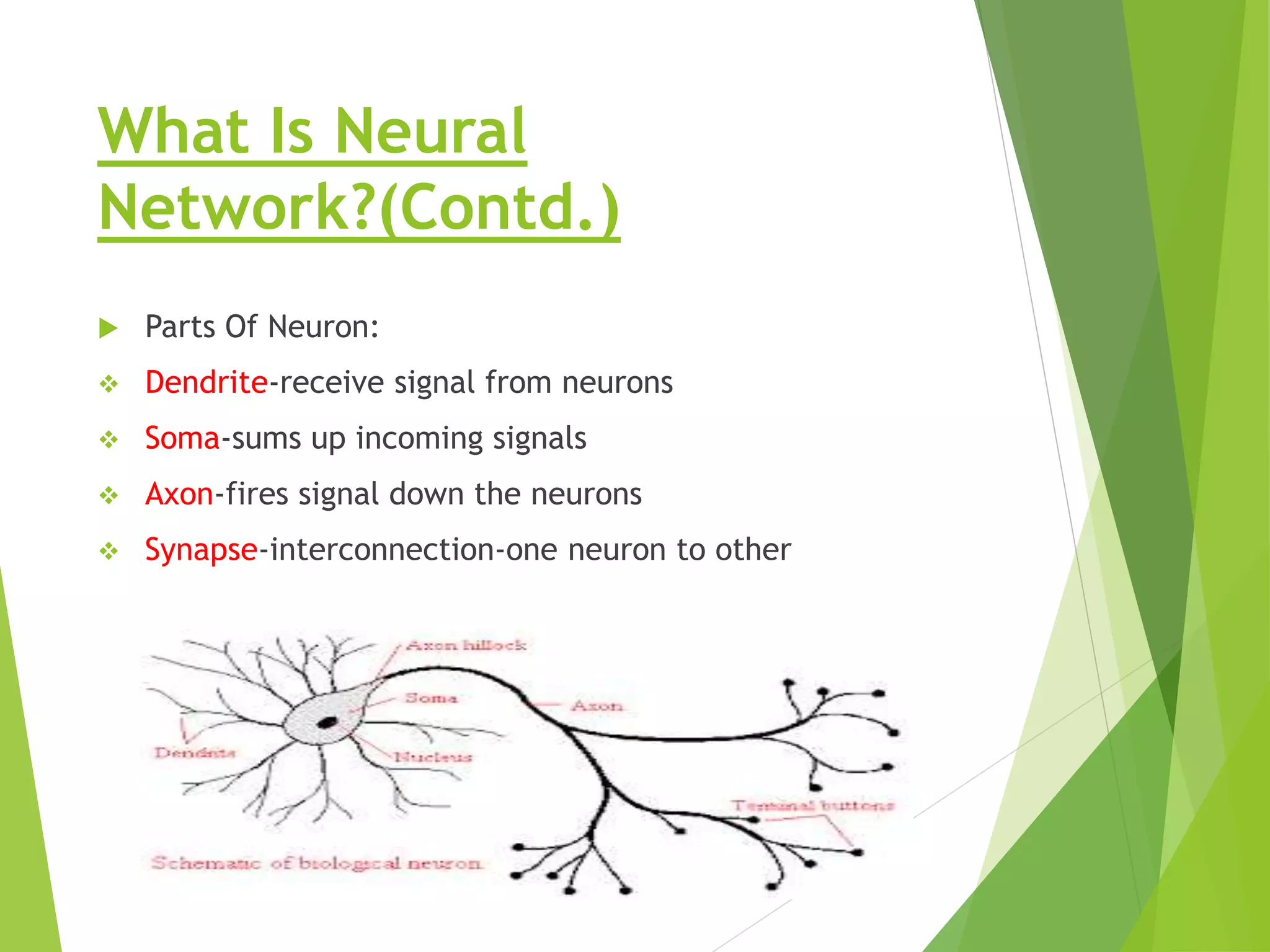
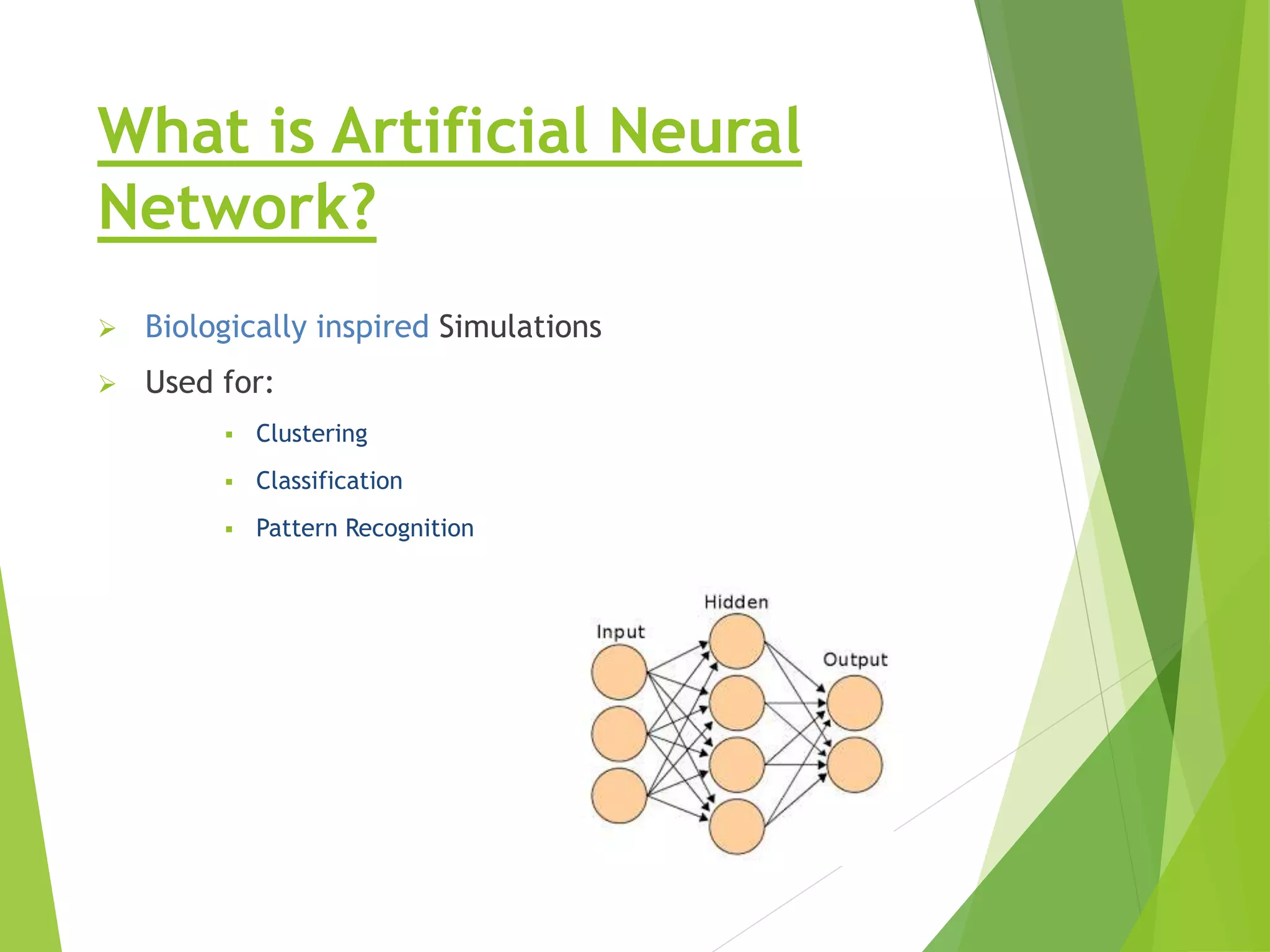
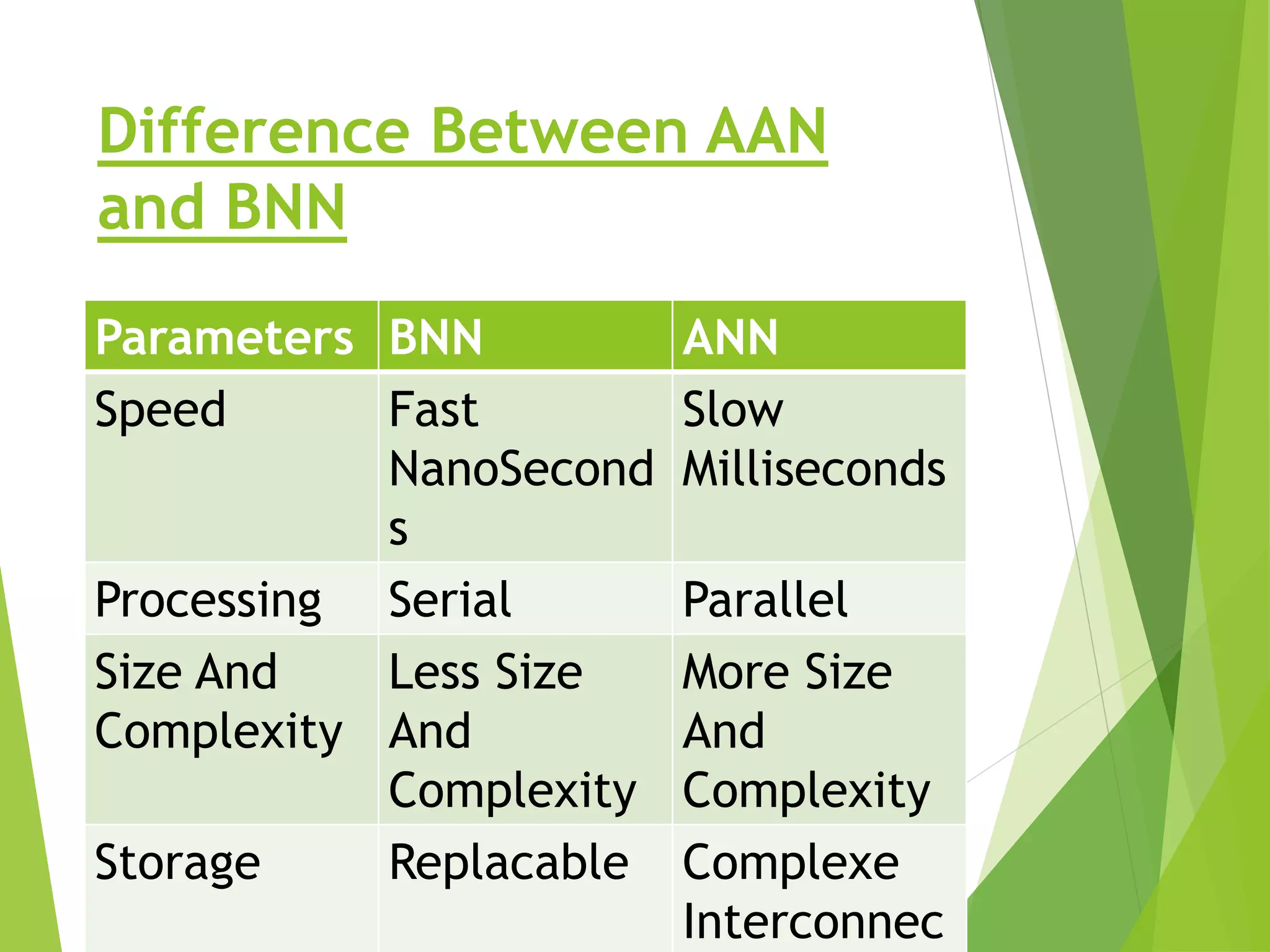
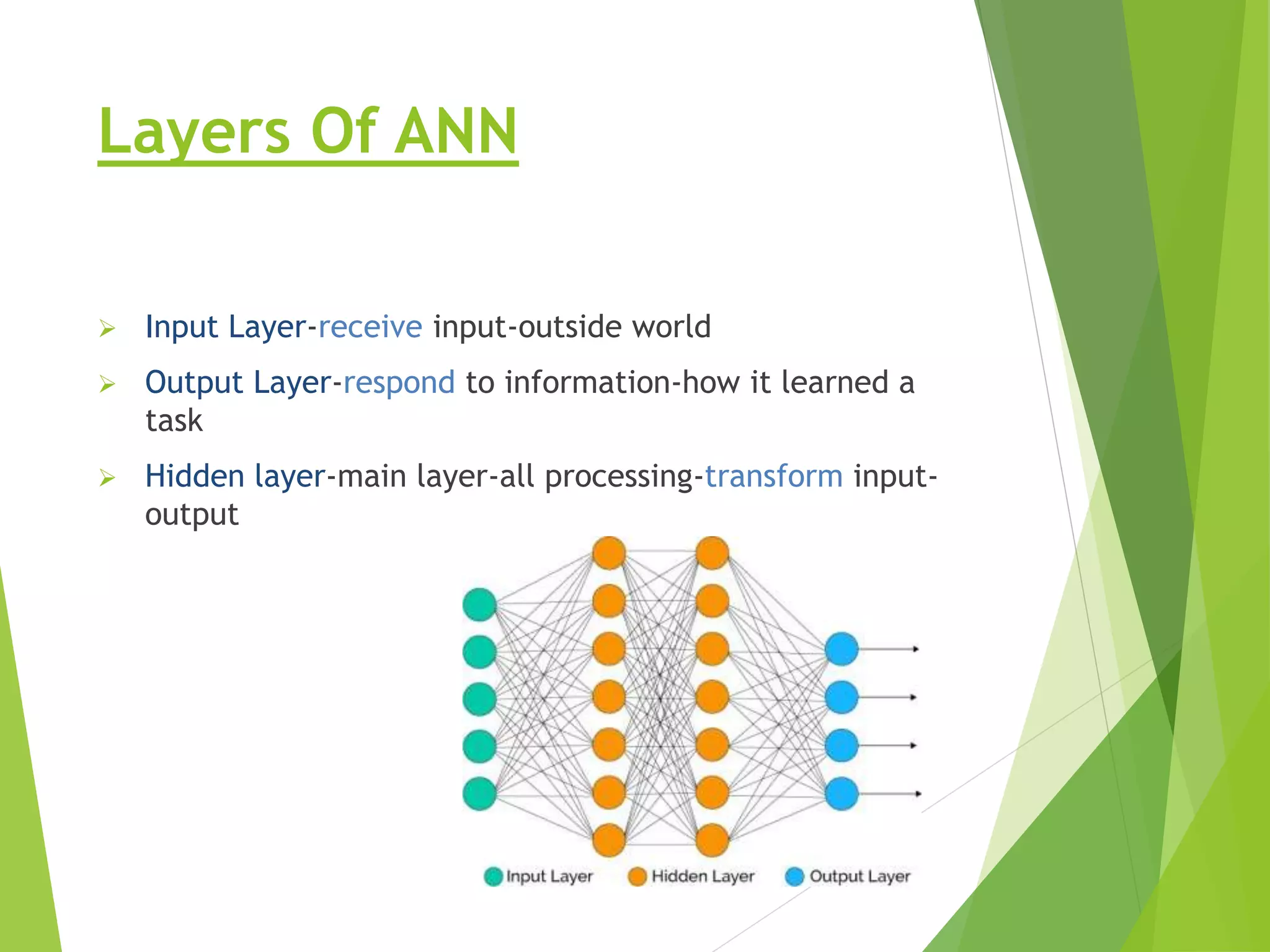
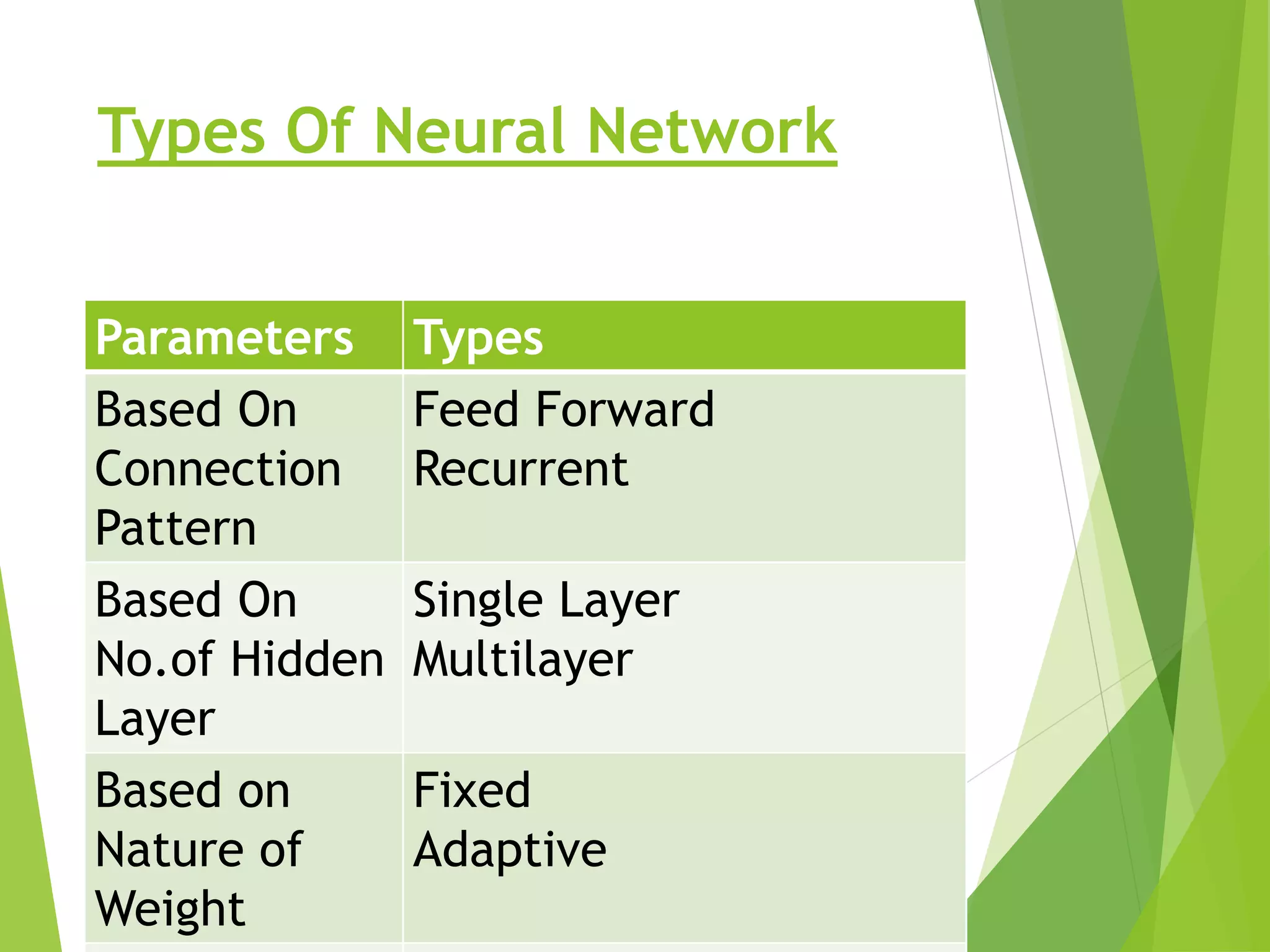
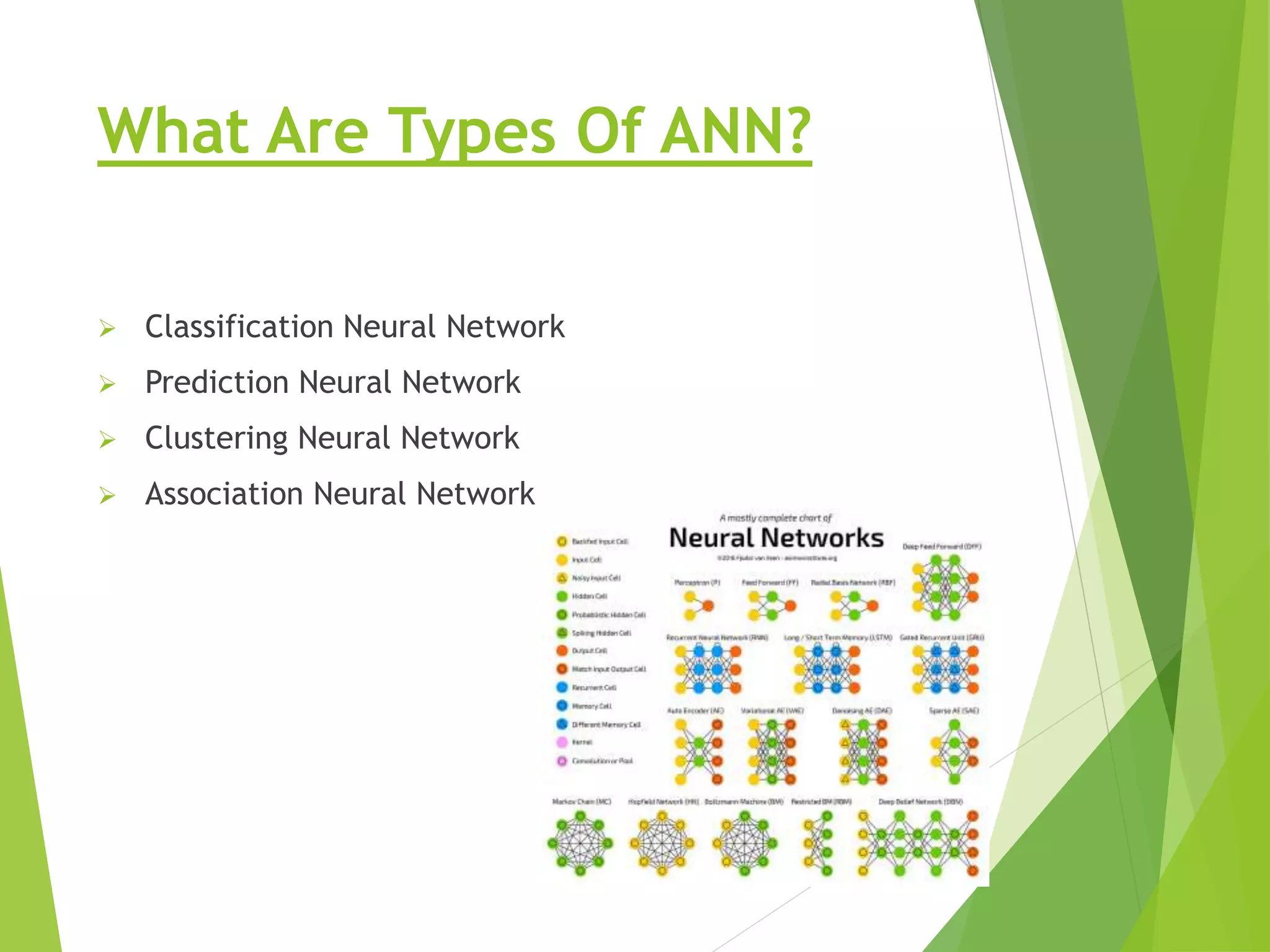
This presentation provides an overview of artificial neural networks (ANN), including what they are, how they work, different types, and applications. It defines ANN as biologically inspired simulations used for tasks like clustering, classification, and pattern recognition. The presentation explains that ANN learn by processing information in parallel through nodes and weighted connections, similar to the human brain. It also outlines various ANN architectures, such as perceptrons, recurrent networks, and convolutional networks. Finally, the presentation discusses common applications of ANN in domains like process control, medical diagnosis, and targeted marketing.