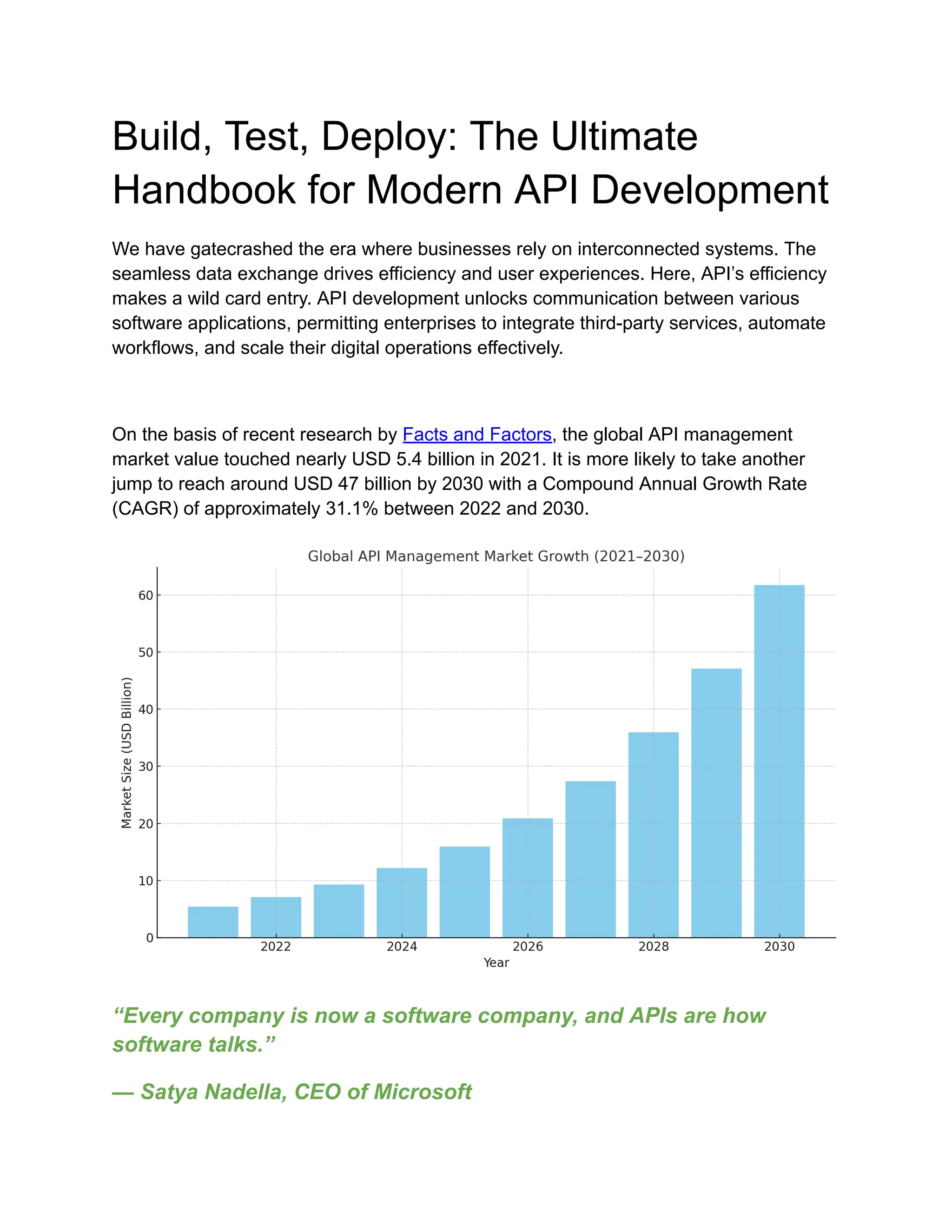
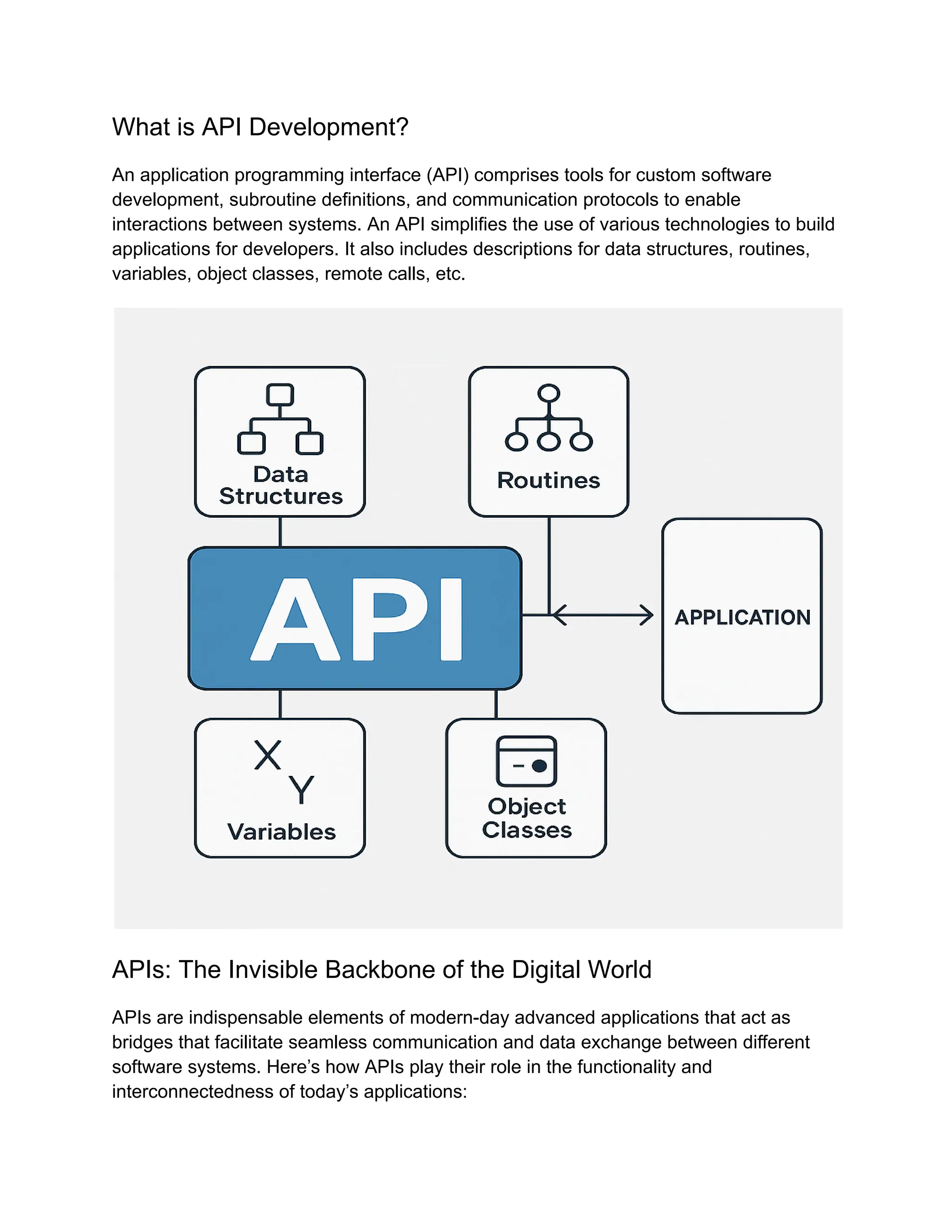
Discover the complete guide to modern API development with our ultimate handbook covering every stage—build, test, and deploy. Learn best practices for designing scalable, secure, and efficient APIs that power seamless integrations and high-performance applications. This handbook offers step-by-step strategies for API design, rigorous testing methods, version control, and smooth deployment processes using the latest tools and frameworks. Whether you’re developing RESTful APIs, GraphQL, or microservices, this resource helps you streamline workflows, ensure reliability, and maintain security throughout the API lifecycle. Perfect for developers and businesses aiming to master API development in today’s fast-paced digital environment.