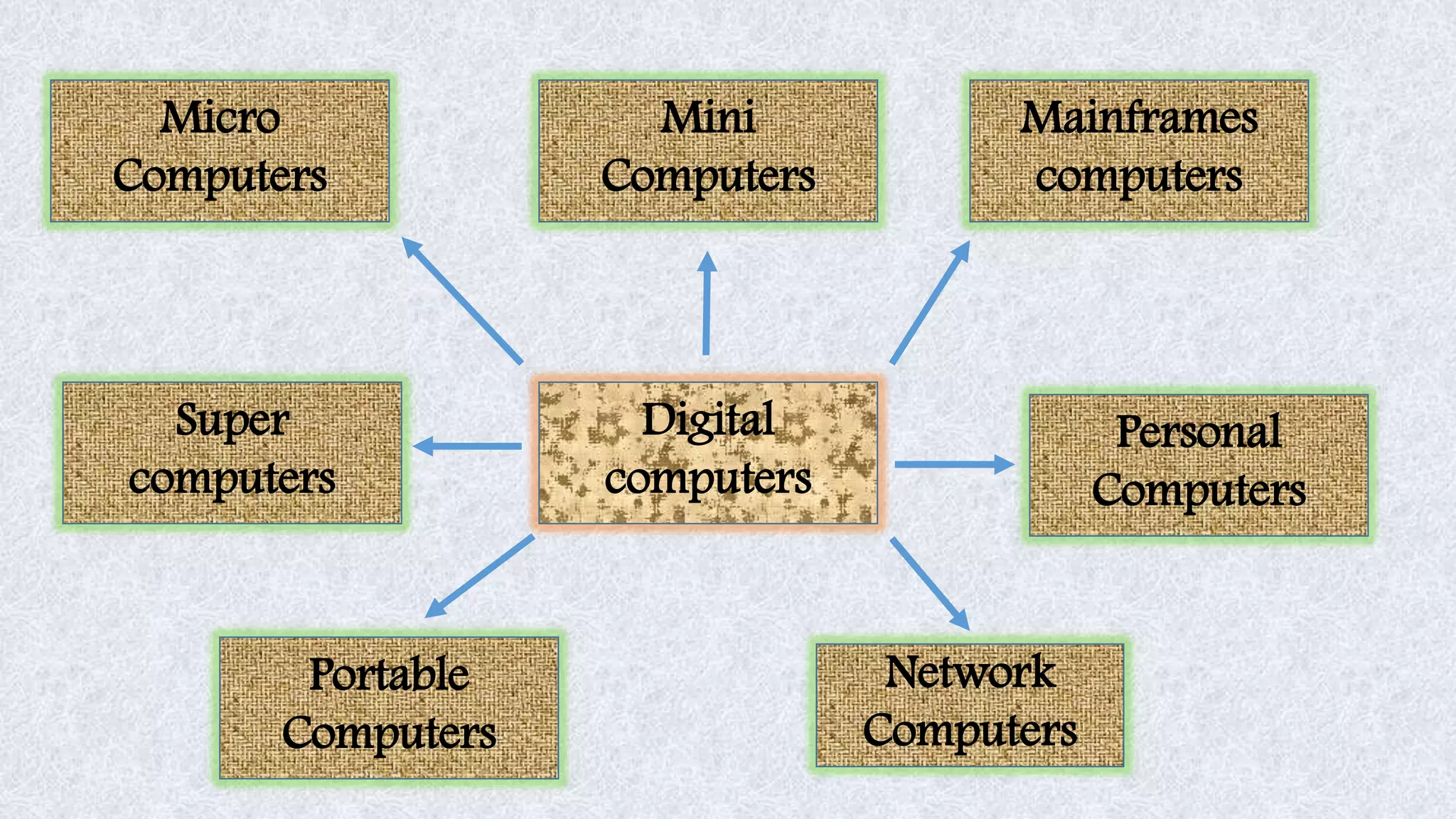
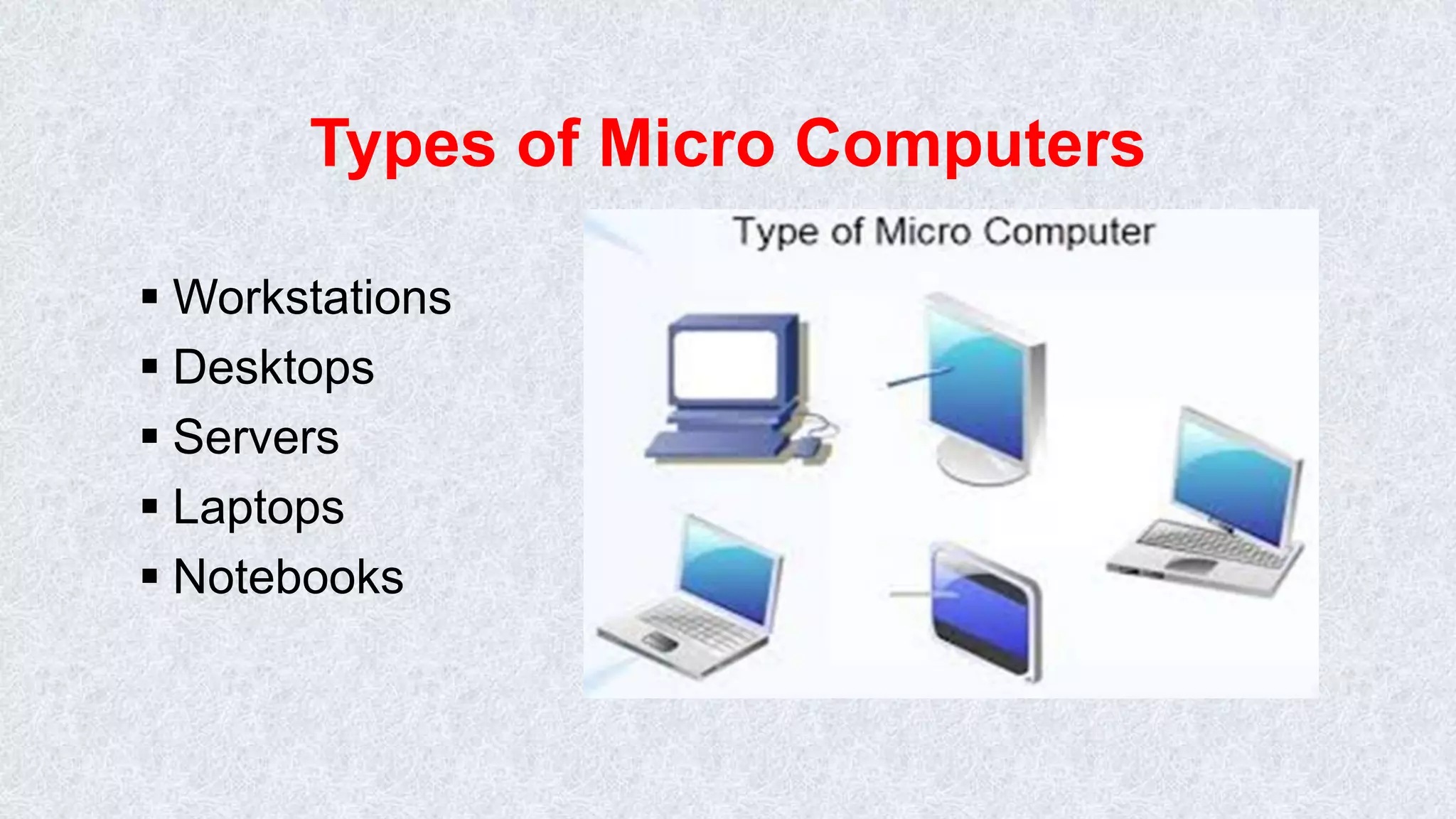
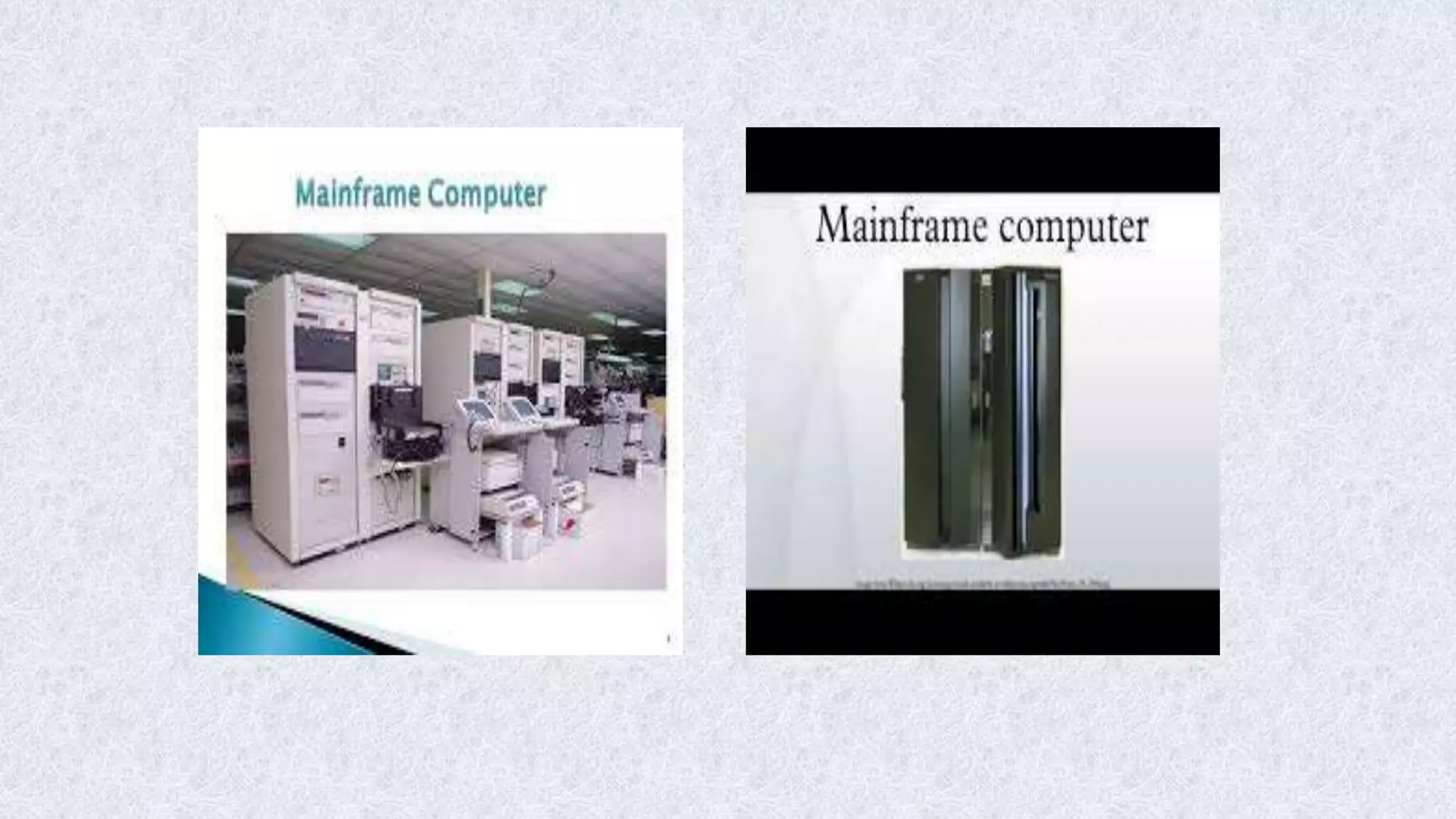
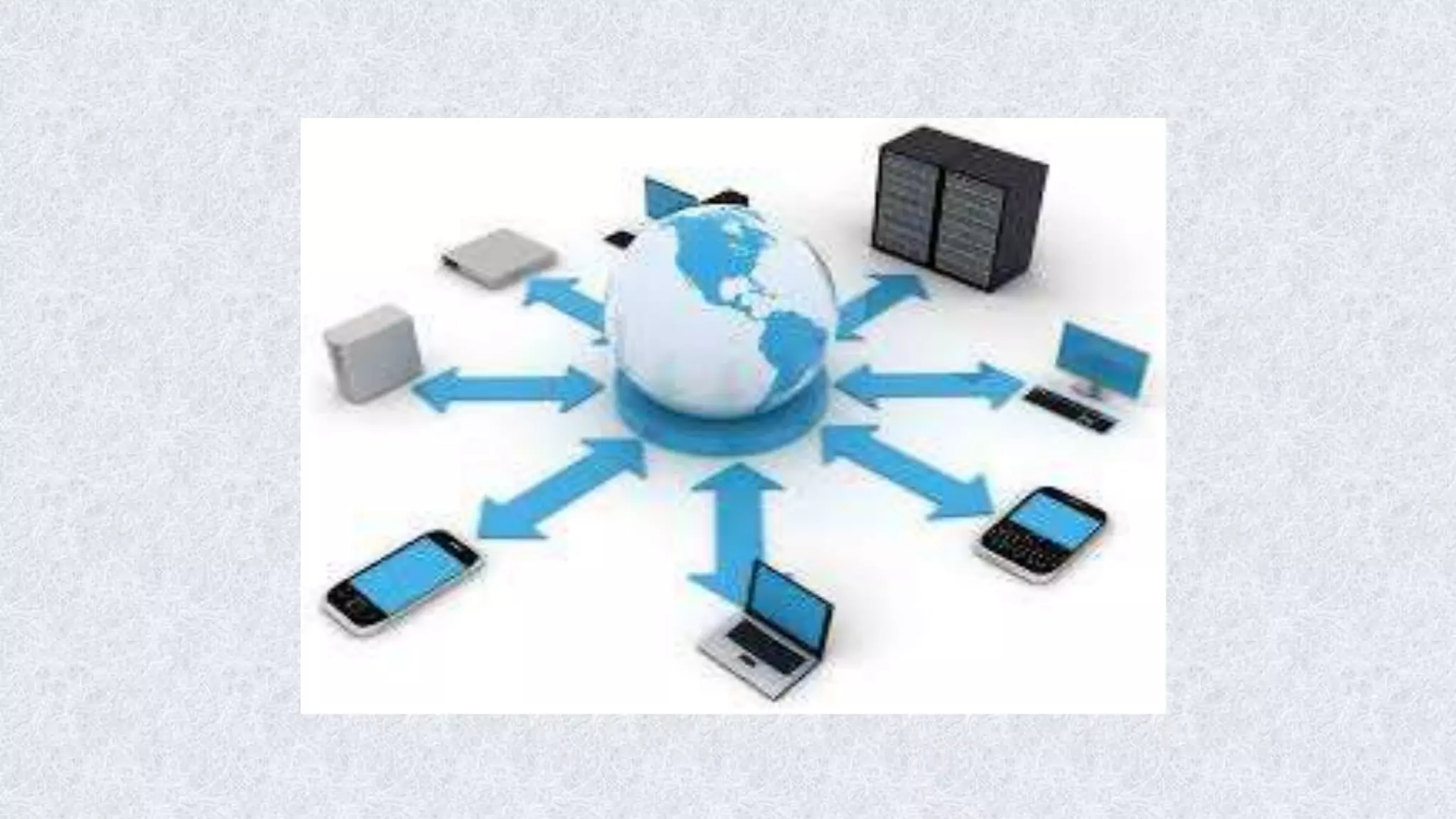
This document classifies different types of digital computers. It discusses microcomputers like PCs, laptops, and PDAs. It also covers mini computers, mainframe computers, network computers, and supercomputers. Microcomputers are the most commonly used personal computers for individual work. Mini computers are mid-sized and used in organizations. Mainframe computers are the largest and process huge amounts of data for banks and other large businesses. Supercomputers provide extremely fast processing for specialized applications like weather forecasting.