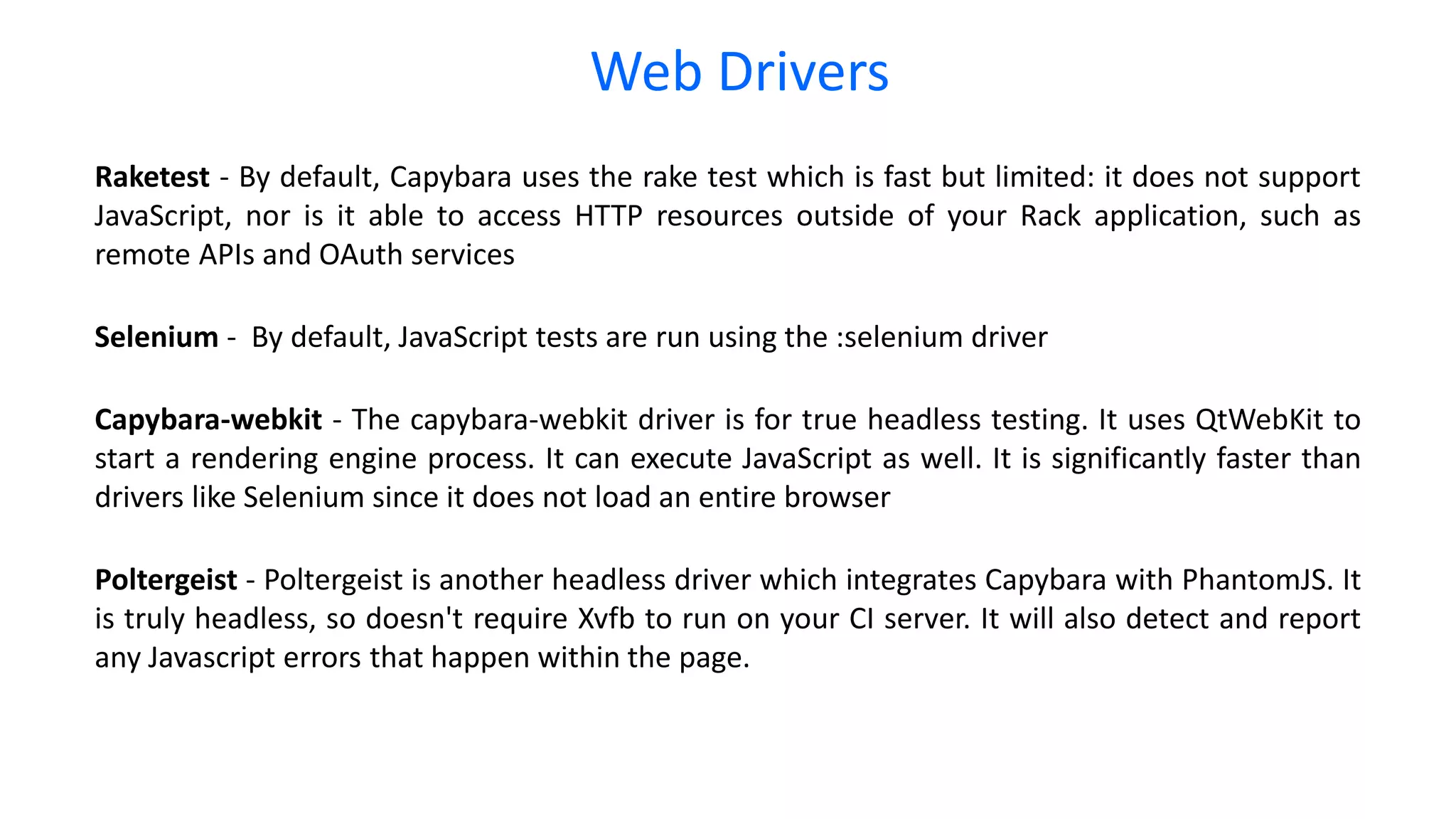
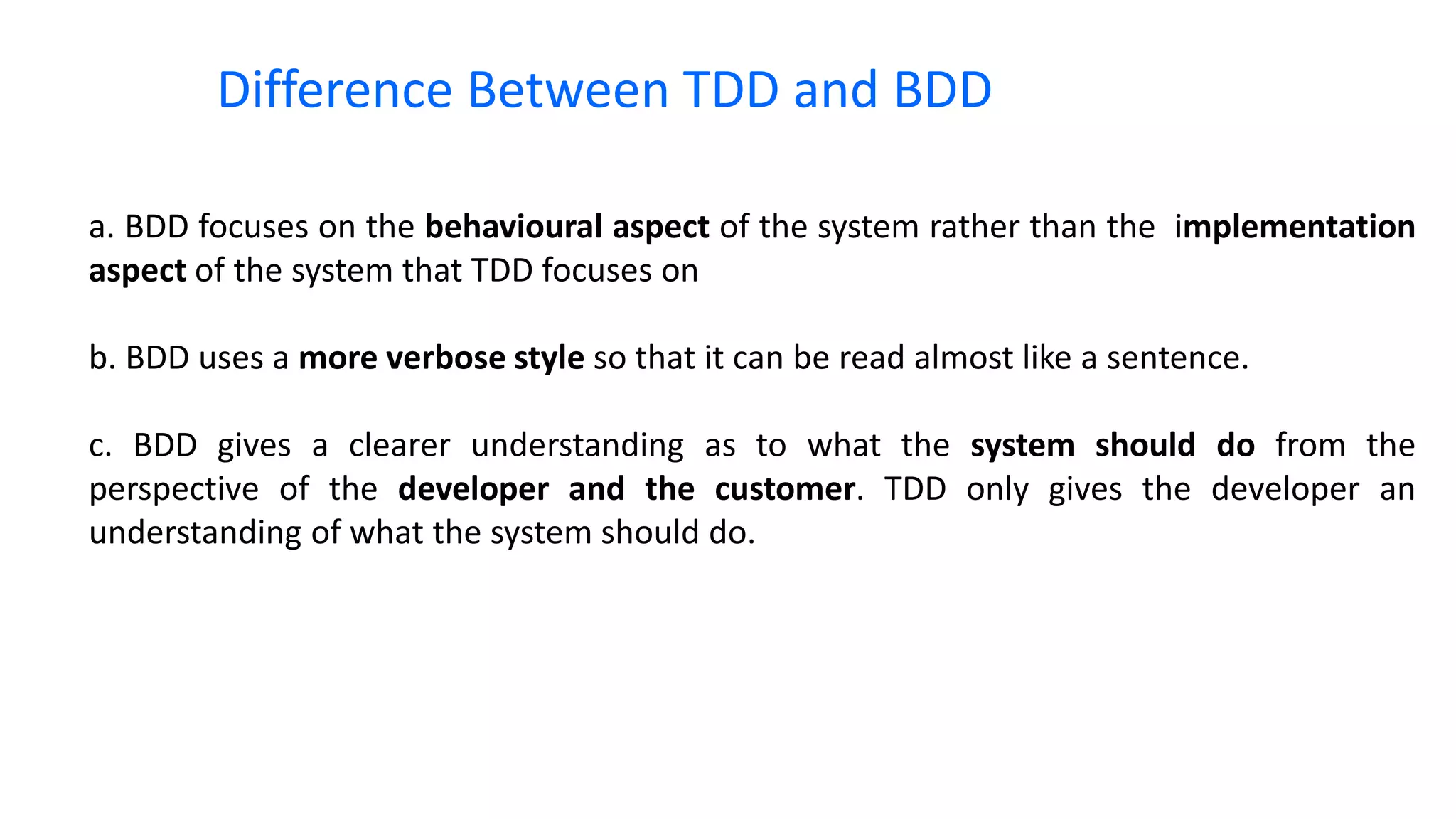
This document provides an overview of behavioural testing for Ruby on Rails applications at scale using RSpec and Cucumber. It discusses unit, integration and acceptance testing. It then covers the Test Driven Development (TDD) and Behaviour Driven Development (BDD) approaches. The rest of the document explains how to implement testing with RSpec, Shoulda-Matchers, Factory Girl, Cucumber, Gherkin and Capybara. It also discusses different web drivers that can be used like Rack Test, Selenium, Capybara-webkit and Poltergeist.






![Rspec Example require 'spec_helper' describe User do describe "firstname validation" do context "firstname is present" do before(:each) do @user = User.new(firstname: "satheesh") end it "does not add an error on the 'firstname' attribute" do @user.valid? expect(@user.errors[:firstname].size).to eq(0) end end end end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rspecandcucumber-210313153725/75/Behavioural-Testing-Ruby-Rails-Apps-Scale-Rspec-Cucumber-9-2048.jpg)