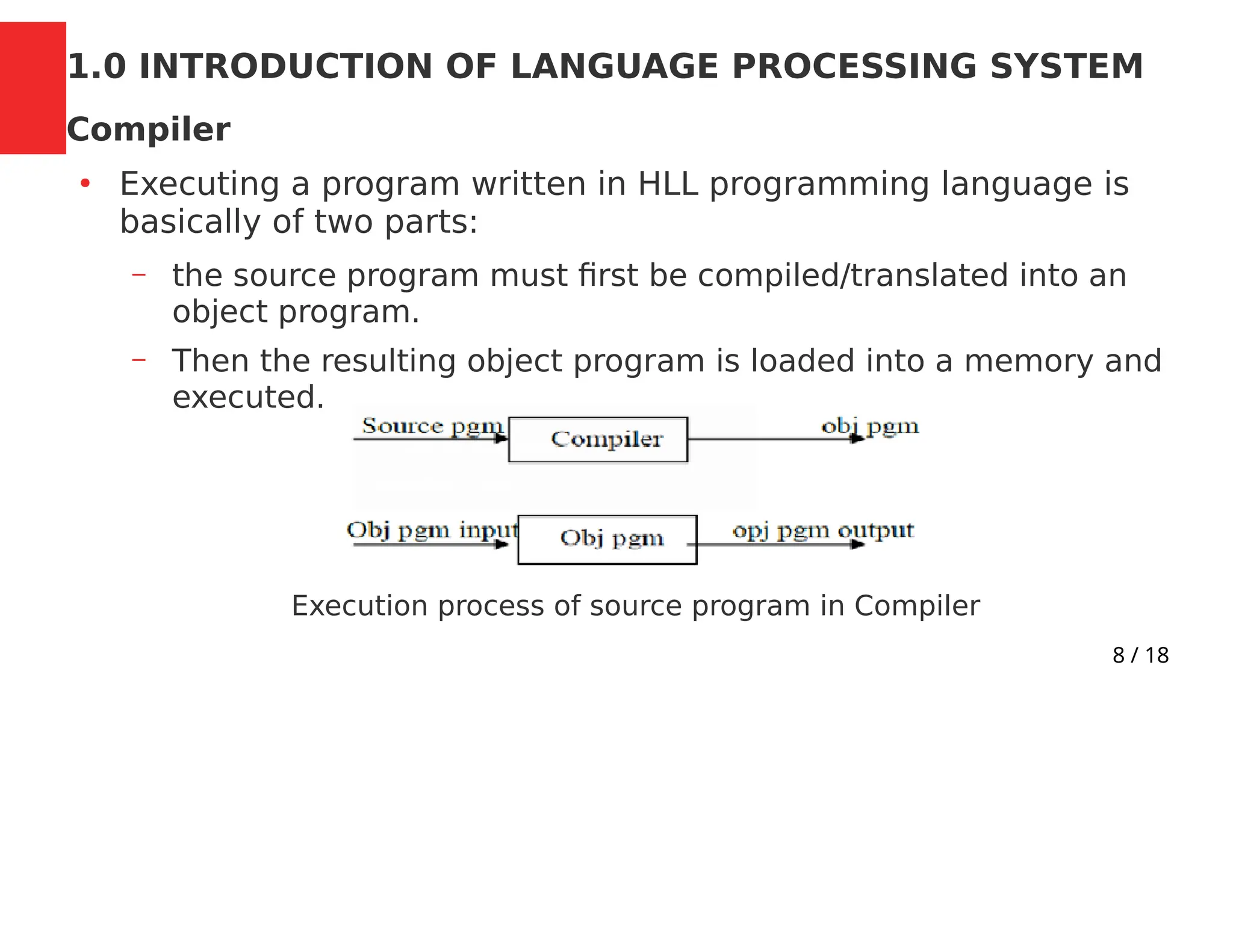
This document outlines the course CSC 401: Compiler Construction for the 2023/2024 academic year. It discusses the mode of assessment, which includes assignments, quizzes, exams, attendance, and main exams. Reading materials from three textbooks on compiler design are also listed. The course is divided into four modules that cover topics such as lexical analysis, syntax analysis, type checking, code generation, and optimization. The document provides an introduction to language processing systems such as preprocessors, compilers, assemblers, and interpreters.