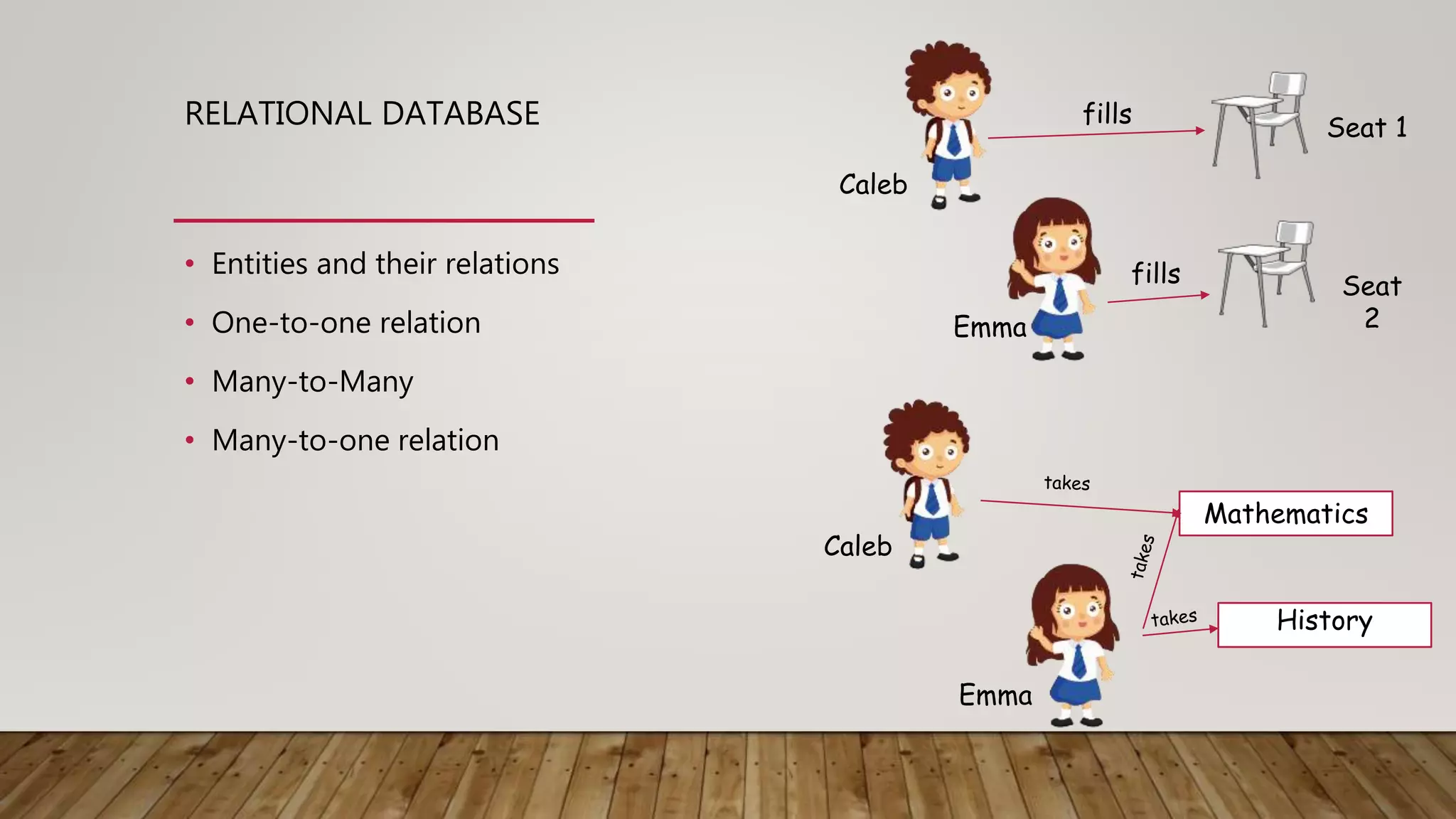
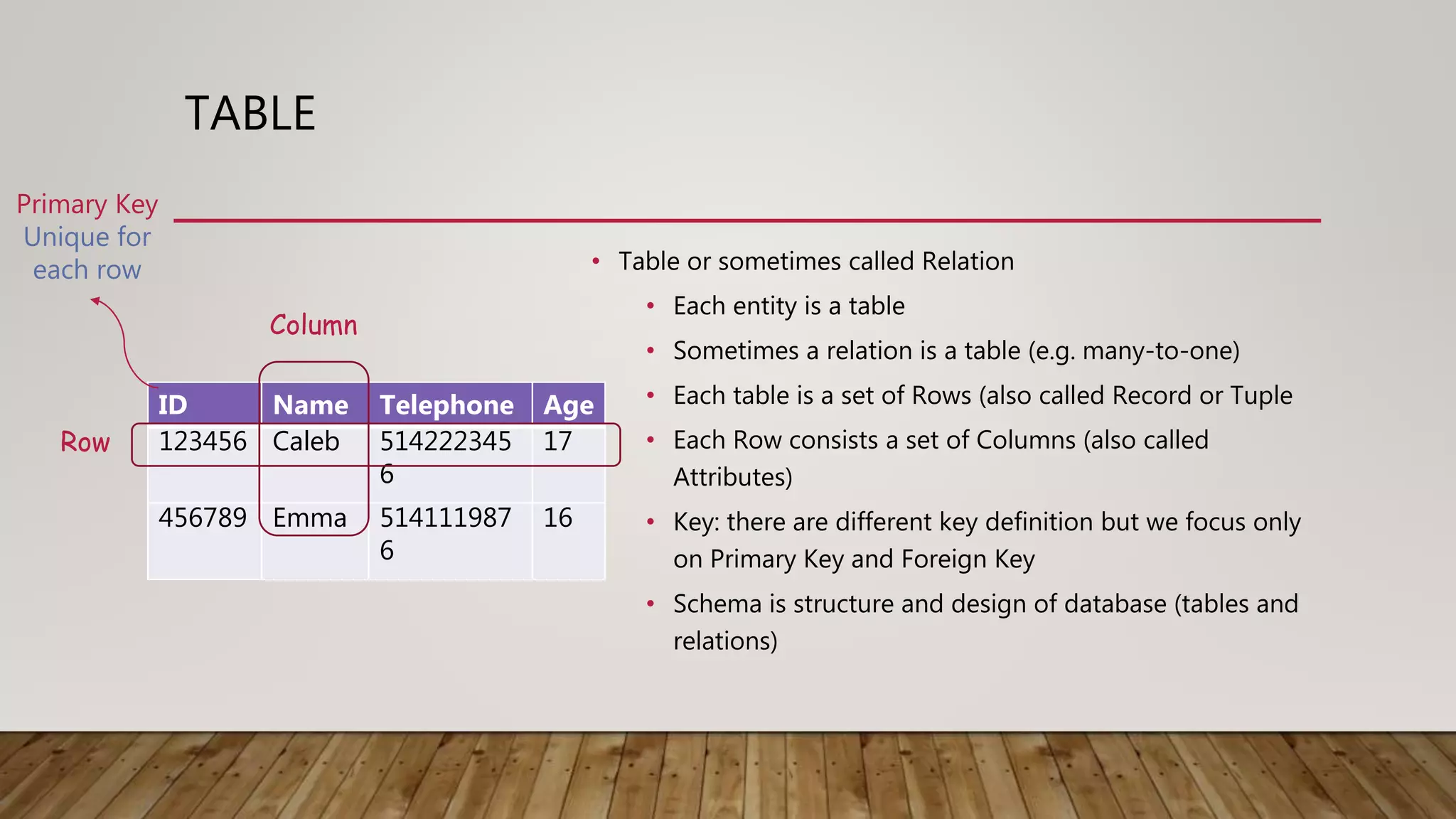
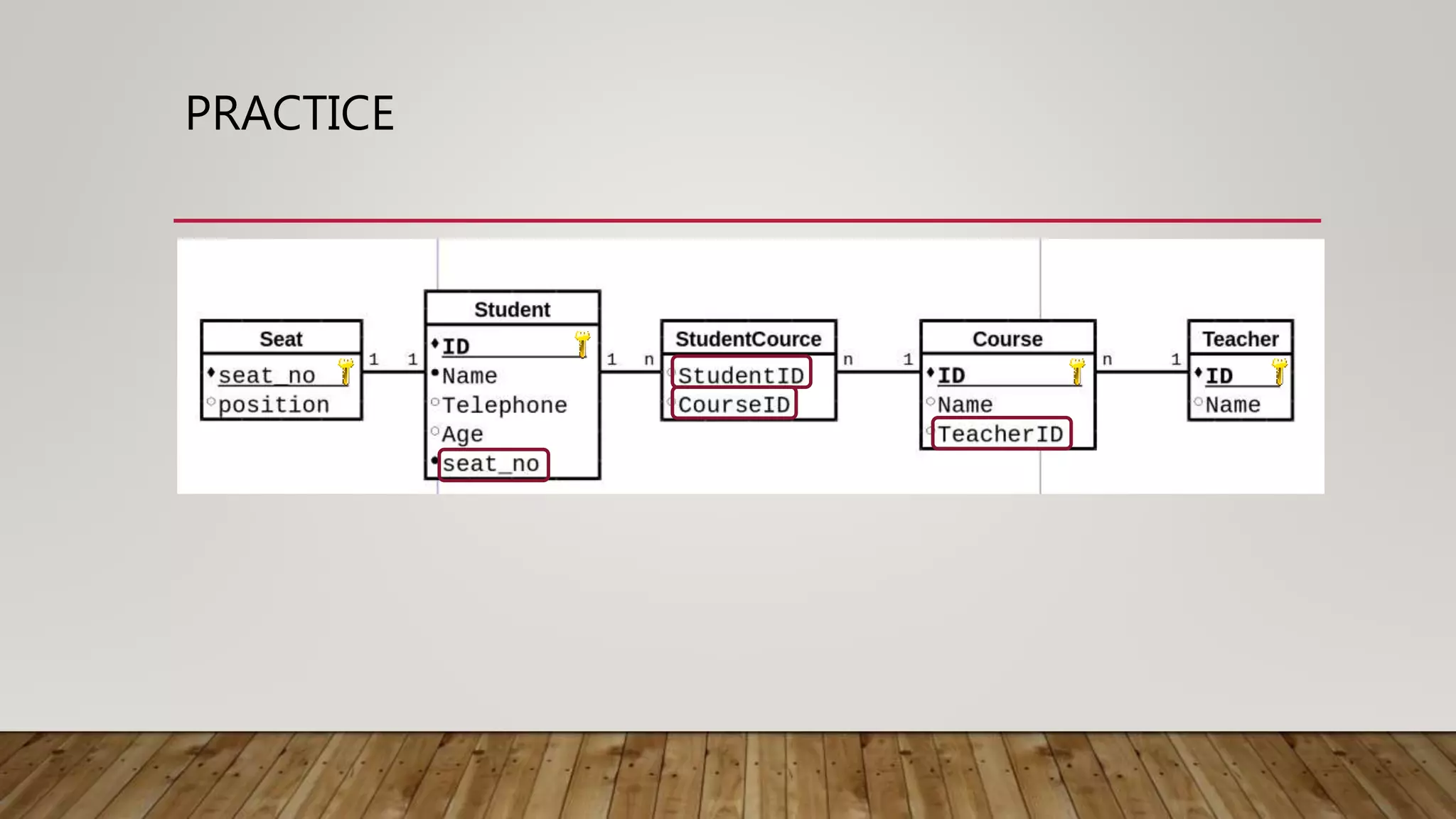
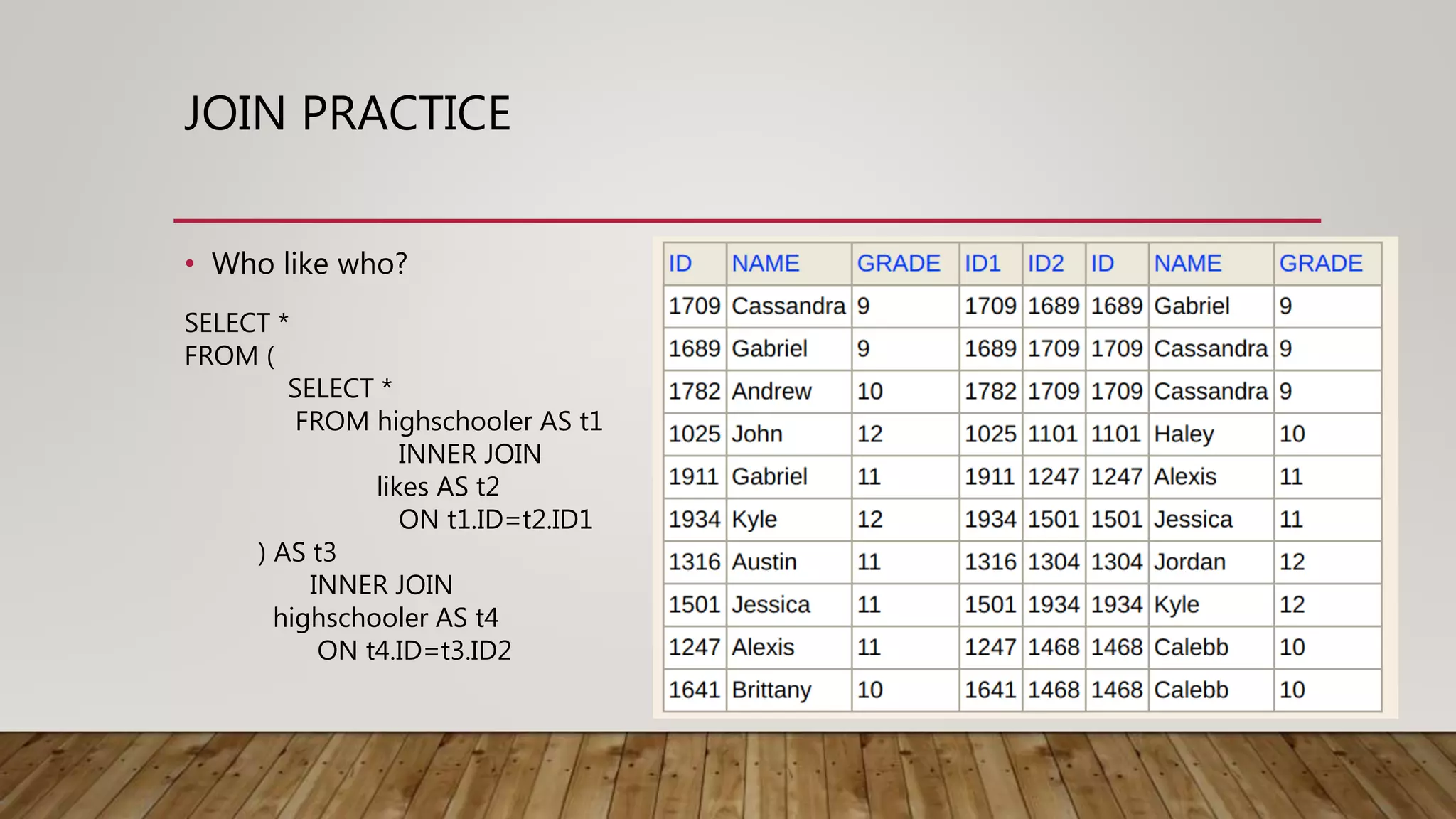
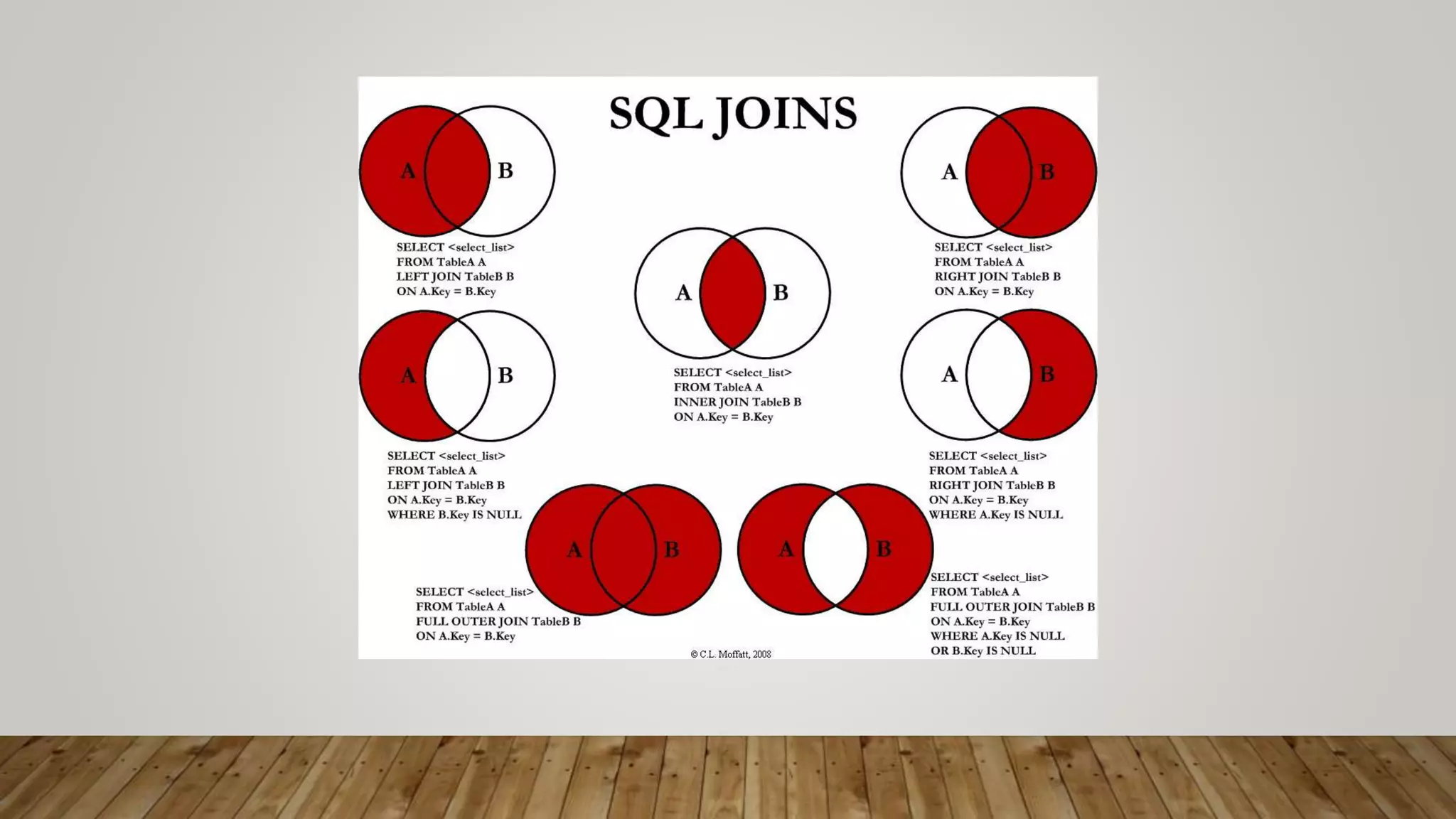
The document provides an overview of relational databases, including concepts like entities, relations, primary and foreign keys, and schema design. It introduces SQL for database interaction, detailing commands for inserting, updating, and selecting data, along with examples of join operations. Additionally, it includes practice queries and resources for further learning about SQL and database management.