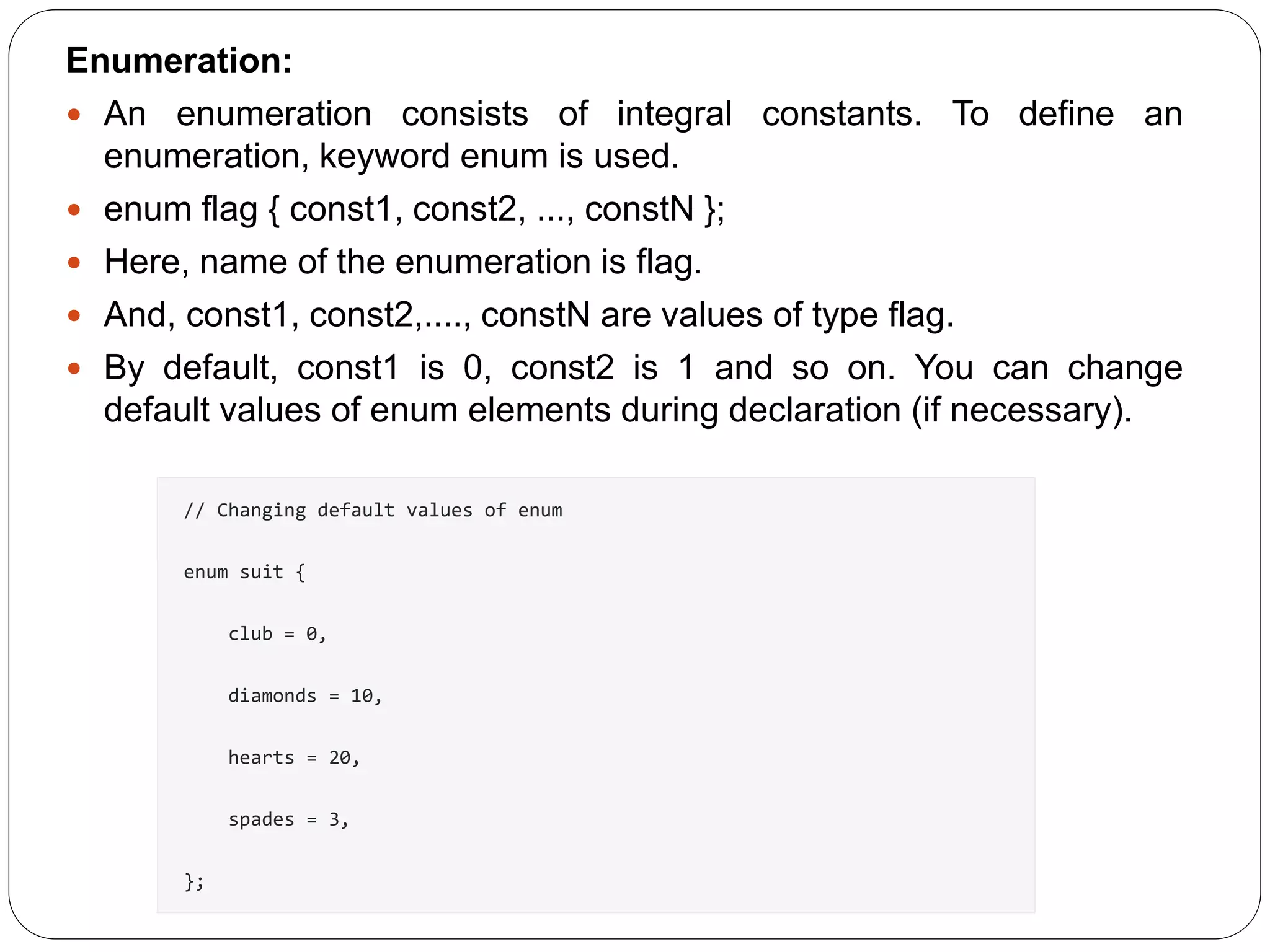
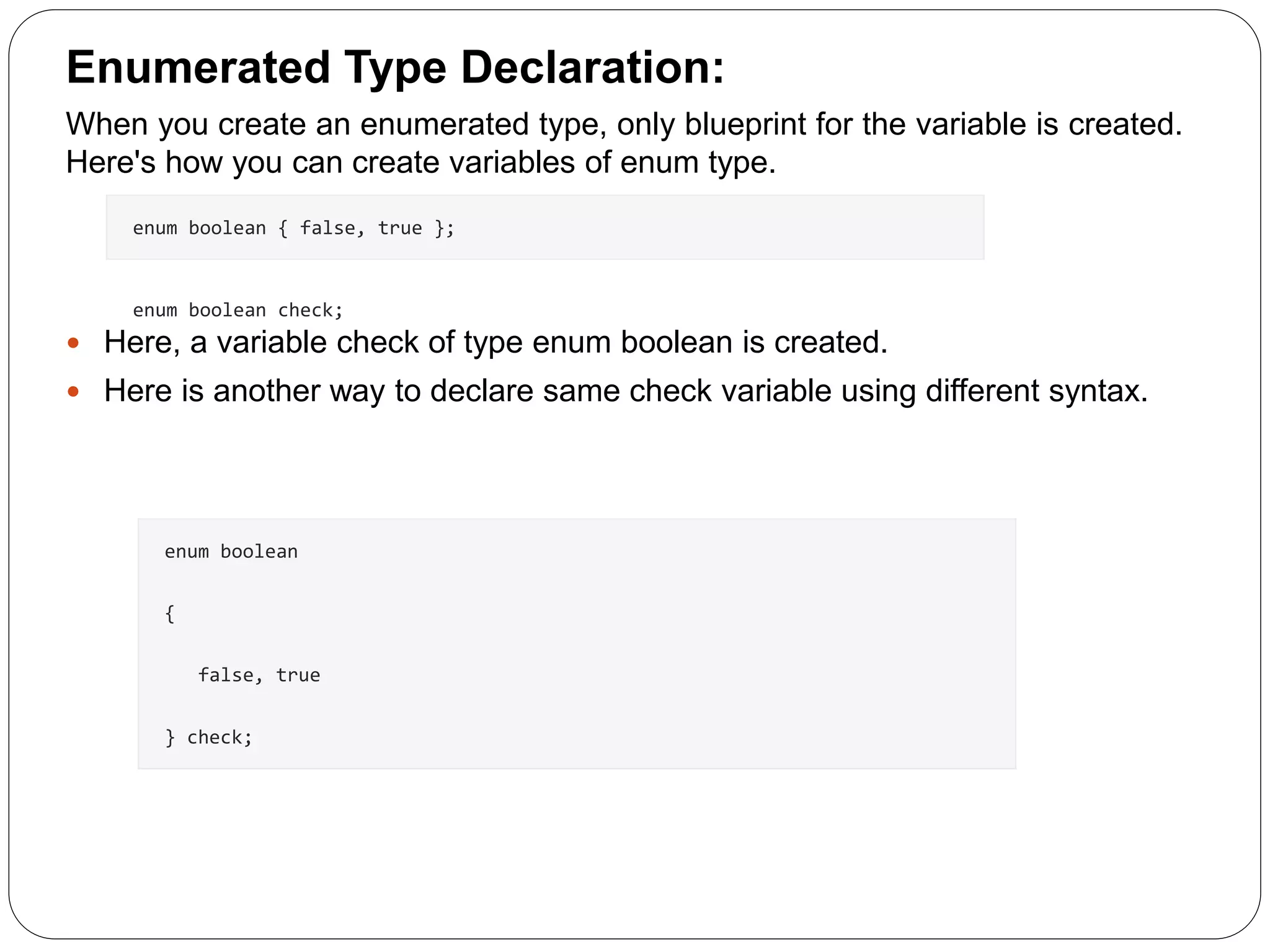
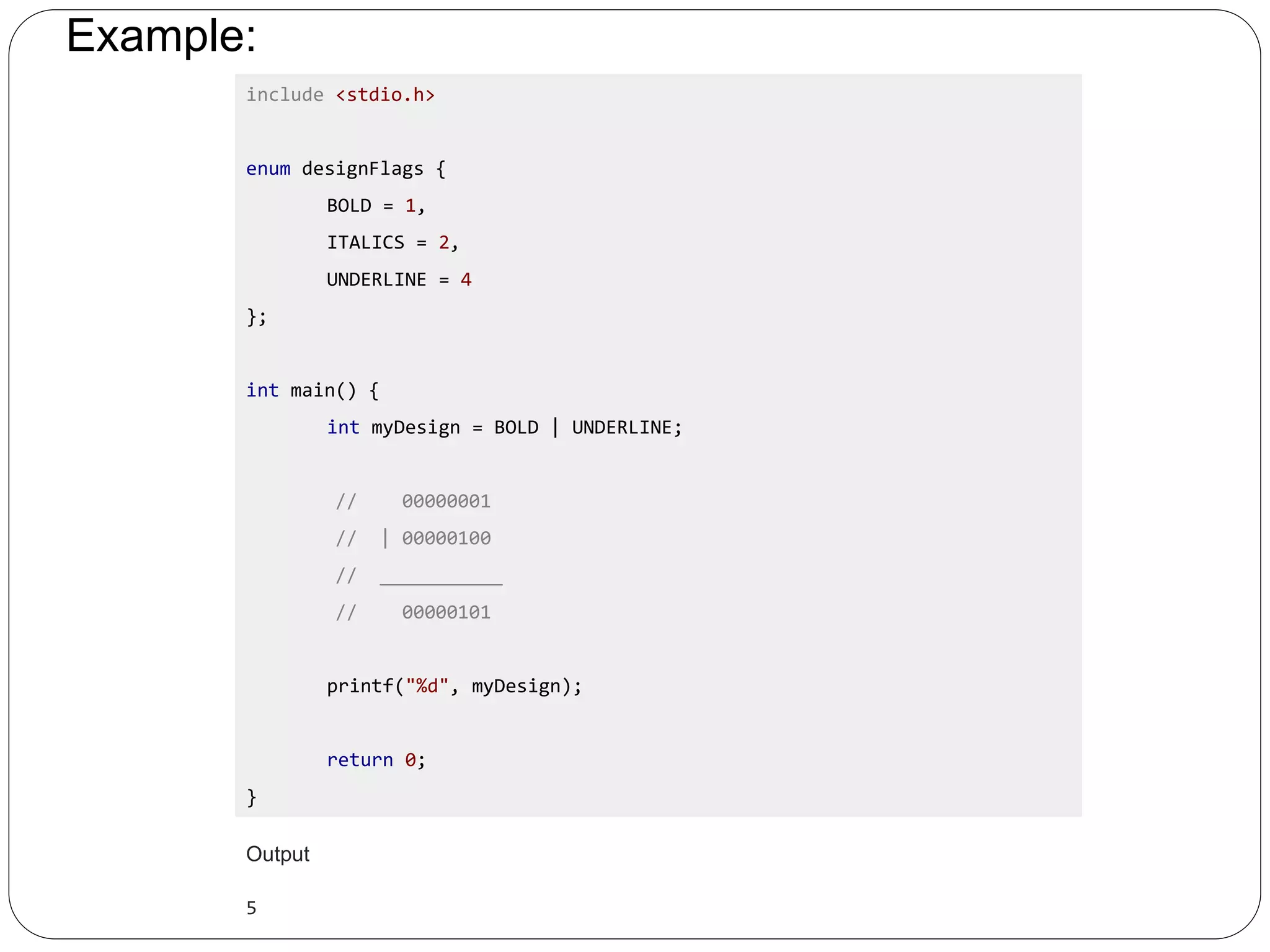
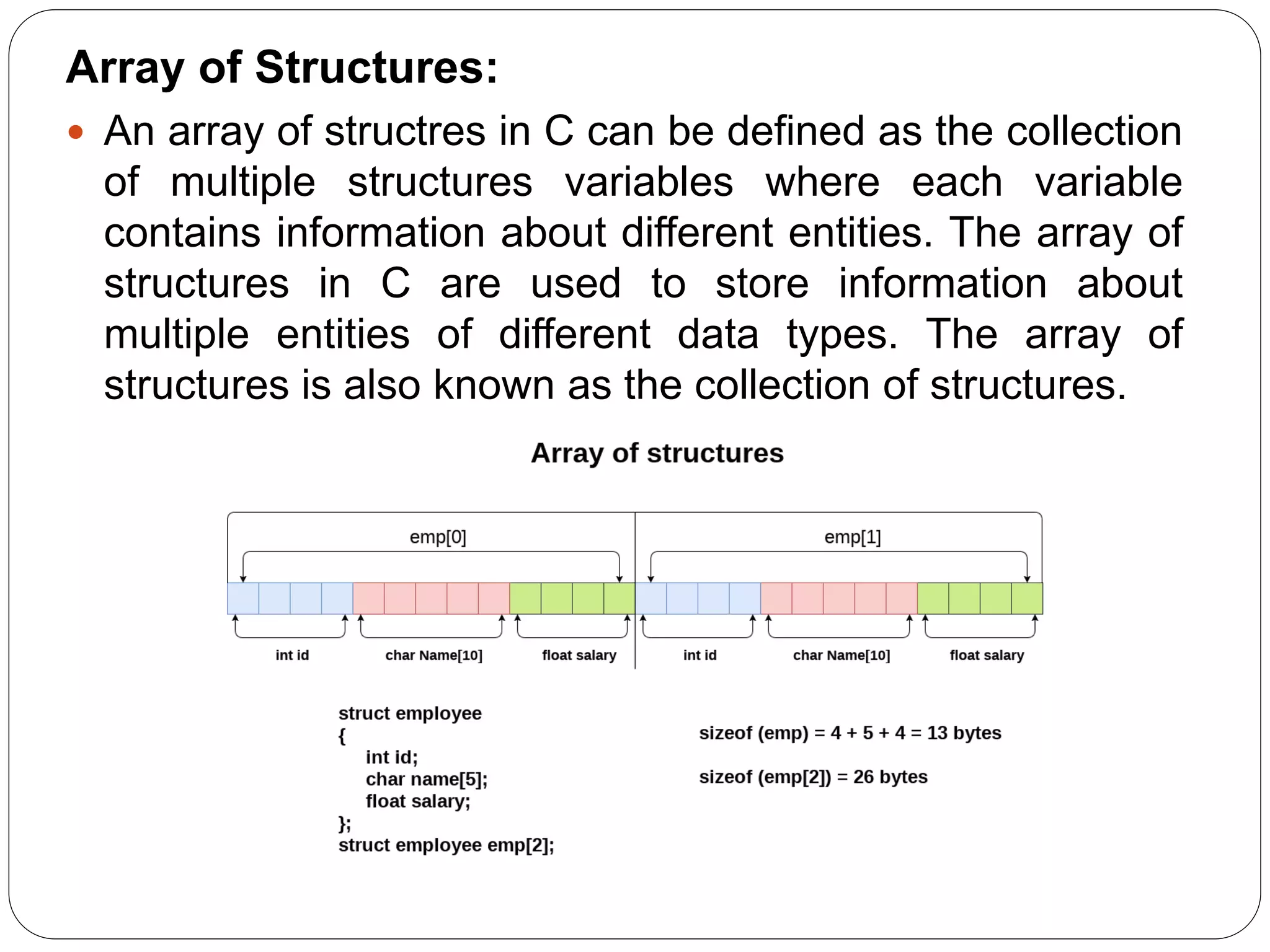
- A structure in C is a user-defined data type that allows storing multiple data types together under one name. - Structures can store different attributes like name, roll number, marks of a student entity together rather than separate arrays. - Structures are defined using the struct keyword followed by the structure name and members. - Structure variables can access members using dot (.) operator. - Arrays of structures can store information of multiple entities. Structures can also be nested to store sub-parts of an attribute together.

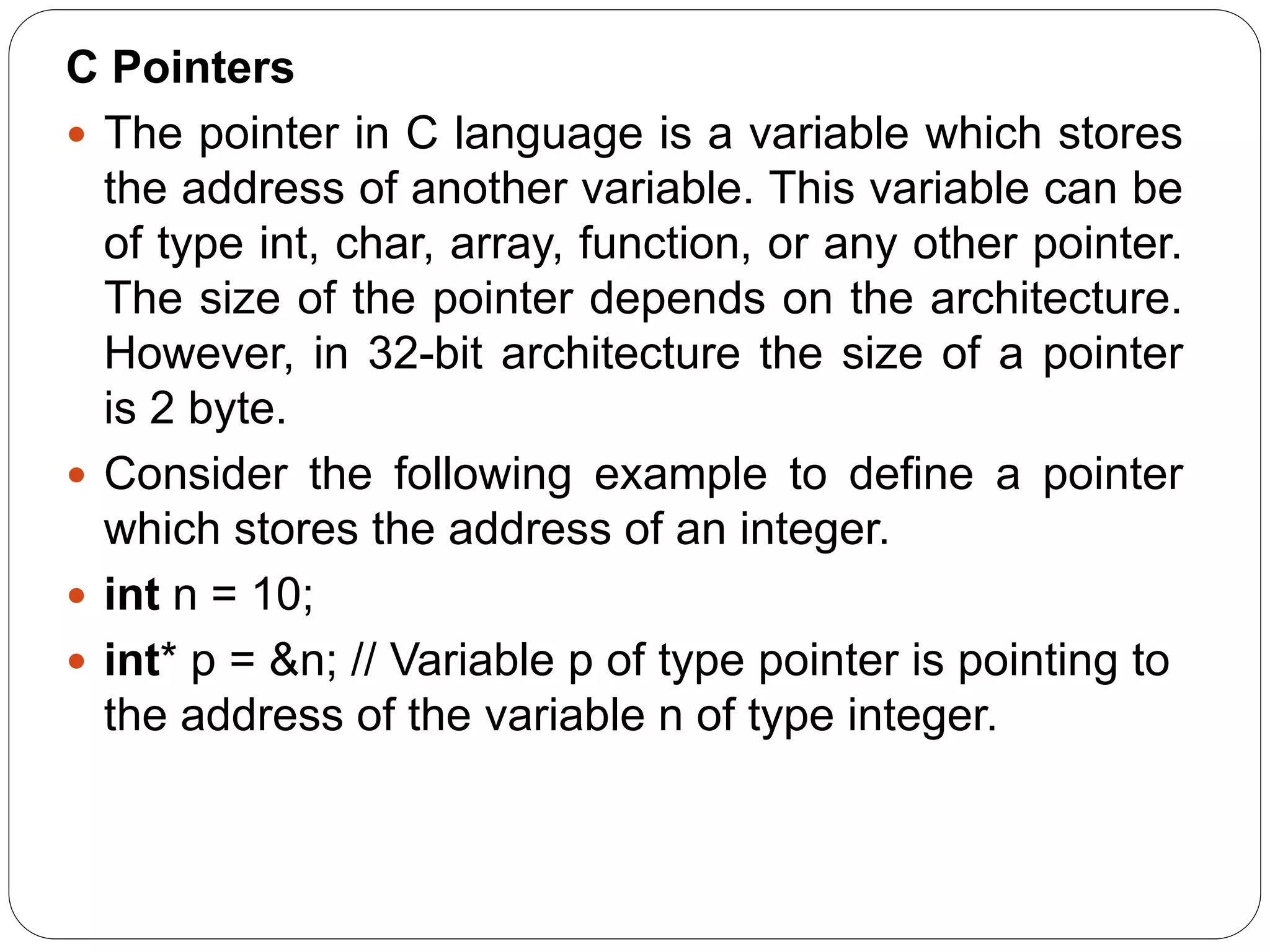











![Pointer to Array of functions in C: Basically, an array of the function is an array which contains the addresses of functions. In other words, the pointer to an array of functions is a pointer pointing to an array which contains the pointers to the functions. Consider the following example: Program: #include<stdio.h> int show(); int showadd(int); int (*arr[3])(); int (*(*ptr)[3])(); int main () { int result1; arr[0] = show; arr[1] = showadd; ptr = &arr; result1 = (**ptr)(); printf("printing the value returned by show : %d",result1); (*(*ptr+1))(result1); } int show() { int a = 65; return a++; } int showadd(int b)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-14-2048.jpg)

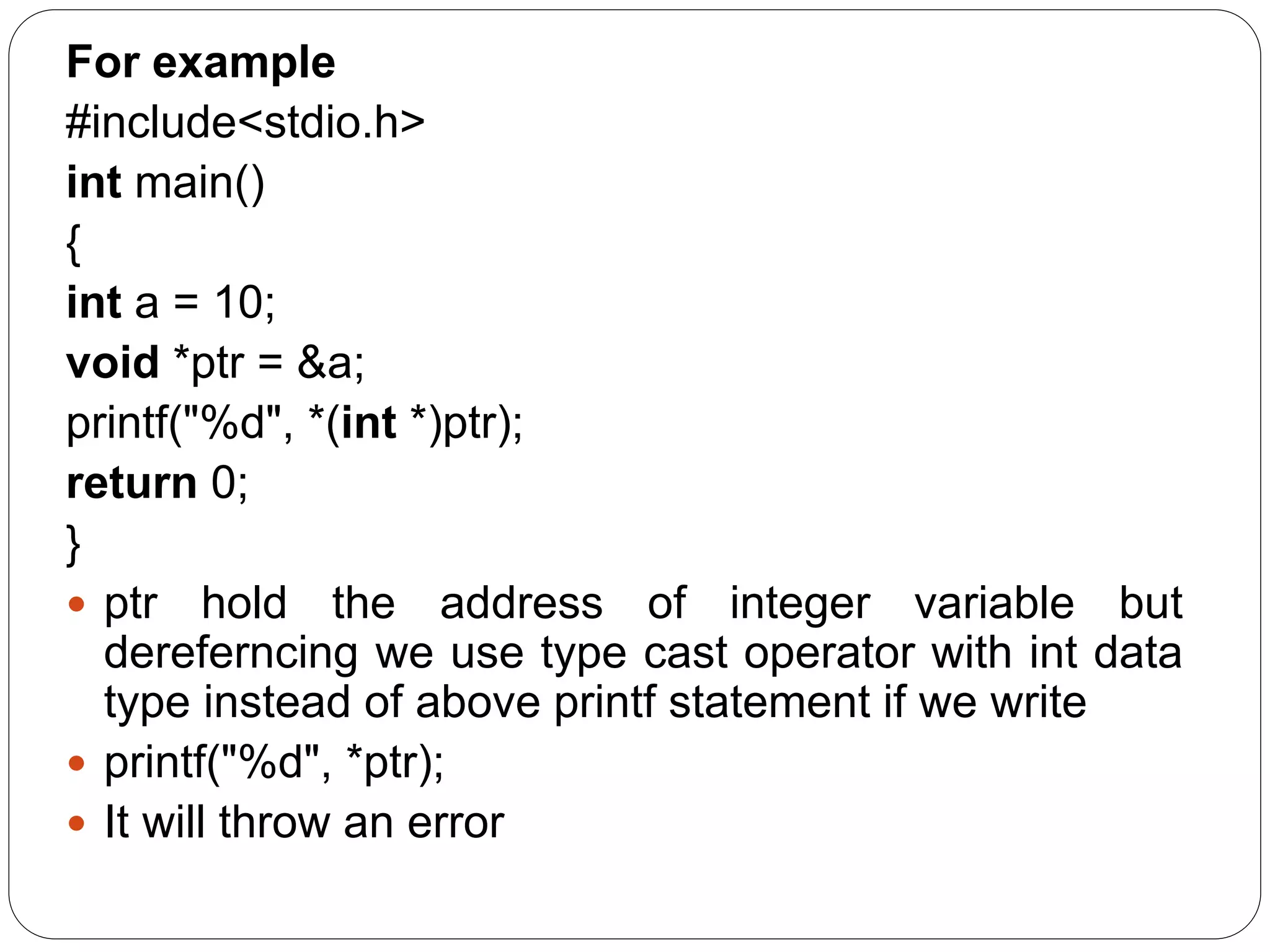
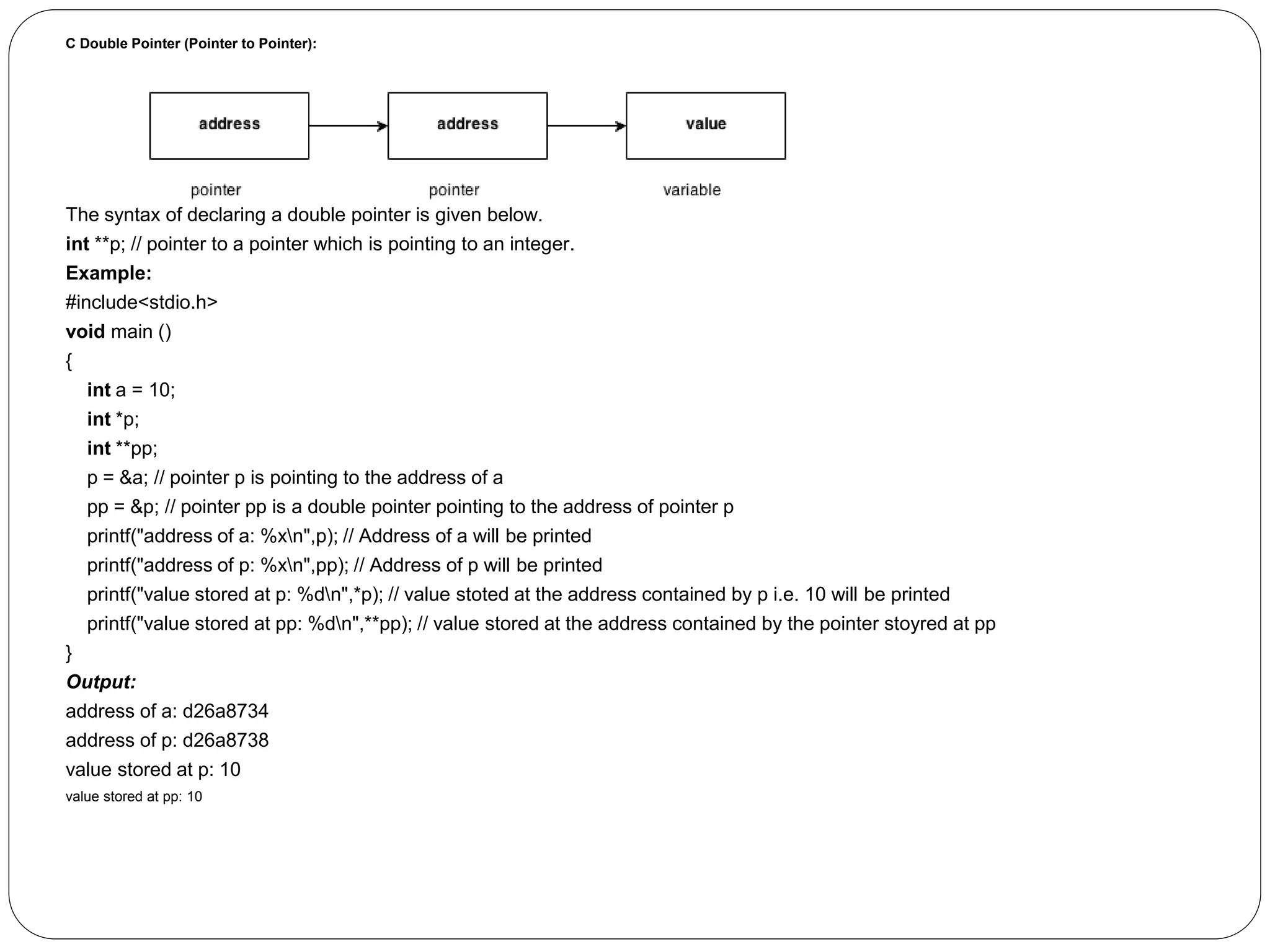

![Program: #include<stdio.h> void main () { char names[2][10],dummy; // 2-dimensioanal character array names is used to store the names of the students int roll_numbers[2],i; float marks[2]; for (i=0;i<3;i++) { printf("Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student %d",i+1); scanf("%s %d %f",&names[i],&roll_numbers[i],&marks[i]); scanf("%c",&dummy); // enter will be stored into dummy character at each iteration } printf("Printing the Student details ...n"); for (i=0;i<3;i++) { printf("%s %d %fn",names[i],roll_numbers[i],marks[i]); } } Output Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student 1Arun 90 91 Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student 2Varun 91 56 Enter the name, roll number, and marks of the student 3Sham 89 69 Printing the Student details... Arun 90 91.000000 Varun 91 56.000000 Sham 89 69.000000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-20-2048.jpg)
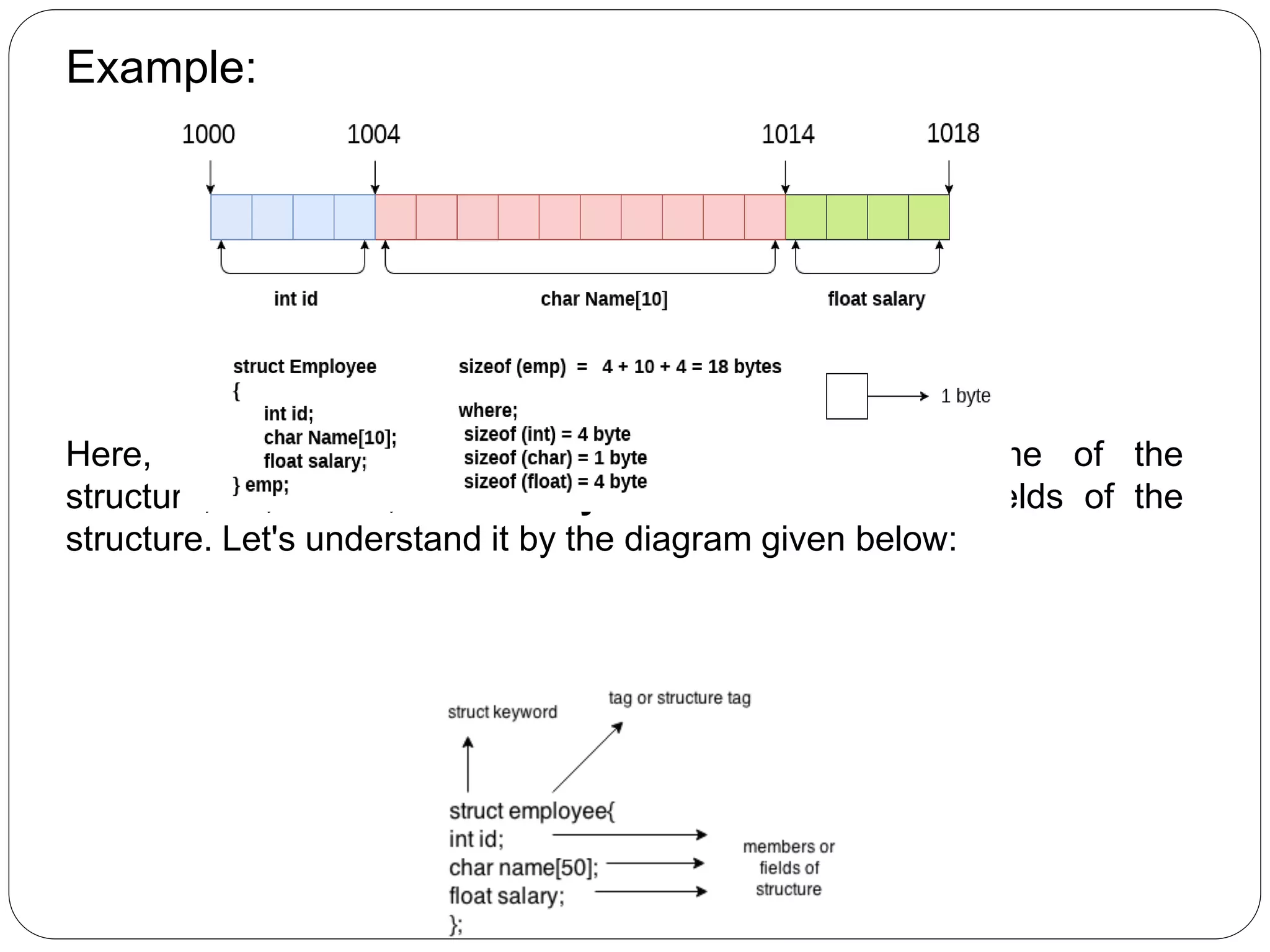
![What is Structure: Structure in c is a user-defined data type that enables us to store the collection of different data types. Each element of a structure is called a member. Structures ca; simulate the use of classes and templates as it can store various information The ,struct keyword is used to define the structure. Let's see the syntax to define the structure in c. struct structure_name { data_type member1; data_type member2; . . data_type memeberN; }; Let's see the example to define a structure for an entity employee in c. struct employee { int id; char name[20]; float salary; };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-21-2048.jpg)
![Declaring structure variable: We can declare a variable for the structure so that we can access the member of the structure easily. There are two ways to declare structure variable: 1. By struct keyword within main() function 2. By declaring a variable at the time of defining the structure. 1st way: Let's see the example to declare the structure variable by struct keyword. It should be declared within the main function. struct employee { int id; char name[50]; float salary; }; Now write given code inside the main() function. struct employee e1, e2; The variables e1 and e2 can be used to access the values stored in the structure. Here, e1 and e2 can be treated in the same way as the objects in C++ and Java. 2nd way: Let's see another way to declare variable at the time of defining the structure. struct employee { int id; char name[50]; float salary; }e1,e2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-23-2048.jpg)

![Let's see another example of the structure in C language to store many employees information. #include<stdio.h> #include <string.h> struct employee { int id; char name[50]; float salary; }e1,e2; //declaring e1 and e2 variables for structure int main( ) { //store first employee information e1.id=101; strcpy(e1.name, "Sonoo Jaiswal");//copying string into char array e1.salary=56000; //store second employee information e2.id=102; strcpy(e2.name, "James Bond"); e2.salary=126000; //printing first employee information printf( "employee 1 id : %dn", e1.id); printf( "employee 1 name : %sn", e1.name); printf( "employee 1 salary : %fn", e1.salary); //printing second employee information printf( "employee 2 id : %dn", e2.id); printf( "employee 2 name : %sn", e2.name); printf( "employee 2 salary : %fn", e2.salary); return 0; } Output: employee 1 id : 101 employee 1 name : Sonoo Jaiswal employee 1 salary : 56000.000000 employee 2 id : 102 employee 2 name : James Bond employee 2 salary : 126000.000000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-25-2048.jpg)
![Pass Structure to a Function By Value in C /* Passing Structure to a Function By Value */ #include <stdio.h> struct Student { char Student_Name[50]; float First_Year_Marks; float Second_Year_Marks; }; void PassBy_Value(struct Student Students); int main() { struct Student Student1; printf("nPlease Enter the Student Name n"); scanf("%s",&Student1.Student_Name); printf("nPlease Enter Student Inter First Year Marks n"); scanf("%f",&Student1.First_Year_Marks); printf("nPlease Enter Student Inter Second Year Marks n"); scanf("%f",&Student1.Second_Year_Marks); PassBy_Value(Student1); return 0; } void PassBy_Value(struct Student Students) { float Sum, Average; Sum = Students.First_Year_Marks + Students.Second_Year_Marks; Average = Sum/2; if(Average > 900) { printf("n %s is Eligible for Scholorship",Students.Student_Name); } else { printf("n %s is Not Eligible for Scholorship",Students.Student_Name); } } Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-27-2048.jpg)
![/* Passing Structure to function by reference */ #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> struct Lecturer { char Lecturer_Name[50]; int Total_Experience; int Experience_In_This_College; }; void PassBy_Reference(struct Lecturer *Lecturers); int main() { struct Lecturer Lecturer1; printf("nPlease Enter the Lecturer Name n"); scanf("%s",&Lecturer1.Lecturer_Name); printf("Please Enter Lecturers Total Years of Experiencen"); scanf("%d",&Lecturer1.Total_Experience); printf("Enter Lecturers Total Years of Experience in this Collegen"); scanf("%d",&Lecturer1.Experience_In_This_College); PassBy_Reference(&Lecturer1); printf("n Lecturer Name = %s", Lecturer1.Lecturer_Name); printf("n Lecturers Total Years of Experience = %d", Lecturer1.Total_Experience); printf("n Years of Experience in this College = %d", Lecturer1.Experience_In_This_College); return 0; } void PassBy_Reference(struct Lecturer *Lecturers) { strcpy(Lecturers->Lecturer_Name, "Tutorial Gateway"); Lecturers->Total_Experience = 5; Lecturers->Experience_In_This_College = 3; } OUTPUT: Pass Structure to a Function By Reference in C Output:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-28-2048.jpg)

![Example: 1. #include<stdio.h> 2. struct address 3. { 4. char city[20]; 5. int pin; 6. char phone[14]; 7. }; 8. struct employee 9. { 10. char name[20]; 11. struct address add; 12. }; 13. void main () 14. { 15. struct employee emp; 16. printf("Enter employee information?n"); 17. scanf("%s %s %d %s",emp.name,emp.add.city, &emp.add.pin, emp.add.phone); 18. printf("Printing the employee information....n"); 19. printf("name: %snCity: %snPincode: %dnPhone: %s",emp.name,emp.add.city,emp.a dd.pin,emp.add.phone); 20. } Output Enter employee information? Arun Delhi 110001 1234567890 Printing the employee information.... name: Arun City: Delhi Pincode: 110001 Phone: 1234567890](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-30-2048.jpg)
![The structure can be nested in the following ways. By separate structure By Embedded structure 1) Separate structure: Here, we create two structures, but the dependent structure should be used inside the main structure as a member. Consider the following example. struct Date { int dd; int mm; int yyyy; }; struct Employee { int id; char name[20]; struct Date doj; }emp1; As you can see, doj (date of joining) is the variable of type Date. Here doj is used as a member in Employee structure. In this way, we can use Date structure in many structures. 2) Embedded structure: The embedded structure enables us to declare the structure inside the structure. Hence, it requires less line of codes but it can not be used in multiple data structures. Consider the following example. struct Employee { int id; char name[20]; struct Date {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-31-2048.jpg)
![Passing structure to function: Program: #include<stdio.h> struct address { char city[20]; int pin; char phone[14]; }; struct employee { char name[20]; struct address add; }; void display(struct employee); void main () { struct employee emp; printf("Enter employee information?n"); scanf("%s %s %d %s",emp.name,emp.add.city, &emp.add.pin, emp.add.phone); display(emp); } void display(struct employee emp) { printf("Printing the details....n"); printf("%s %s %d %s",emp.name,emp.add.city,emp.add.pin,emp.add.phone); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-32-2048.jpg)

![Defining union: The union keyword is used to define the union. Let's see the syntax to define union in c. union union_name { data_type member1; data_type member2; . . data_type memeberN; }; Example to define union for an employee in c. union employee { int id; char name[50]; float salary; };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-34-2048.jpg)
![Example Program: 1. #include <stdio.h> 2. #include <string.h> 3. union employee 4. { int id; 5. char name[50]; 6. }e1; //declaring e1 variable for union 7. int main( ) 8. { 9. //store first employee information 10. e1.id=101; 11. strcpy(e1.name, "Sonoo Jaiswal");//copying string into char array 12. //printing first employee information 13. printf( "employee 1 id : %dn", e1.id); 14. printf( "employee 1 name : %sn", e1.name); 15. return 0; 16. } Output: employee 1 id : 1869508435 employee 1 name : Sonoo Jaiswal](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ppt4-190810161800/75/C-Programming-Unit-4-35-2048.jpg)