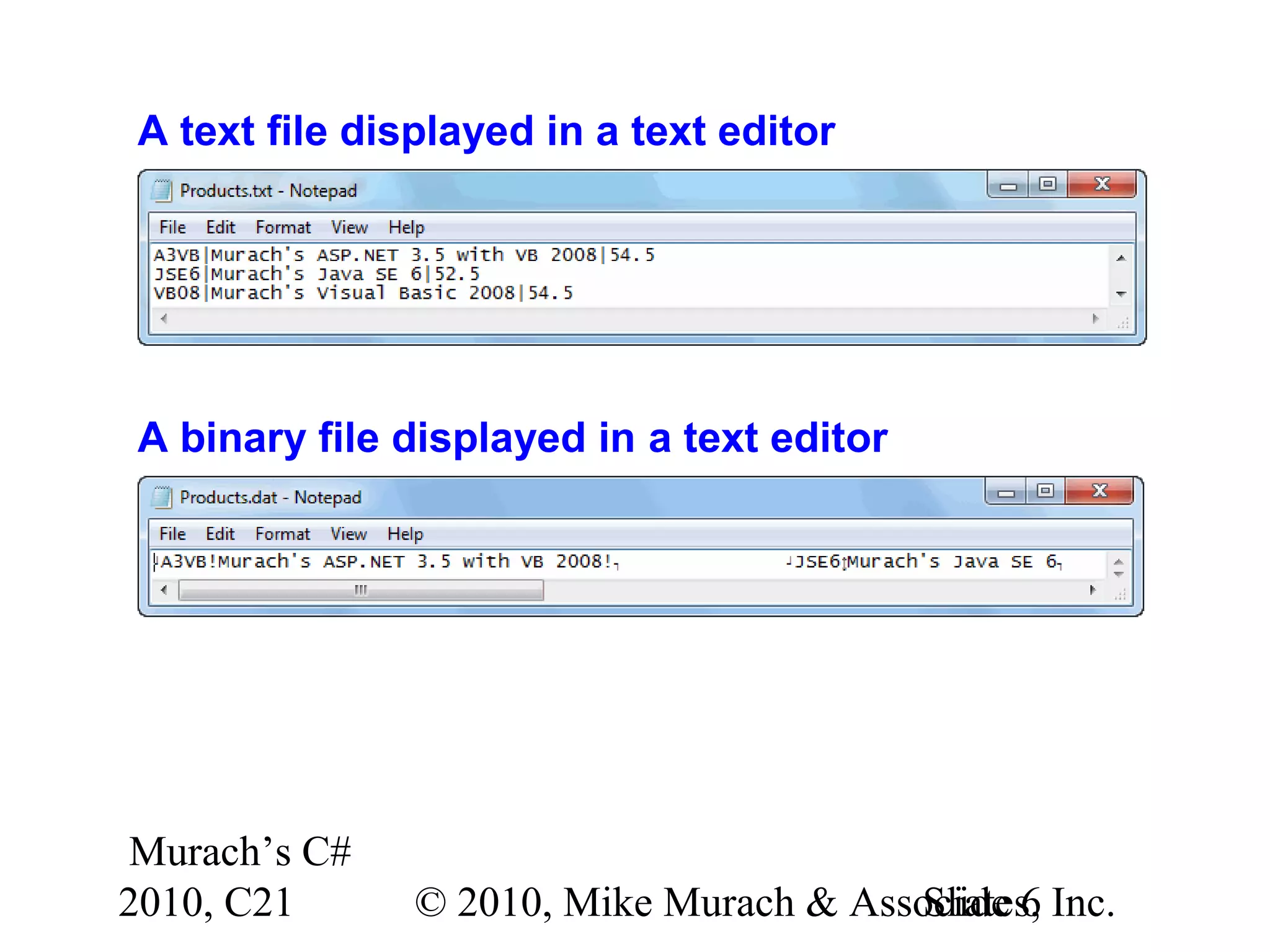
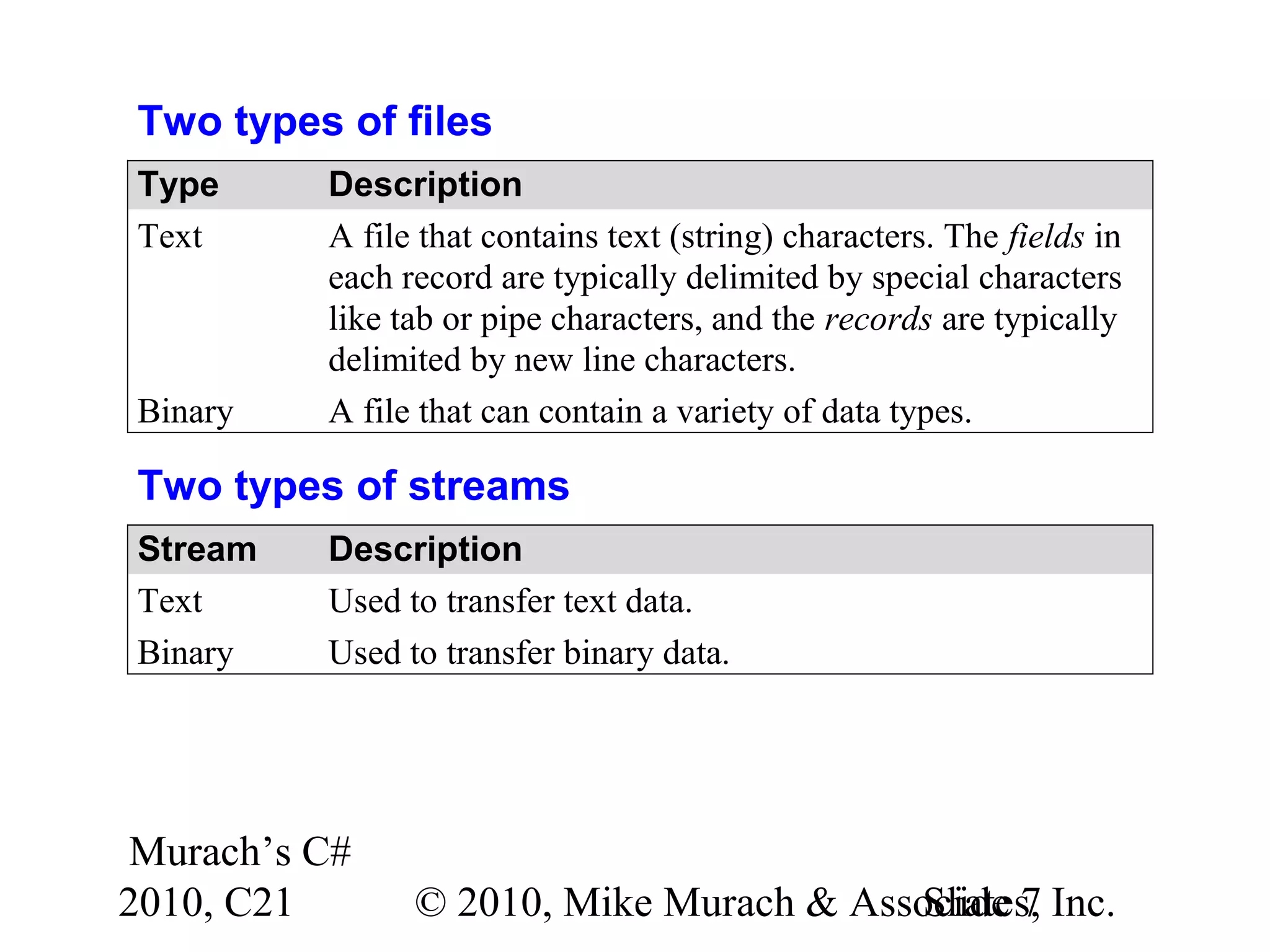
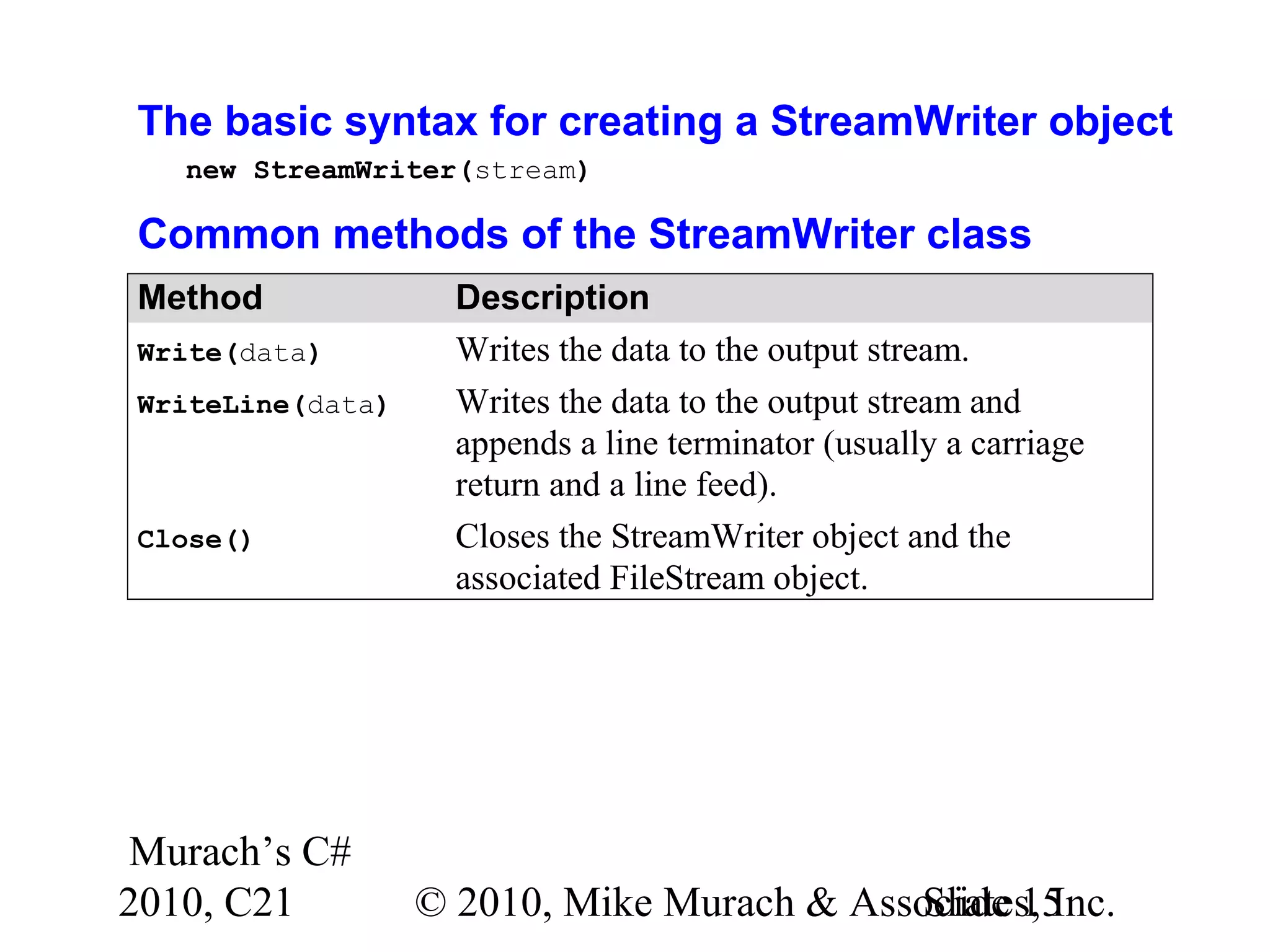
This document discusses working with files and data streams in C#. It covers text files versus binary files, and classes for working with files like FileStream, StreamReader, StreamWriter, BinaryReader, and BinaryWriter. Specific methods of these classes are described for reading and writing data to files. Exceptions that can occur during file I/O are also covered. Code examples demonstrate how to read and write data to both text and binary files, and how to handle potential exceptions. A ProductDB class is presented that encapsulates common file operations for a product database stored in files.






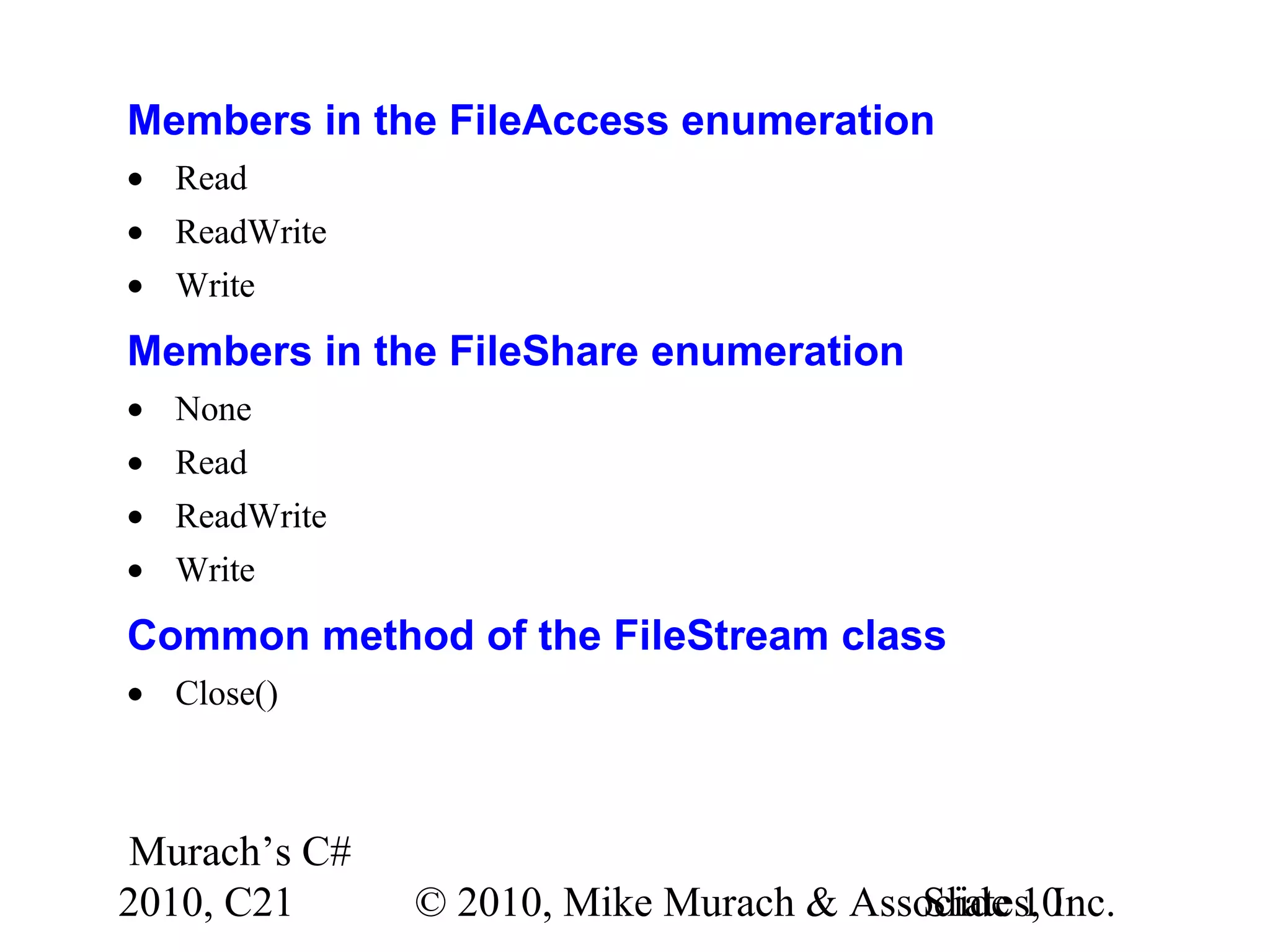
![Murach’s C# 2010, C21 © 2010, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.Slide 9 The syntax for creating a FileStream object new FileStream(path, mode[, access[, share]]) Members in the FileMode enumeration • Append • Create • CreateNew • Open • OpenOrCreate • Truncate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/murach-chapter-21-slides-170327125940/75/C-Tutorial-MSM_Murach-chapter-21-slides-9-2048.jpg)





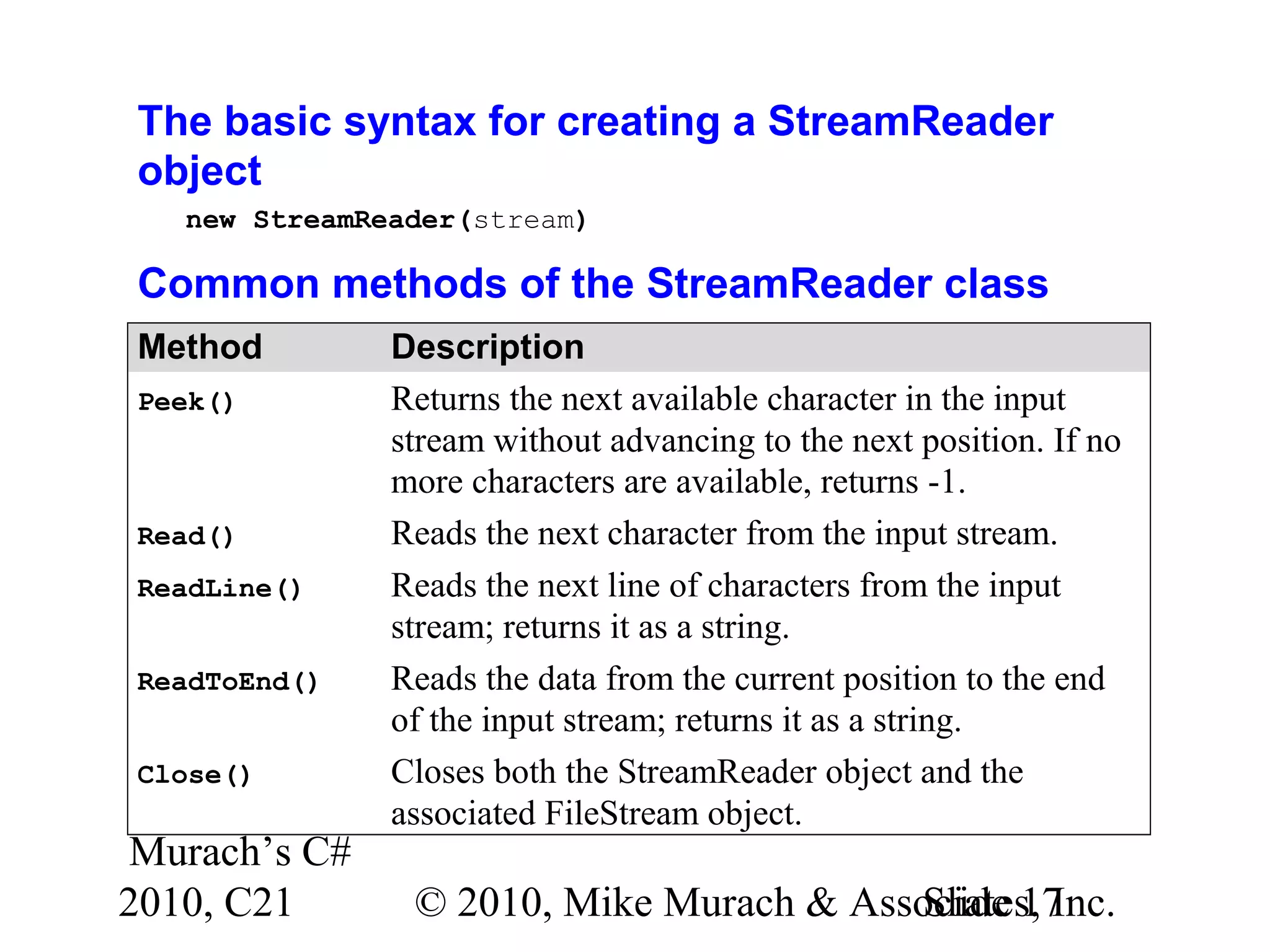
![Murach’s C# 2010, C21 © 2010, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.Slide 18 Code that reads data from a text file into a collection of Product objects StreamReader textIn = new StreamReader( new FileStream( path, FileMode.OpenOrCreate, FileAccess.Read)); List<Product> products = new List<Product>(); while (textIn.Peek() != -1) { string row = textIn.ReadLine(); string[] columns = row.Split('|'); Product product = new Product(); product.Code = columns[0]; product.Description = columns[1]; product.Price = Convert.ToDecimal(columns[2]); products.Add(product); } textIn.Close();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/murach-chapter-21-slides-170327125940/75/C-Tutorial-MSM_Murach-chapter-21-slides-18-2048.jpg)

![Murach’s C# 2010, C21 © 2010, Mike Murach & Associates, Inc.Slide 20 A class that works with a text file (cont.) List<Product> products = new List<Product>(); while (textIn.Peek() != -1) { string row = textIn.ReadLine(); string[] columns = row.Split('|'); Product product = new Product(); product.Code = columns[0]; product.Description = columns[1]; product.Price = Convert.ToDecimal(columns[2]); products.Add(product); } textIn.Close(); return products; }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/murach-chapter-21-slides-170327125940/75/C-Tutorial-MSM_Murach-chapter-21-slides-20-2048.jpg)







