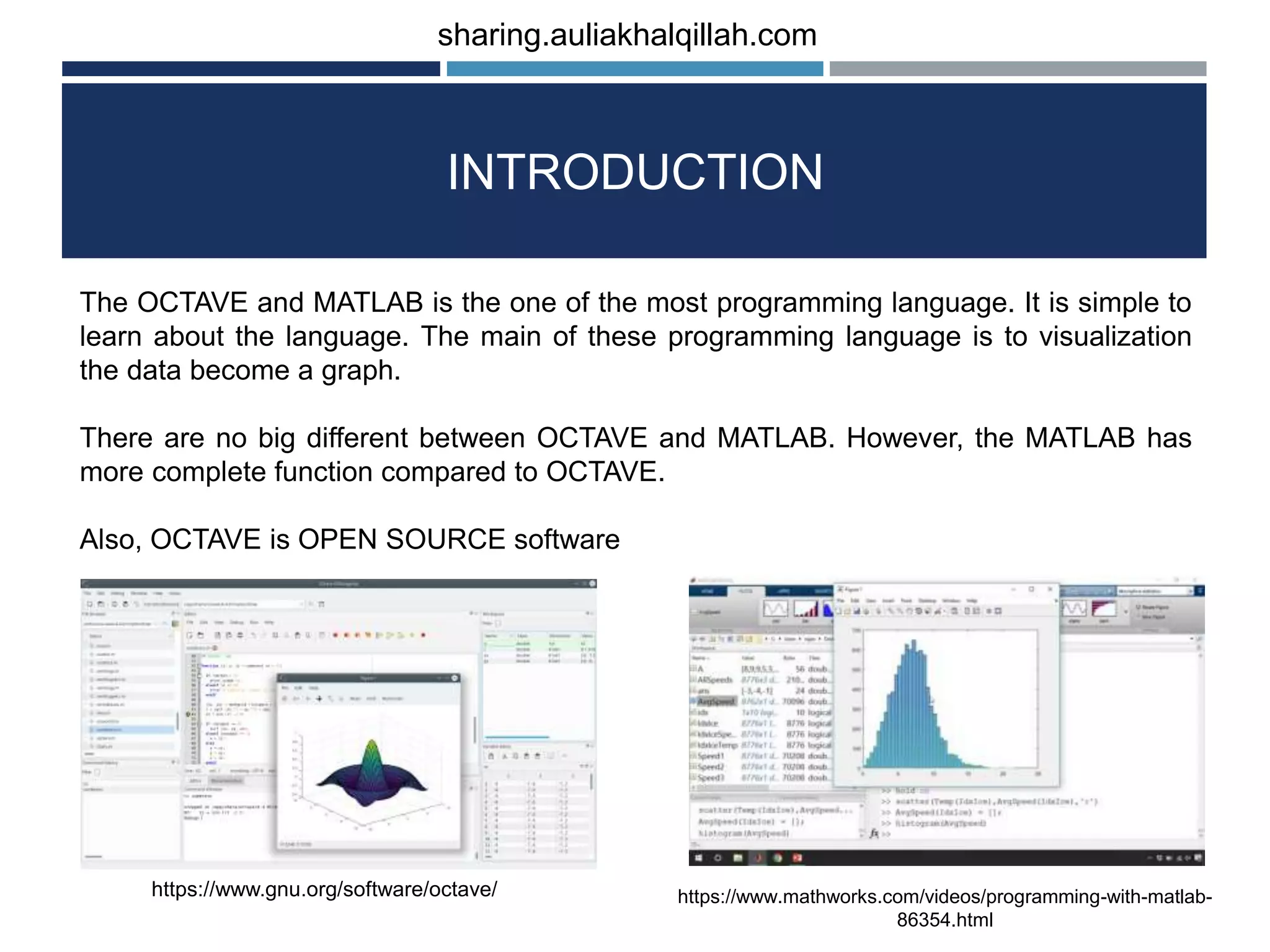
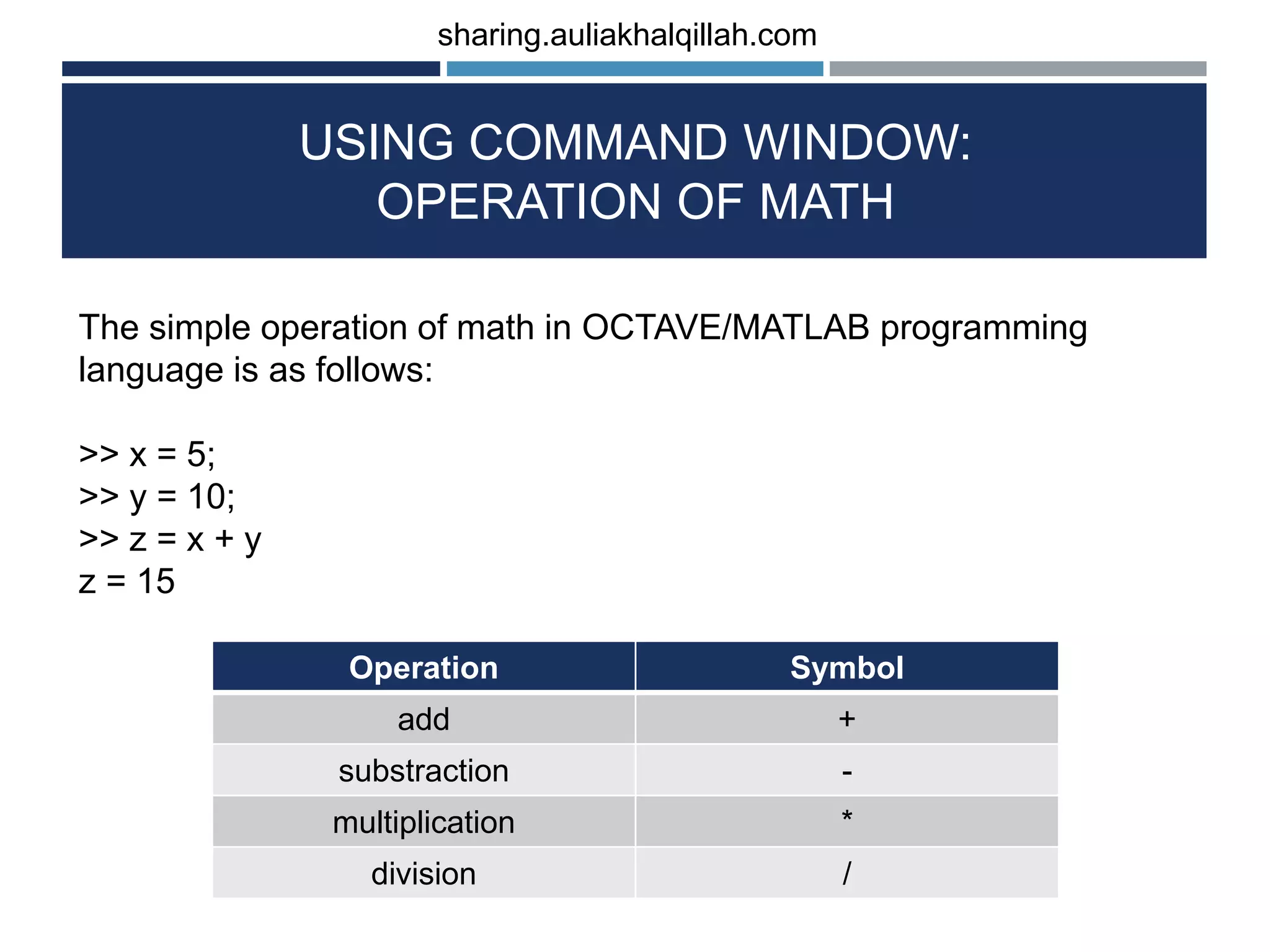
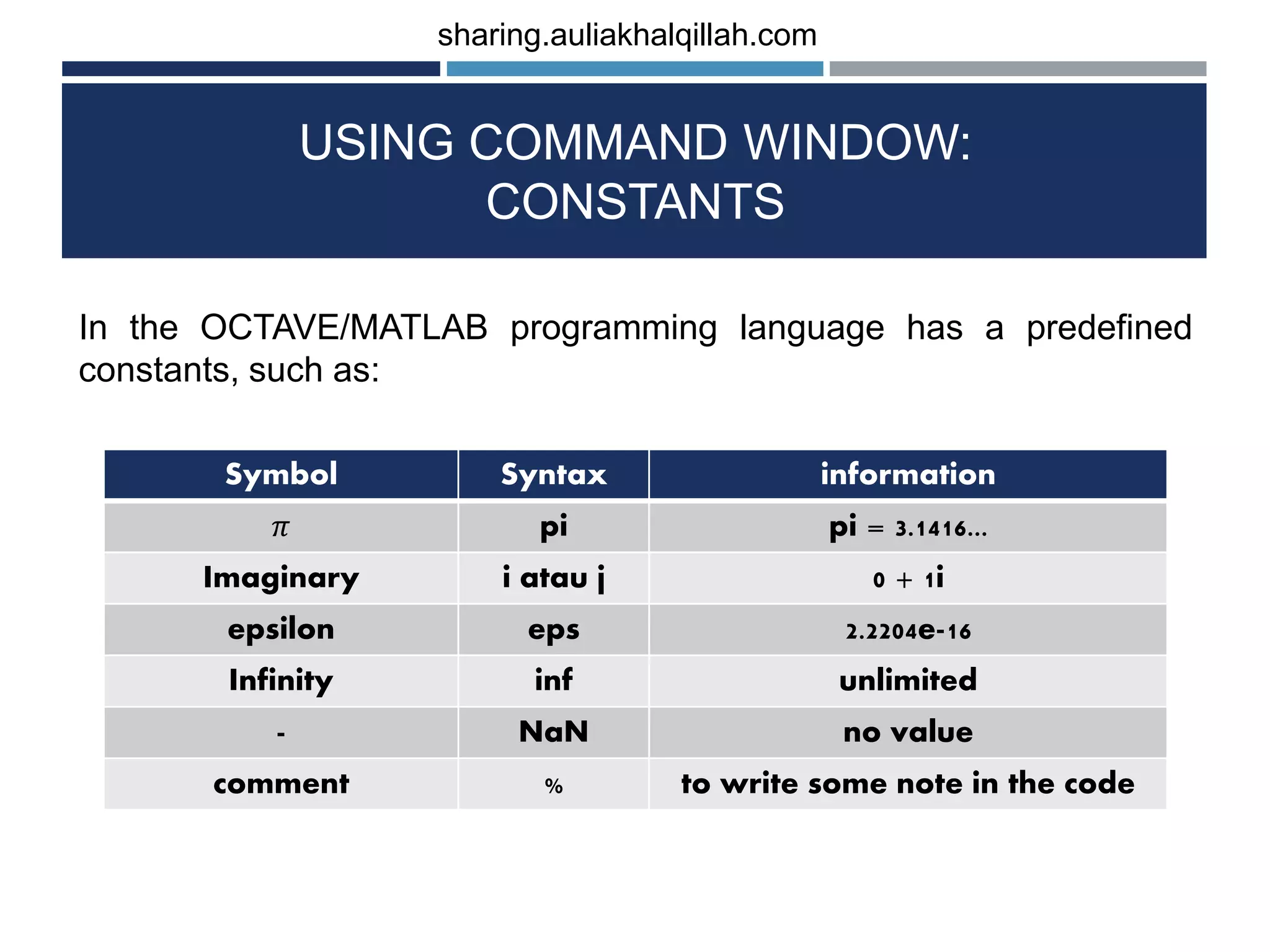
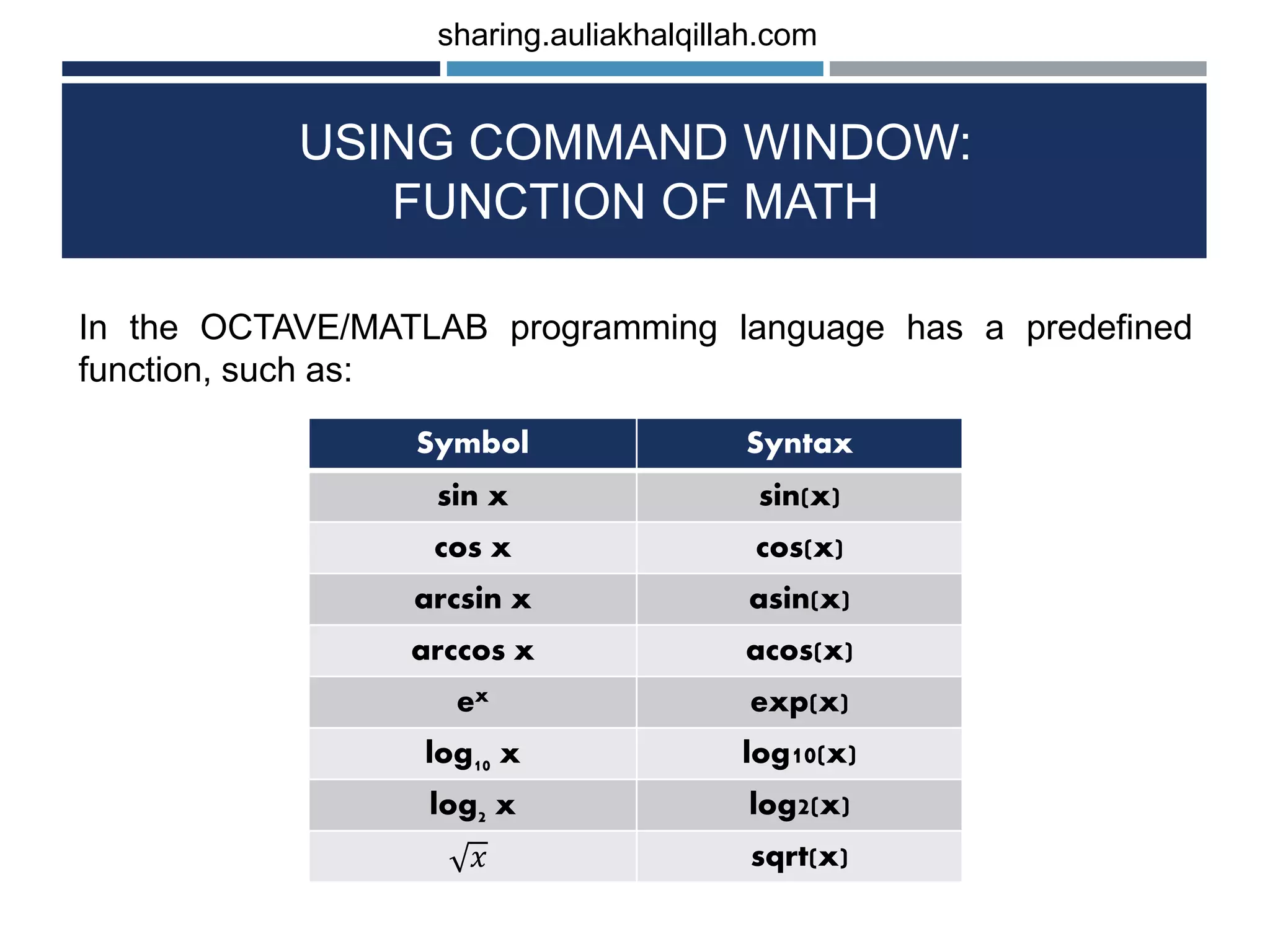
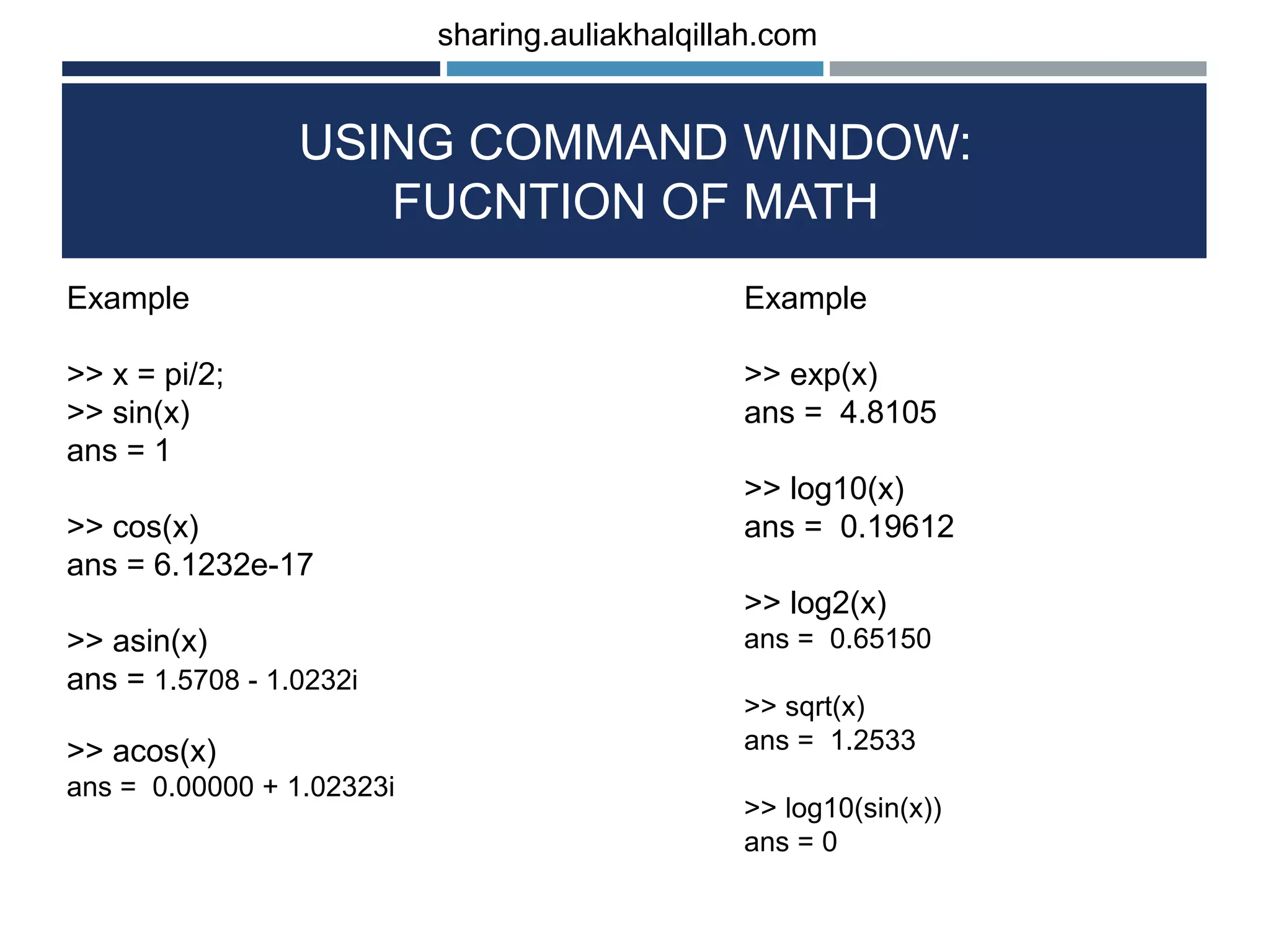
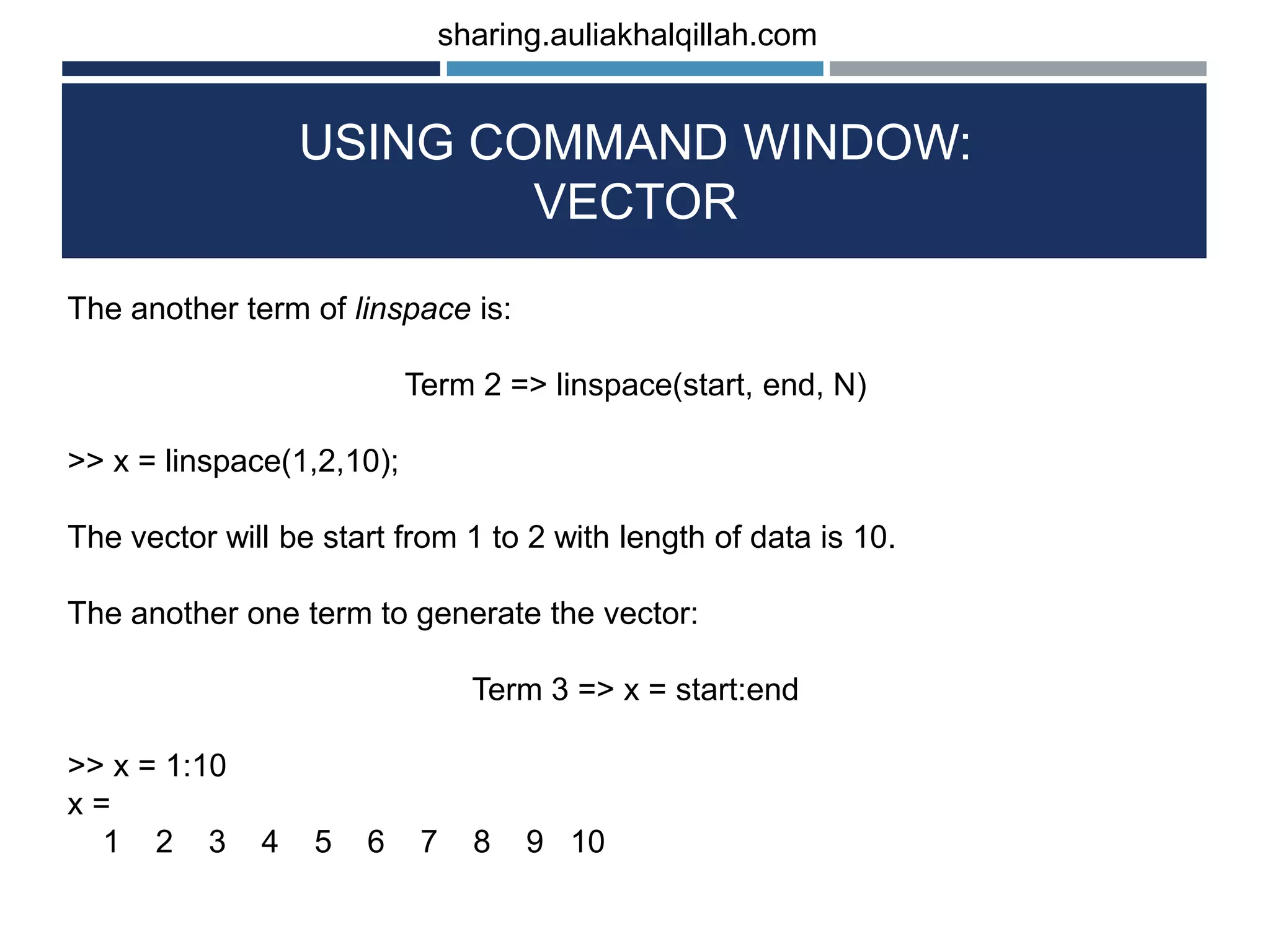
The document provides an introduction to the basics of programming in Octave/MATLAB. It discusses key aspects such as variables, vectors, matrices, built-in math functions, and basic operations. The programming can be done using the command window or by writing full scripts. Some key points covered include generating vectors using functions like linspace and colon operator, indexing and selecting elements of matrices, and performing basic arithmetic operations on vectors and matrices.




![USING COMMAND WINDOW: VECTOR >> x = [1 2] % Term 1 x = 1 2 >> x = [1;2] % Term 2 x = 1 2 Term 1 have the output horizontally or as the row Term 2 have the output vertically or as the column sharing.auliakhalqillah.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofoctave-matlabprogramminglanguage-190113043216/75/Basic-of-octave-matlab-programming-language-10-2048.jpg)
![USING COMMAND WINDOW: VECTOR If you want to make the vector (e.g. 1, 2, 3, ...., etc), you can type the command as follows: >> x = [1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10] % Row vector x = 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 >> x = [1;2;3;4;5] % Column vector x = 1 2 3 4 5 sharing.auliakhalqillah.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofoctave-matlabprogramminglanguage-190113043216/75/Basic-of-octave-matlab-programming-language-11-2048.jpg)


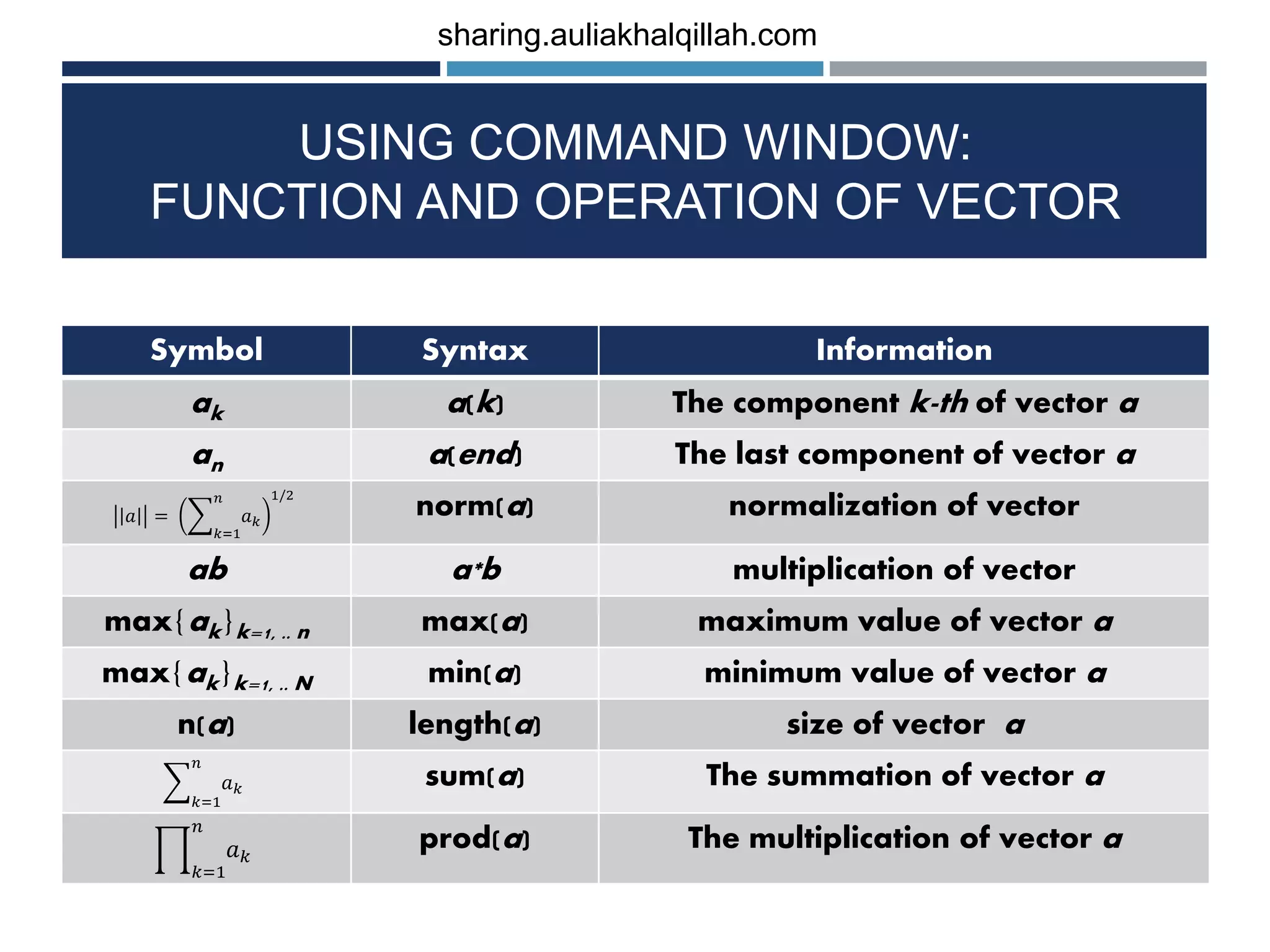
![USING COMMAND WINDOW: FUNCTION AND OPERATION OF VECTOR Symbol Syntax Information 𝑘=1 𝑛 𝑎 𝑘 𝑏 𝑘 dot(a,b) dot product between vector a and b (a1b1, ....., anbn) a.*b multiplication between components Example: >> x = [3 2 5]; >> y = [4 1 6]; >> length(x) ans = 3 >> length(y) ans = 3 Example: >> norm(x) ans = 6.1644 >> dot(x,y) ans = 44 >> z = x.*y z = 12 2 30 Example >> max(x) ans = 5 >> max(y) ans = 6 sharing.auliakhalqillah.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofoctave-matlabprogramminglanguage-190113043216/75/Basic-of-octave-matlab-programming-language-16-2048.jpg)
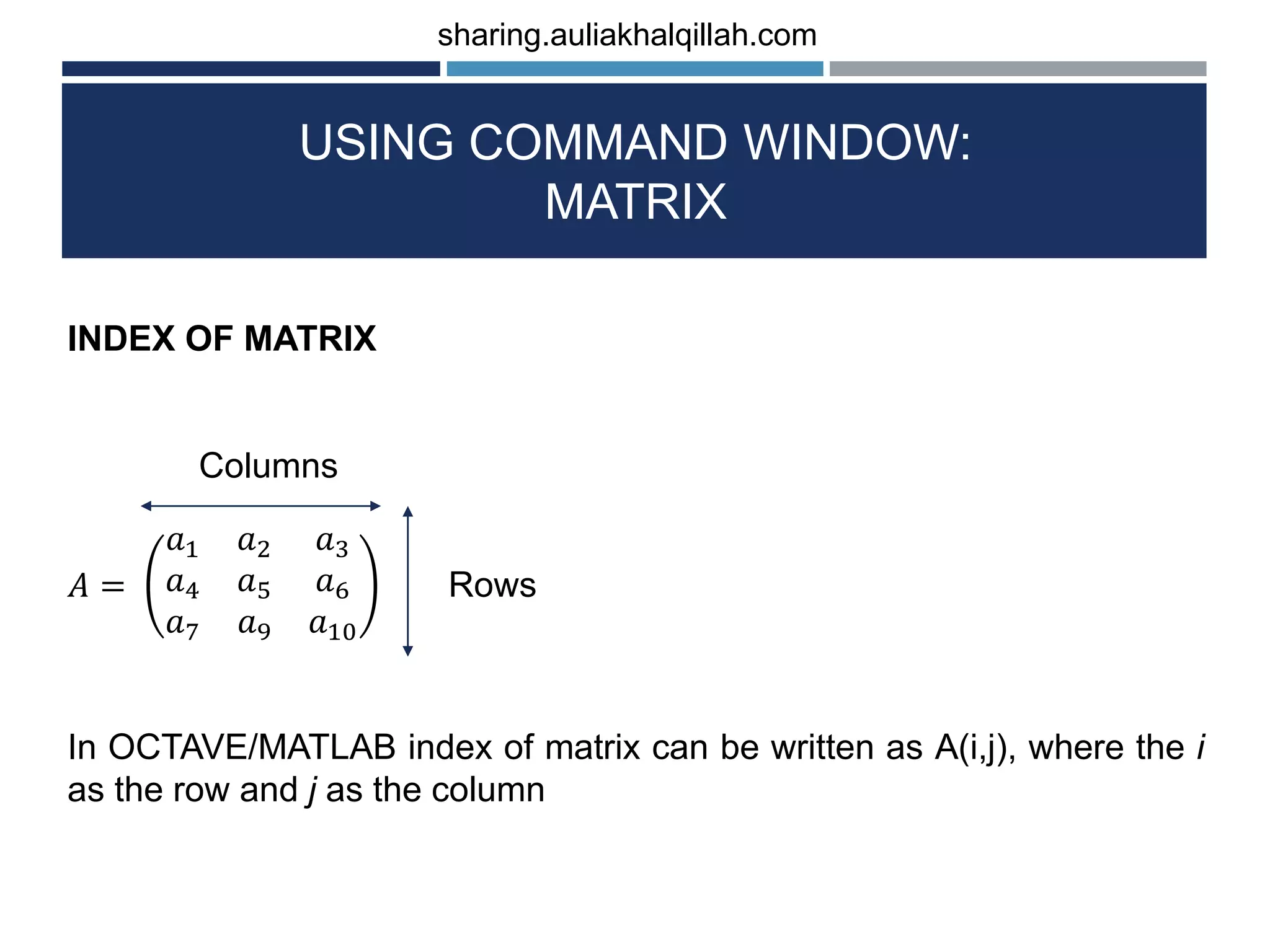
![USING COMMAND WINDOW: MATRIX To produce the matrix, you can type: >> x = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9] x = 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 The output is the example of matrix with size 3 x 3. The sign of (;) as the new row for the matrix. sharing.auliakhalqillah.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofoctave-matlabprogramminglanguage-190113043216/75/Basic-of-octave-matlab-programming-language-17-2048.jpg)
![USING COMMAND WINDOW: MATRIX EXAMPLE >> A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9] A = 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 If you want to take the element from the third row and the second column of the matrix A, you can type: >> AA = A(3,2) AA = 8 EXAMPLE >> A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9] A = 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 If you want to take the element from the first column, you can type: >> AA = A(:,1) AA = 1 4 7 sharing.auliakhalqillah.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofoctave-matlabprogramminglanguage-190113043216/75/Basic-of-octave-matlab-programming-language-19-2048.jpg)
![PENGGUNAAN COMMAND WINDOW: MATRIKS EXAMPLE >> A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9] A = 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 If you want to take the element from first row and second row, you can type: >> AA = A(1:2,:) AA = 1 2 3 4 5 6 EXAMPLE >> A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9] A = 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 If you want to take the element second column and third column, you can type: >> AA = A(:,2:3) AA = 2 3 5 6 8 9 sharing.auliakhalqillah.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofoctave-matlabprogramminglanguage-190113043216/75/Basic-of-octave-matlab-programming-language-20-2048.jpg)
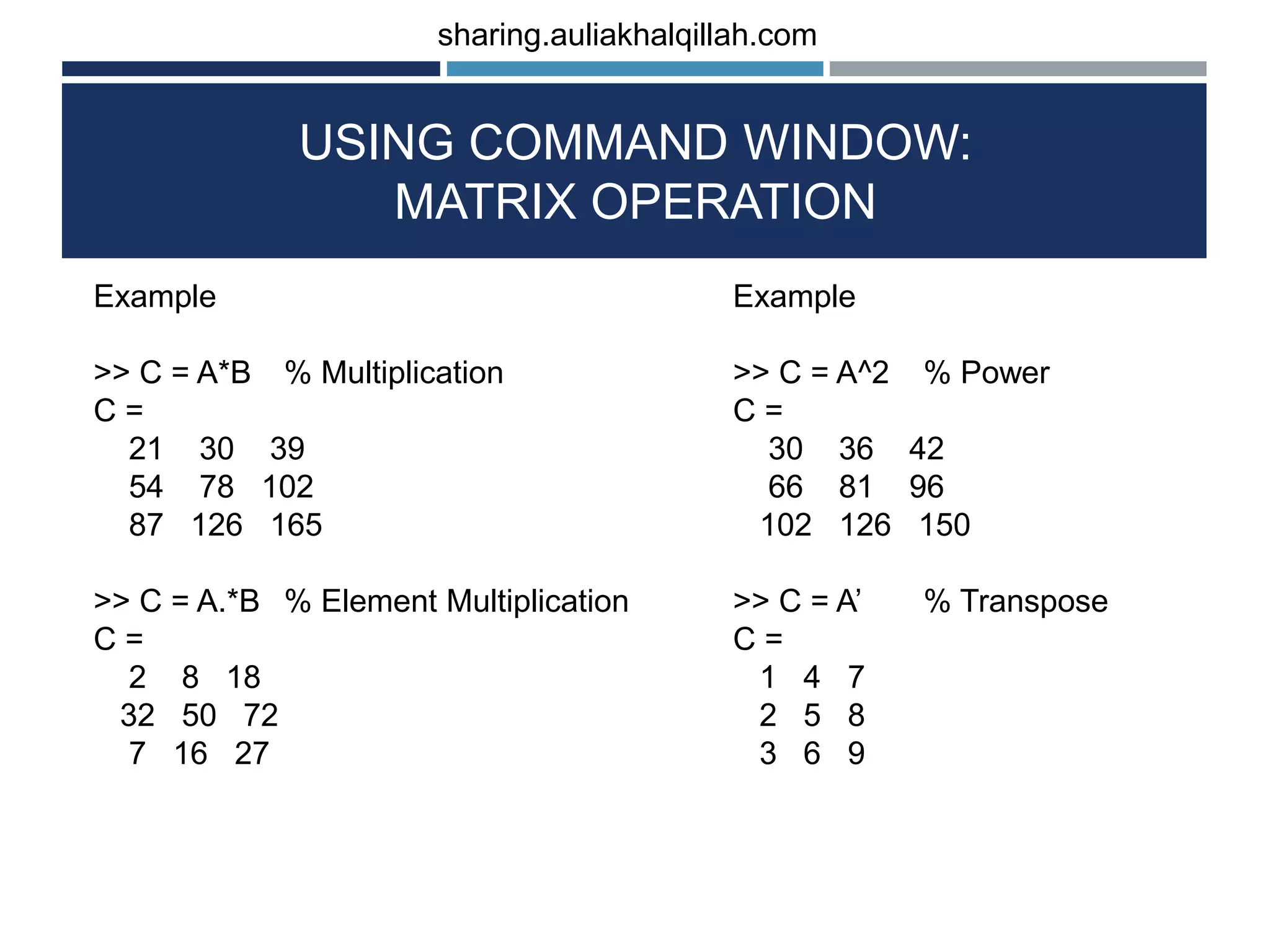
![USING COMMAND WINDOW: MATRIX OPERATION The operation of math in matrix as follows: ADDITION (+), SUBSTRACTION(-), MULTIPLICATION (*), MULTIPLICATION BETWEEN ELEMENT(.*), POWER (^), TRANSPOSE (‘), LEFT DIVISION (), RIGHT DIVISION (/). EXAMPLE >> A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9]; >> B = [2 4 6;8 10 12; 1 2 3]; >> C = A+B % Add C = 3 6 9 12 15 18 8 10 12 >> C = A-B % Substrac C = -1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 6 6 6 sharing.auliakhalqillah.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofoctave-matlabprogramminglanguage-190113043216/75/Basic-of-octave-matlab-programming-language-21-2048.jpg)
![USING COMMAND WINDOW: MATRIX OPERATION LEFT DIVISION () => C = AB = A-1B RIGHT DIVISION (/) => C = A/B = AB-1 Example: >> A = [1 2 3;4 5 6;7 8 9]; >> B = [2 4 6;8 10 12; 1 2 3]; >> C = AB % LEFT DIVISION C = -2.305556 -3.611111 -4.916667 -0.055556 -0.111111 -0.166667 2.194444 3.388889 4.583333 sharing.auliakhalqillah.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basicofoctave-matlabprogramminglanguage-190113043216/75/Basic-of-octave-matlab-programming-language-23-2048.jpg)
