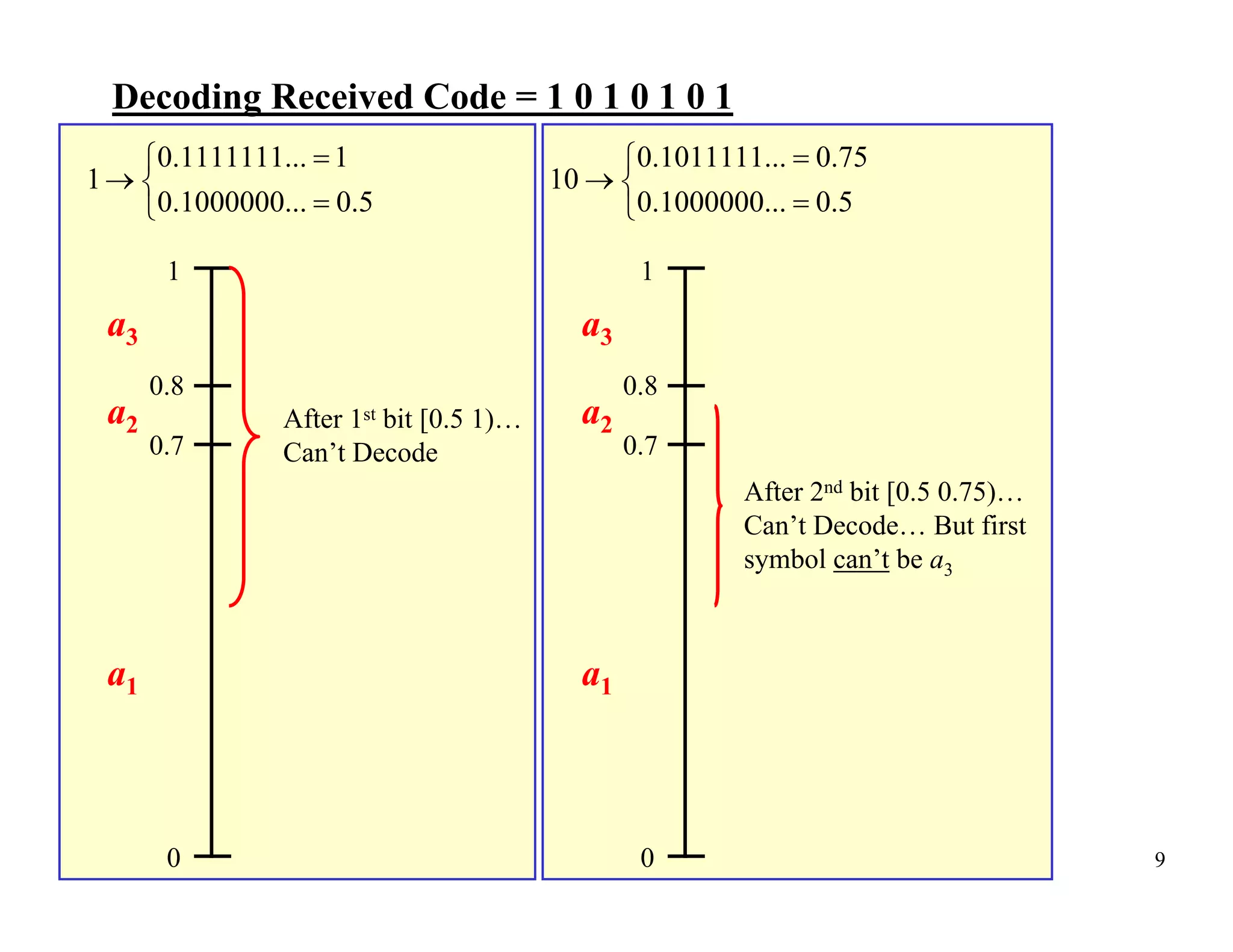
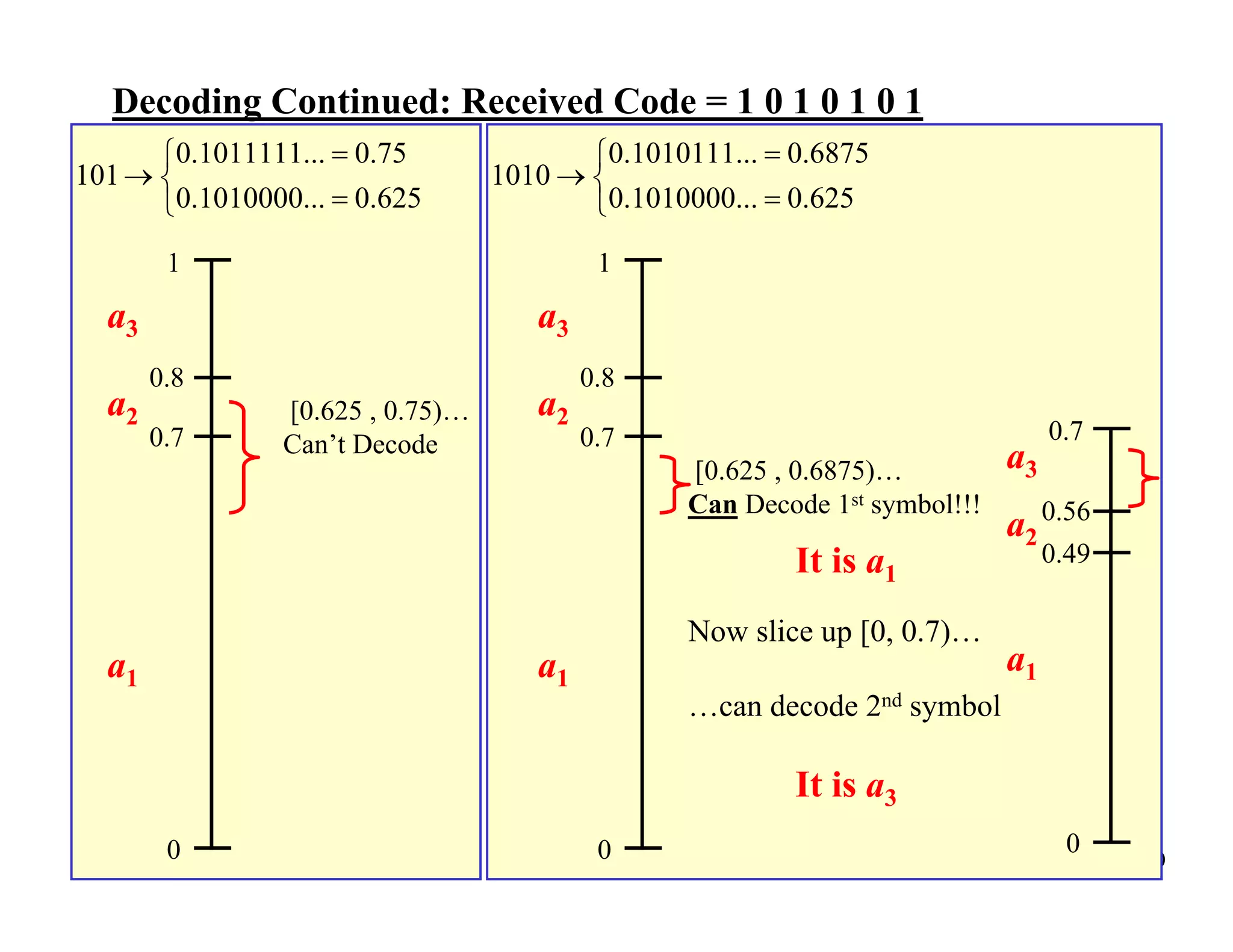
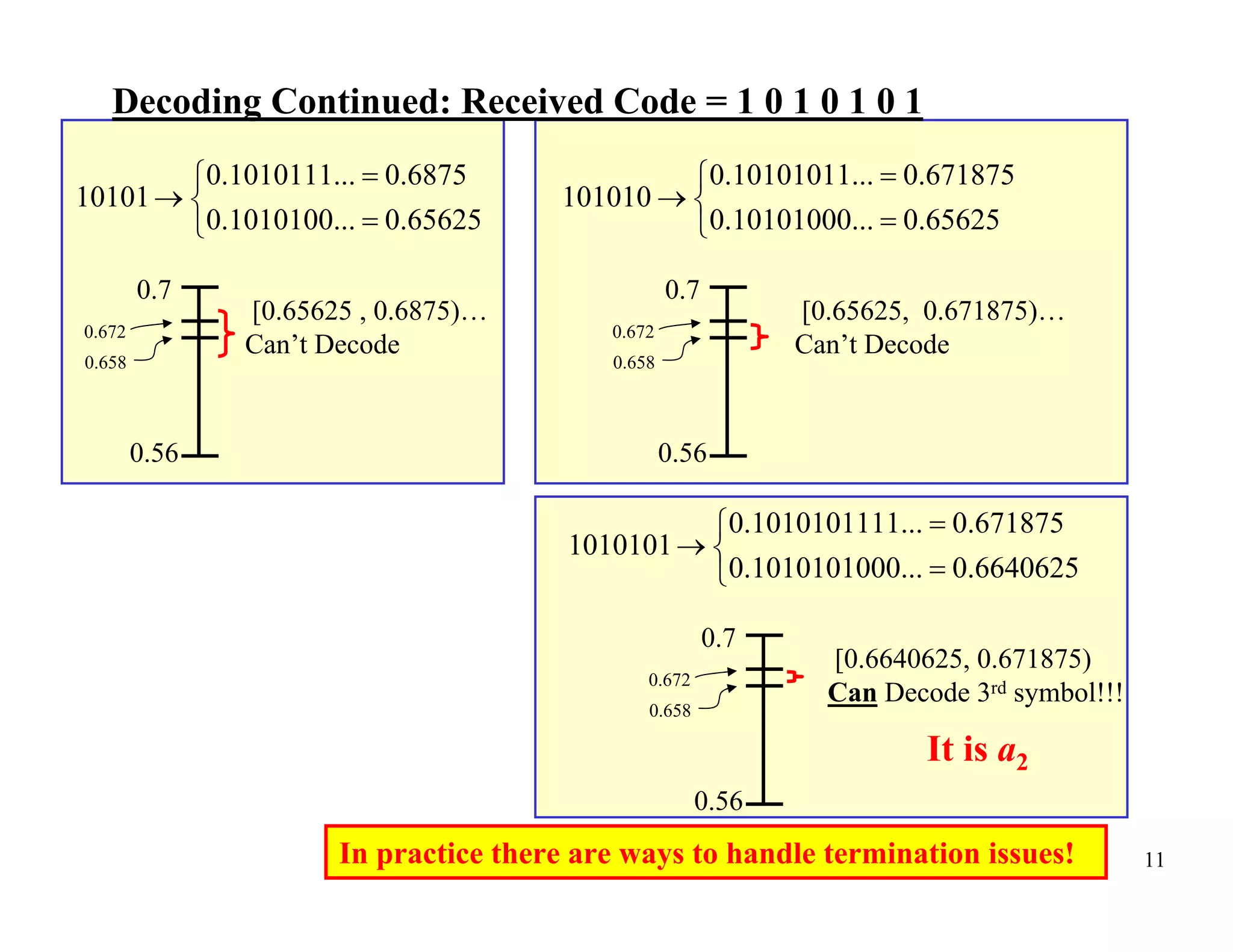
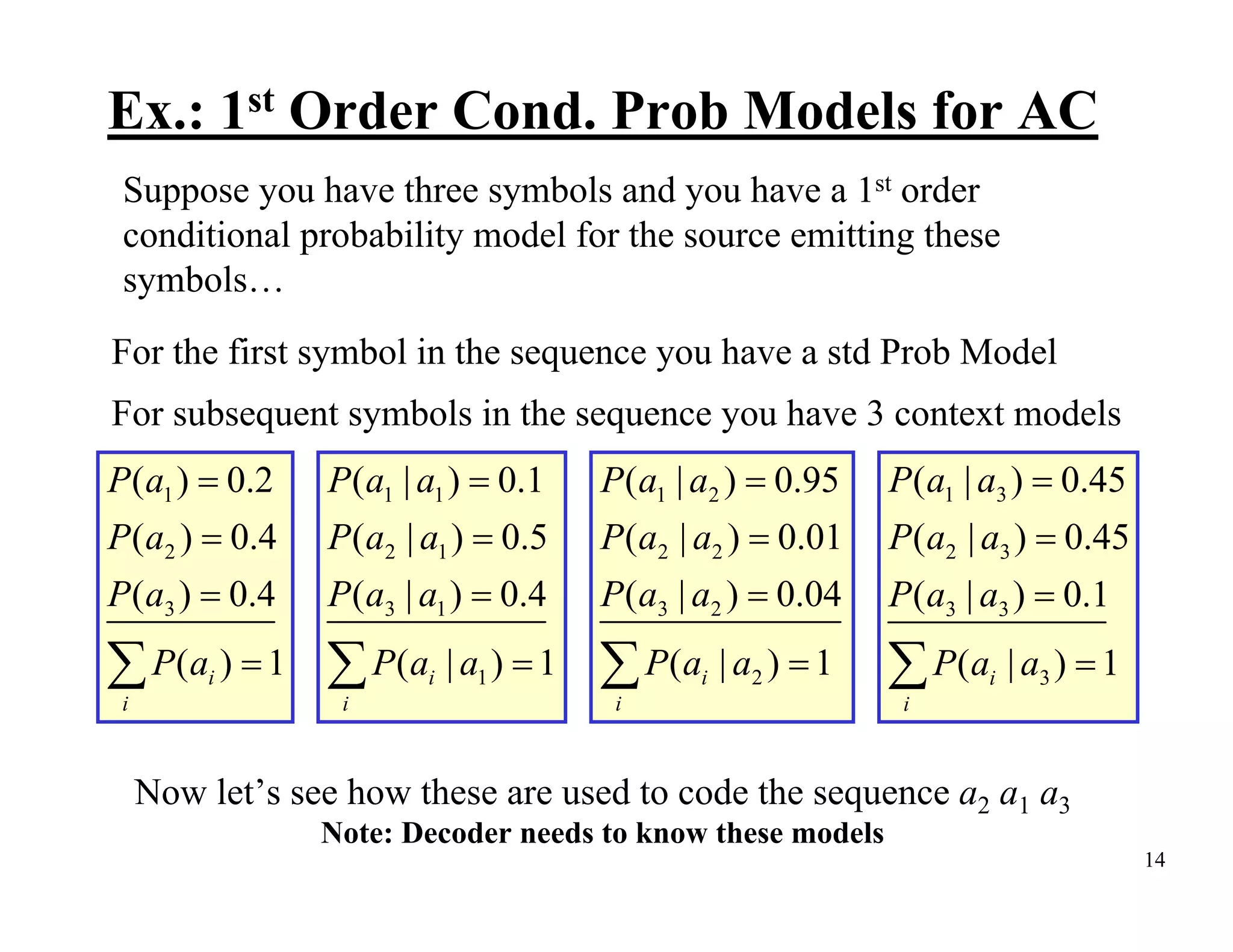
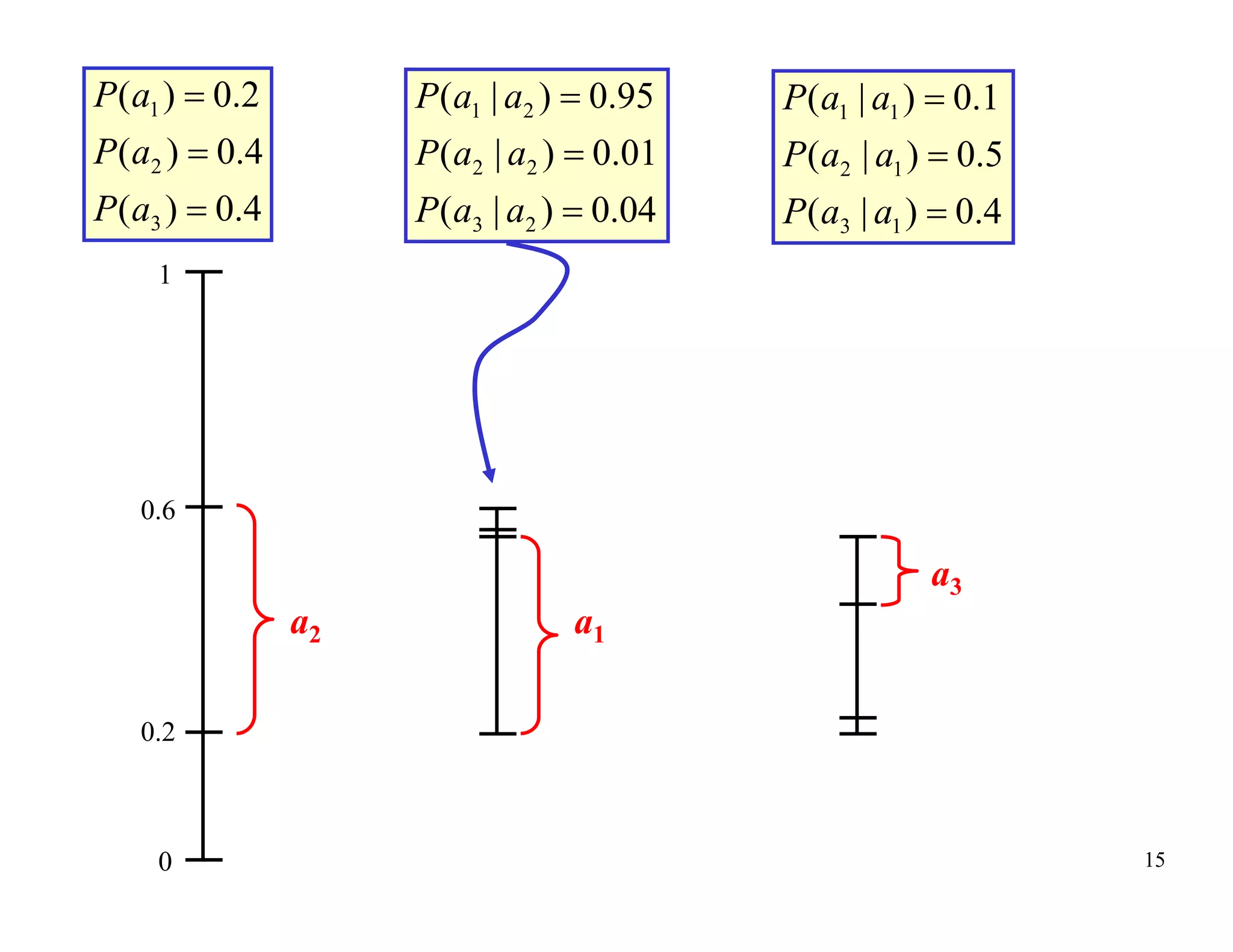
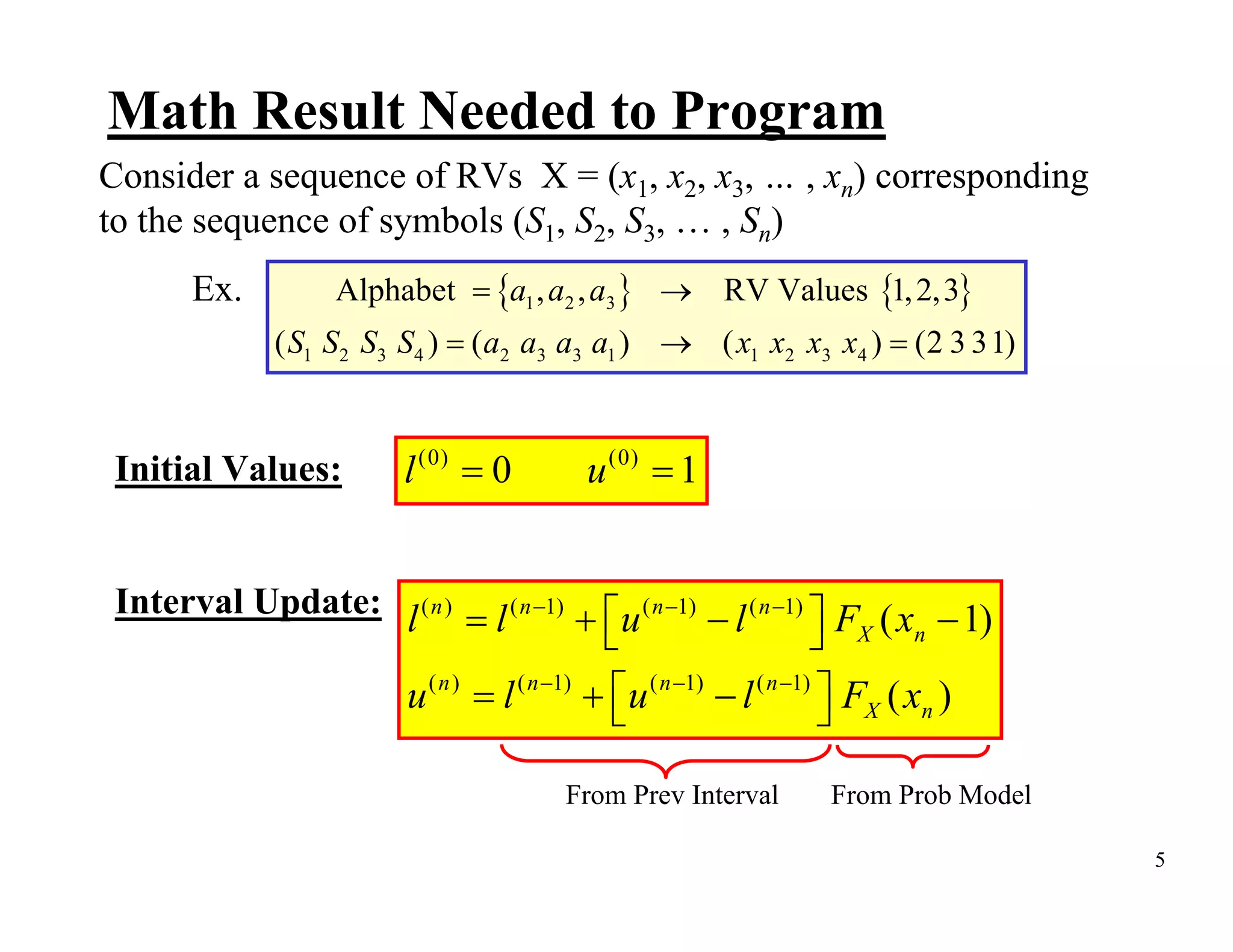
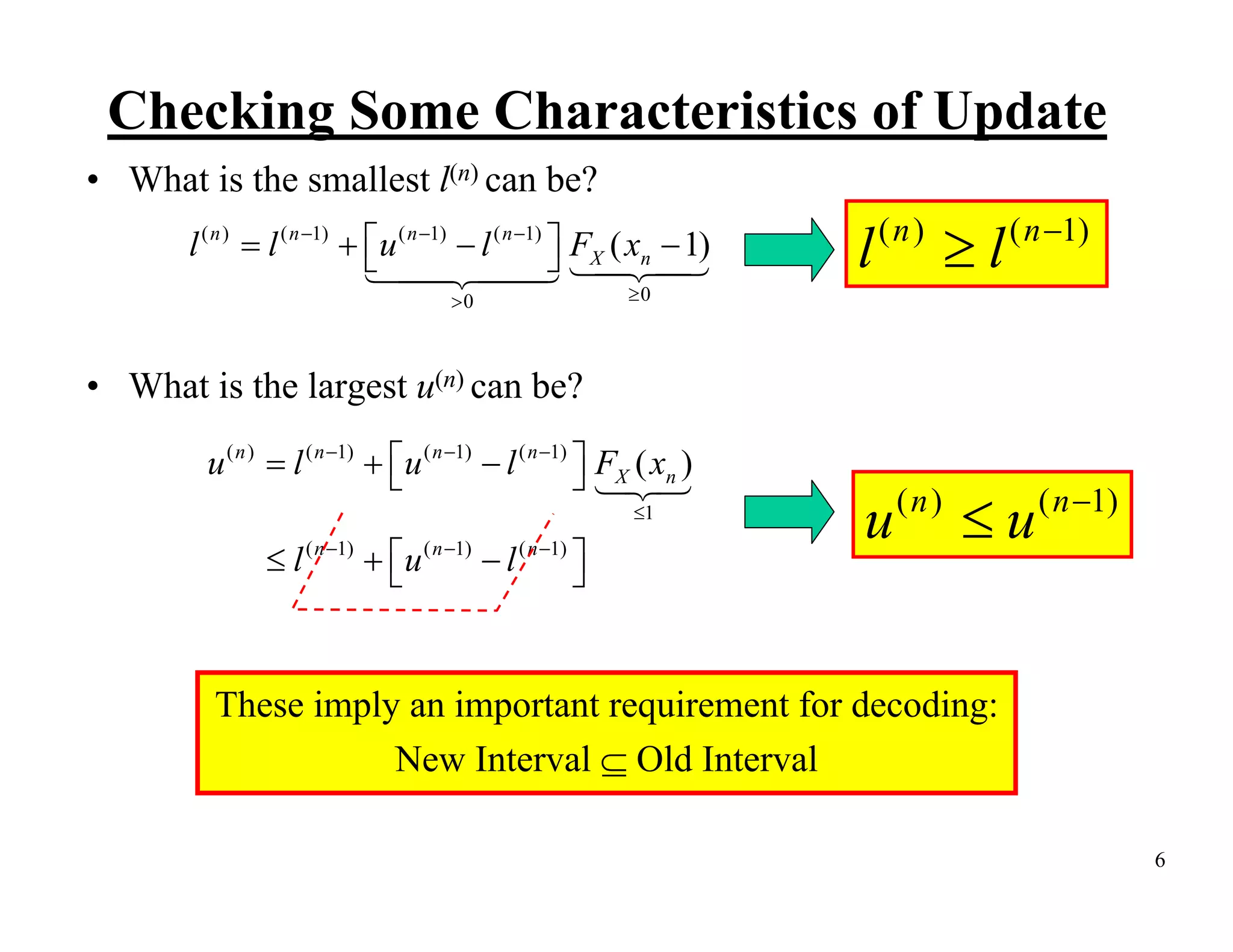
Arithmetic coding is an entropy encoding technique that maps a sequence of symbols to a number between 0 and 1. Each possible sequence is assigned a unique interval within this range. As symbols are processed, the interval boundaries are updated based on the symbol probabilities. This allows arithmetic coding to efficiently encode sequences without needing to pre-determine codes for all possible sequences. It can achieve compression close to the entropy limit for long sequences, and easily supports adaptive and context modeling to handle non-IID sources. The interval updates ensure a unique number can be sent to decode the full sequence.


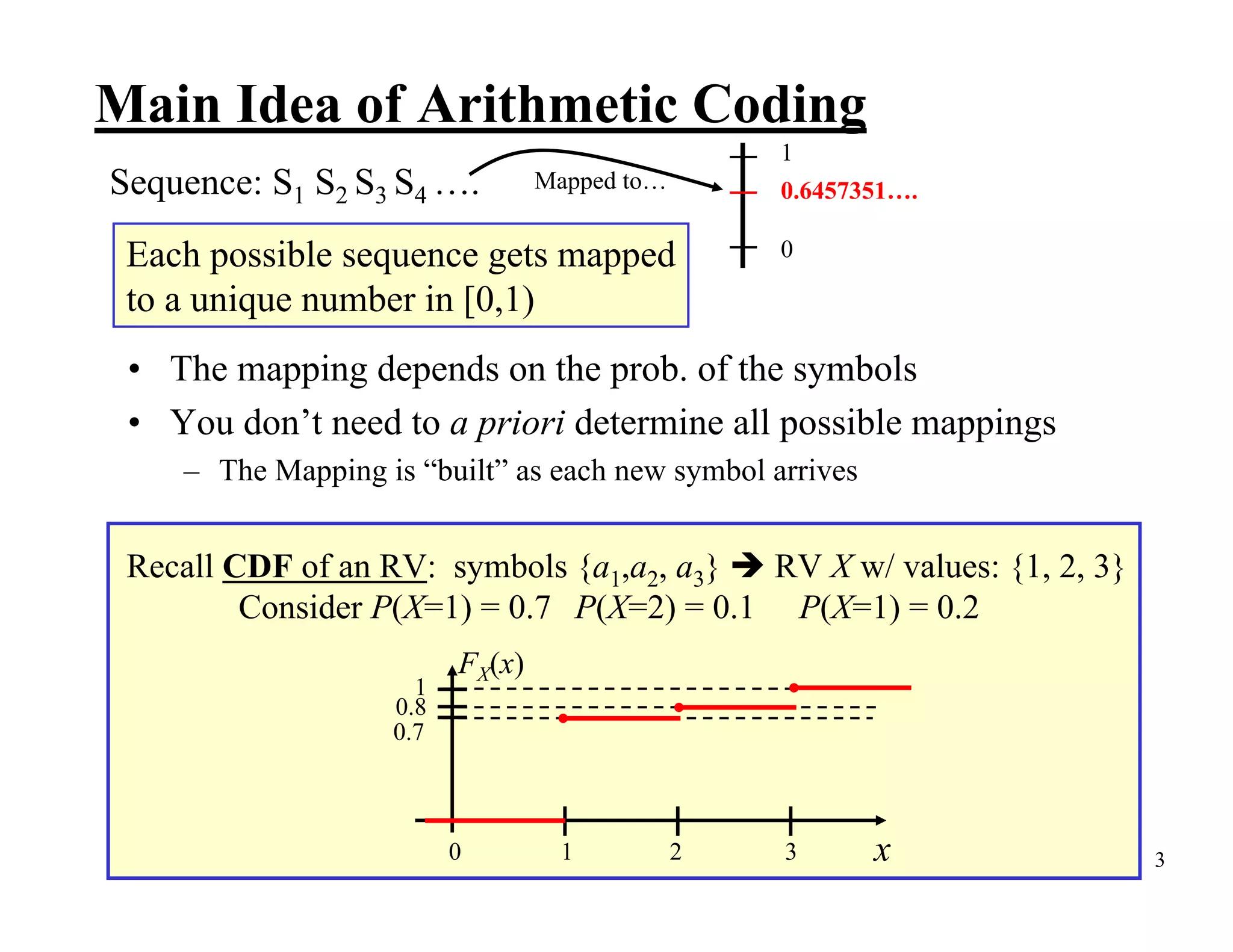
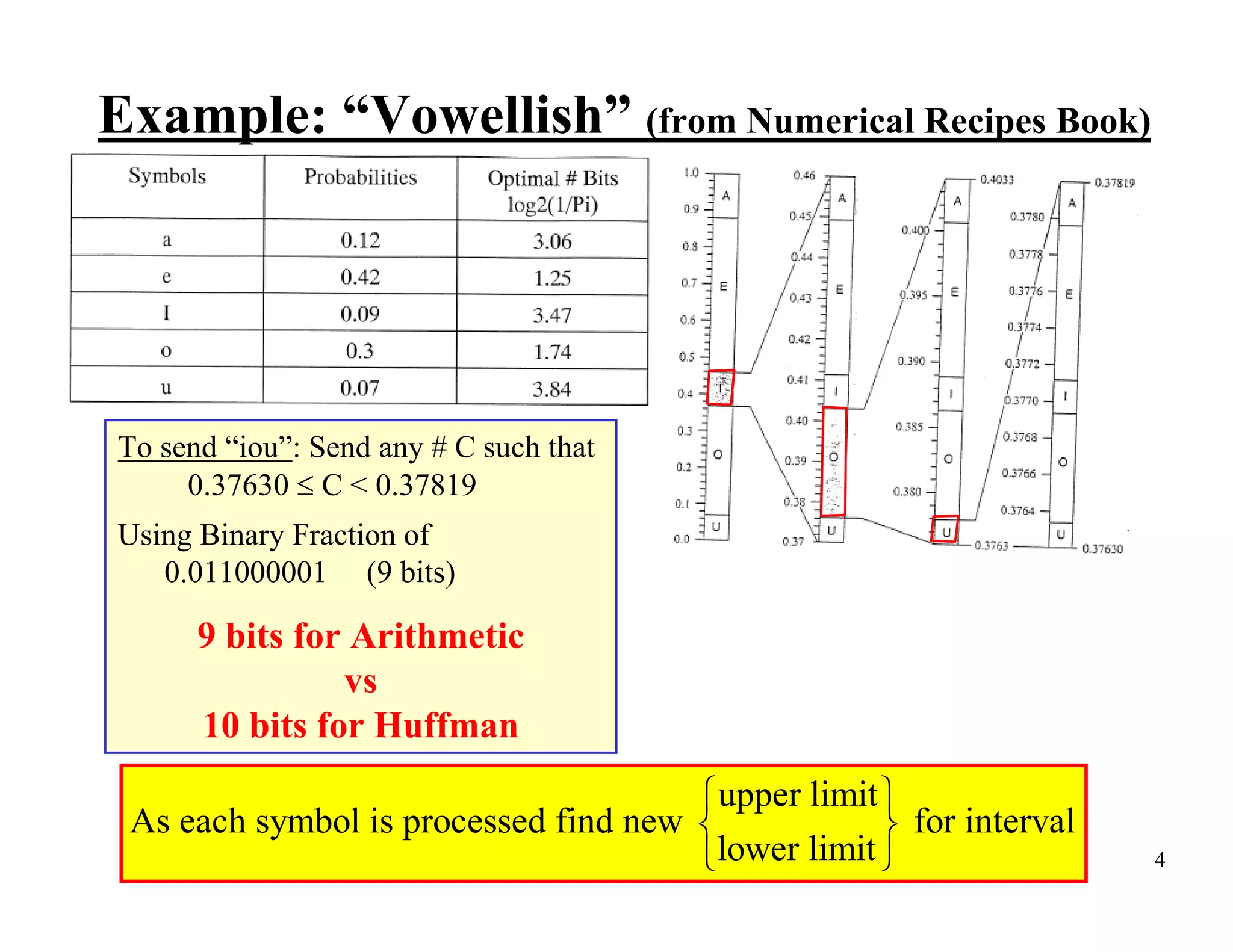
![Example of Applying the Interval Update Symbols {a1,a2, a3} RV X w/ values: {1, 2, 3} Consider P(X=1) = 0.7 P(X=2) = 0.1 P(X=1) = 0.2 FX(x) 1 0.8 CDF for this 0.7 alphabet/RV 0 1 2 3 x Consider the sequence (a1 a3 a2) → (1 3 2) To process the first symbol “1” FX(0) l (1) = l (0) + ⎡u (0) − l (0) ⎤ FX (1 − 1) = 0 + [1 − 0] × 0 = 0 ⎣ ⎦ u (1) = l (0) + ⎡u (0) − l (0) ⎤ FX (1) ⎣ ⎦ = 0 + [1 − 0] × 0.7 = 0.7 FX(1) 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch04arithmeticcodingppt-100209005019-phpapp02/75/Ch-04-Arithmetic-Coding-P-P-T-7-2048.jpg)
![To process the 2nd symbol “3” FX(2) l (2) = l (1) + ⎡u (1) − l (1) ⎤ FX (3 − 1) = 0 + [0.7 − 0] × 0.8 = 0.56 ⎣ ⎦ u (2) = l (1) + ⎡u (1) − l (1) ⎤ FX (3) ⎣ ⎦ = 0 + [0.7 − 0] × 1 = 0.7 FX(3) To process the 3rd symbol “2” FX(1) 1010101000 l (3) = l (2) + ⎡u (2) − l (2) ⎤ FX (2 − 1) = 0.56 + [0.7 − 0.56] × 0.7 = 0.658 ⎣ ⎦ u (3) = l (2) + ⎡u (2) − l (2) ⎤ FX (2) ⎣ ⎦ = 0.56 + [0.7 − 0.56] × 0.8 = 0.672 FX(2) So… send a number in the interval [0.658,0.672) Pick 0.6640625 0.664062510 = 0.10101012 Code = 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch04arithmeticcodingppt-100209005019-phpapp02/75/Ch-04-Arithmetic-Coding-P-P-T-8-2048.jpg)