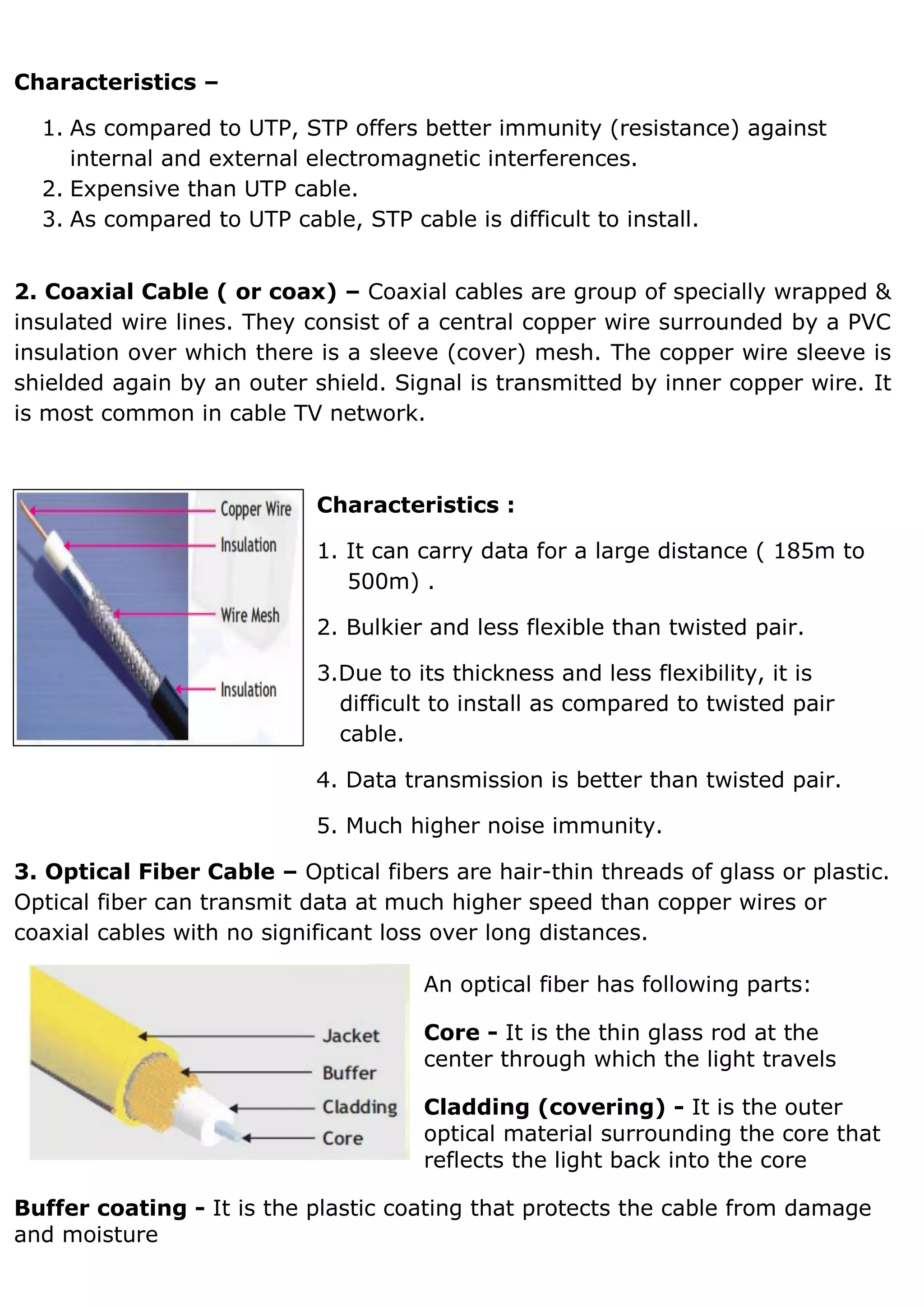
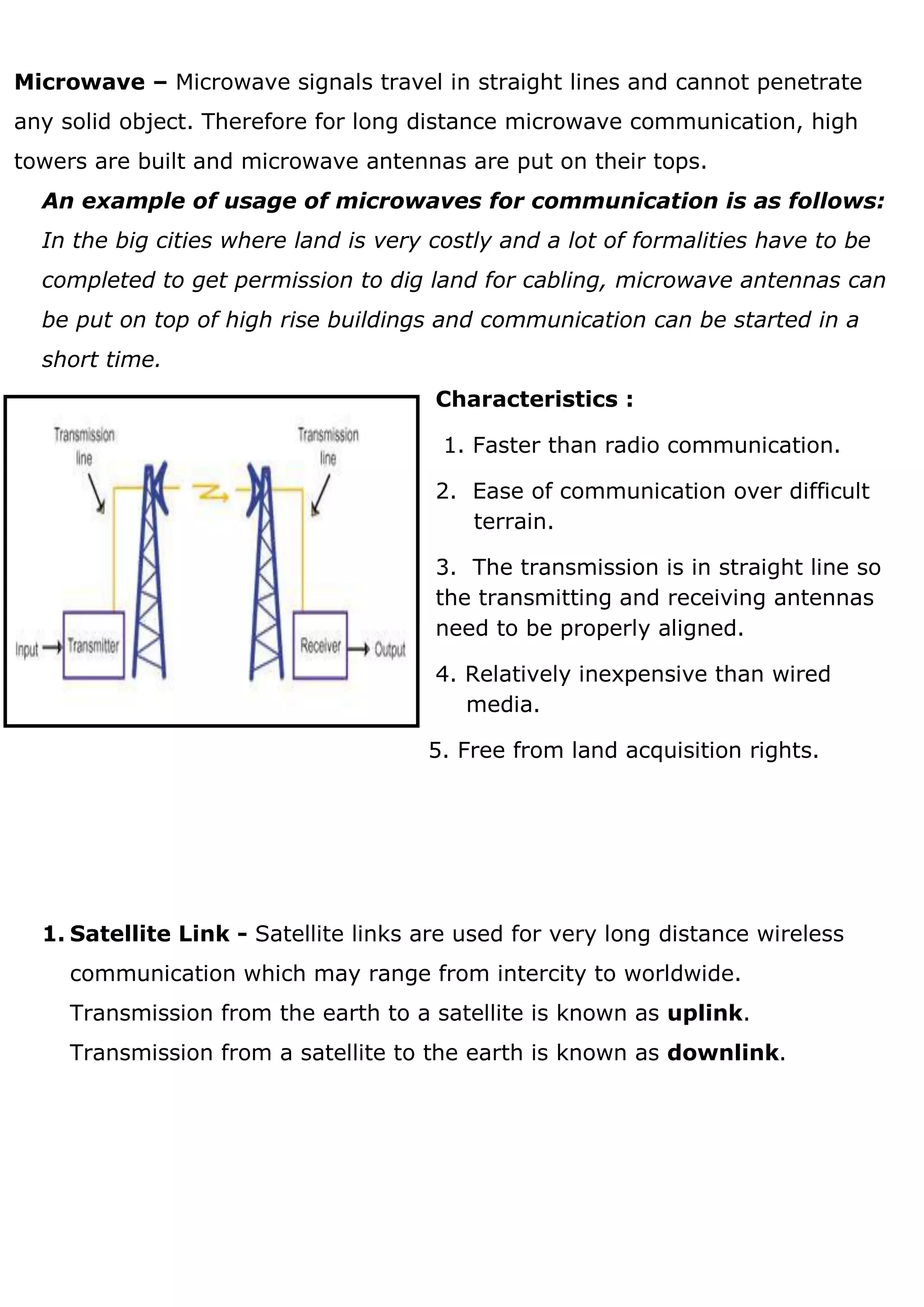
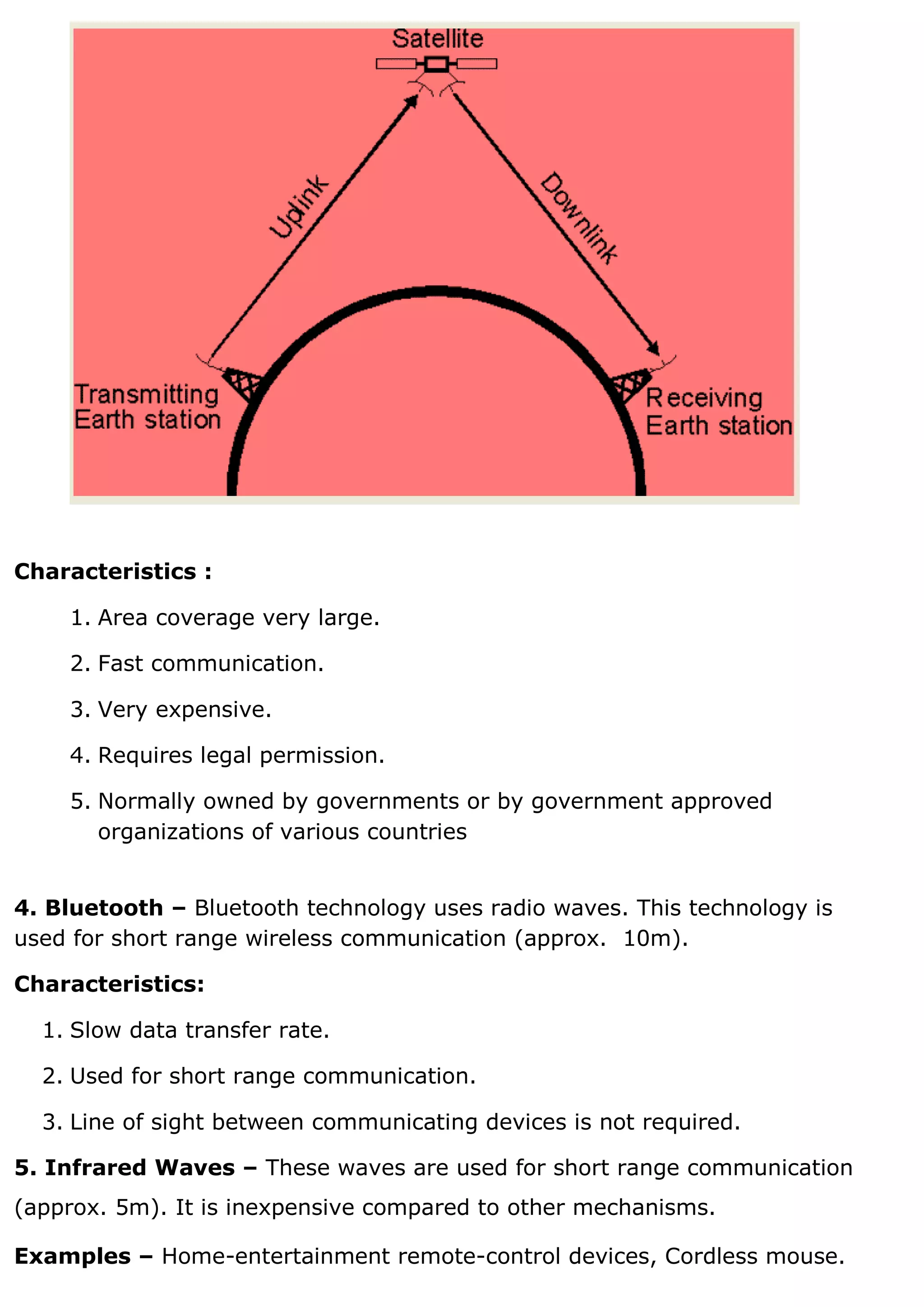
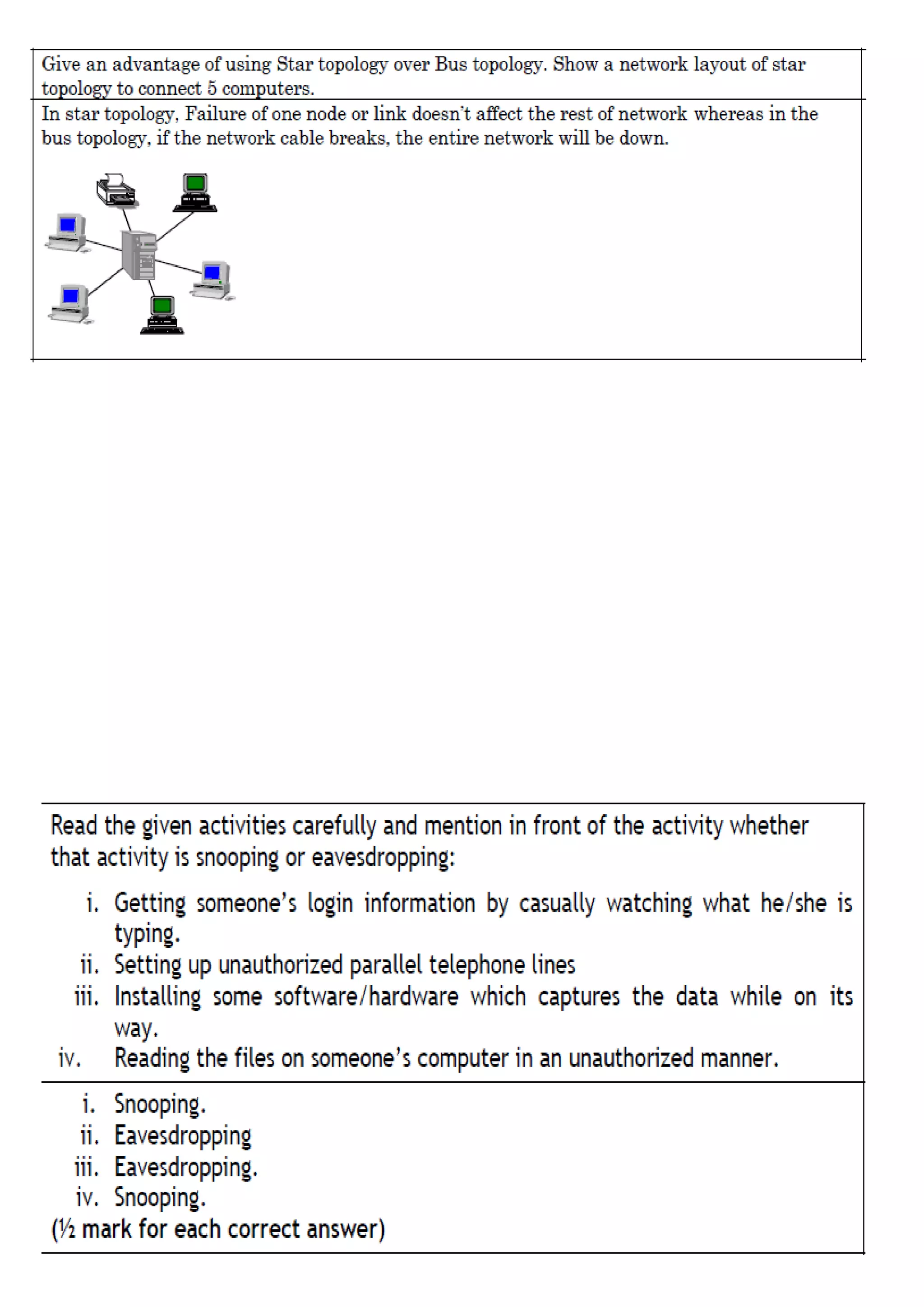
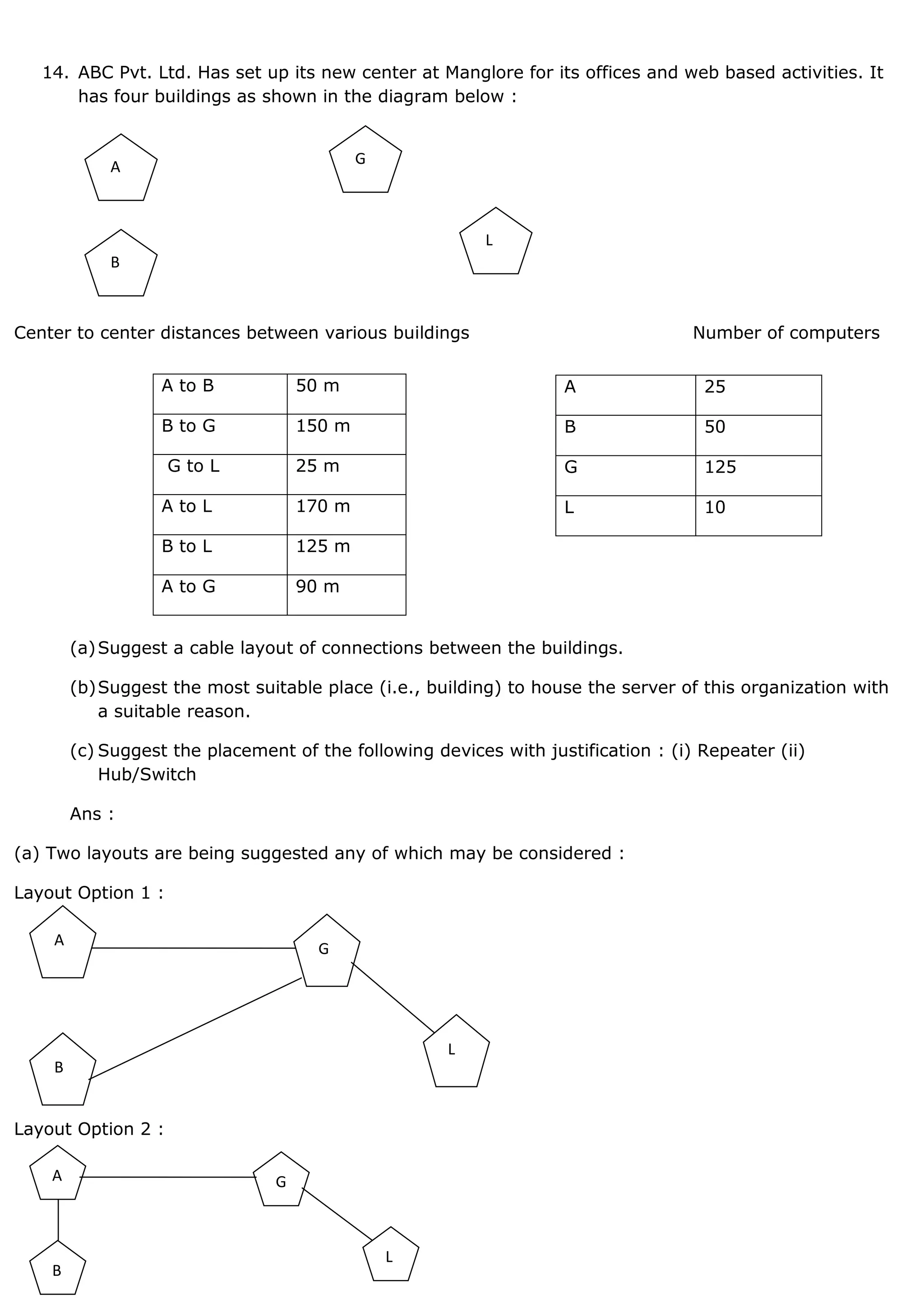
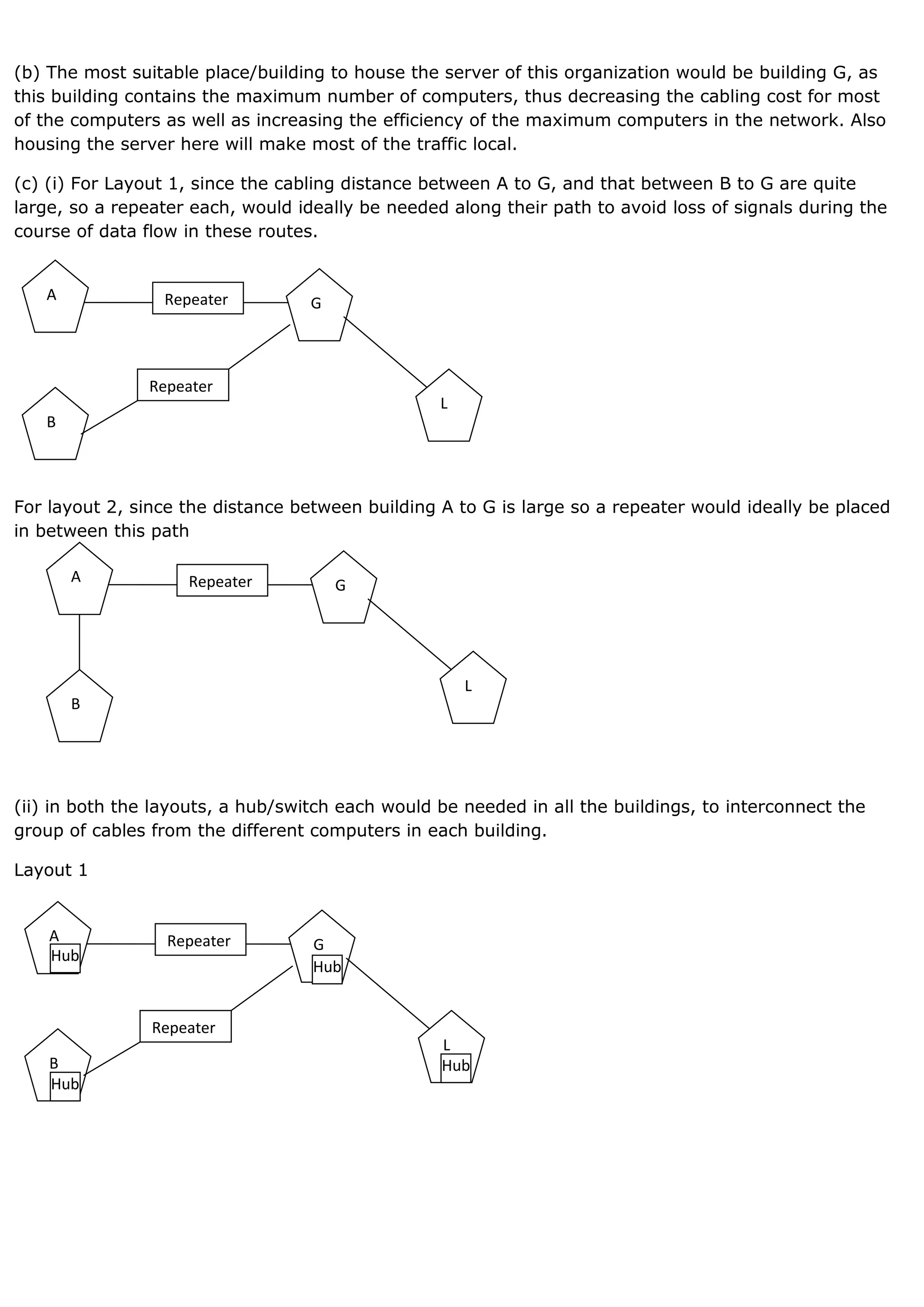
1. A computer network connects devices together to share resources and communicate. It allows sharing of data, printers, and faster more reliable communication between users. 2. Common network hardware includes transmission media like Ethernet cables, WiFi routers, and switches which connect devices and direct data traffic. Wireless technologies like Bluetooth enable short-range connectivity while fiber optics cables allow for high-speed long-distance communication. 3. Network security aims to protect networks from threats like denial of service attacks, intrusions, eavesdropping and snooping. Techniques include passwords, firewalls, file permissions and antivirus software. Proper network configuration and monitoring helps maintain the security of connected devices and data.