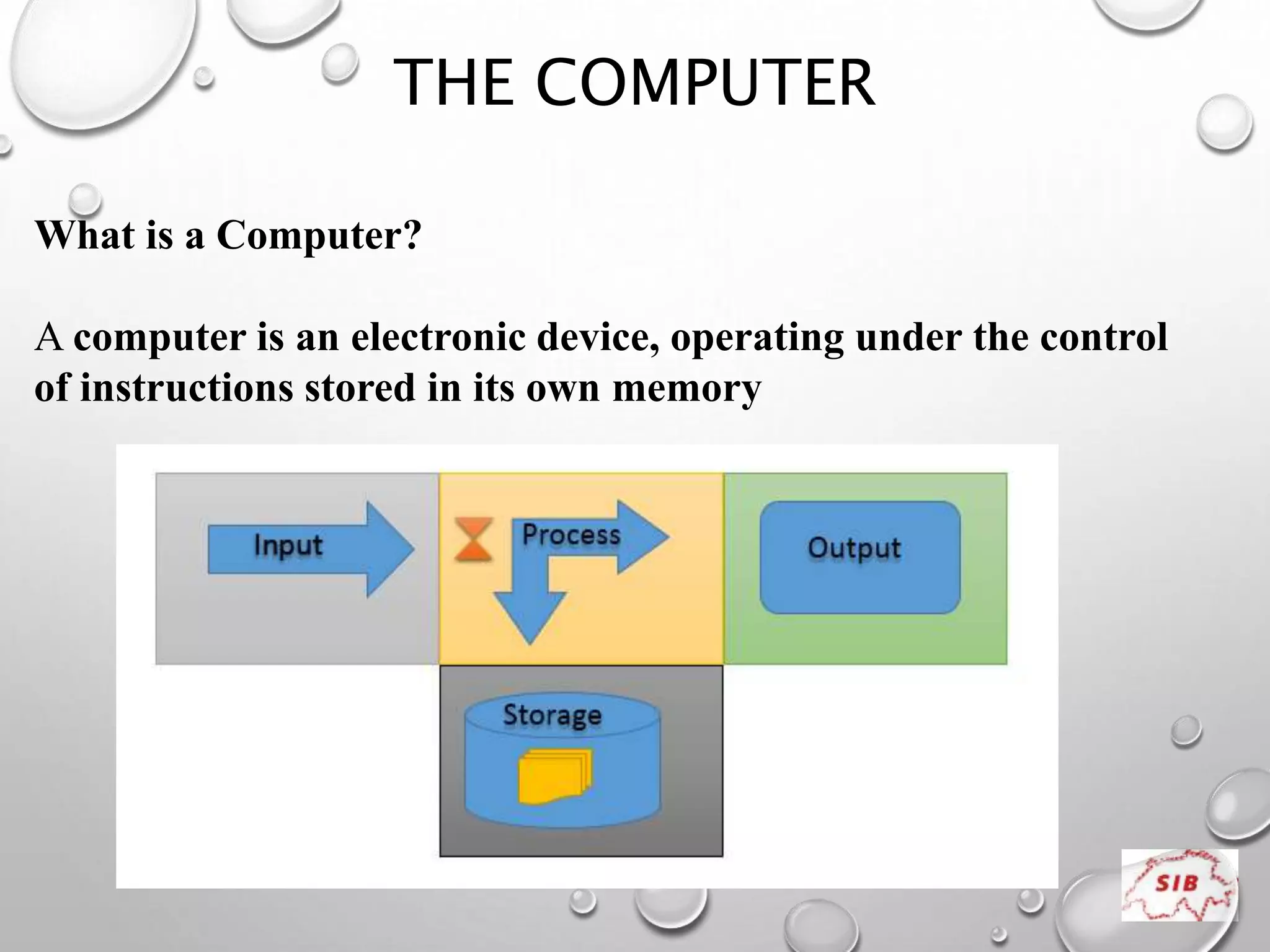
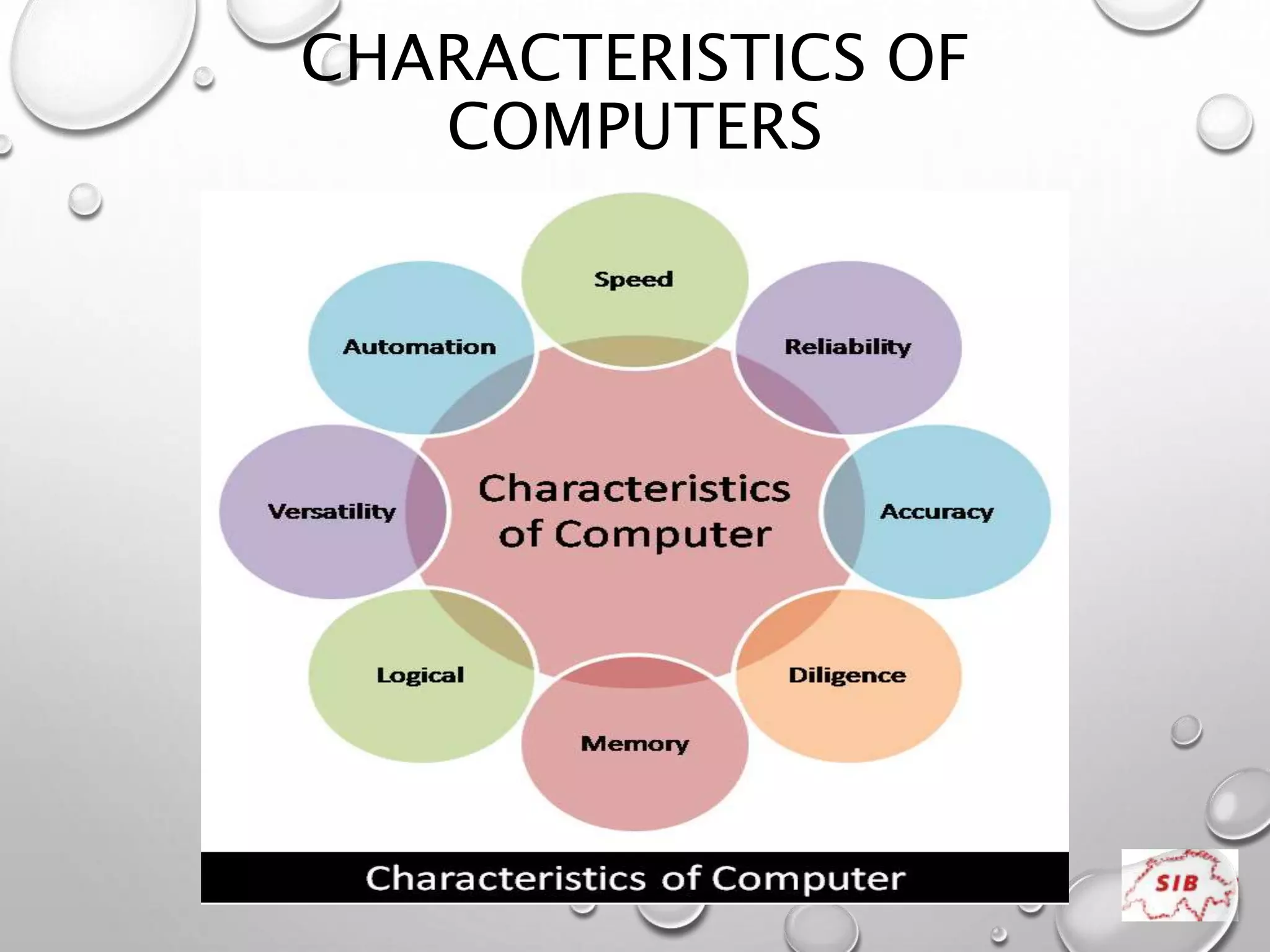
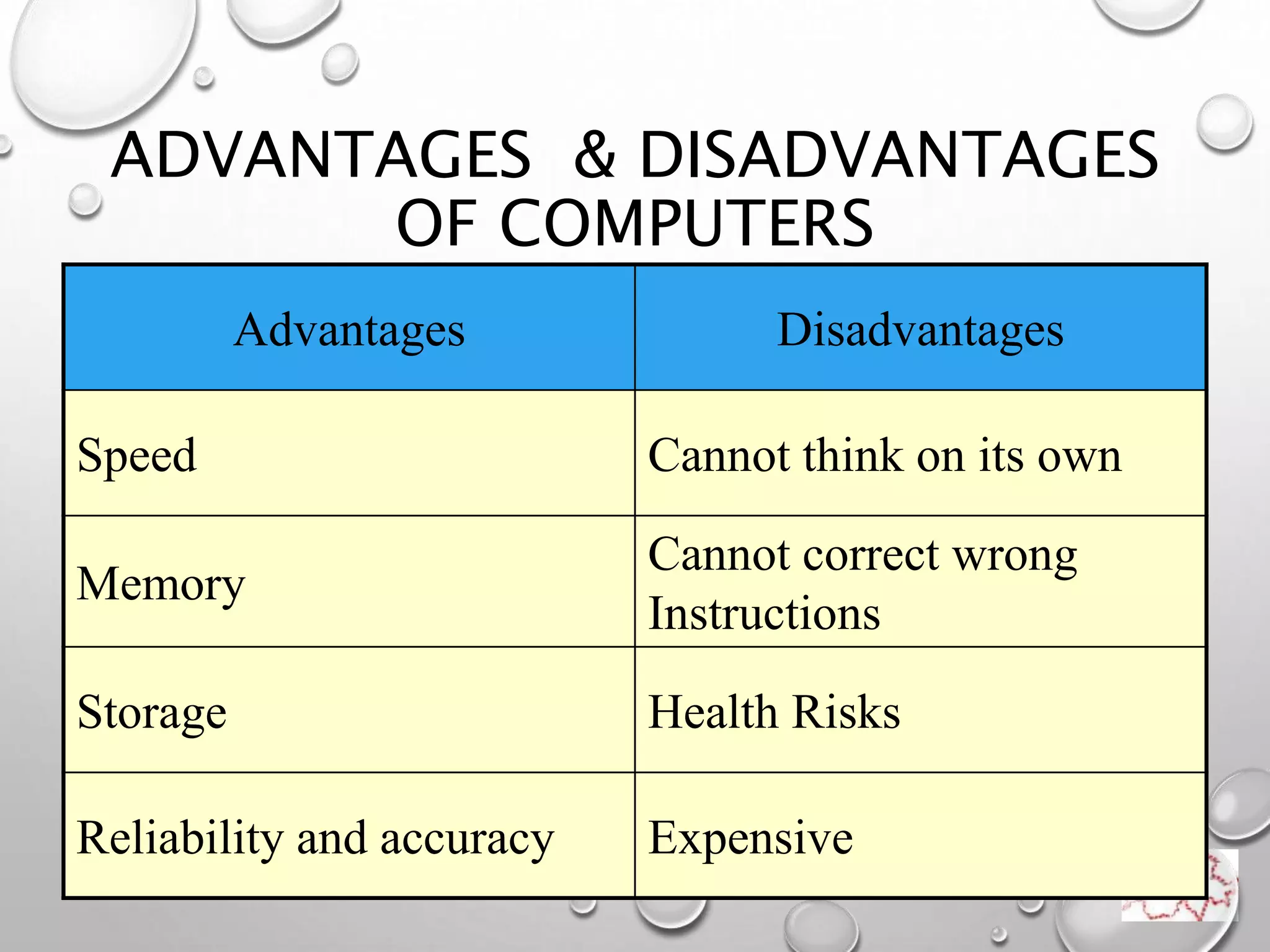
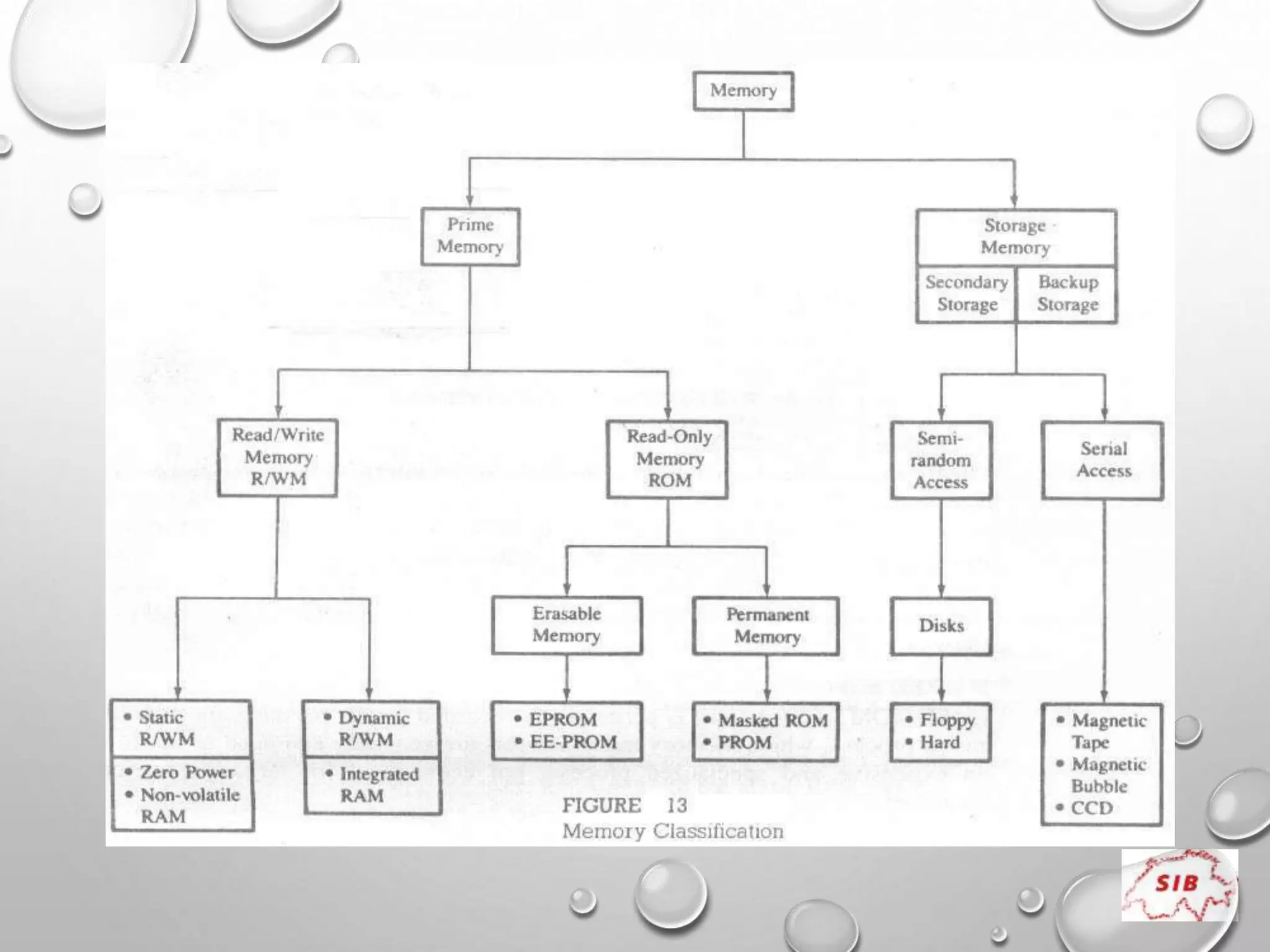
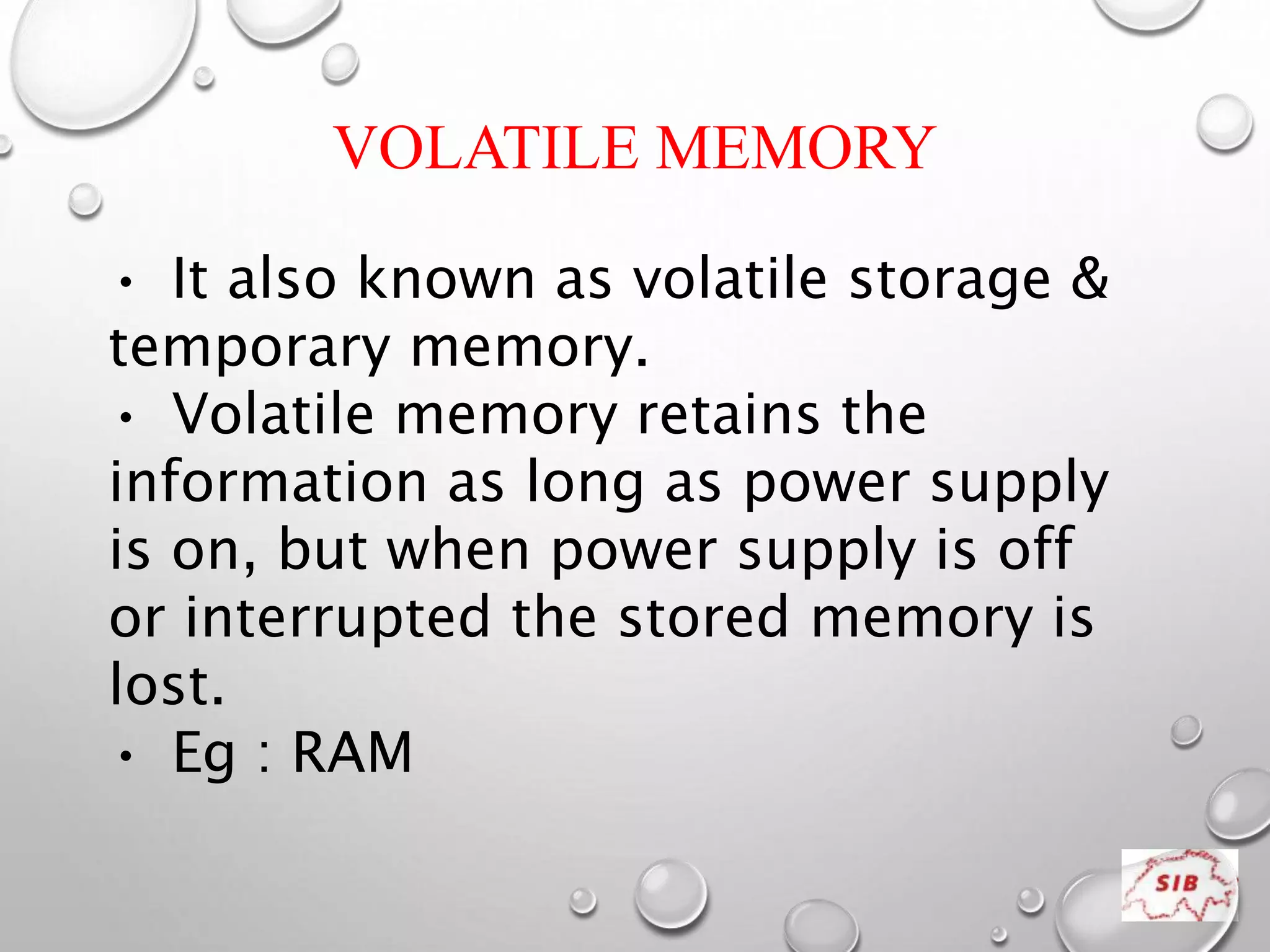
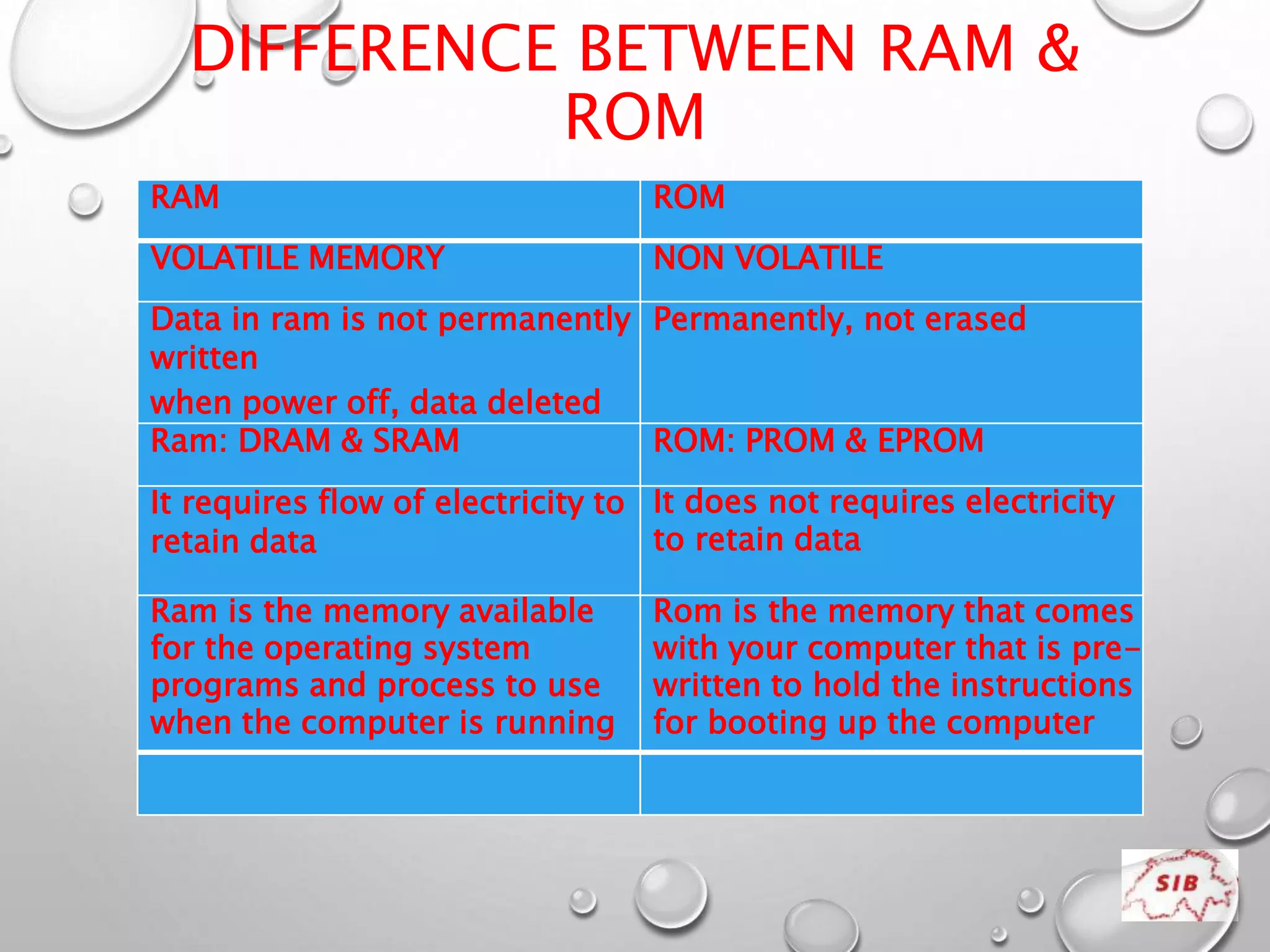
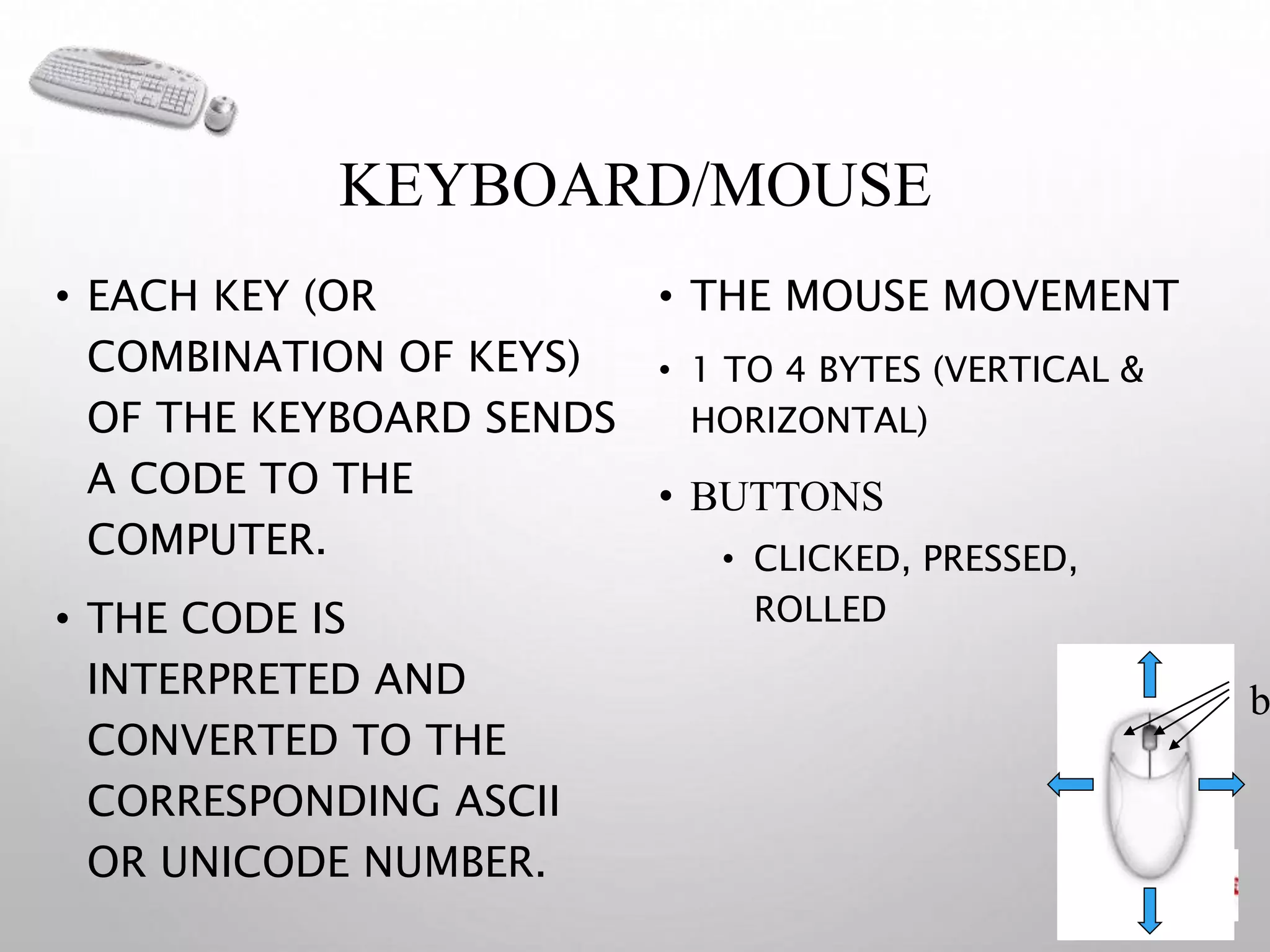
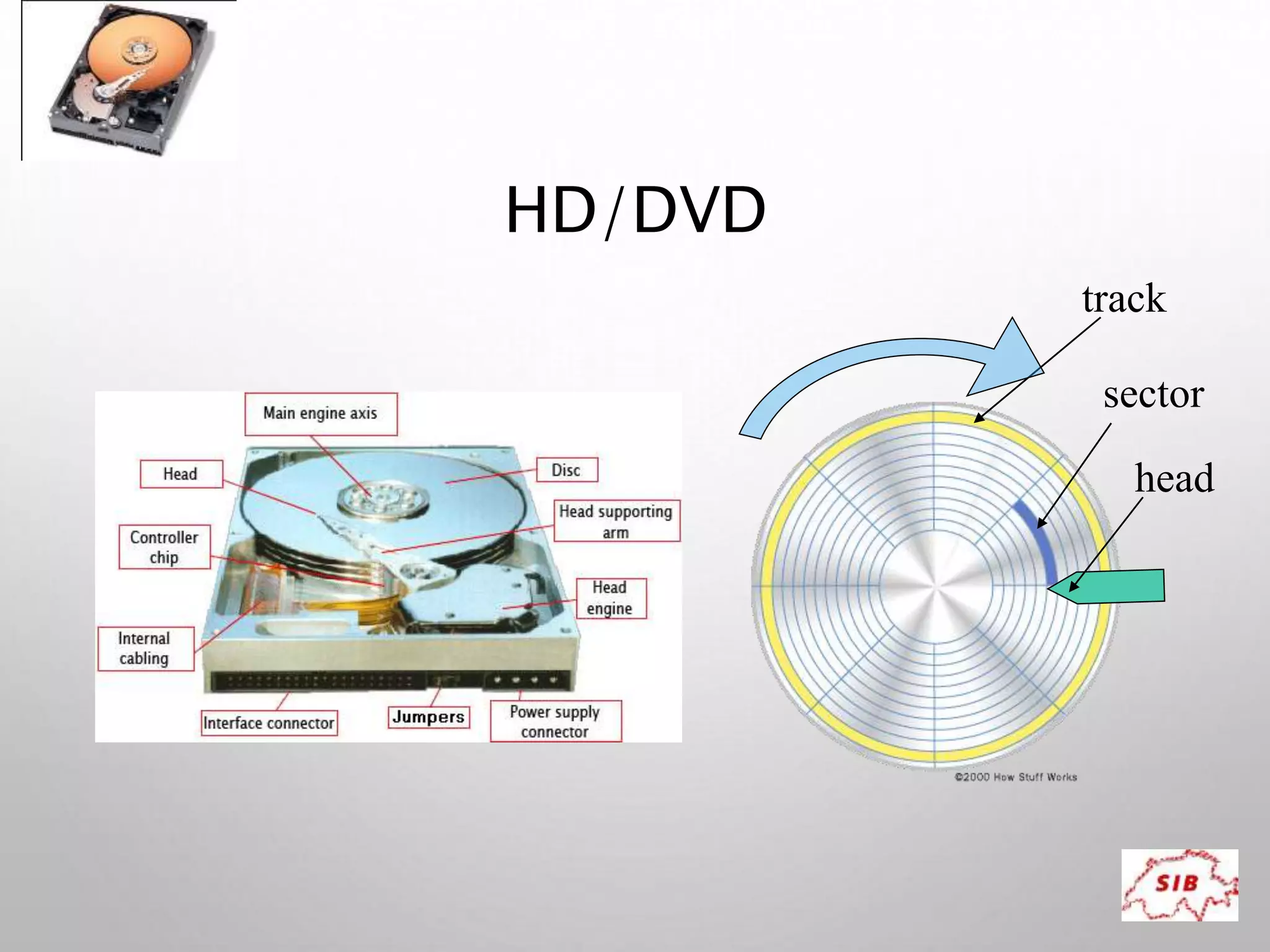
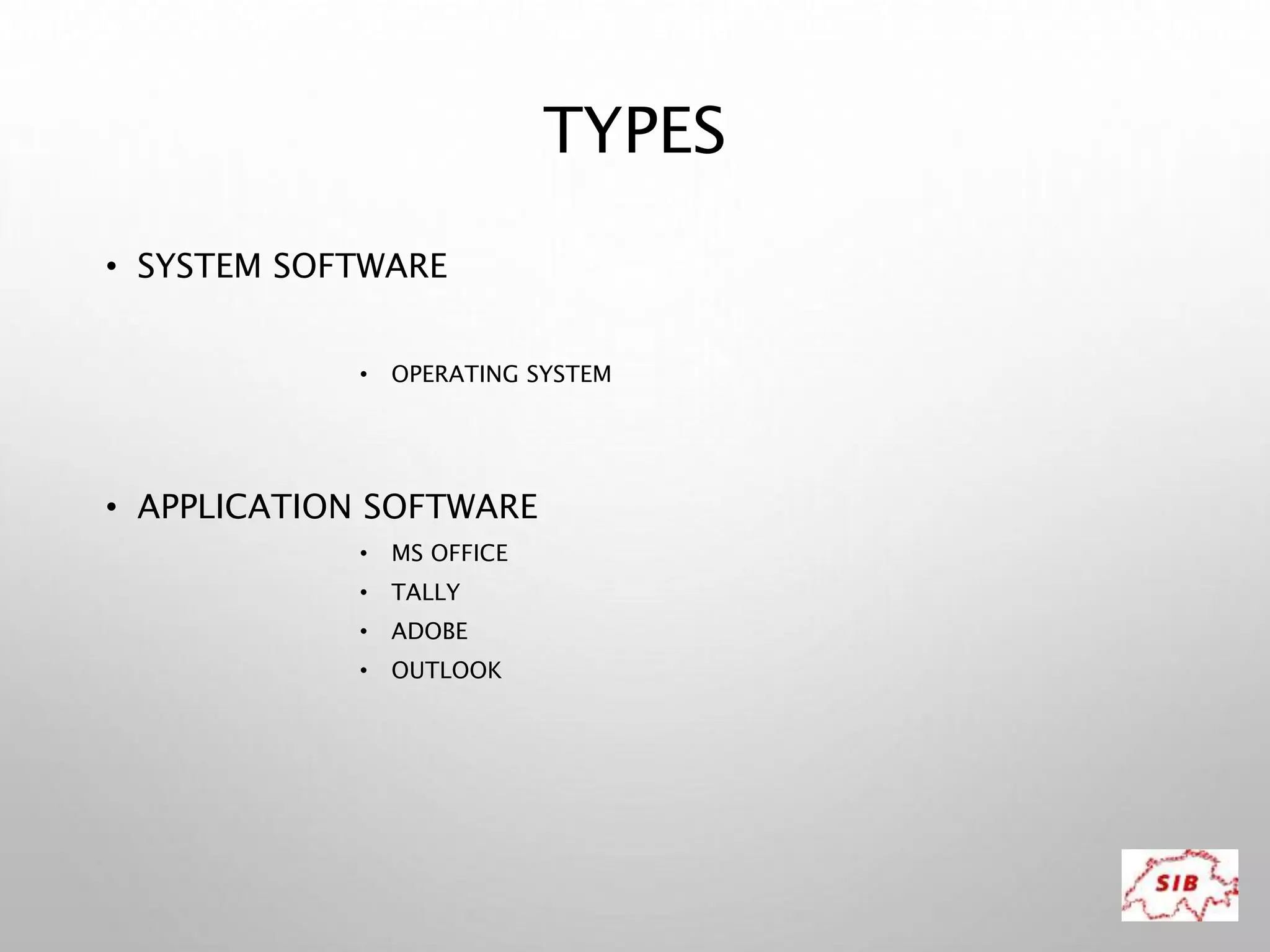
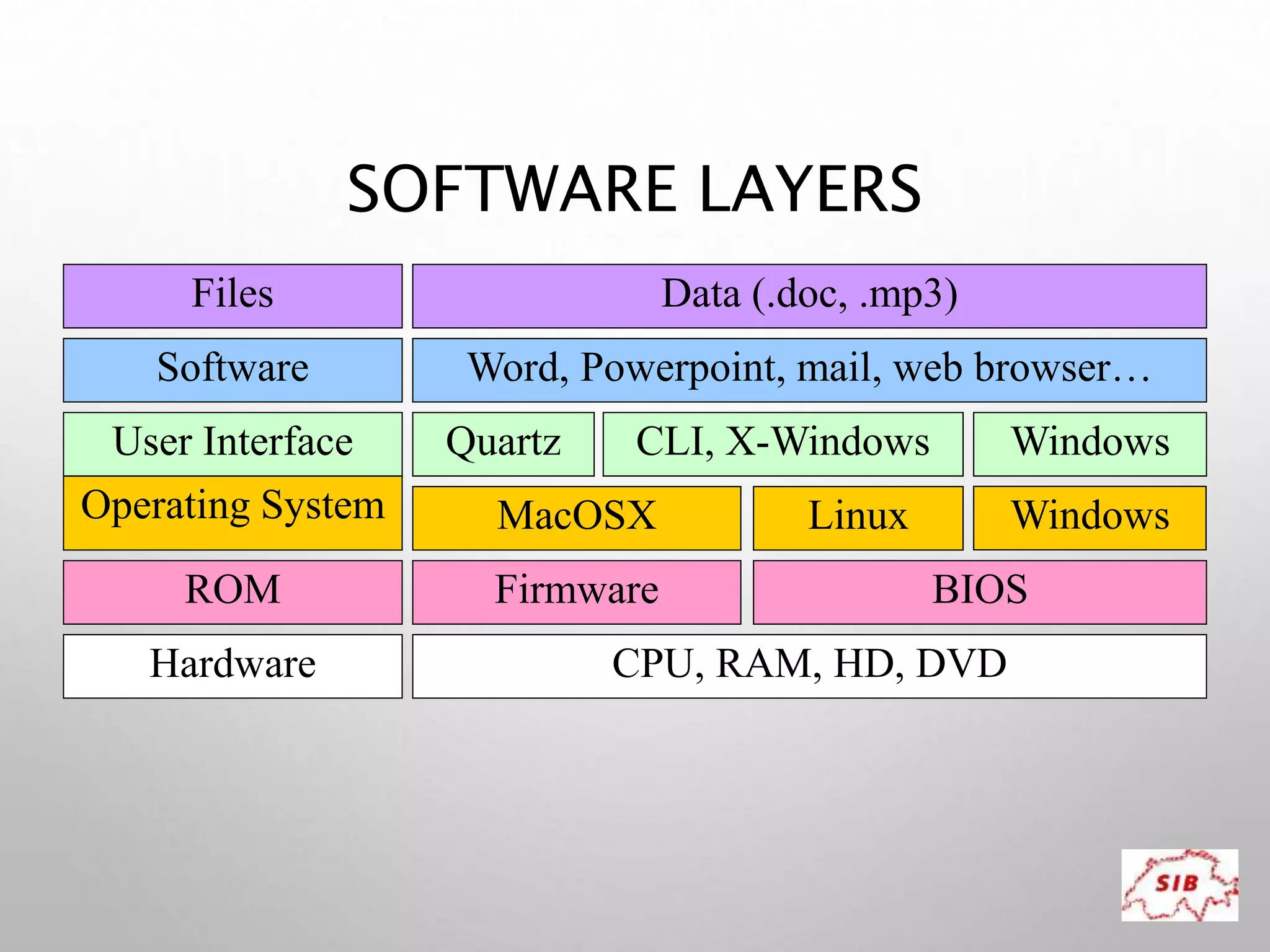
A computer is an electronic device that operates under instructions stored in its memory to perform tasks. It has advantages like speed, memory, and storage but also disadvantages such as inability to think independently and potential health risks. There are different types of computers ranging from personal computers for individuals to supercomputers that process extremely large amounts of data. A computer consists of both hardware and software - hardware refers to the physical components while software refers to programs and applications. Key hardware components include the CPU, memory, storage devices, input devices like keyboards and mice, and output devices like monitors and printers. Software includes operating systems and applications.