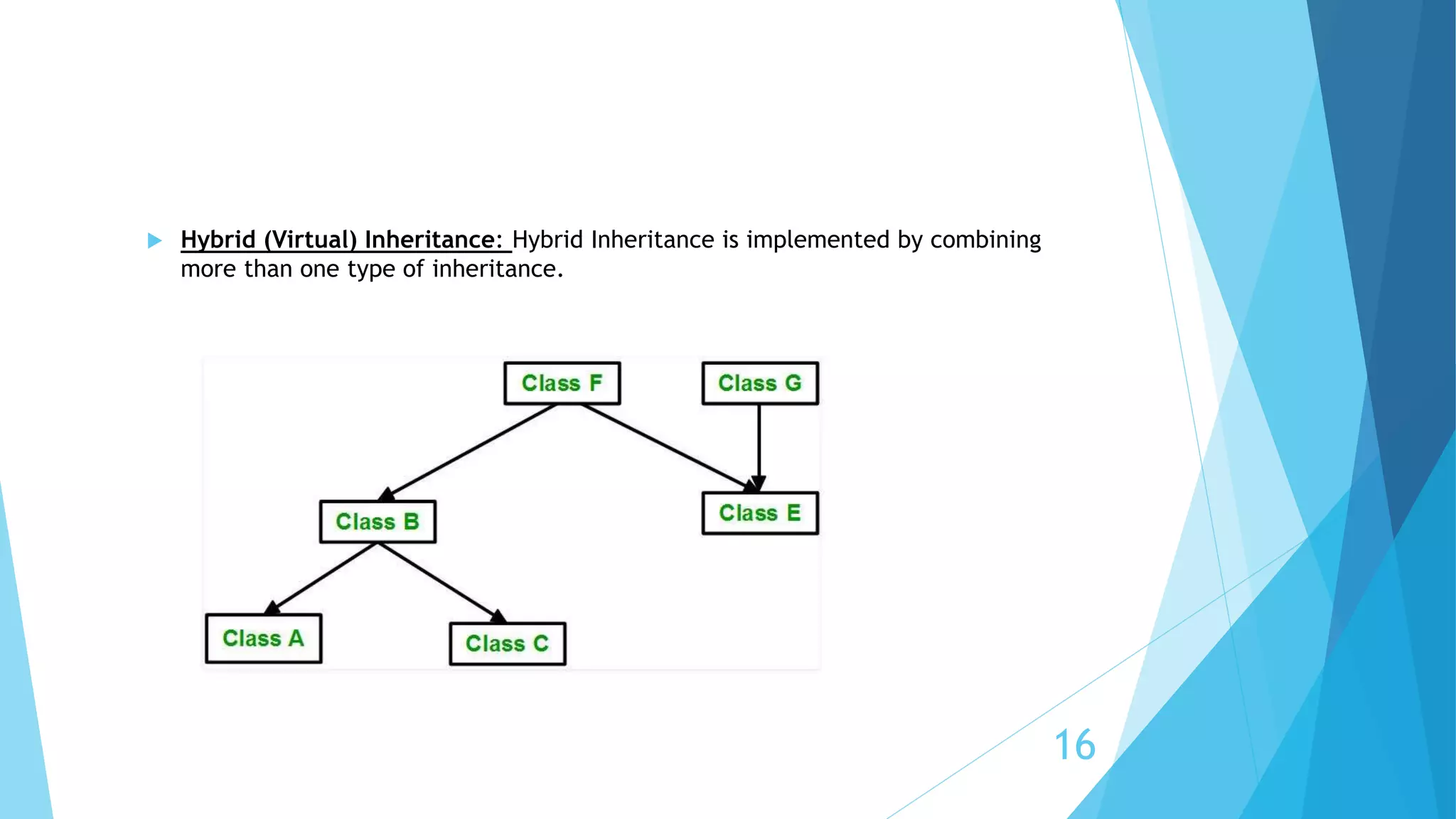
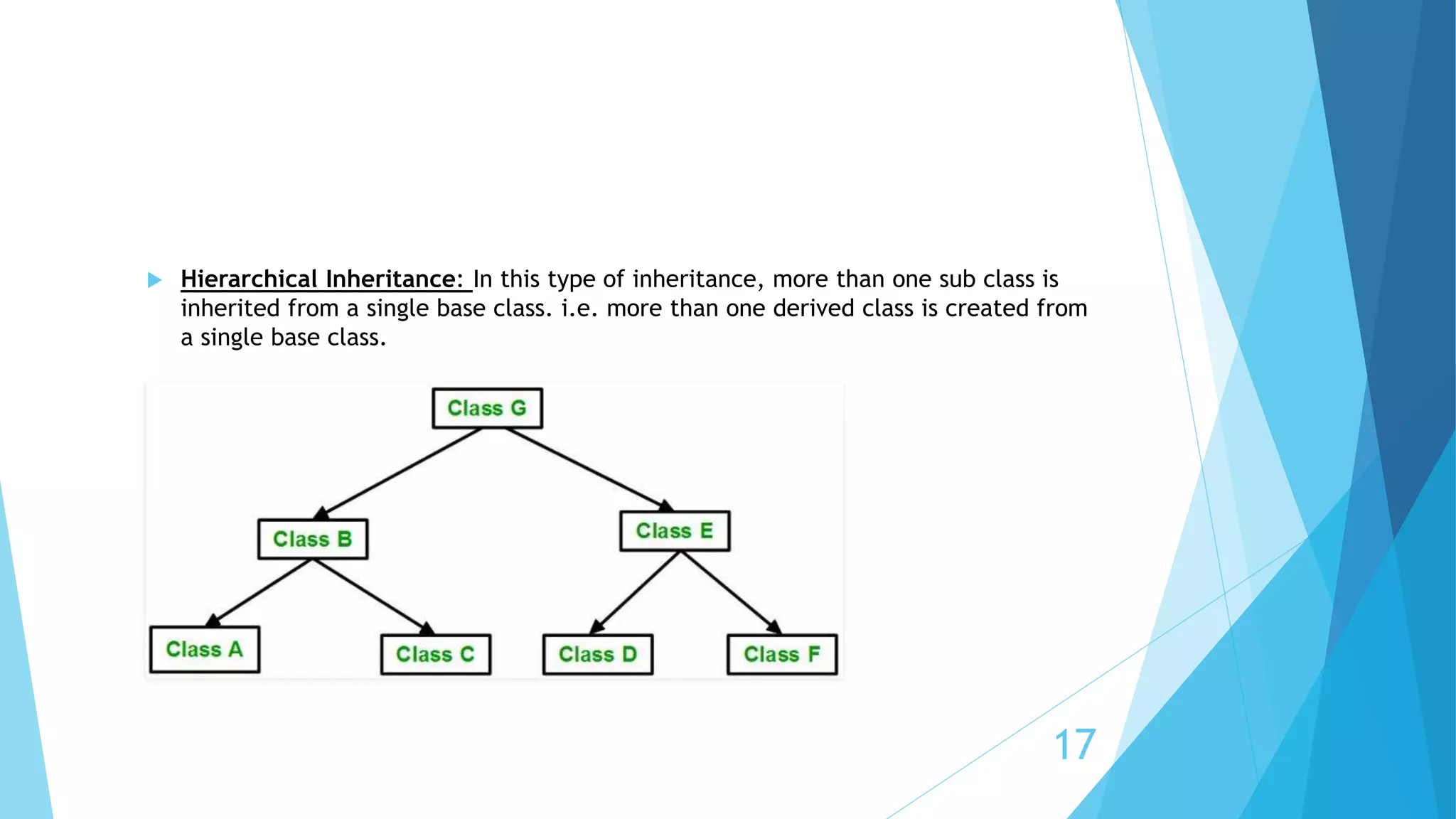
The document covers key concepts in C++ including structures, arrays of structures, file input/output, and object-oriented programming (OOP) principles. It explains various concepts of OOP such as classes, objects, data abstraction, encapsulation, constructors, destructors, and different types of inheritance. Additionally, it highlights methods for sequential and random access in file handling.

![Array of structure Structure is collection of different data type. An object of structure represents a single record in memory, if we want more than one record of structure type, we have to create an array of structure or object. struct struct-name { datatype var1; datatype var2; - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - datatype varN; }; struct-name obj [ size ]; 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structures-191004144327/75/Computer-programming-C-Structures-3-2048.jpg)