The document explains branching structures in programming, specifically focusing on algorithms and their implementation in Pascal. It covers types of branching, including one case, two cases, three/many cases, and many conditions branching, providing algorithm notations and examples for each type. Additionally, it describes case structures and includes example algorithms for practical understanding.













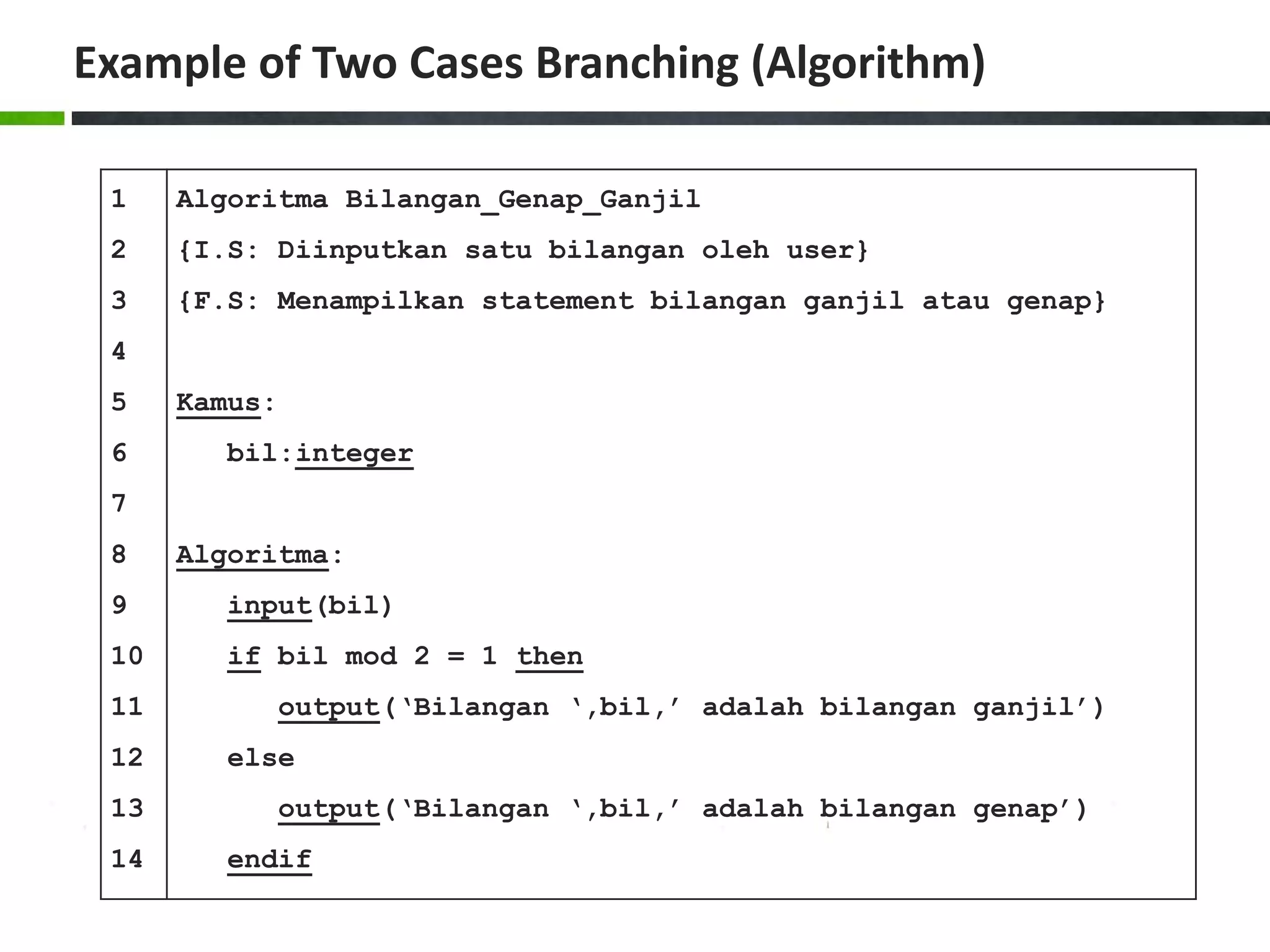

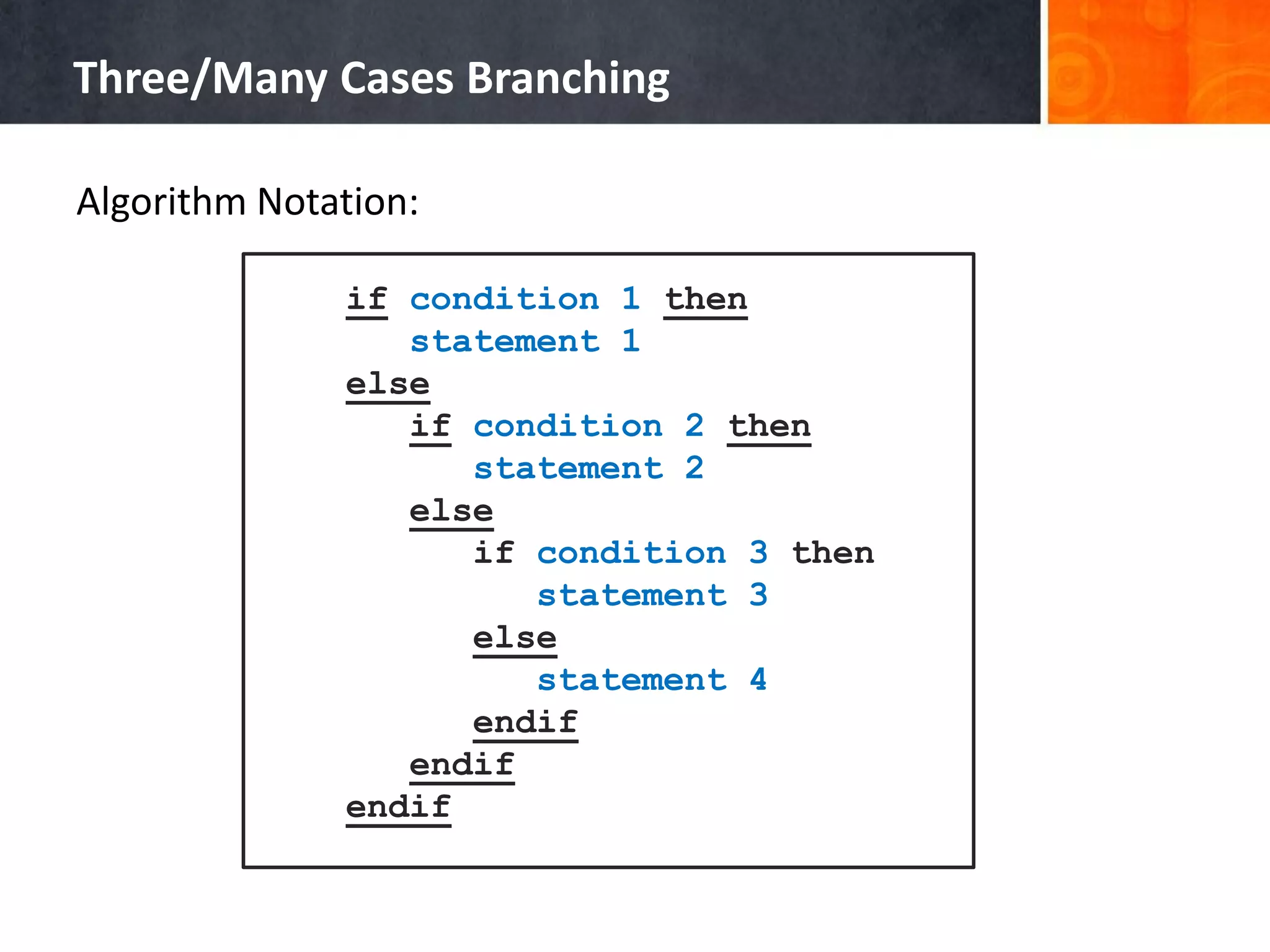



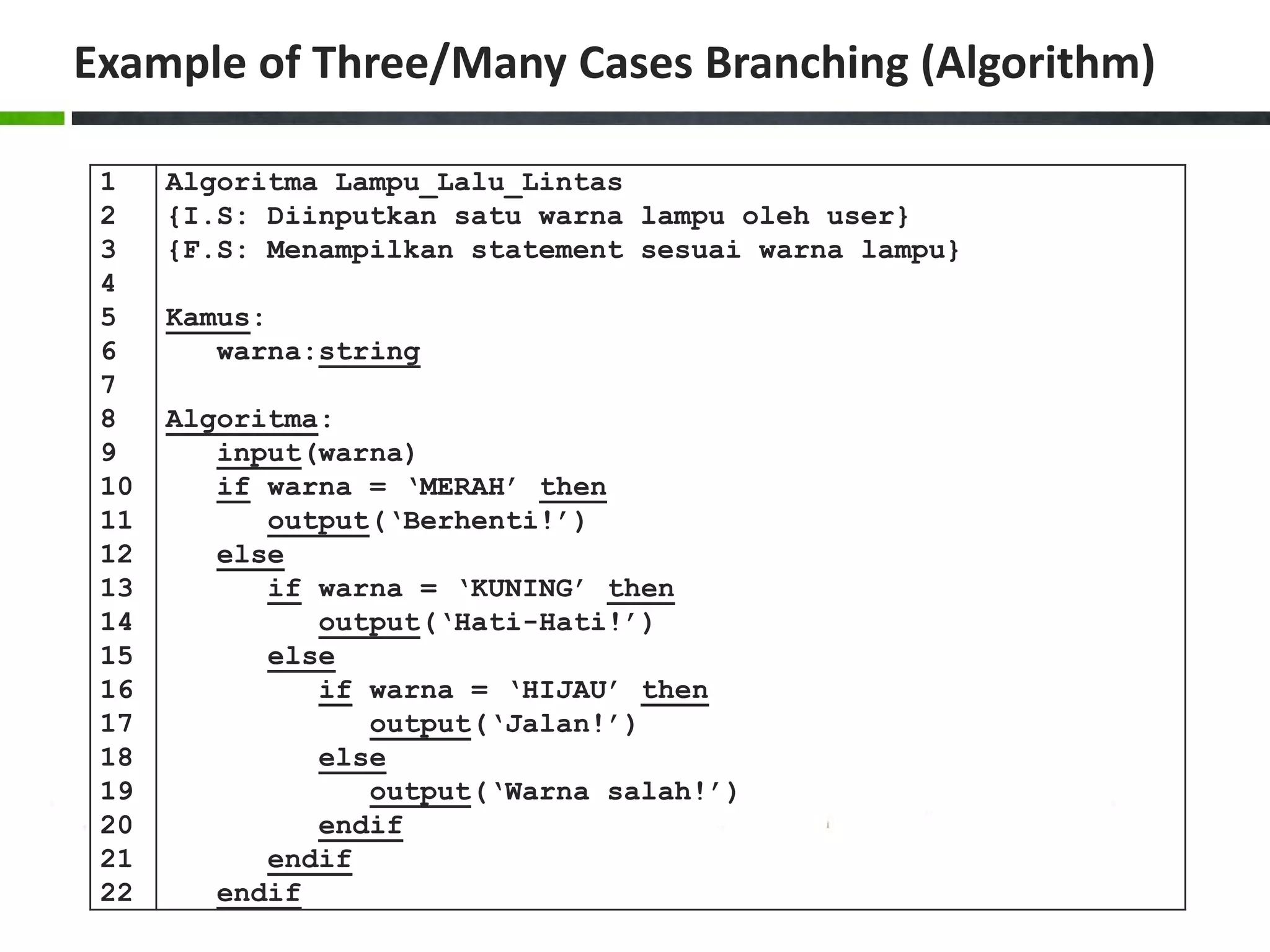
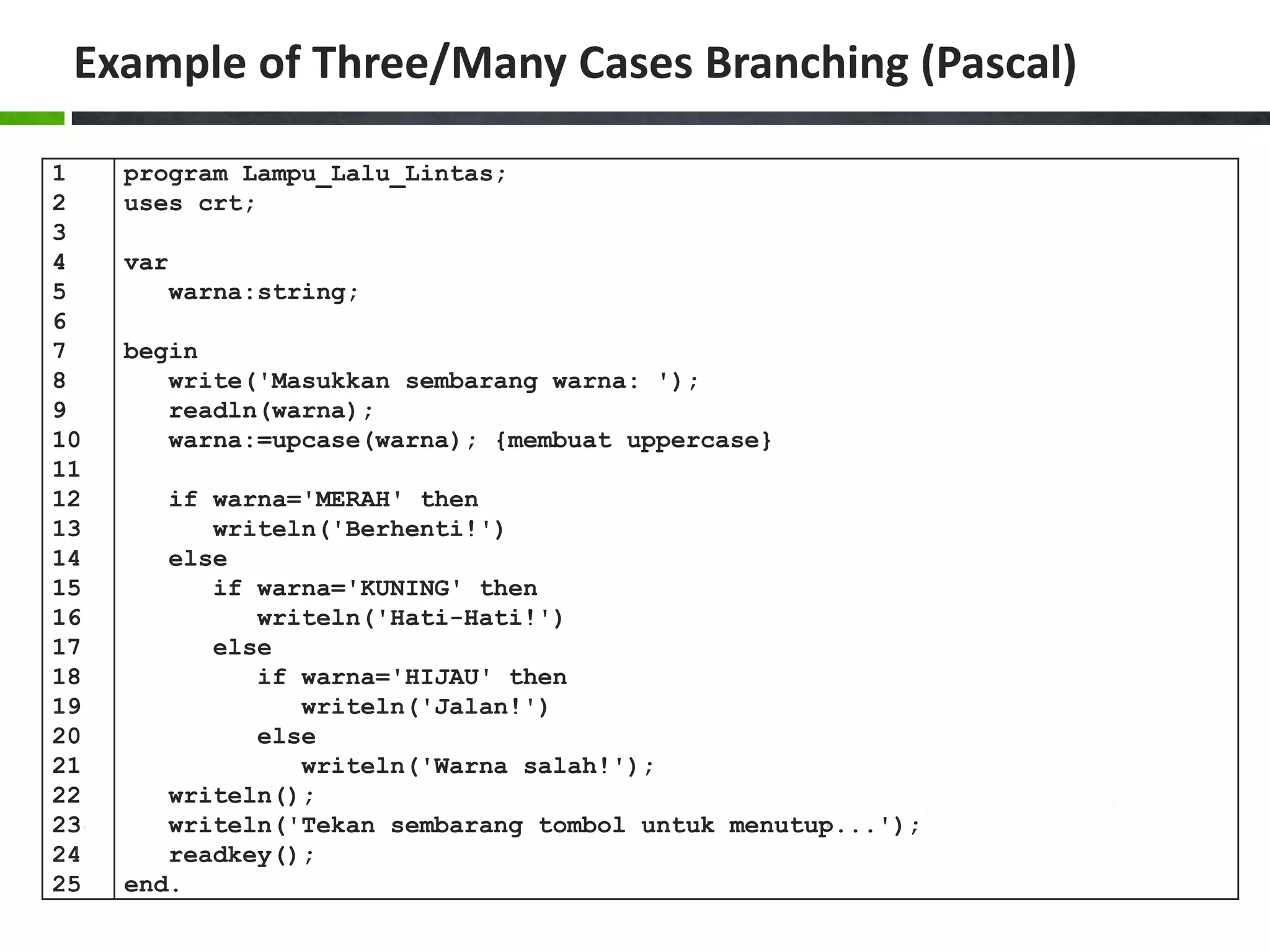


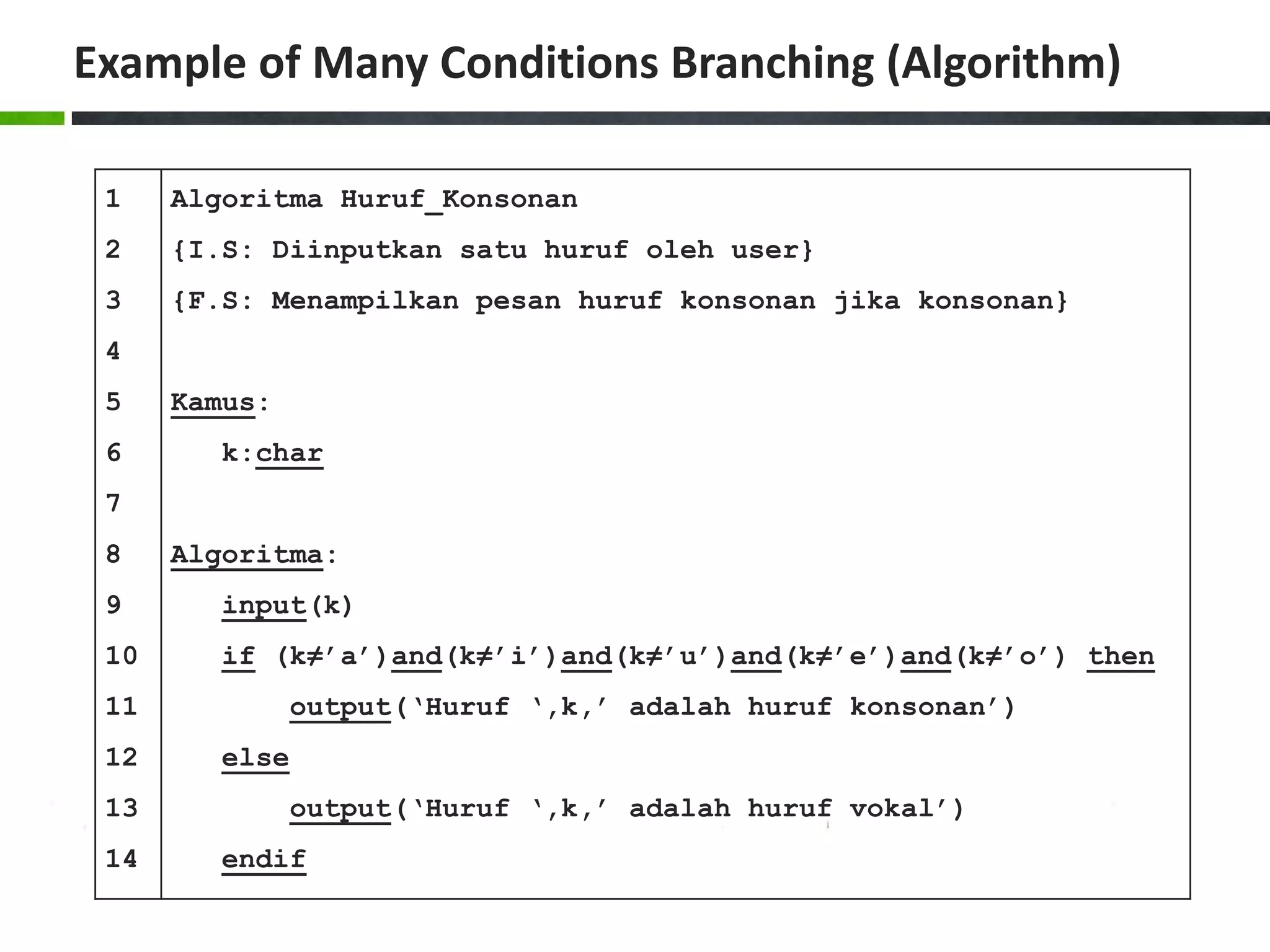
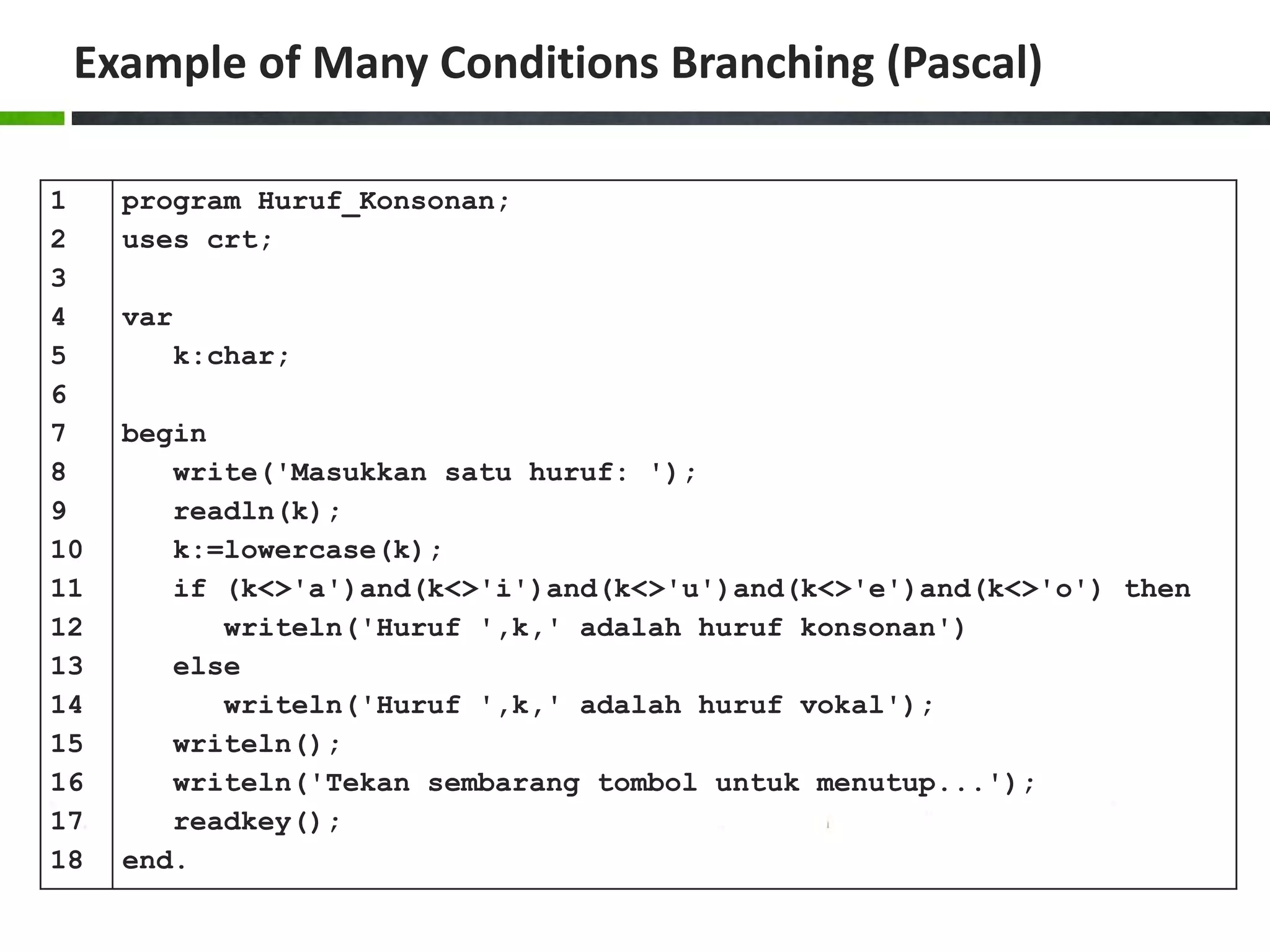


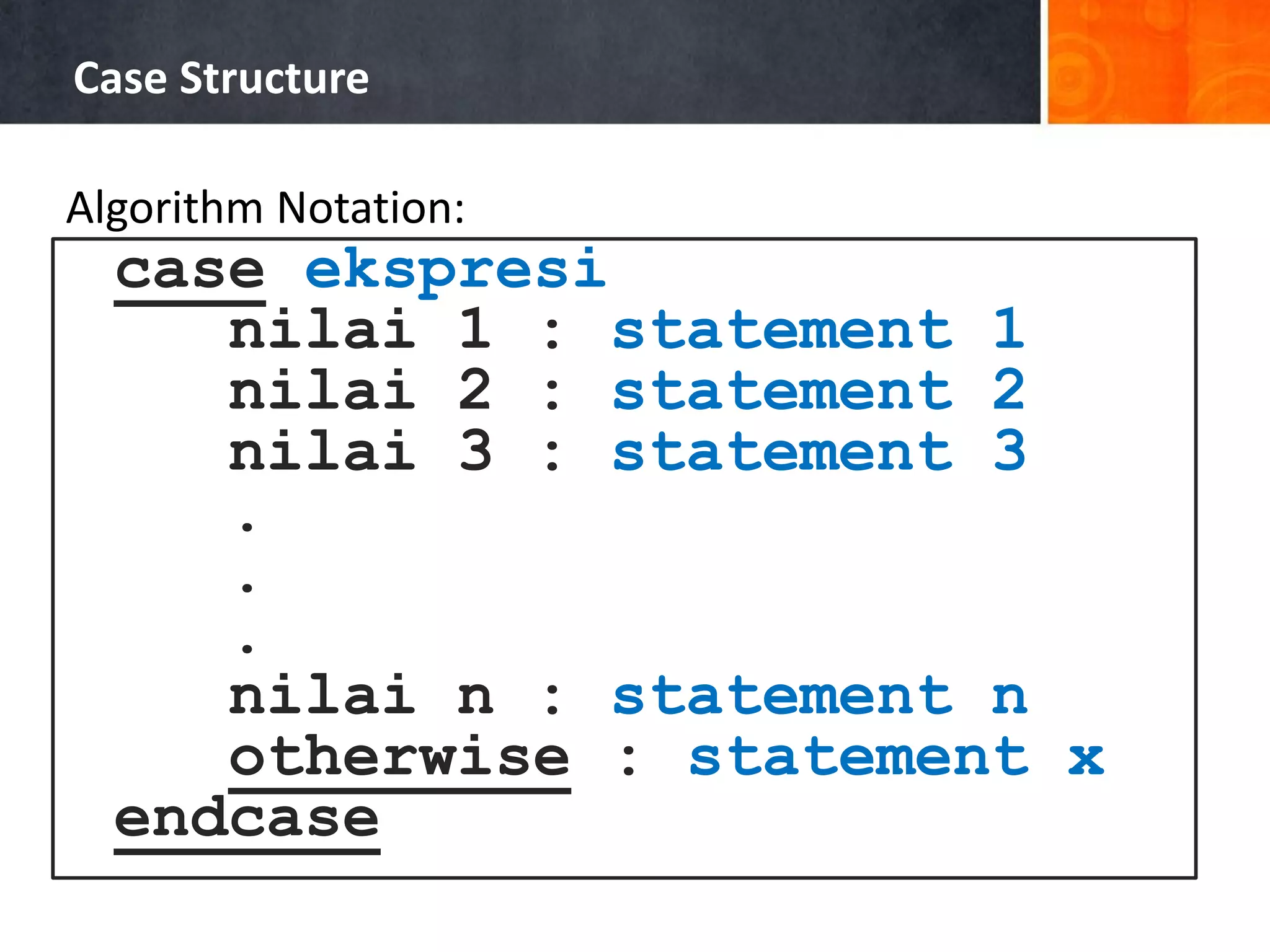


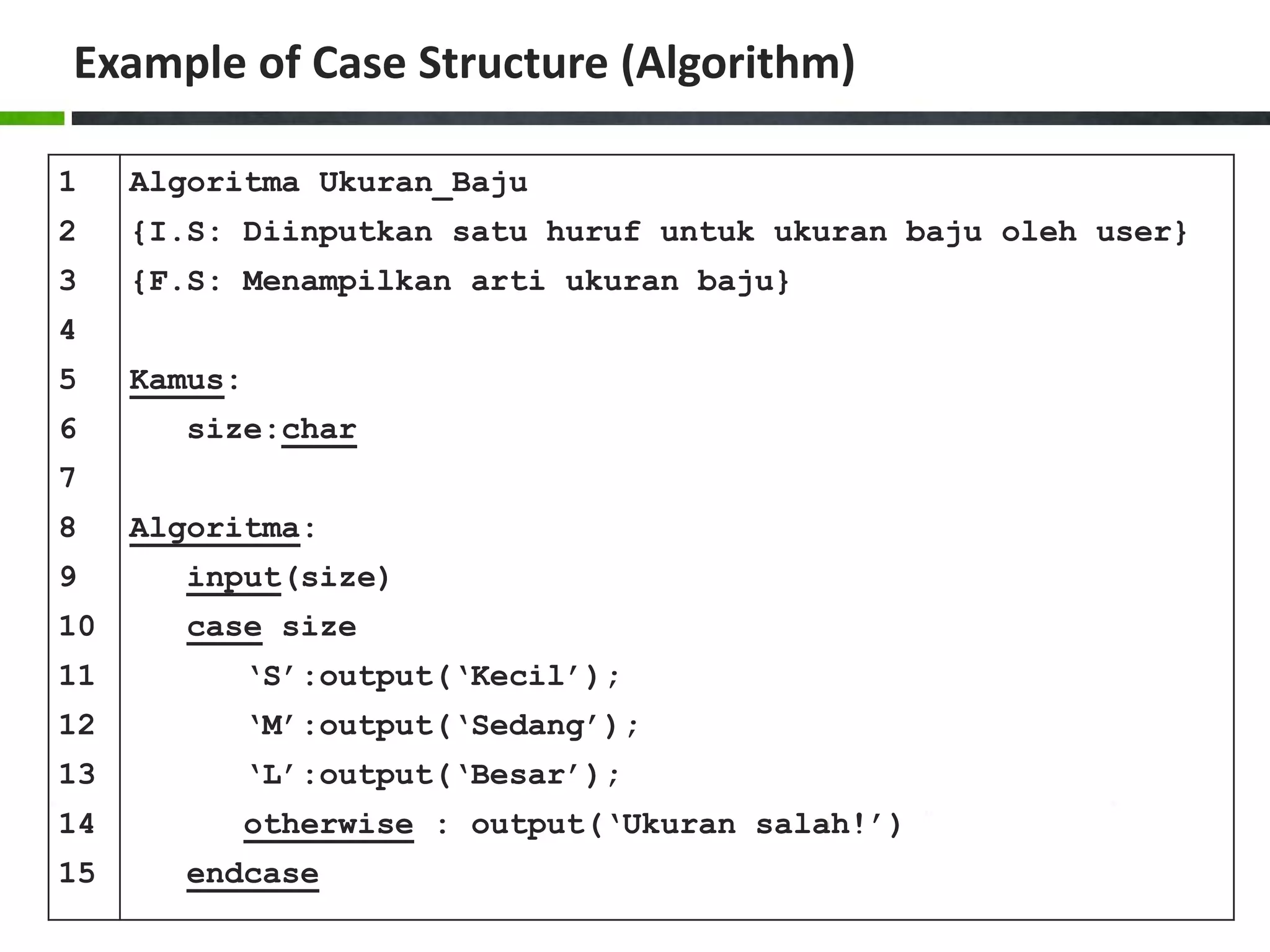
![Example of Case Structure (Pascal) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 program Ukuran_Baju; uses crt; var size:char; begin write('Masukkan ukuran baju [S/M/L]: '); readln(size); size:=upcase(size); case size of 'S':writeln('Kecil'); 'M':writeln('Sedang'); 'L':writeln('Besar'); else writeln('Ukuran salah!'); end; writeln(); writeln('Tekan sembarang tombol untuk menutup...'); readkey(); end.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4-branchingstructure-161018111503/75/Algorithm-and-Programming-Branching-Structure-36-2048.jpg)
