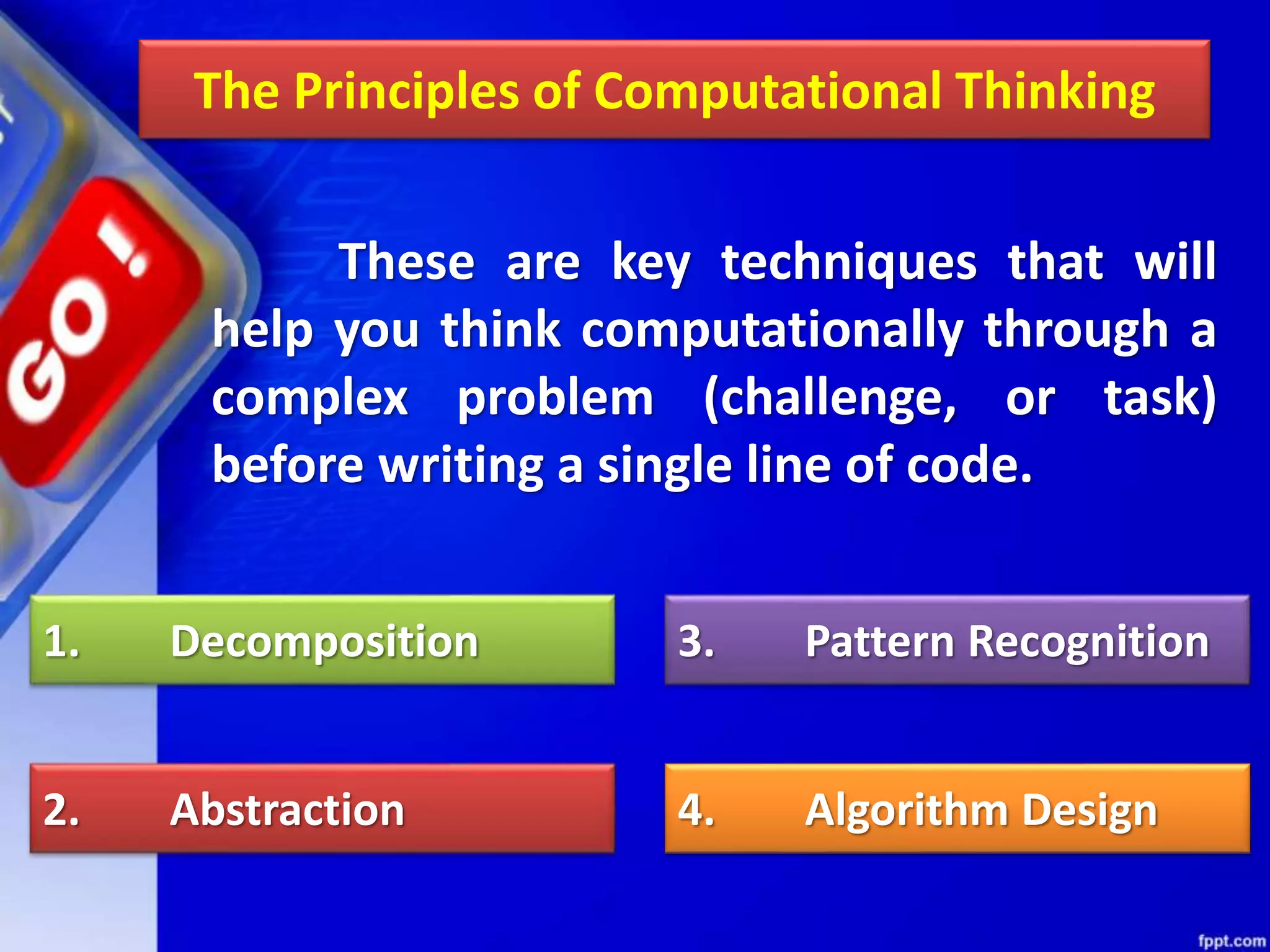
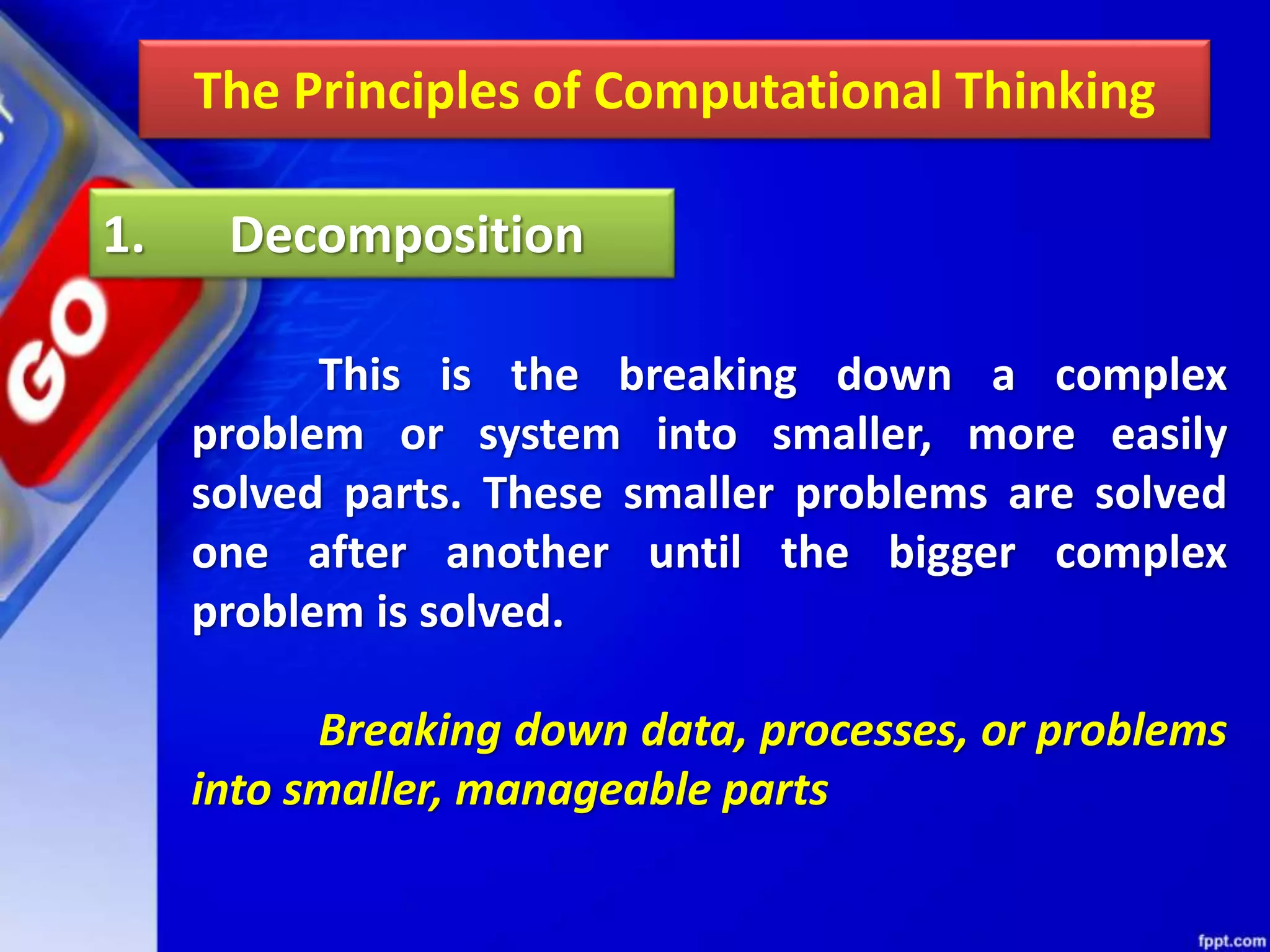
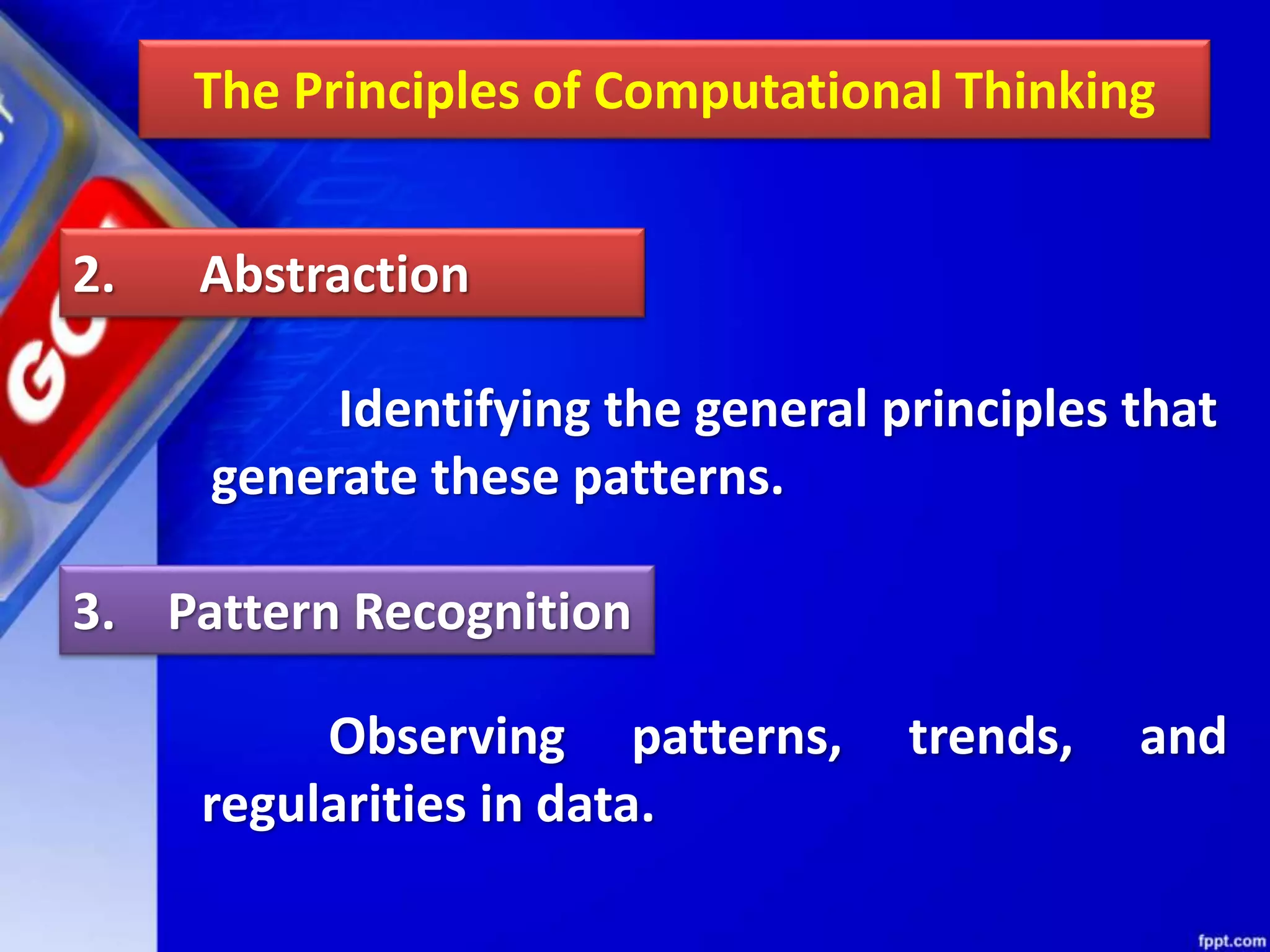
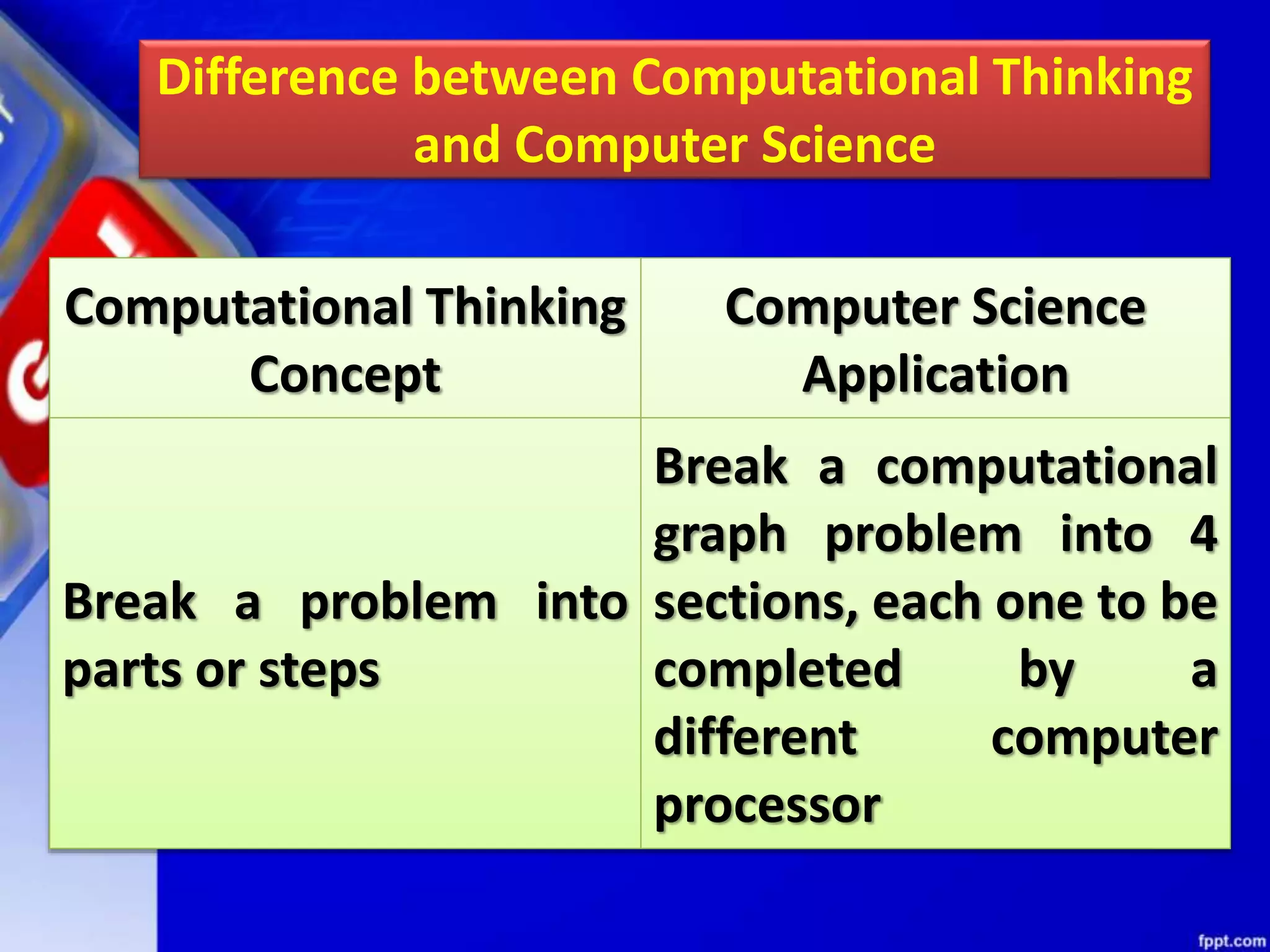
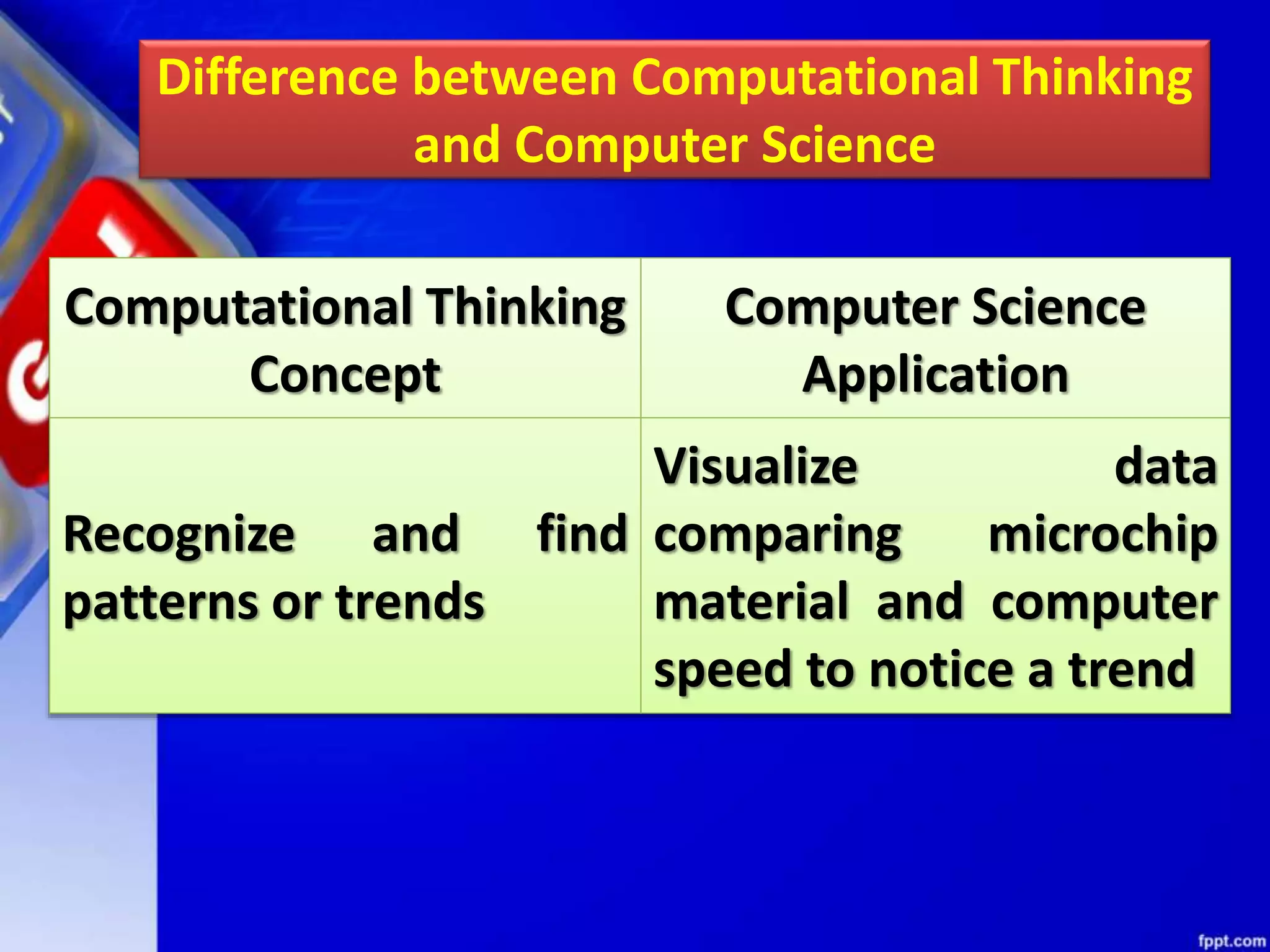
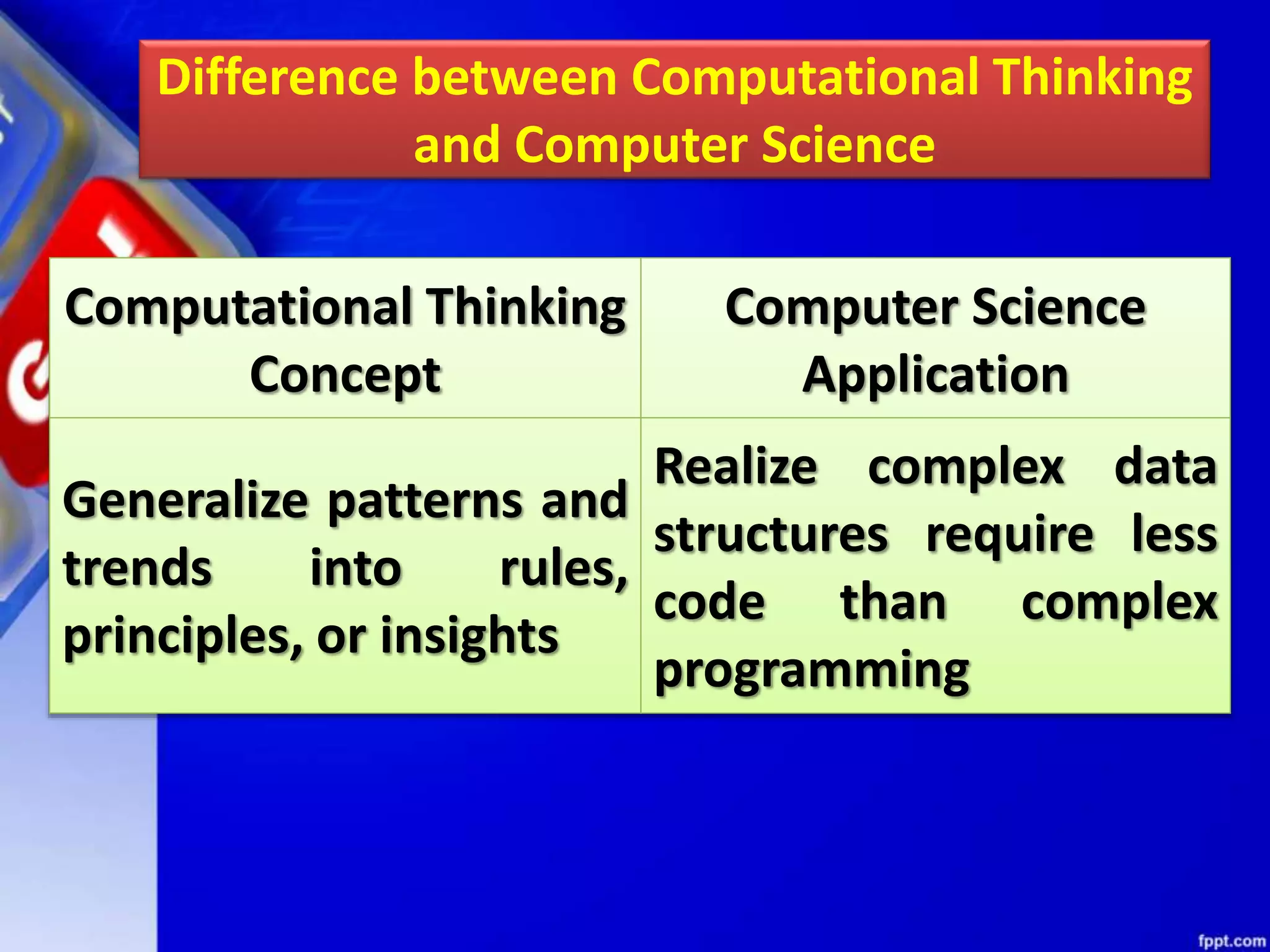
Computational thinking (CT) is a problem-solving process that involves decomposition, pattern recognition, abstraction, and algorithm design. CT can be used to solve problems across many disciplines. The key principles of CT are: 1) Decomposition, which is breaking down complex problems into smaller parts; 2) Pattern recognition, which is observing patterns in data; 3) Abstraction, which identifies general principles; and 4) Algorithm design, which develops step-by-step instructions. CT is a concept that focuses on problem-solving techniques, while computer science is the application of those techniques through programming. CT can be applied to solve problems in any field, while computer science specifically implements computational solutions.