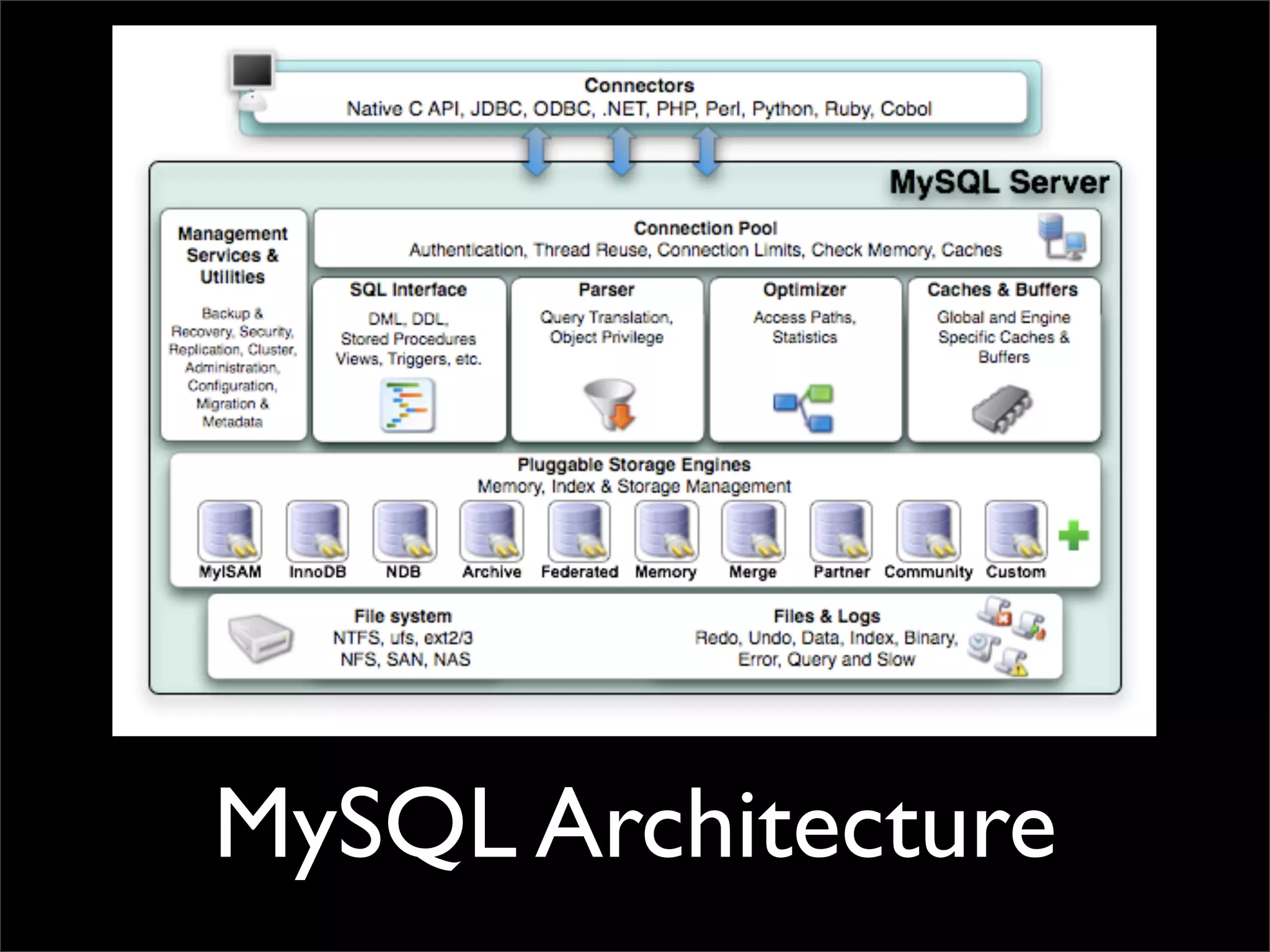
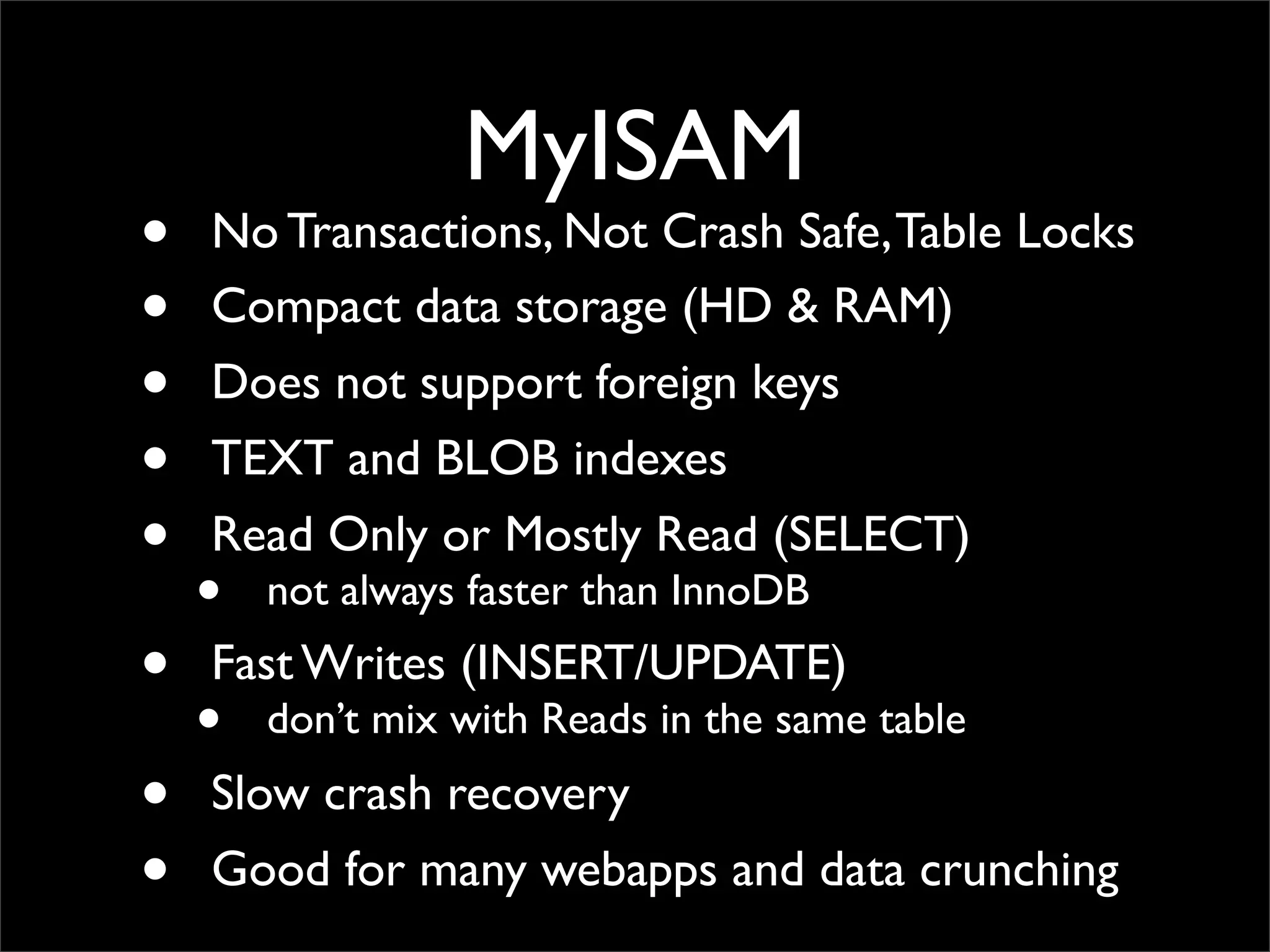
The document presents an introduction to MySQL performance optimization, emphasizing the importance of diagnosing performance issues with data and tools before implementing changes. It covers various aspects such as profiling applications, database architecture, index types, and optimal query strategies, including the use of MyISAM and InnoDB storage engines. Additionally, it references various resources for further learning about MySQL performance enhancement.