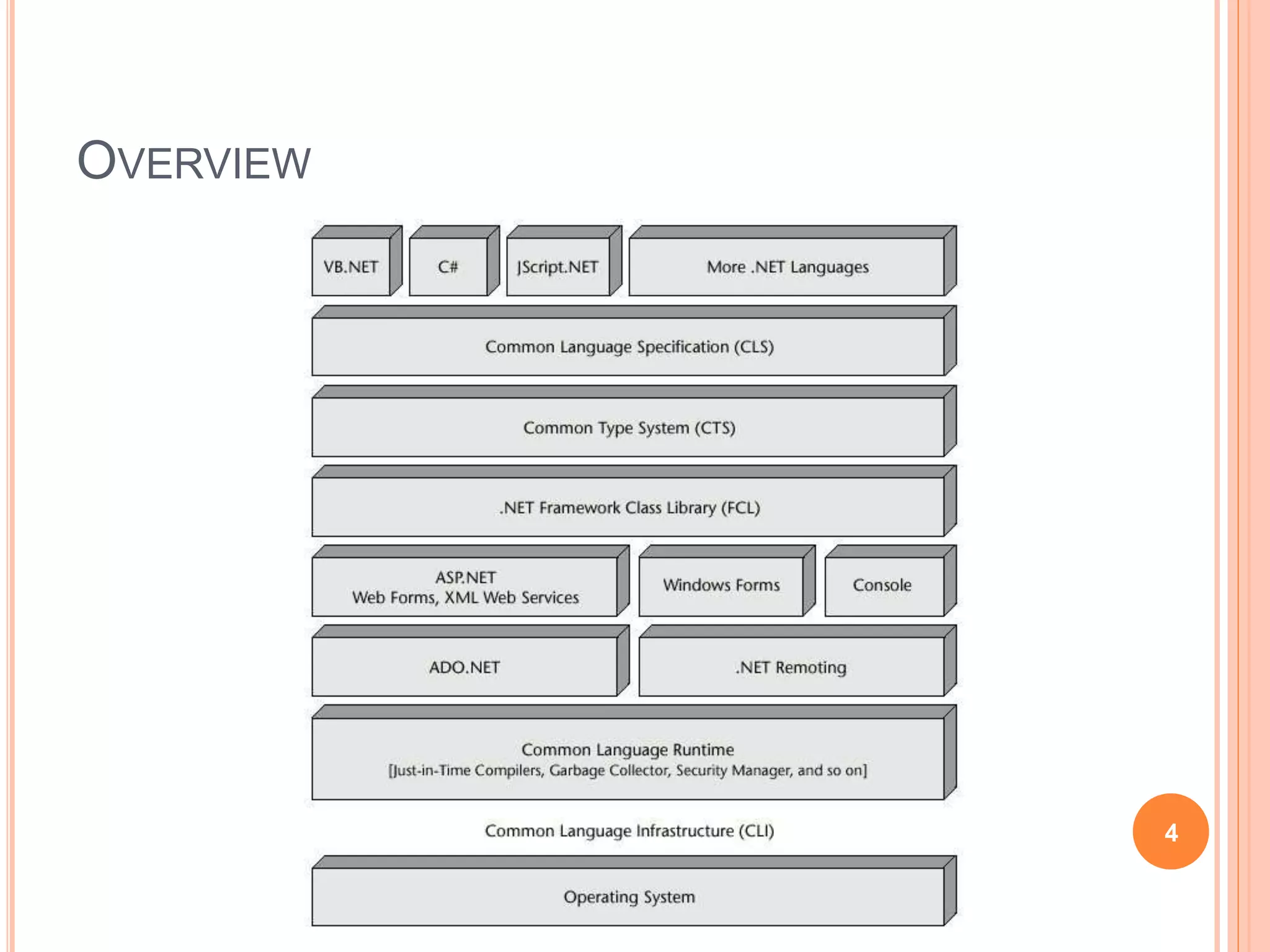
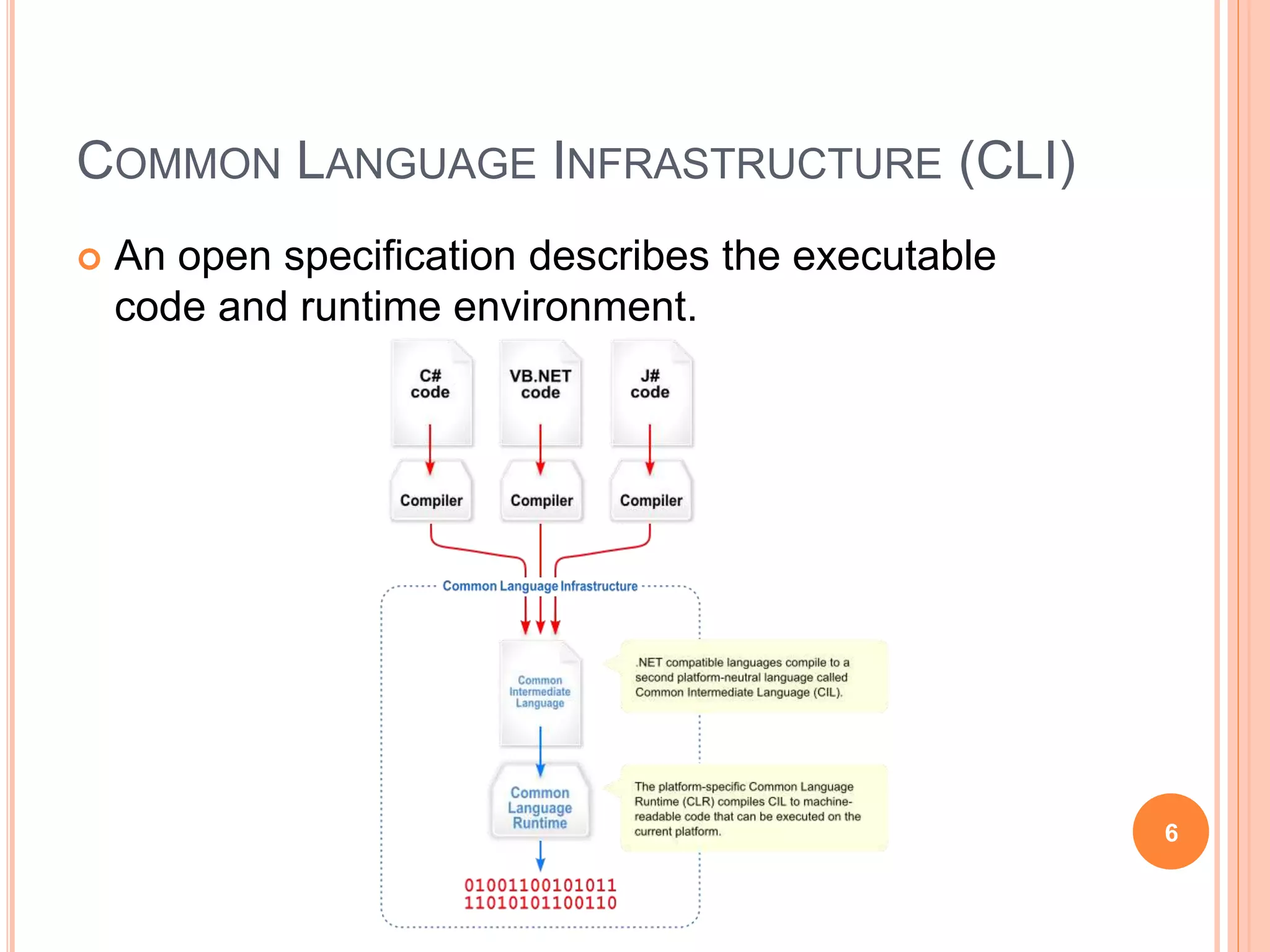
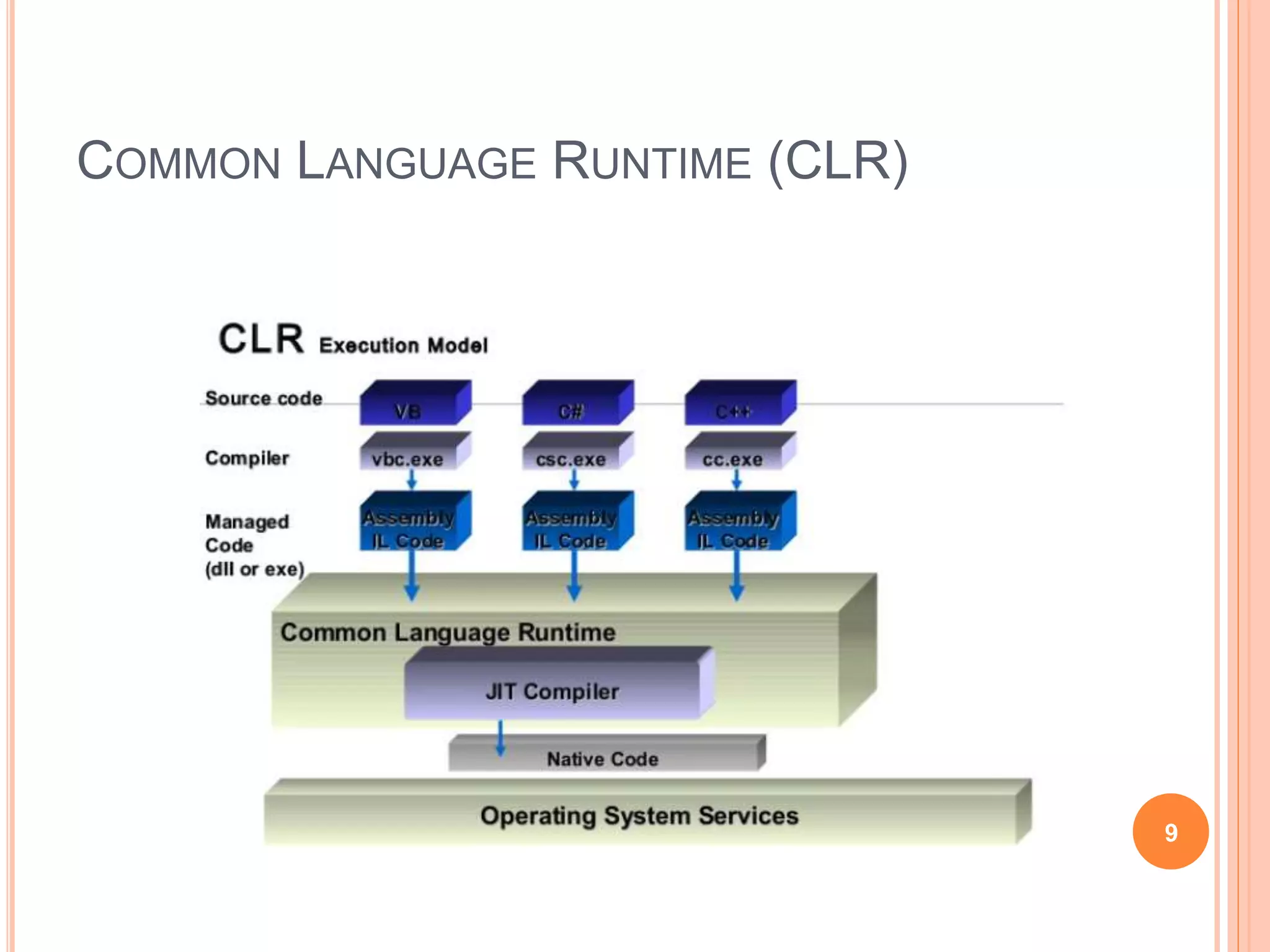
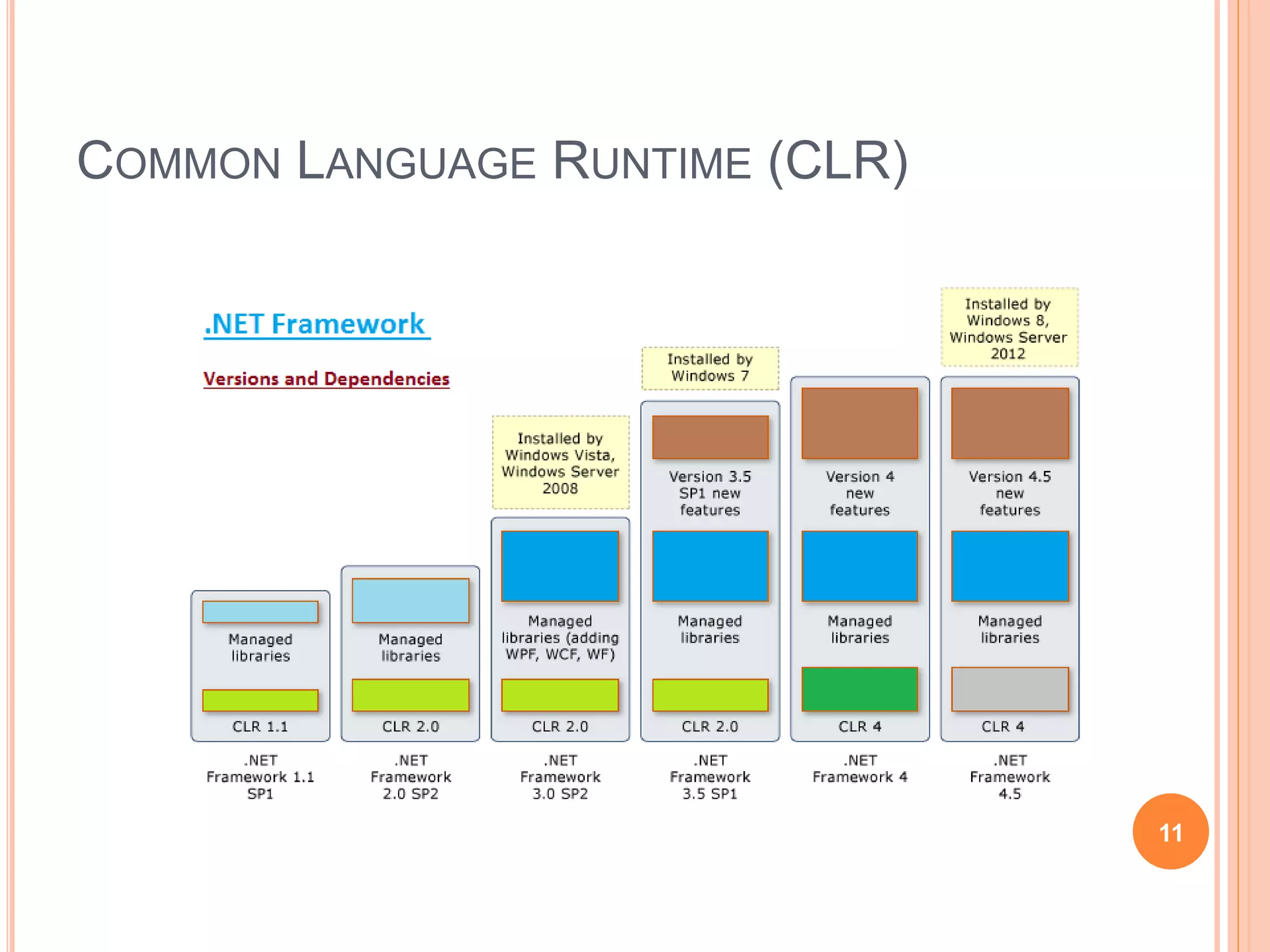
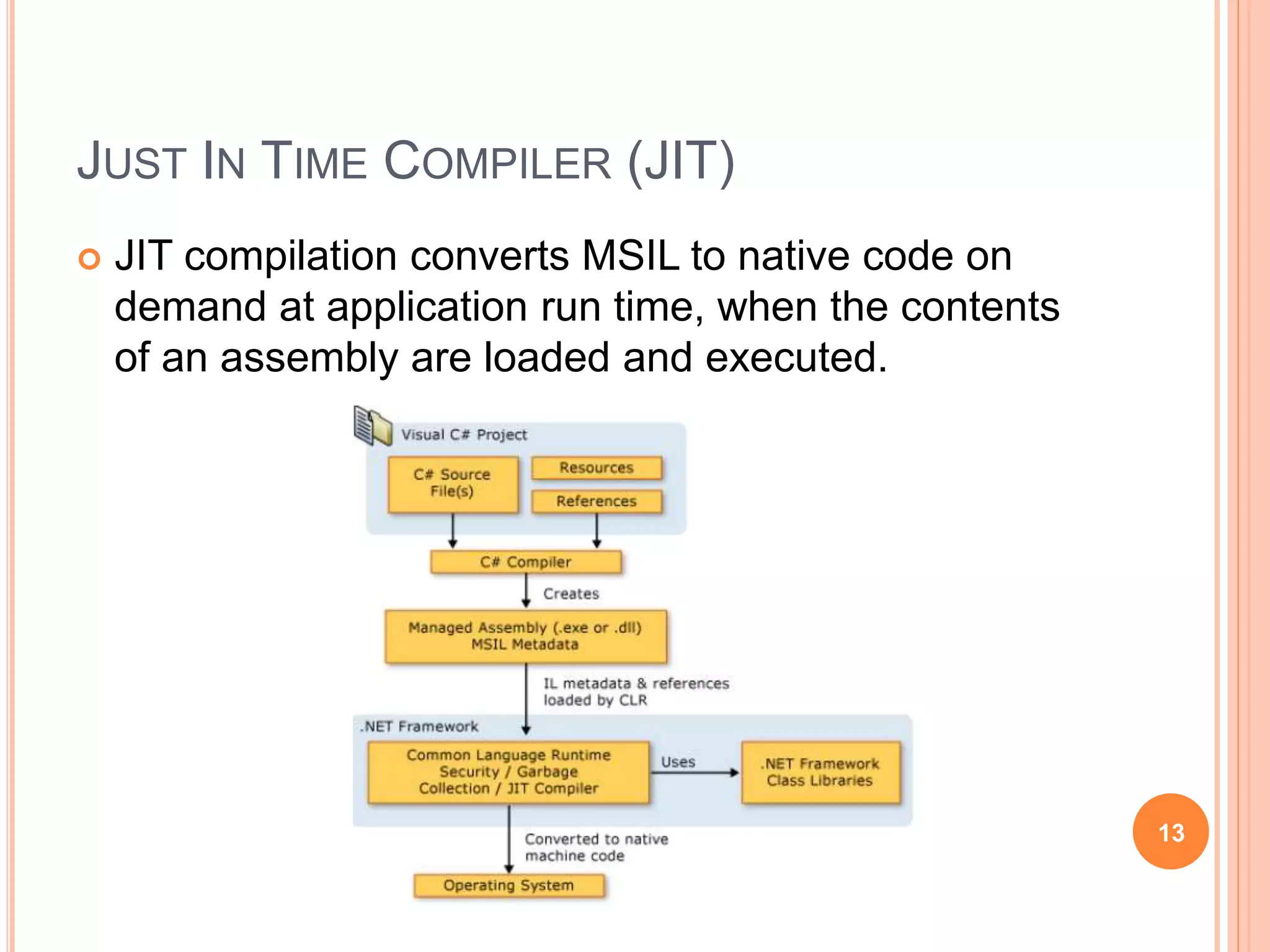
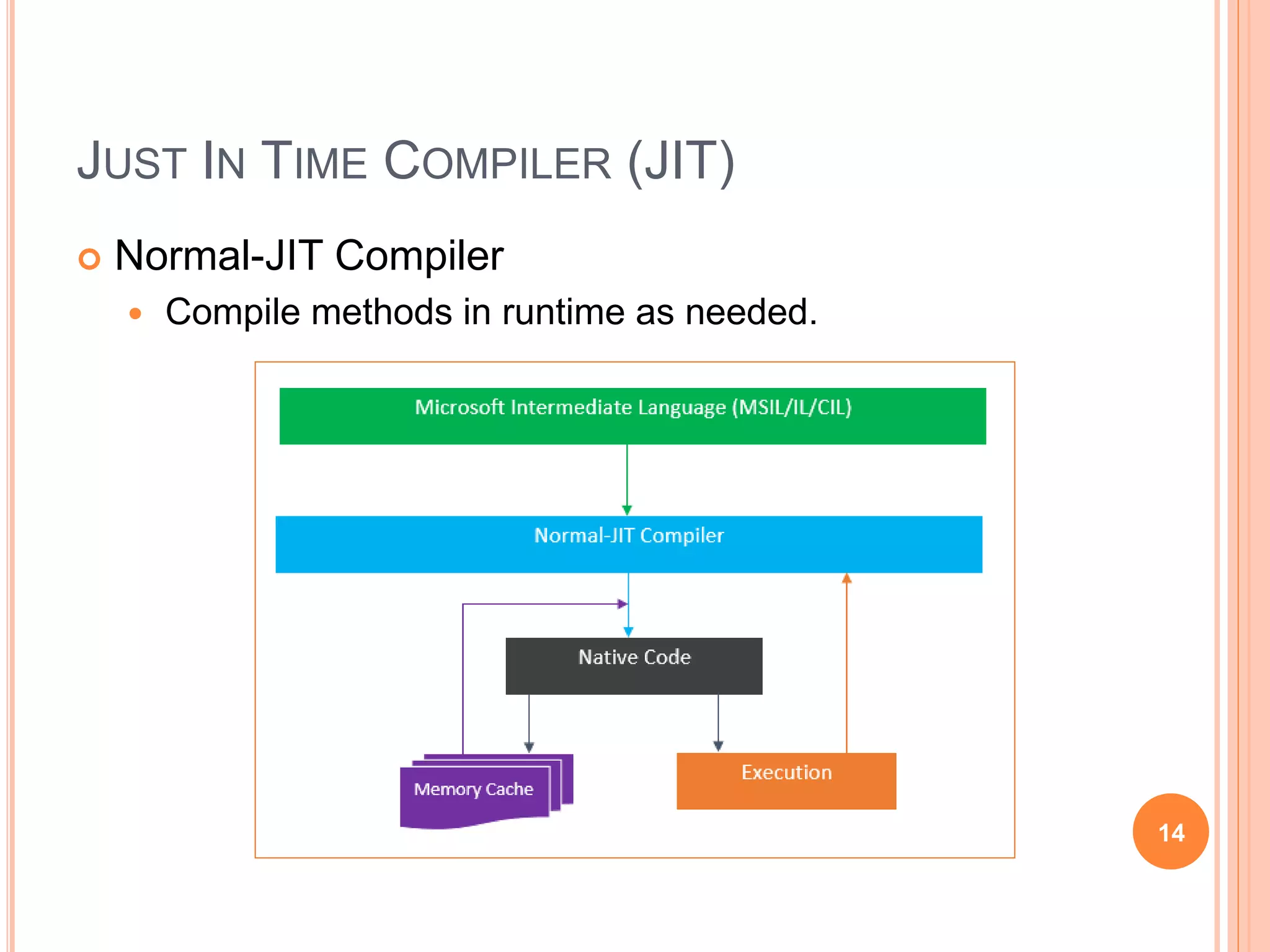
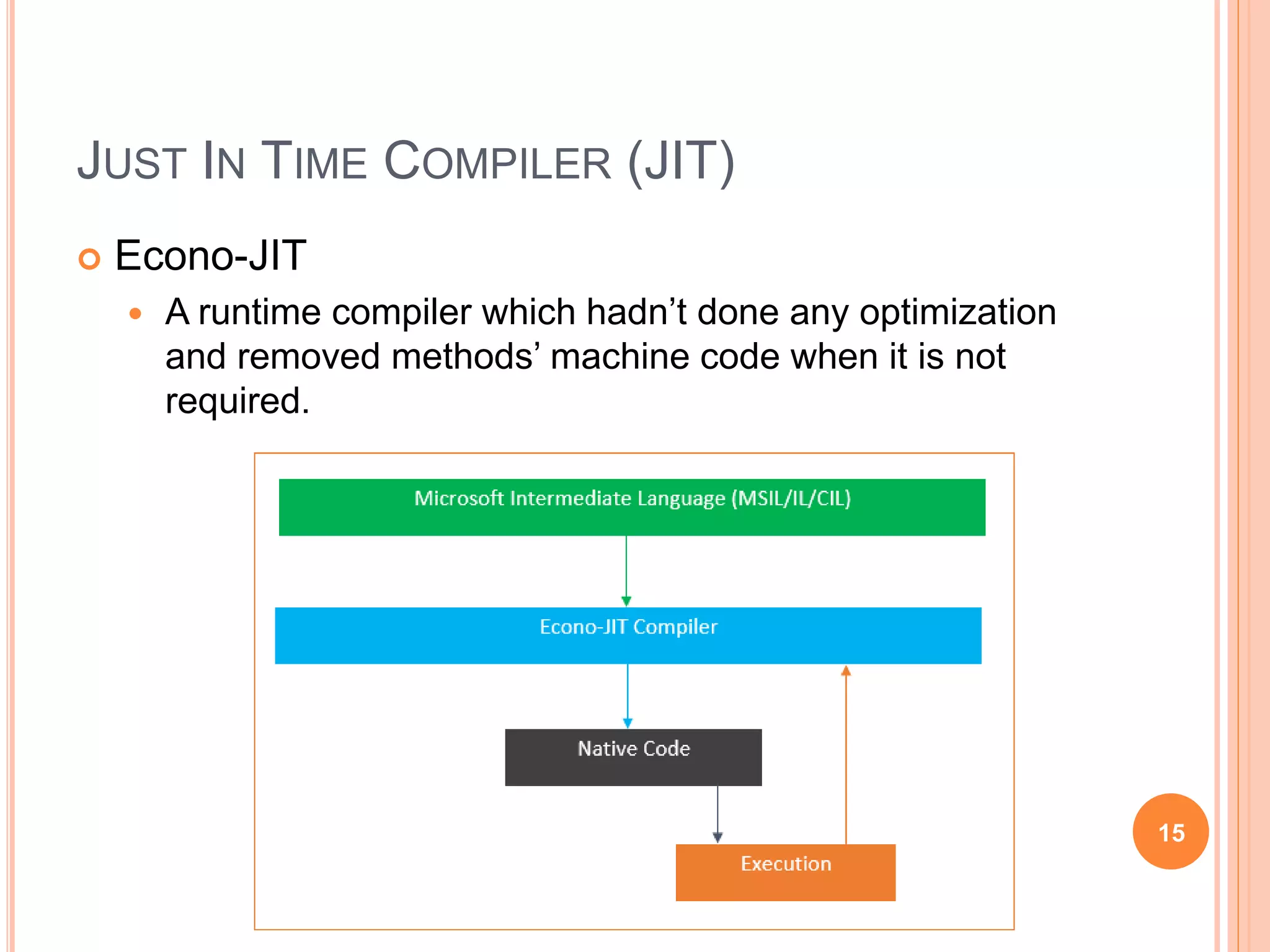
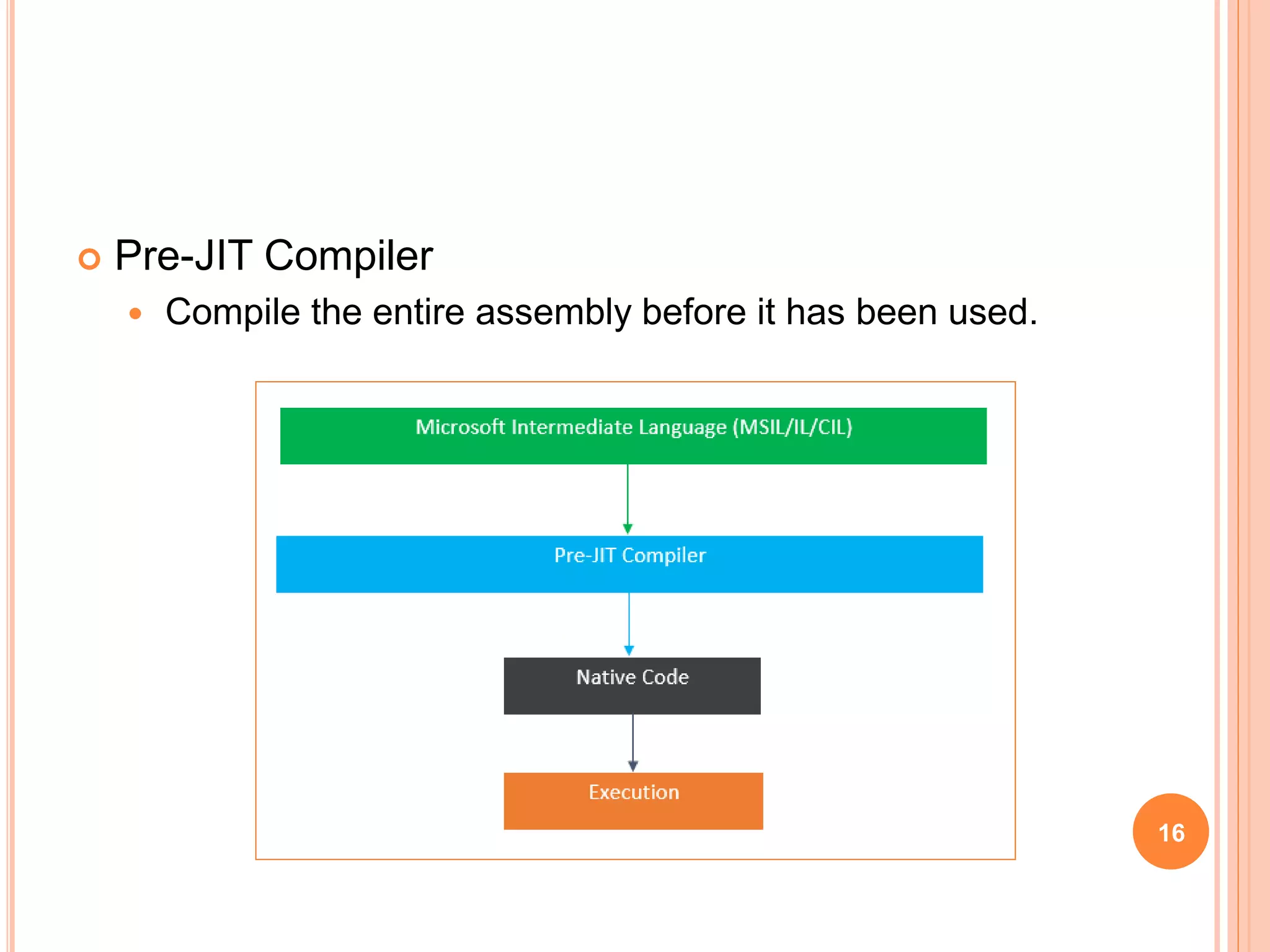
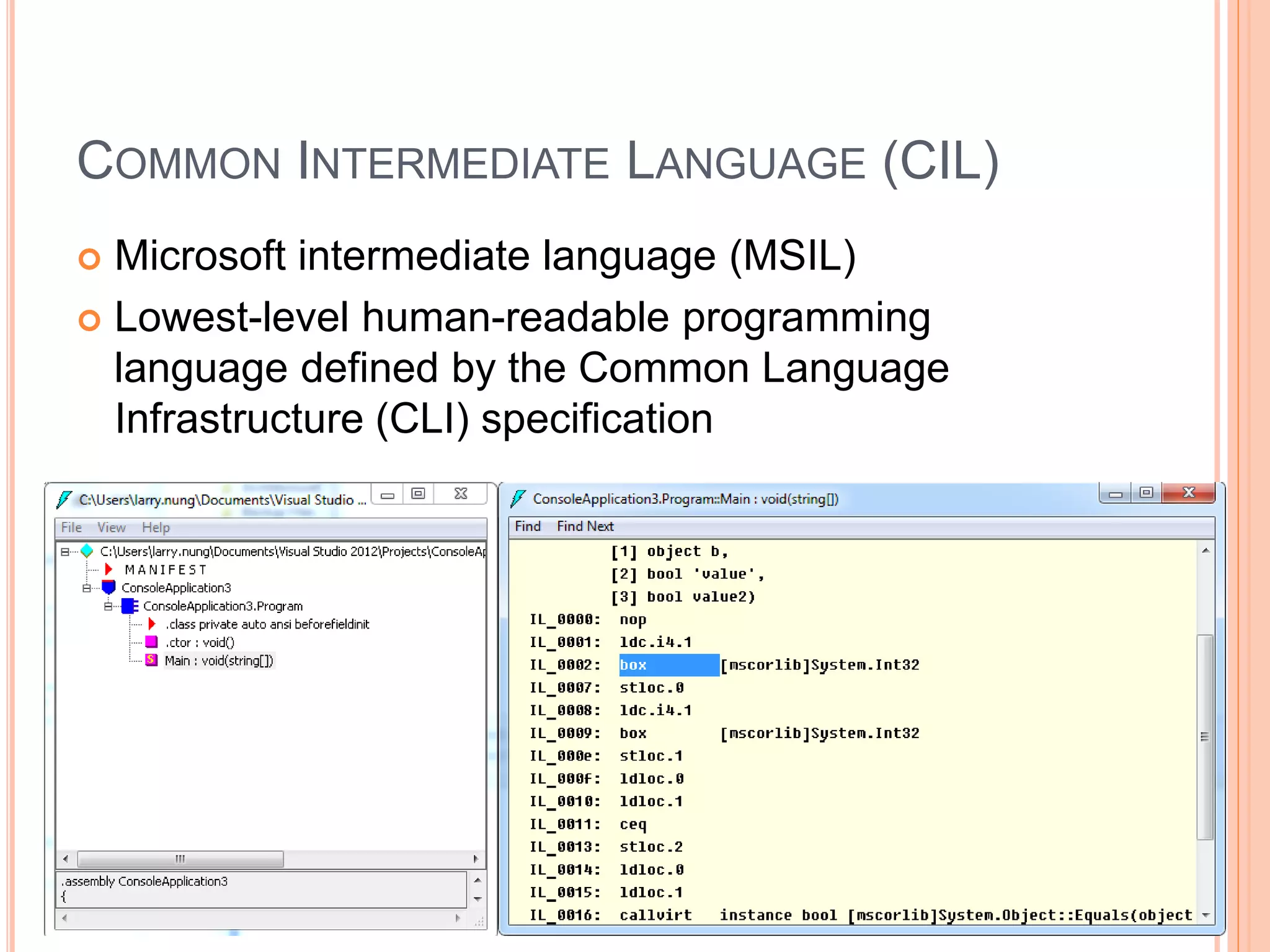
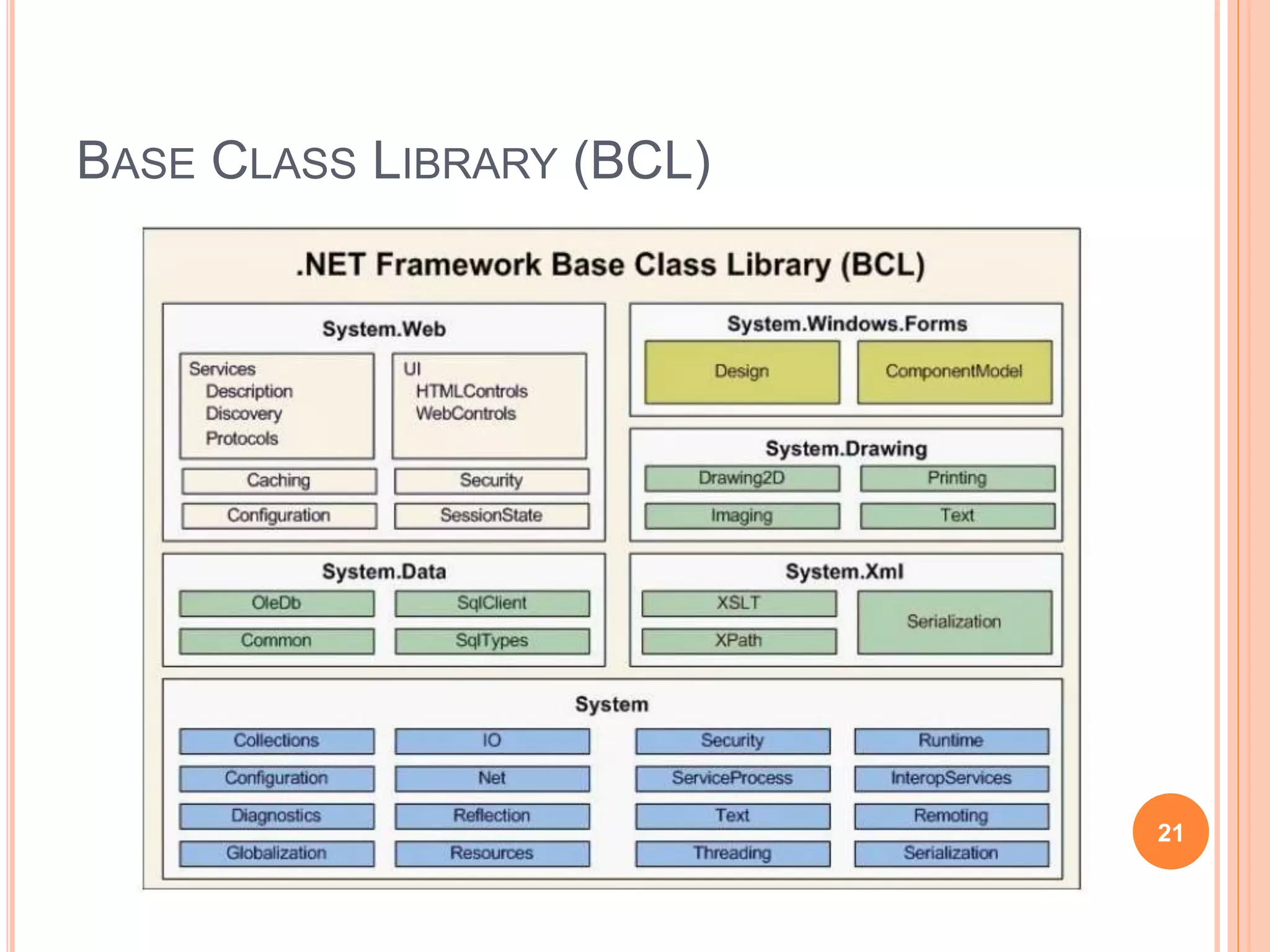
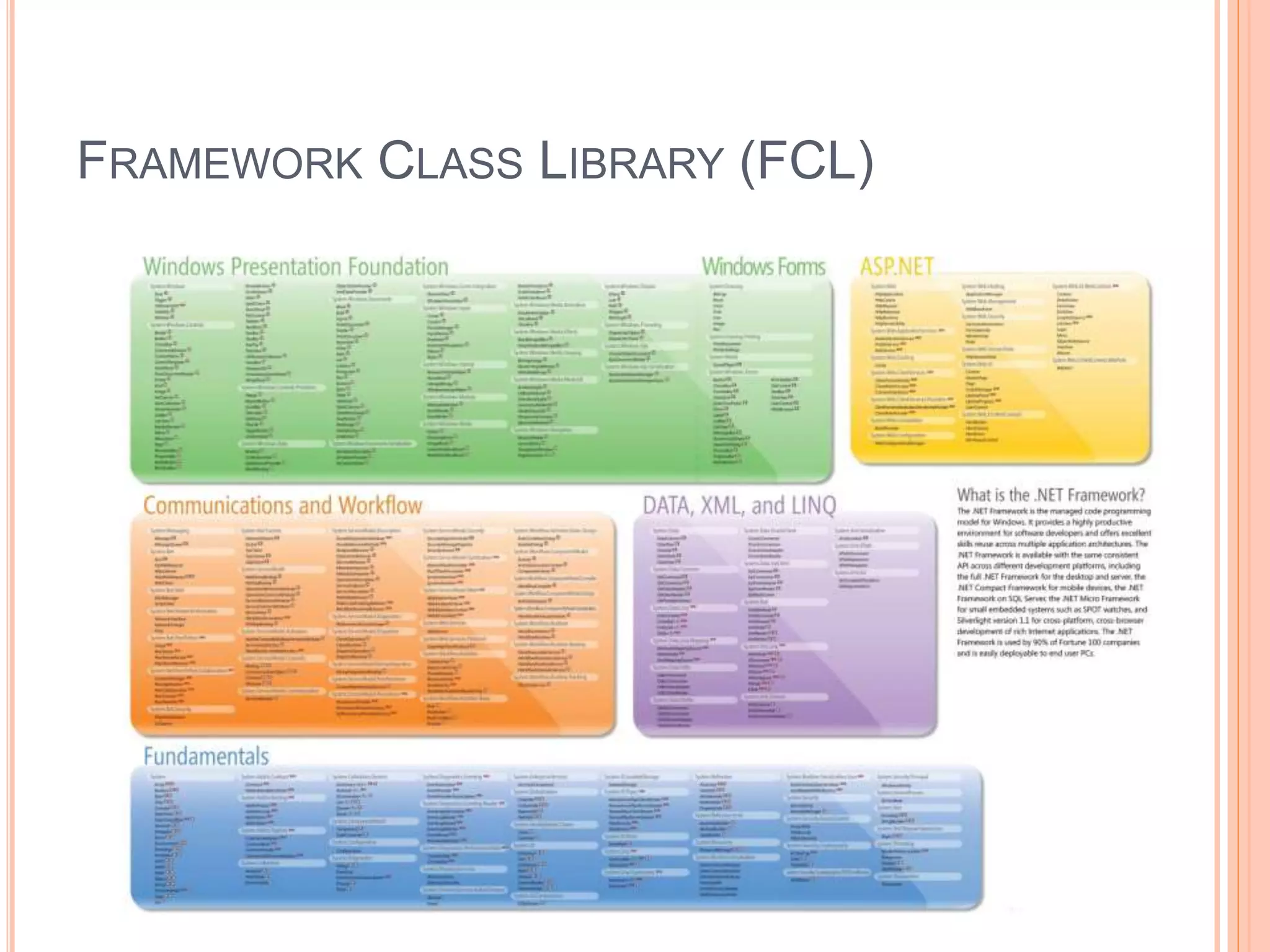
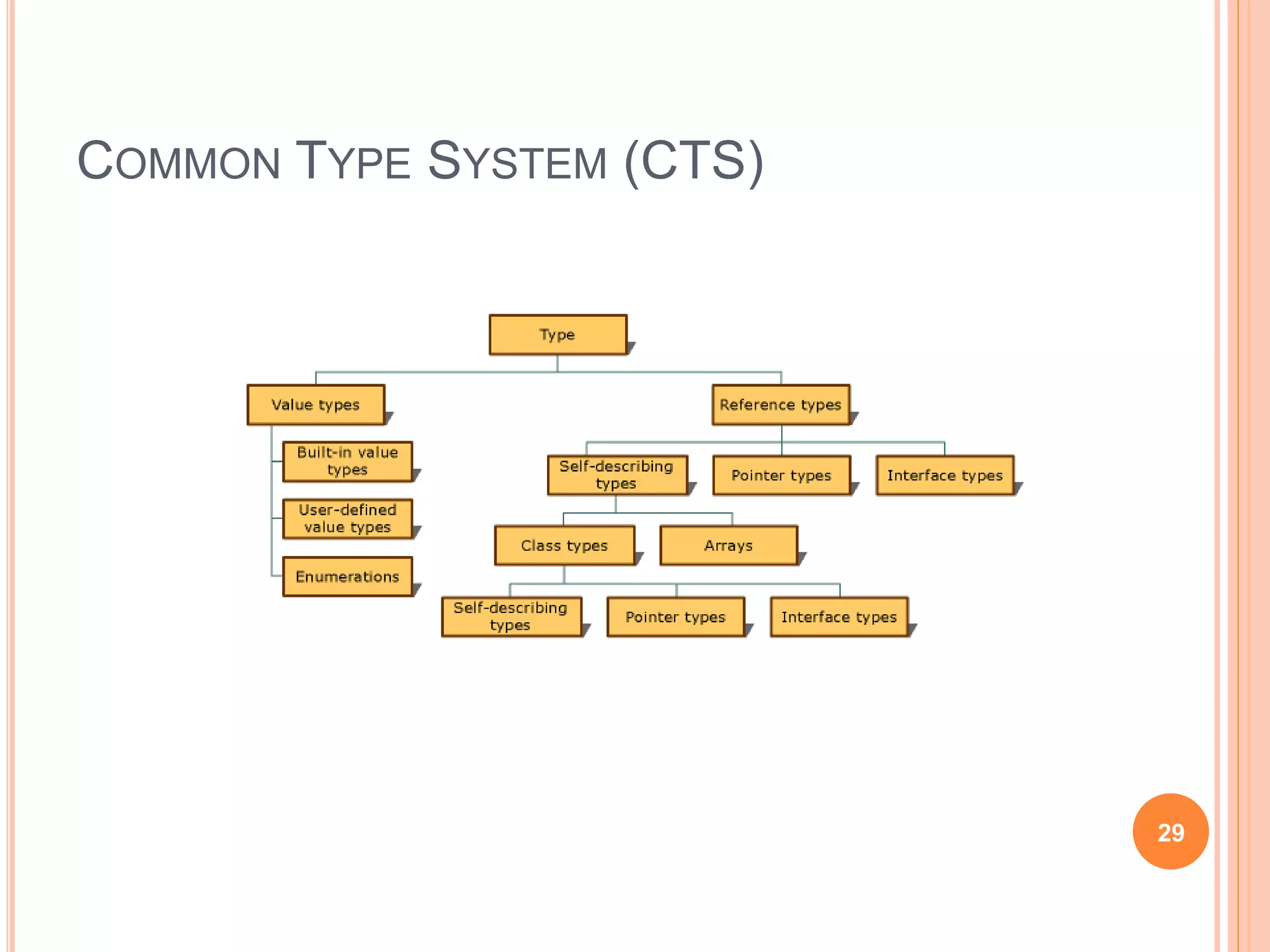
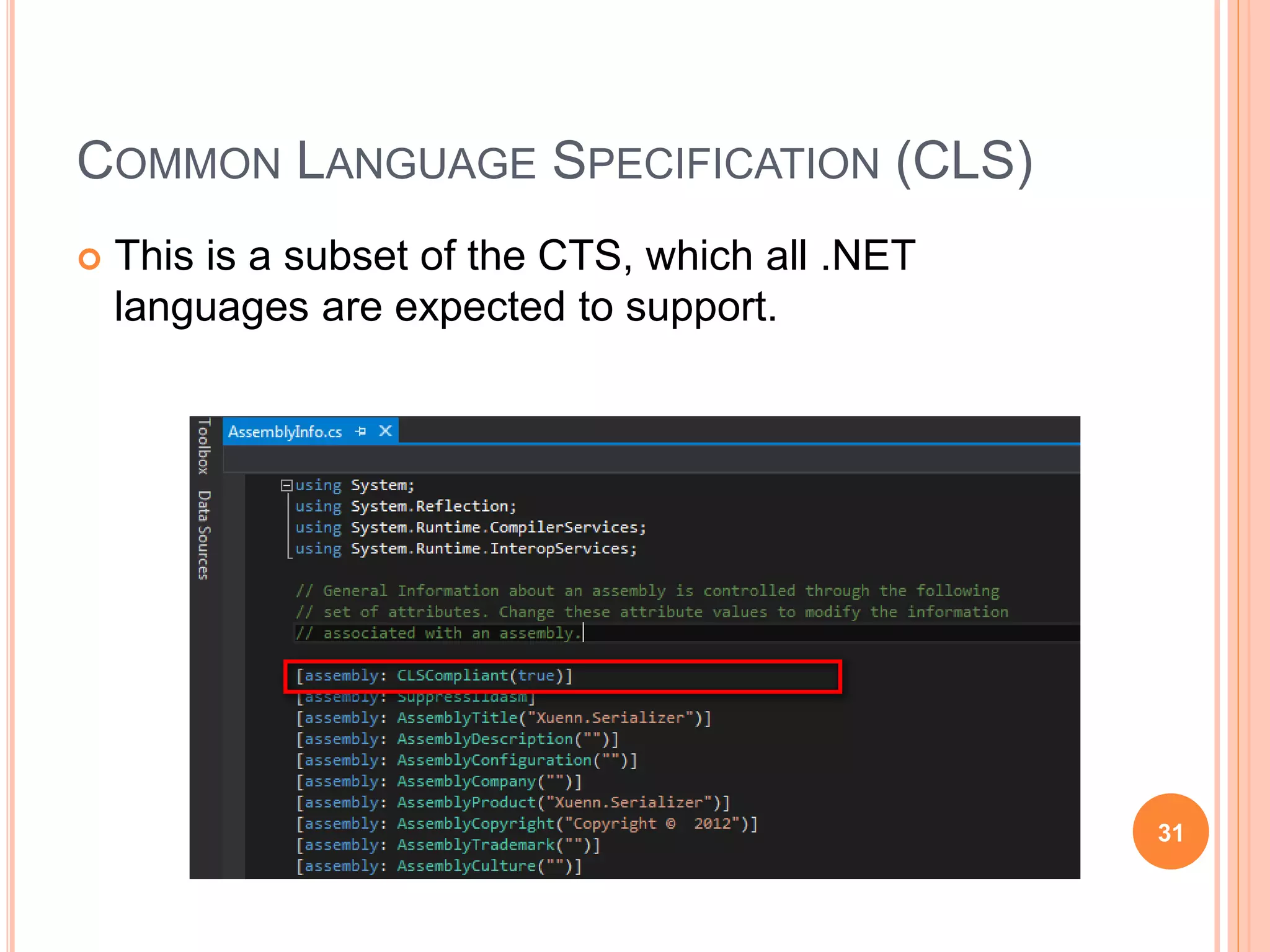
The document discusses key concepts in .NET architecture, including the Common Language Infrastructure (CLI) specification, Common Language Runtime (CLR), Just-In-Time compiler (JIT), Common Intermediate Language (CIL), Base Class Library (BCL), Framework Class Library (FCL), Common Type System (CTS), and Common Language Specification (CLS). The CLR provides a runtime environment and services that make development easier. The JIT compiles CIL to native code when assemblies are loaded. The CTS and CLS define type safety and interoperability standards.