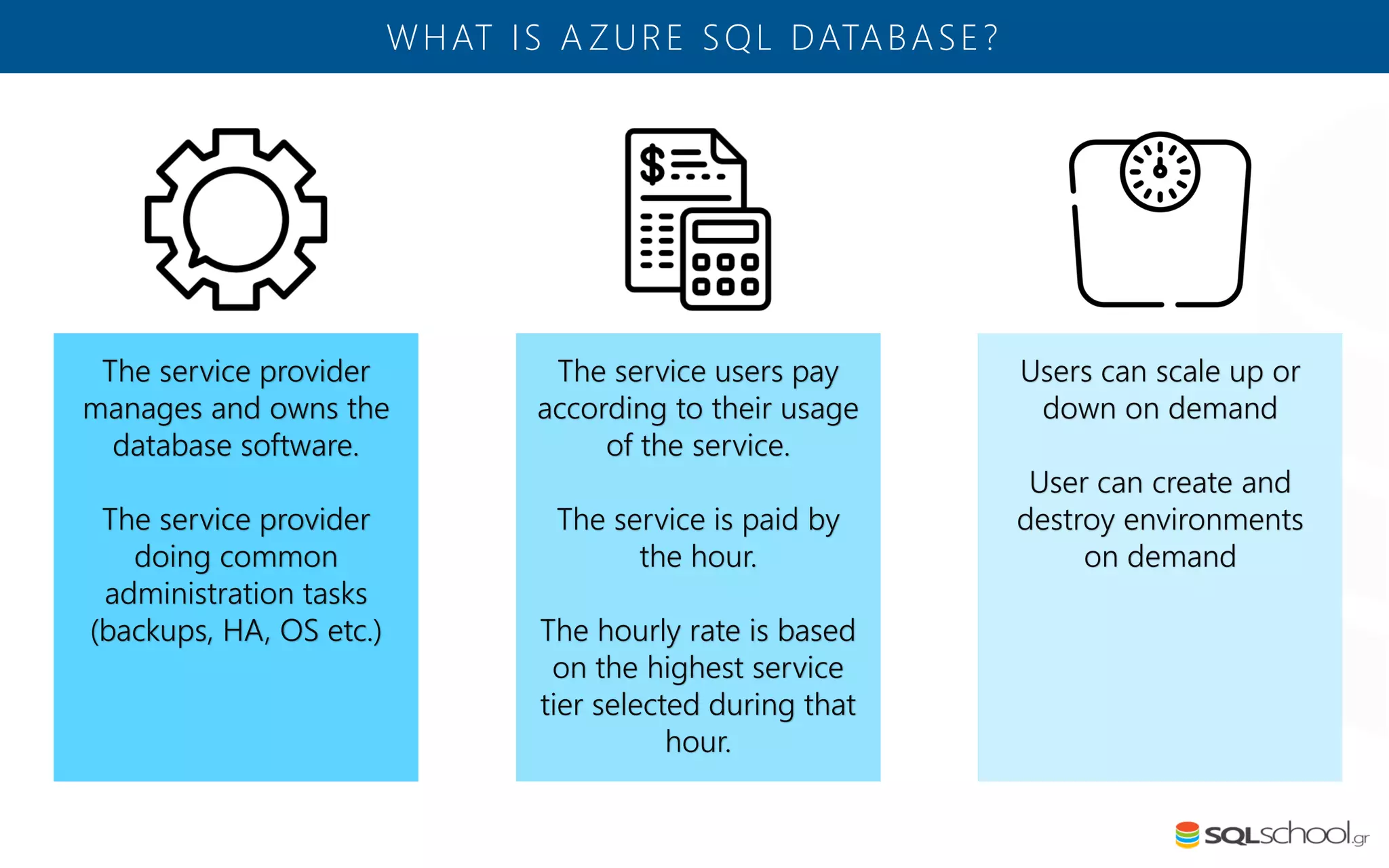
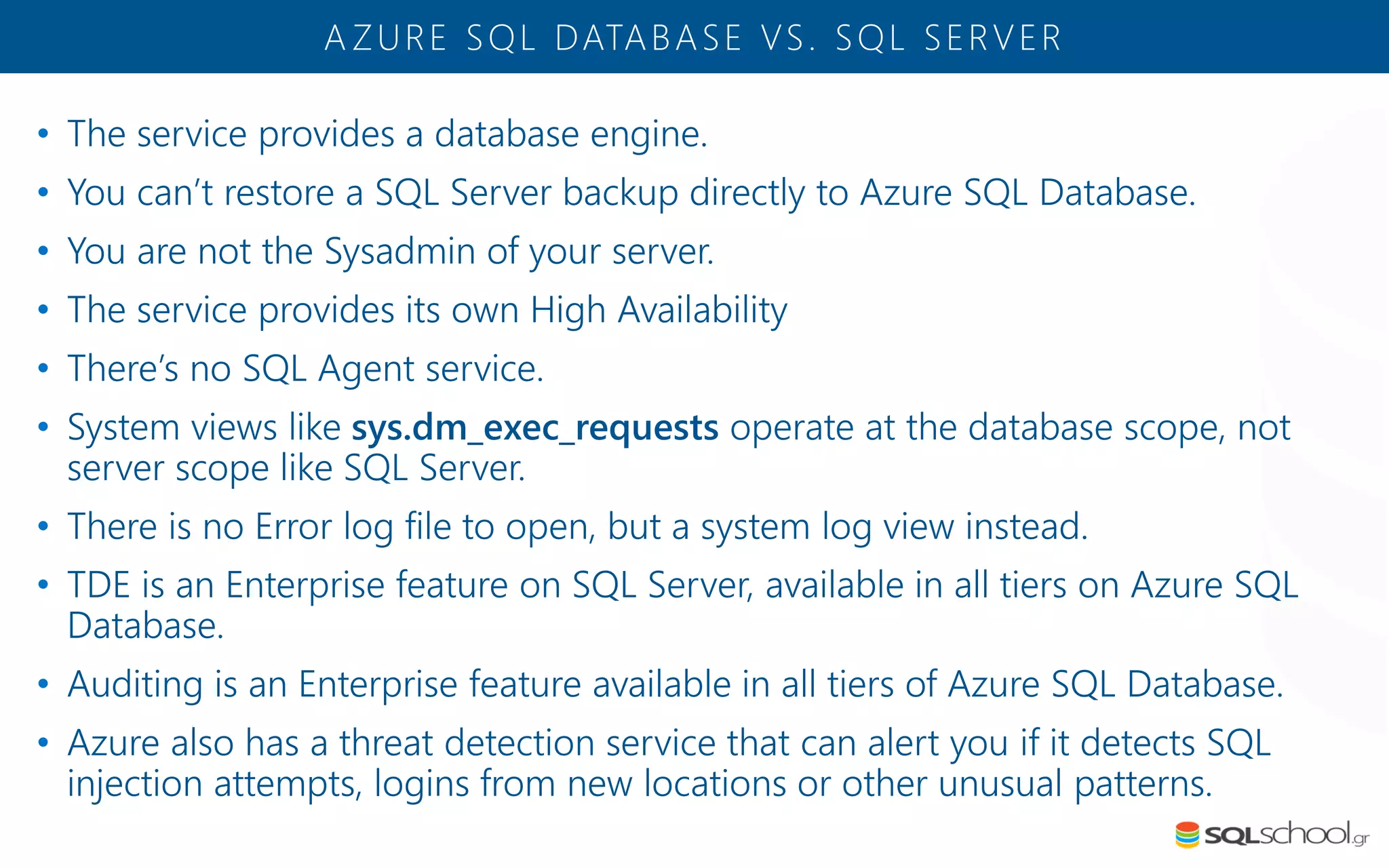
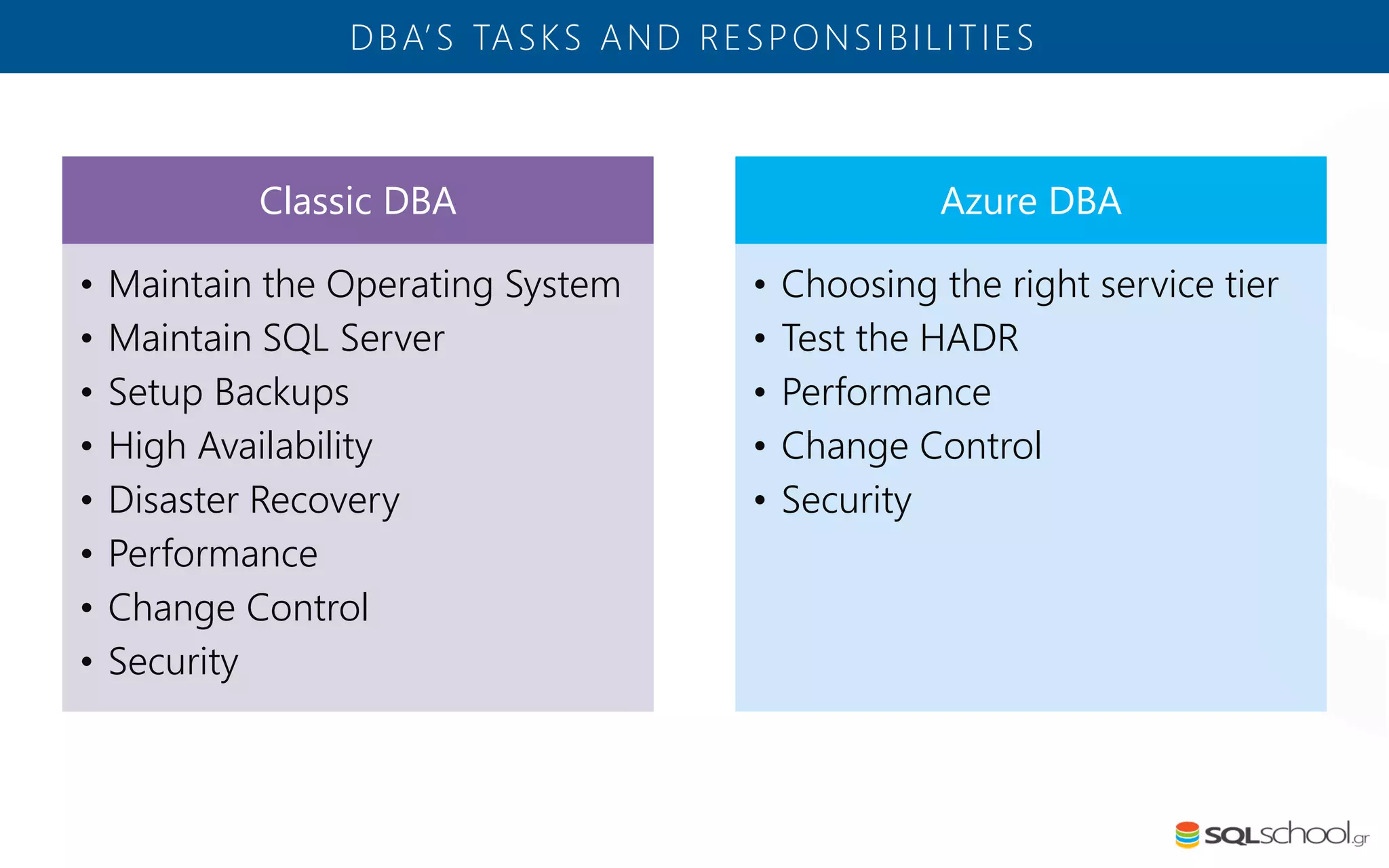
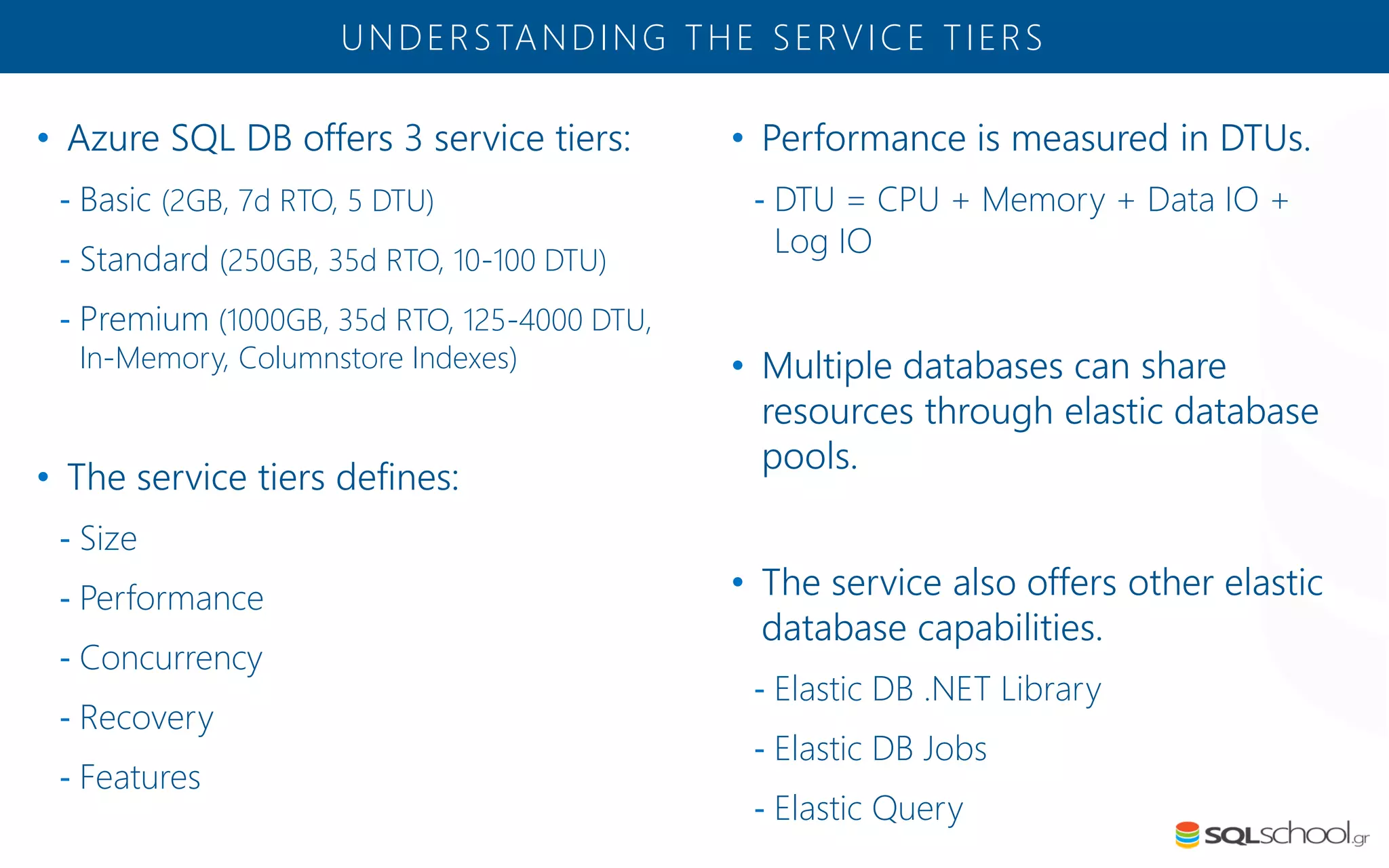
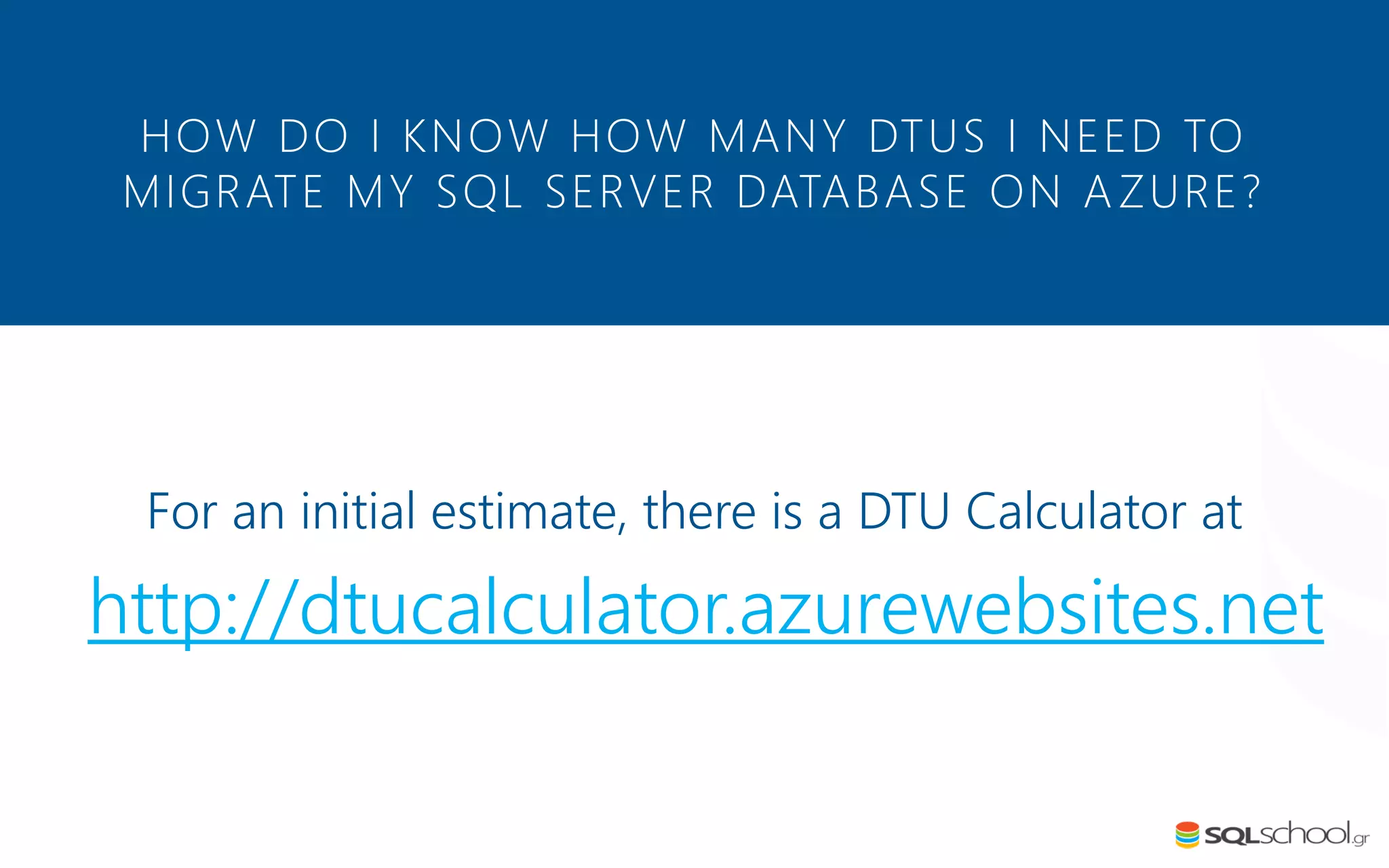
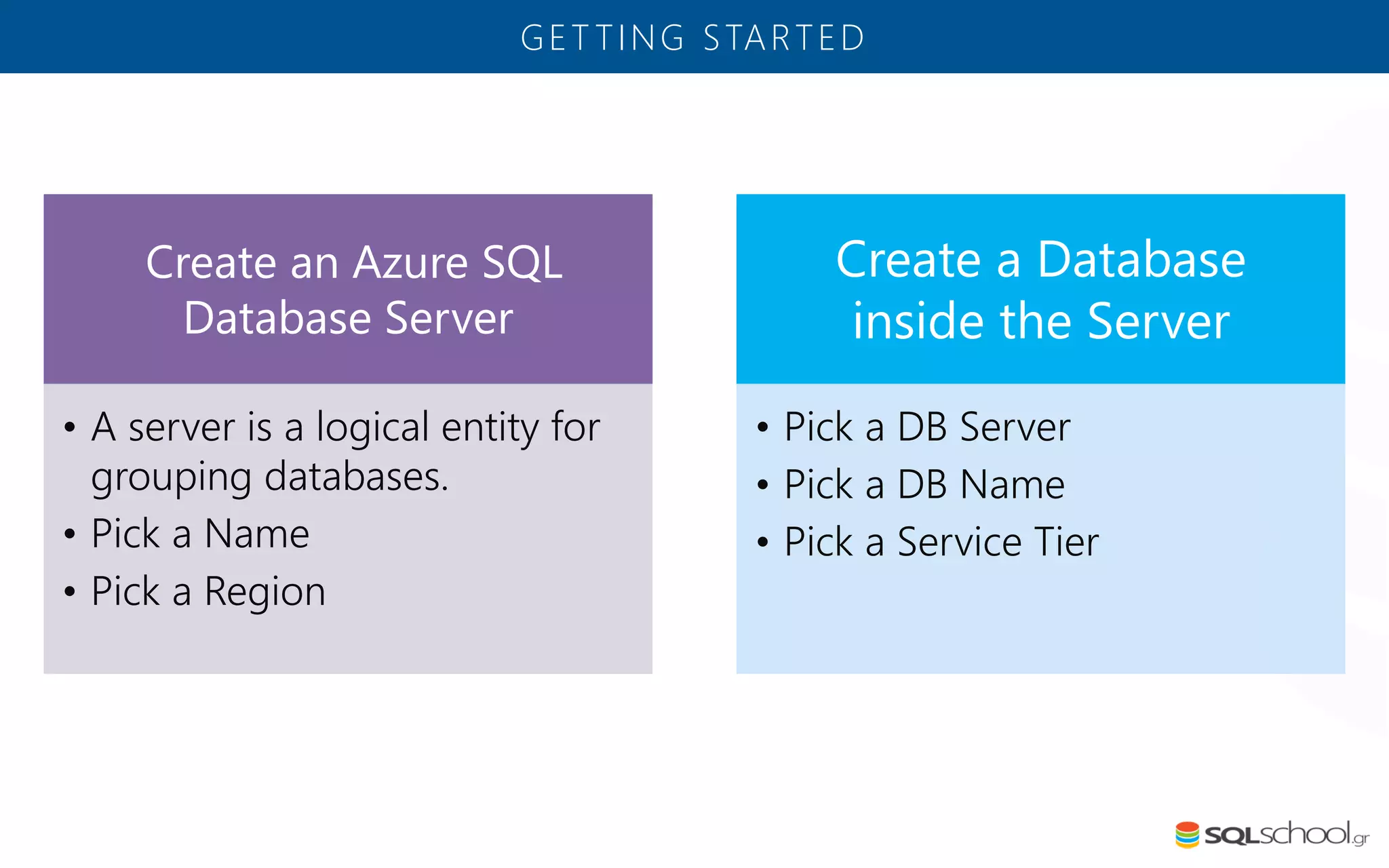
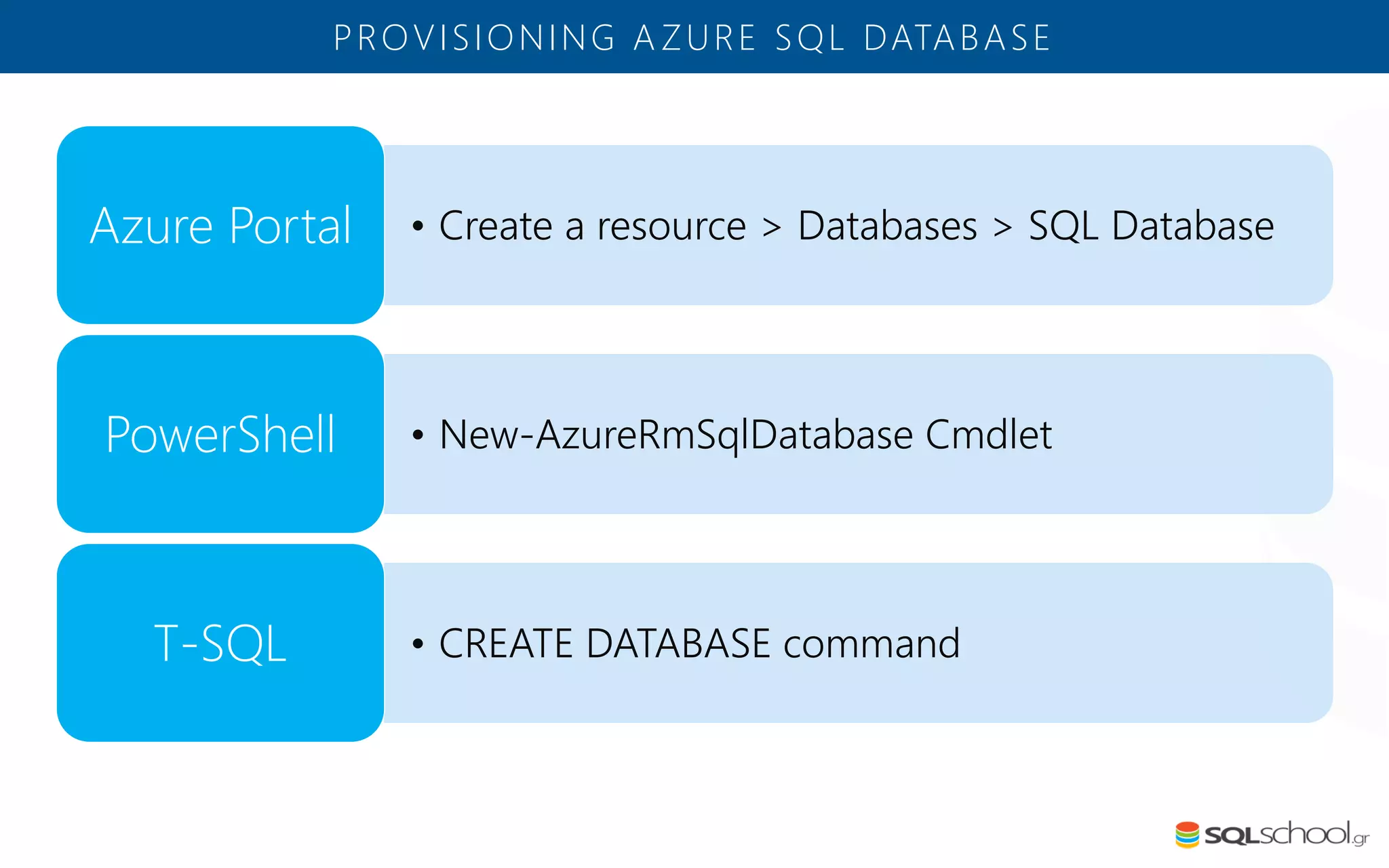
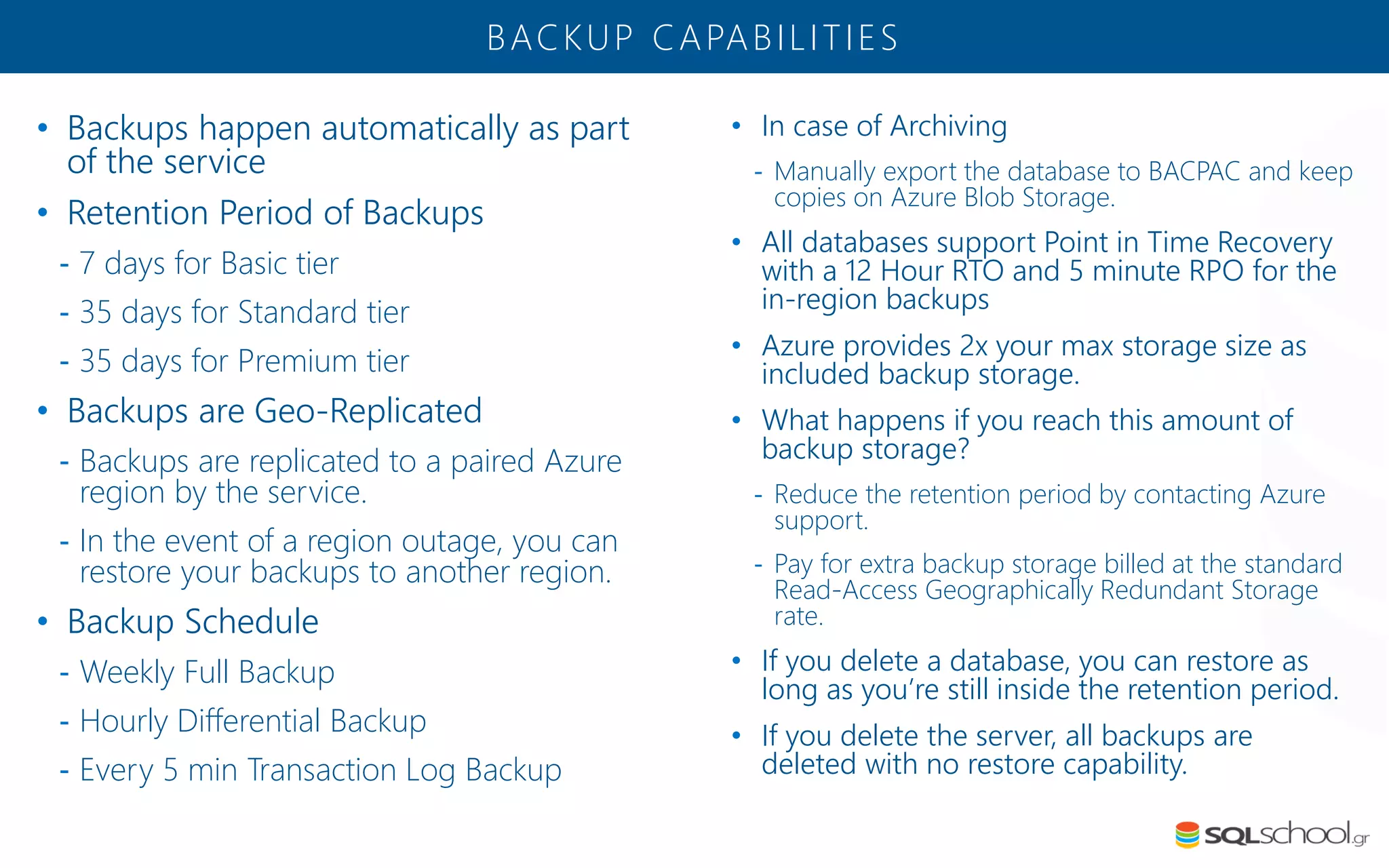
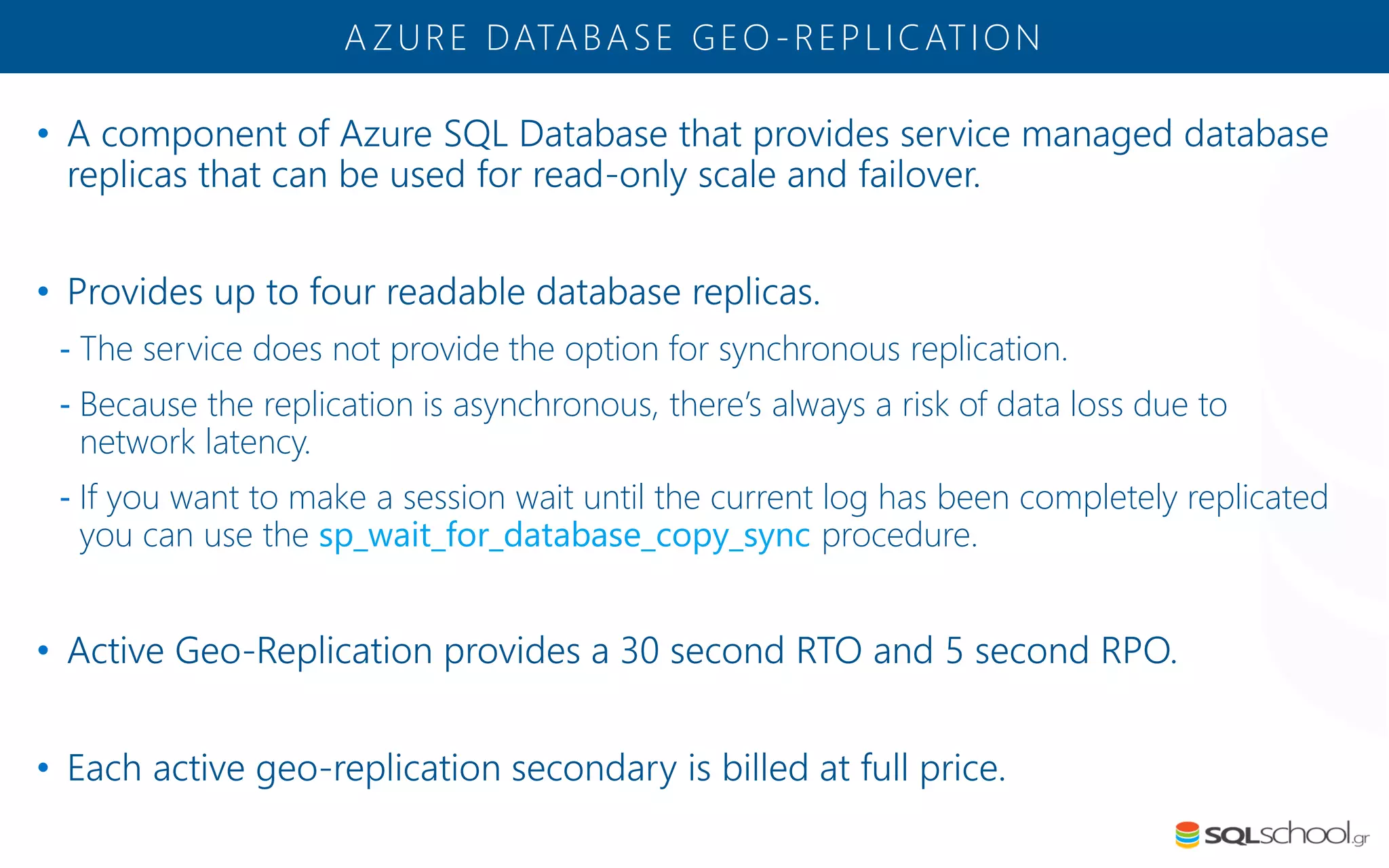
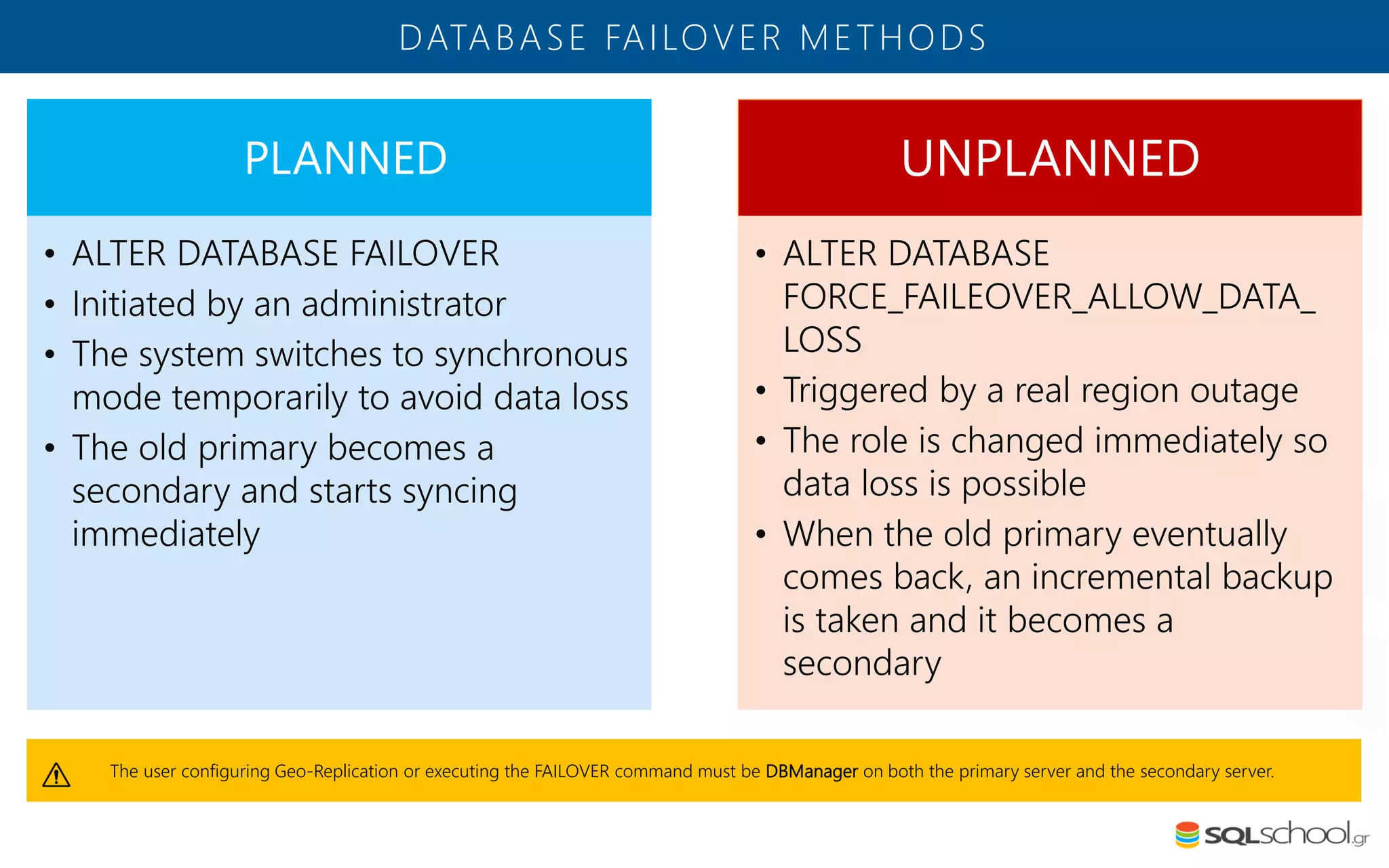
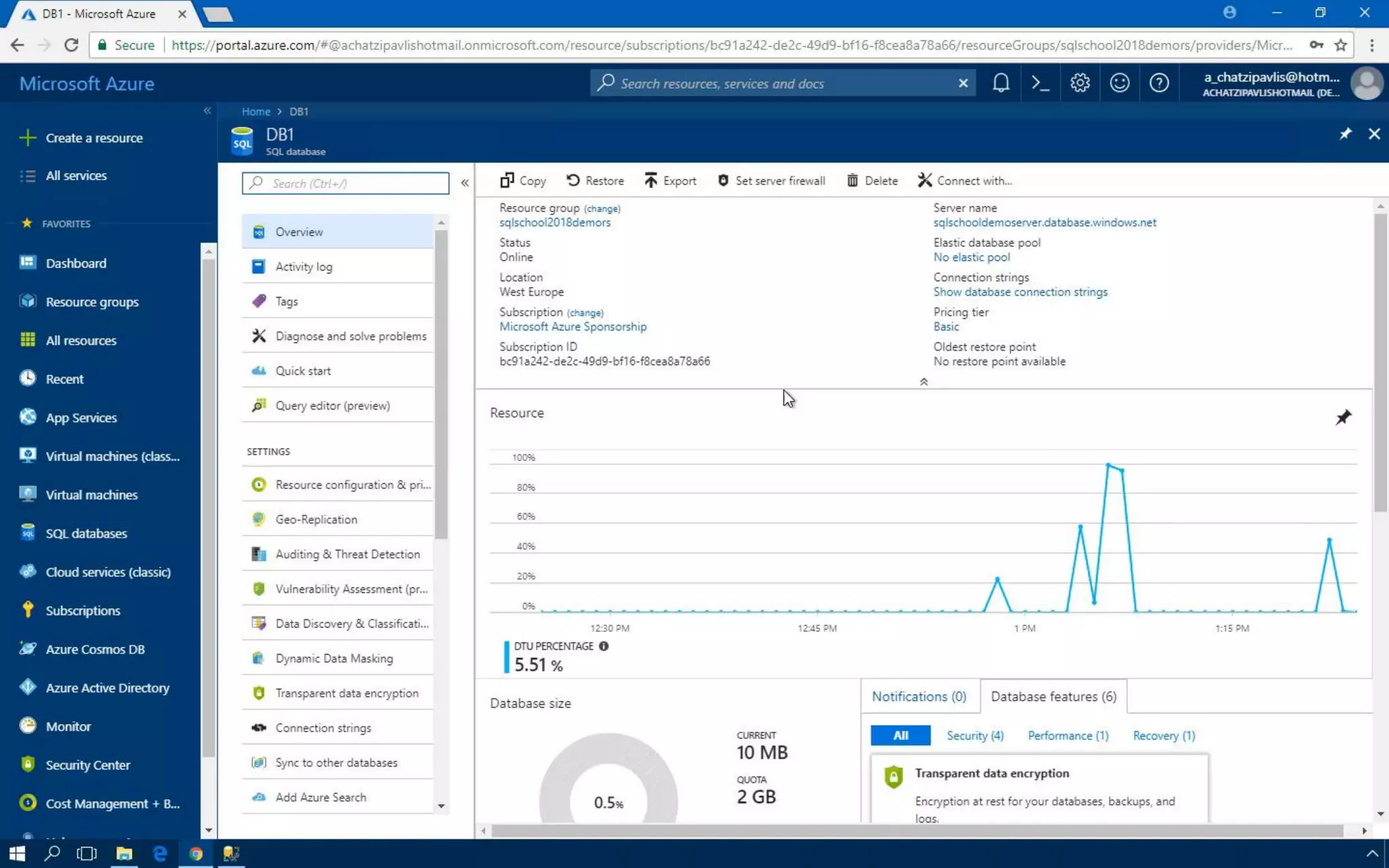
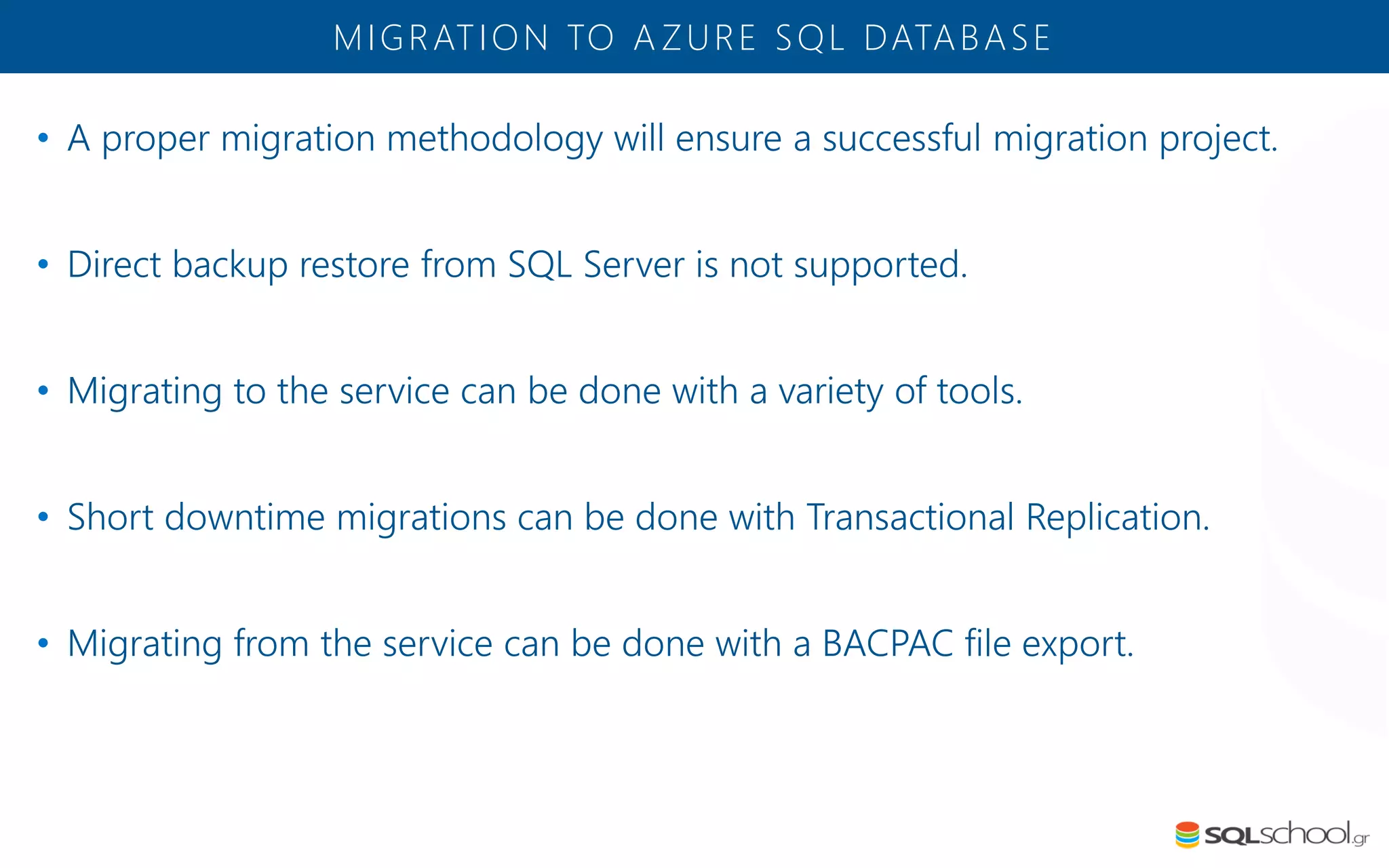
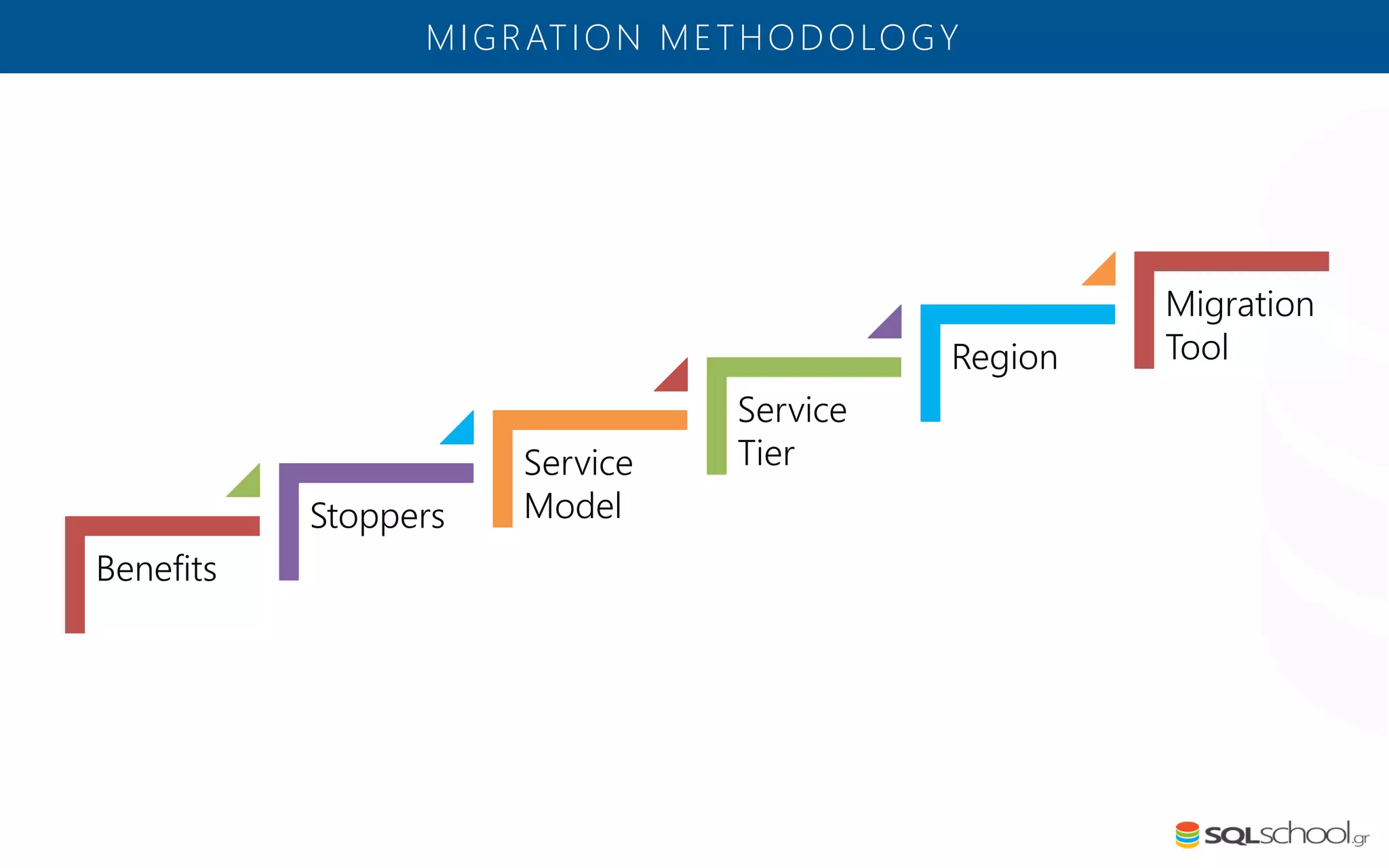
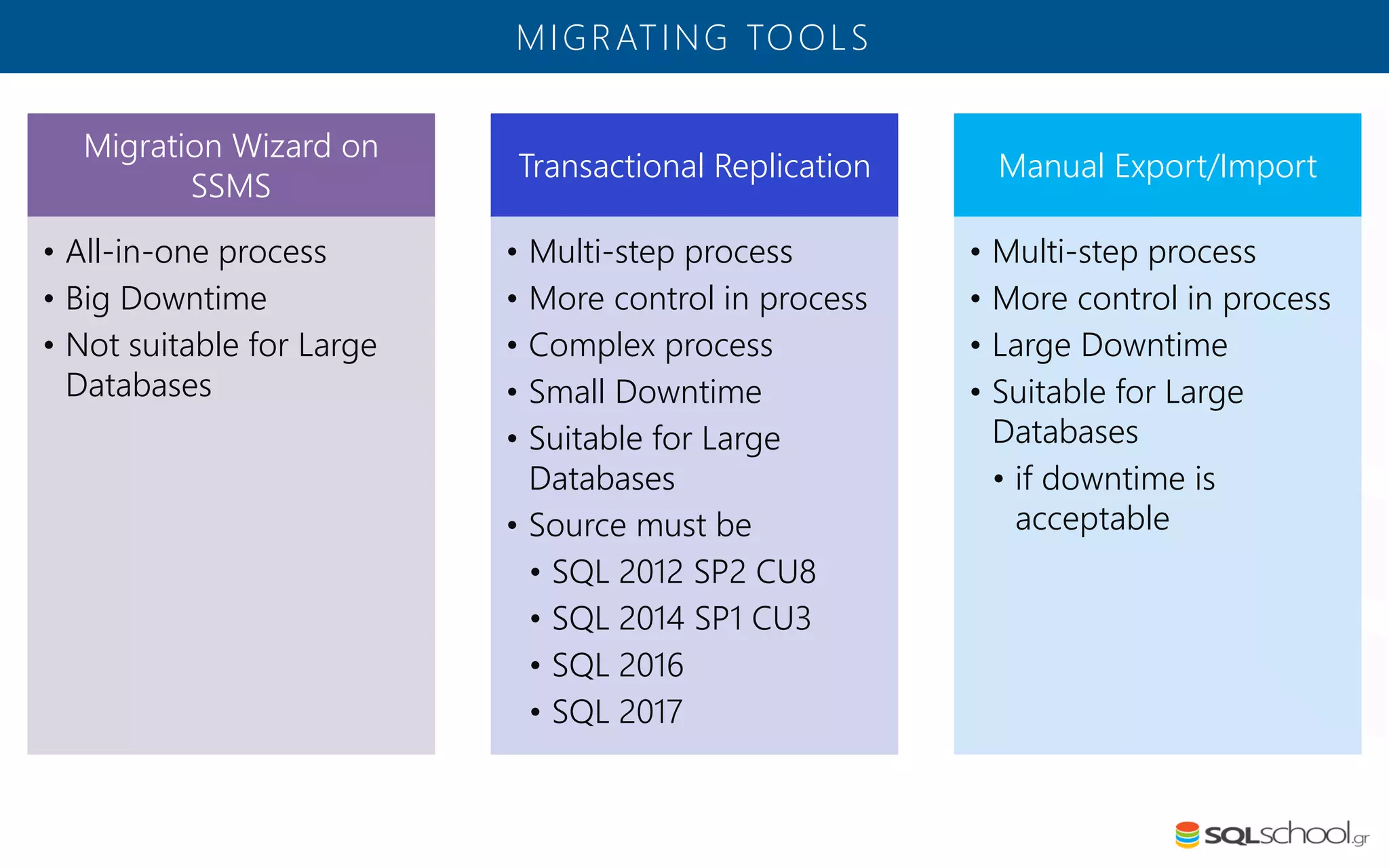
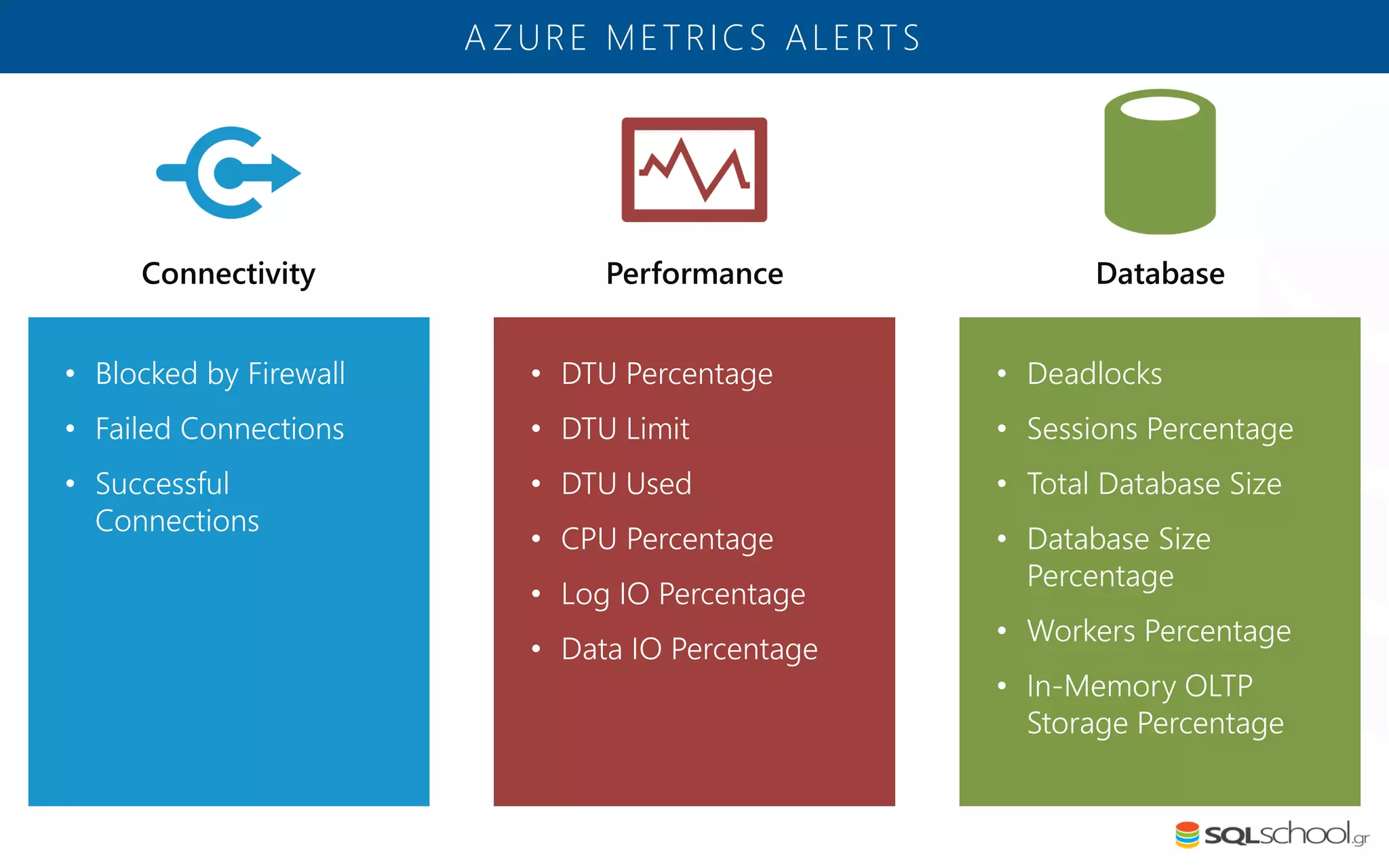
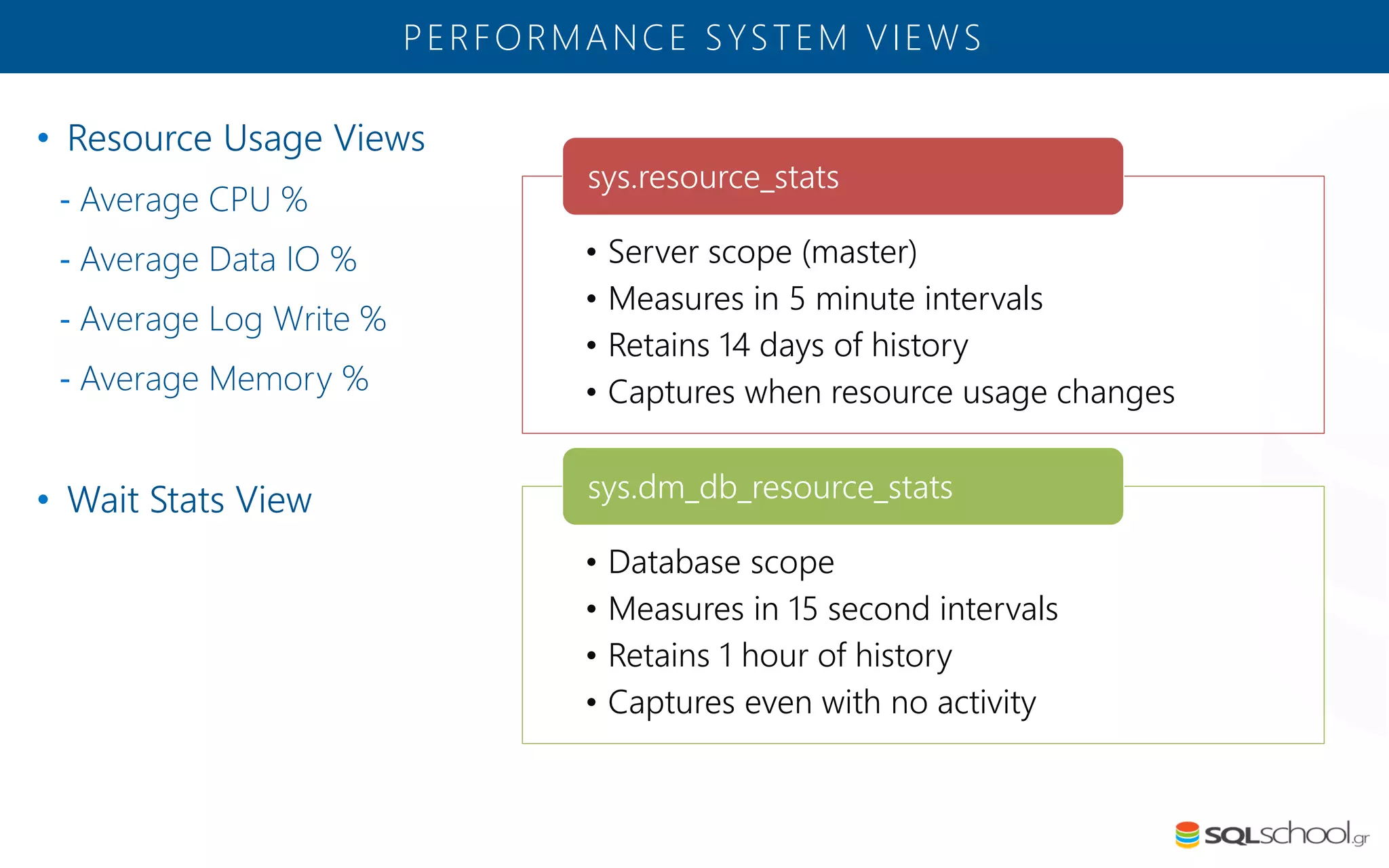
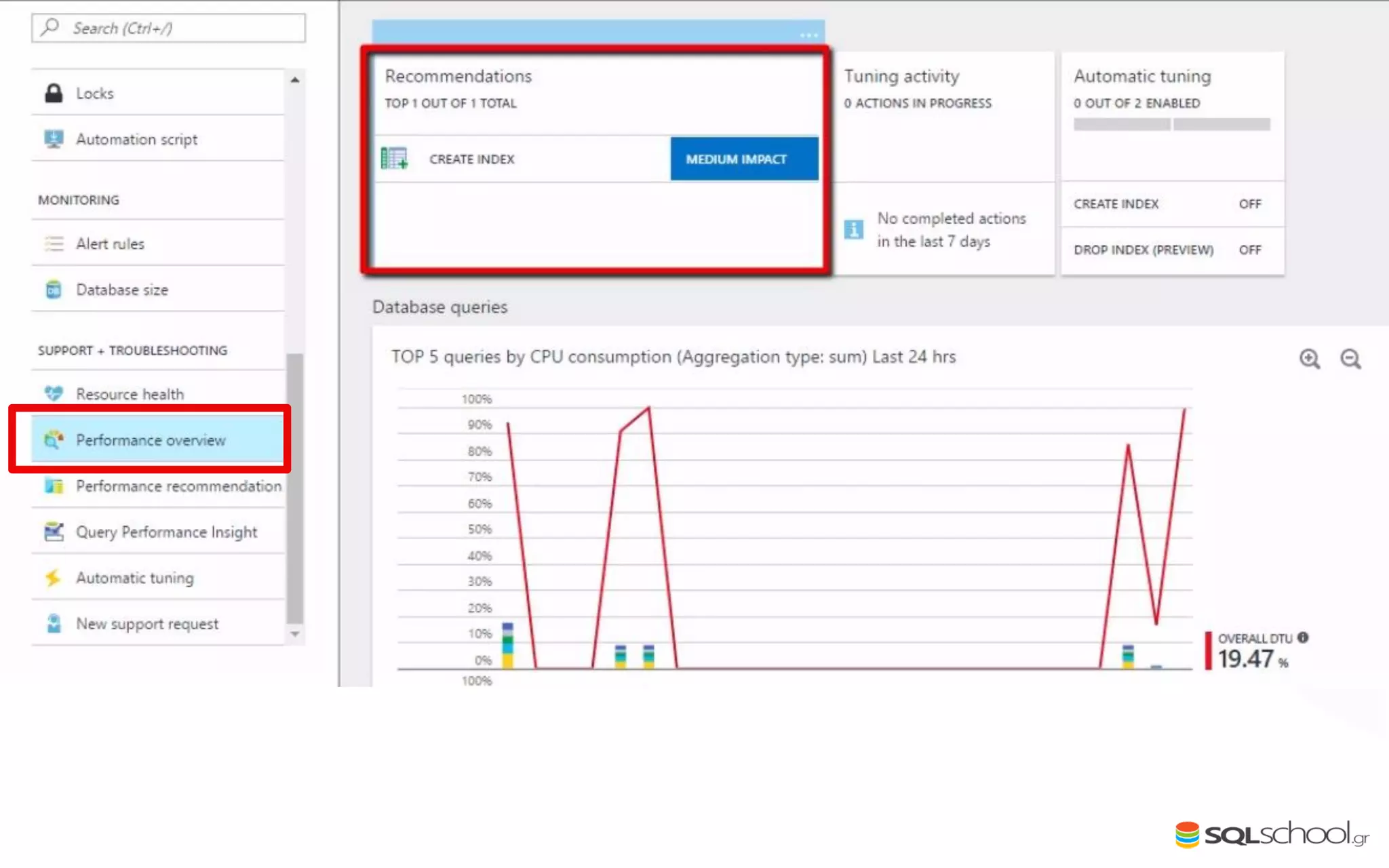
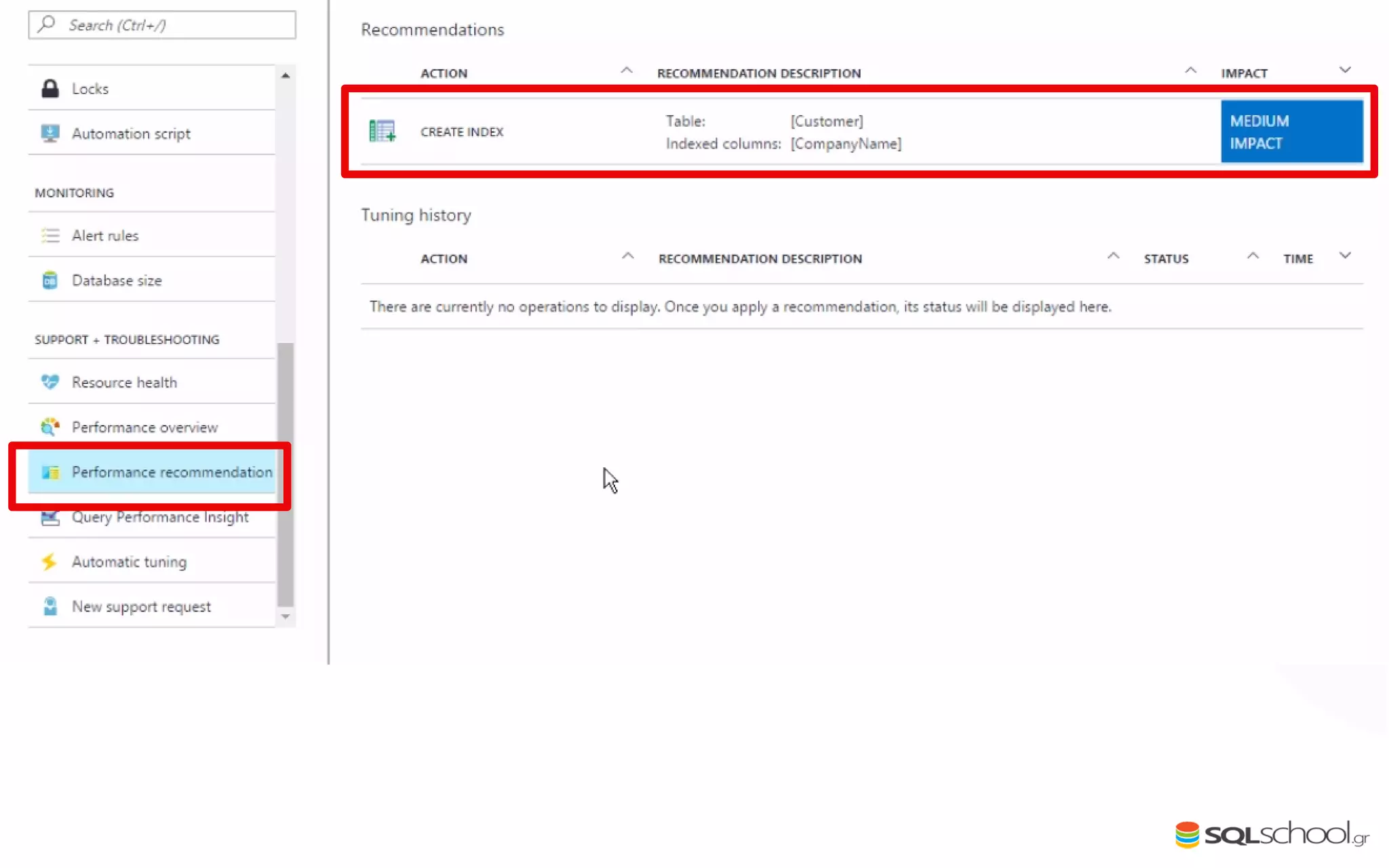
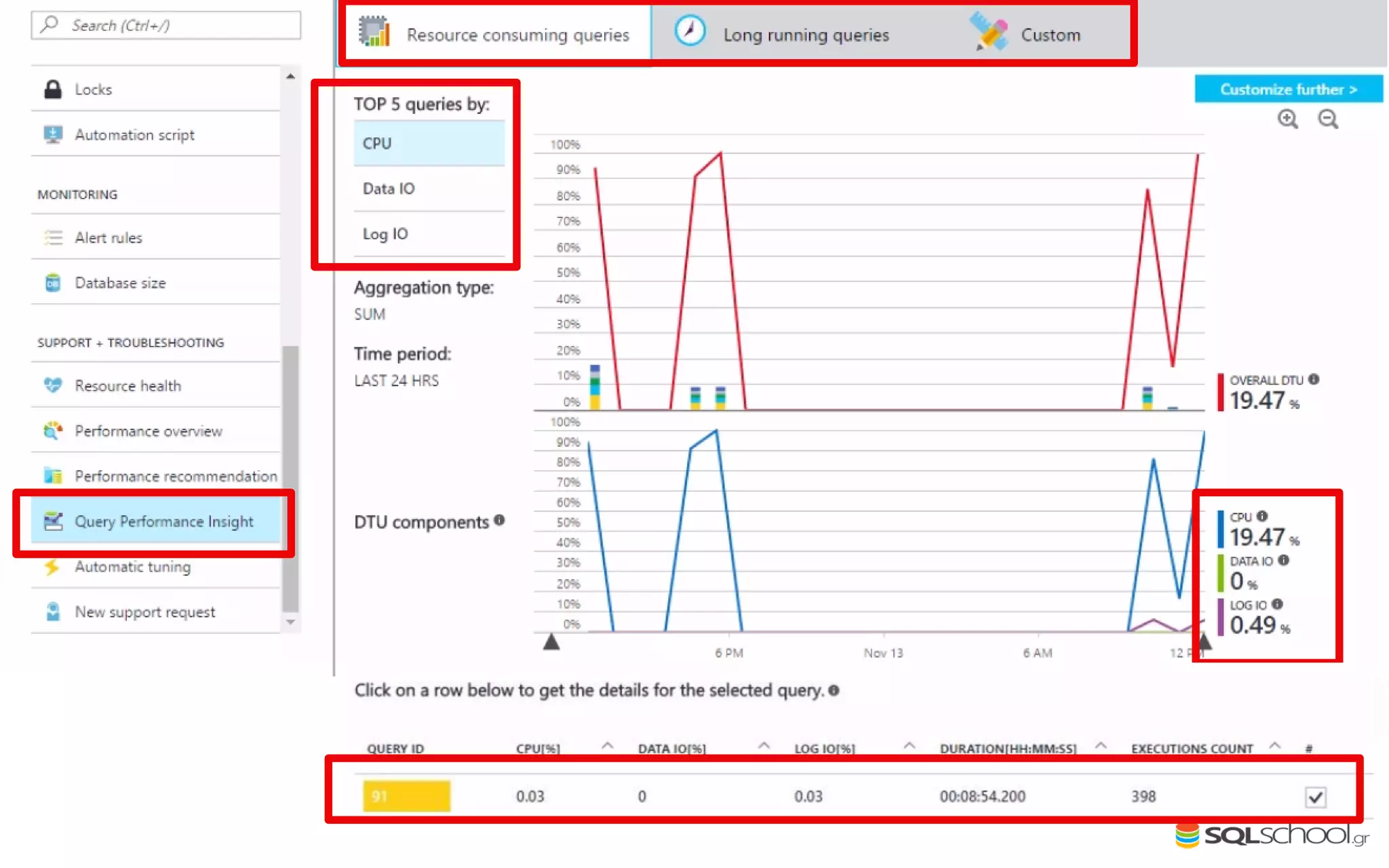
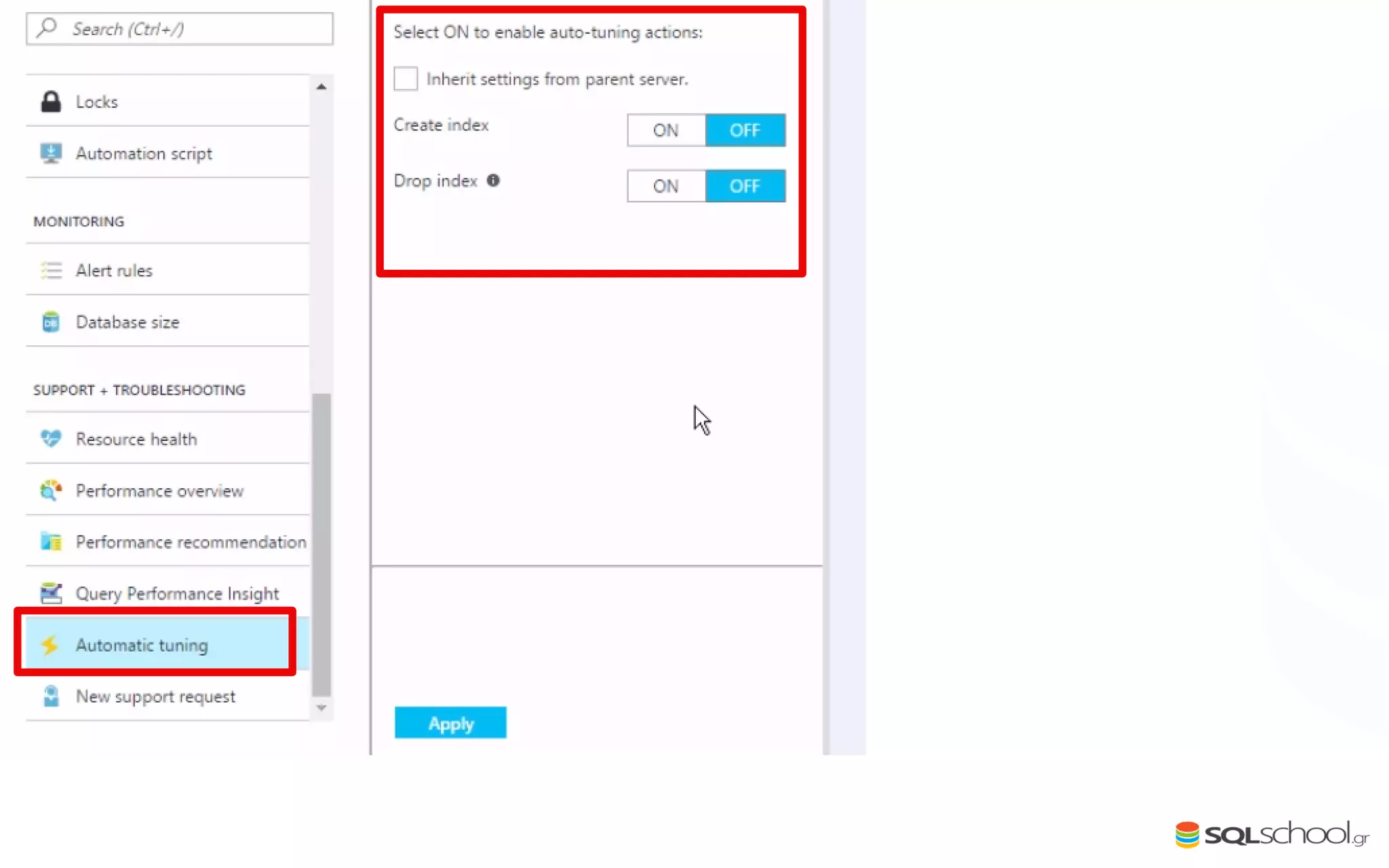
Azure SQL Database is a managed database service hosted in Microsoft's Azure cloud. Some key differences from SQL Server include: the service is paid by the hour based on the selected service tier; users can dynamically scale resources up or down; backups and high availability are managed by the service provider; and common administration tasks are handled by the provider rather than the user. The service offers automatic backups, point-in-time restore, and geo-restore capabilities along with built-in high availability through replication across three copies in the primary region.