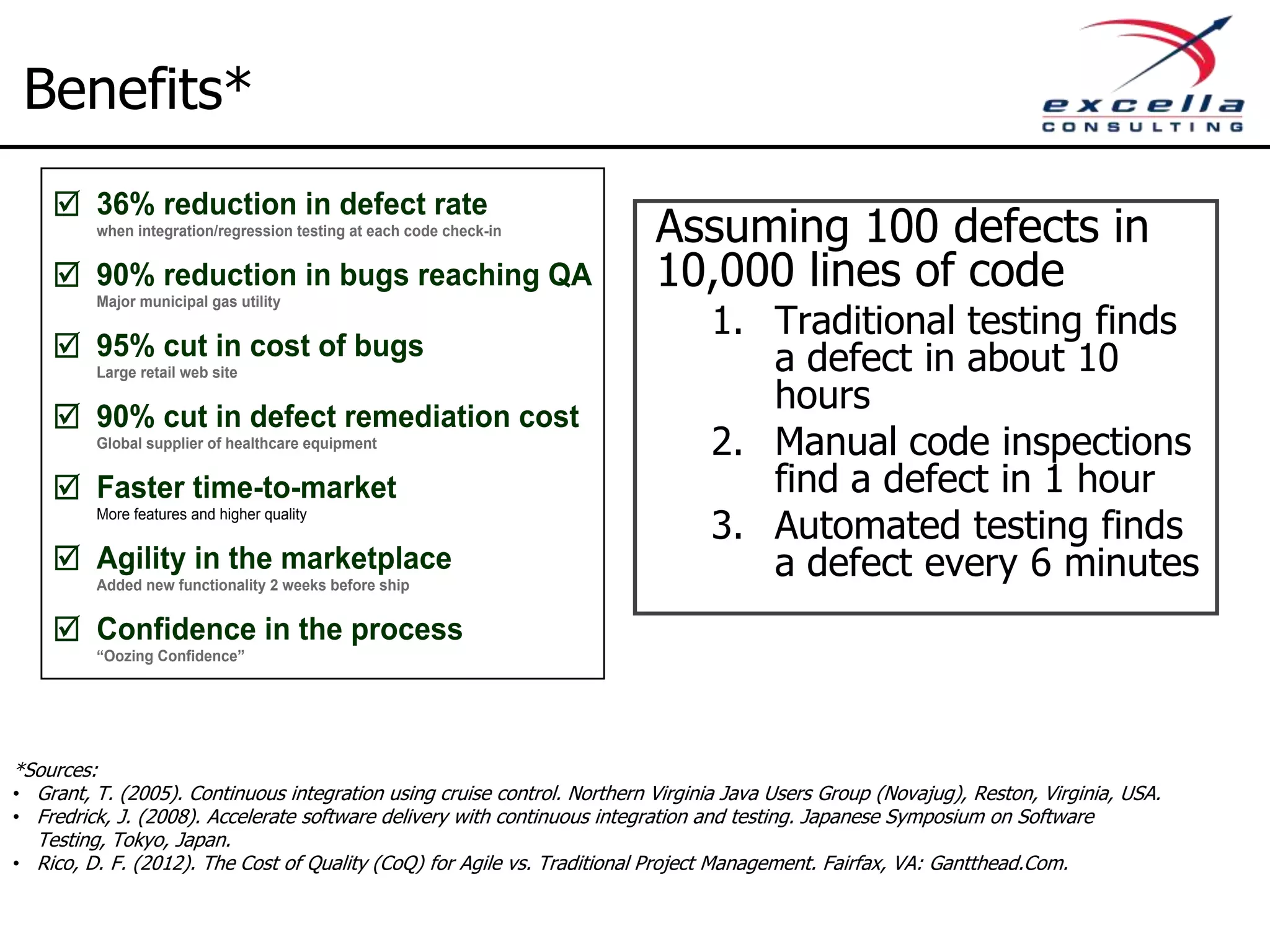
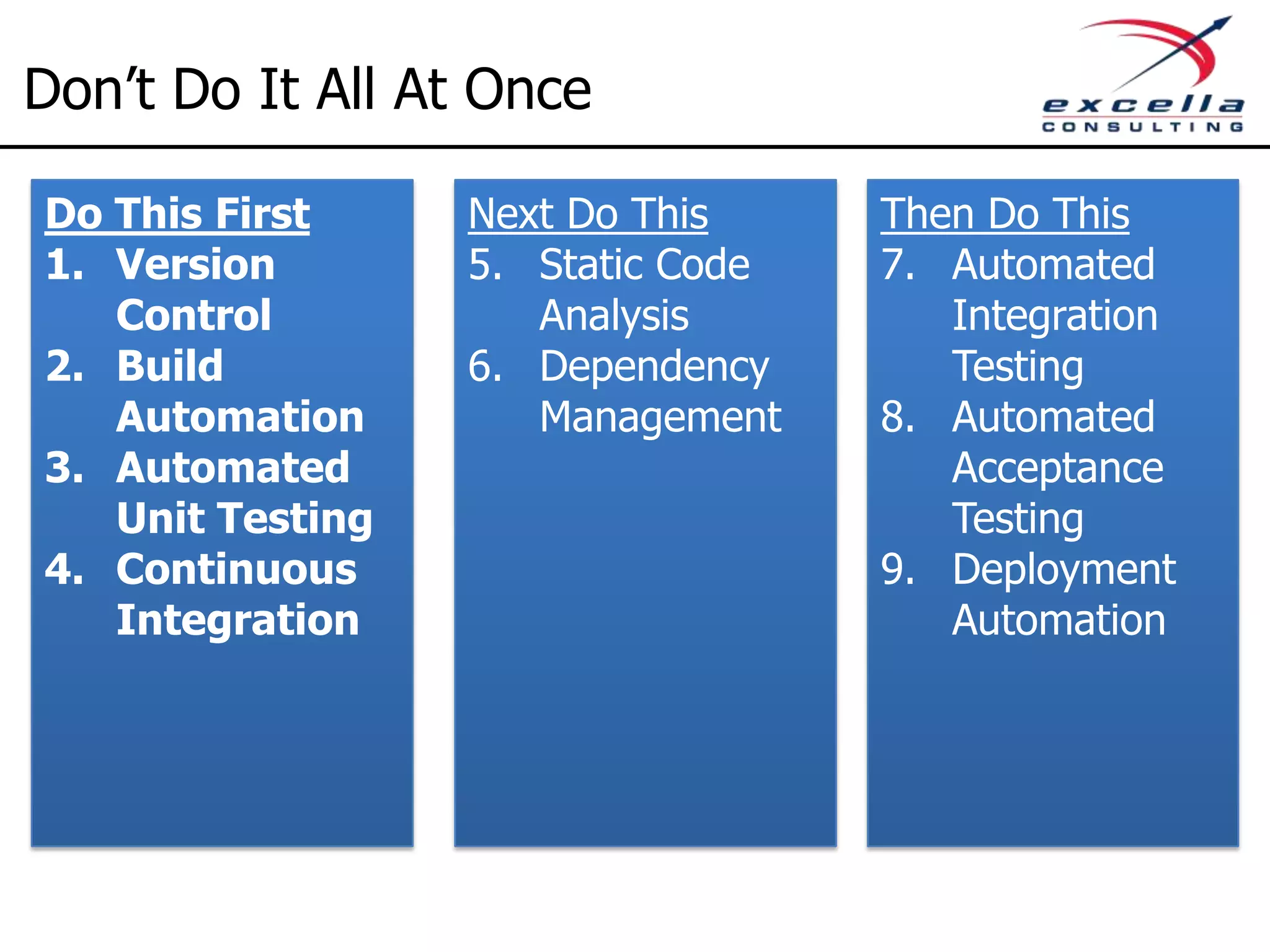
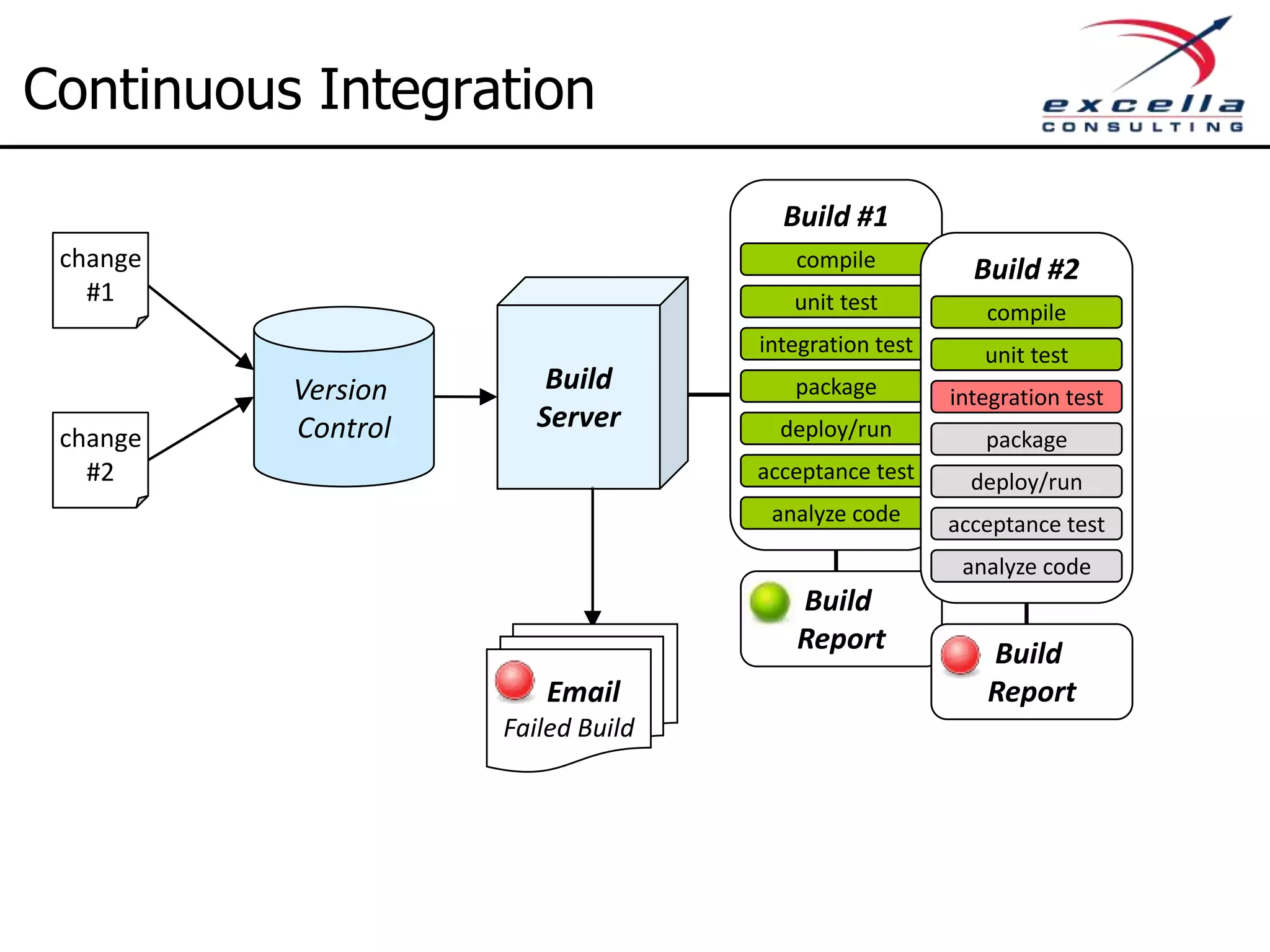
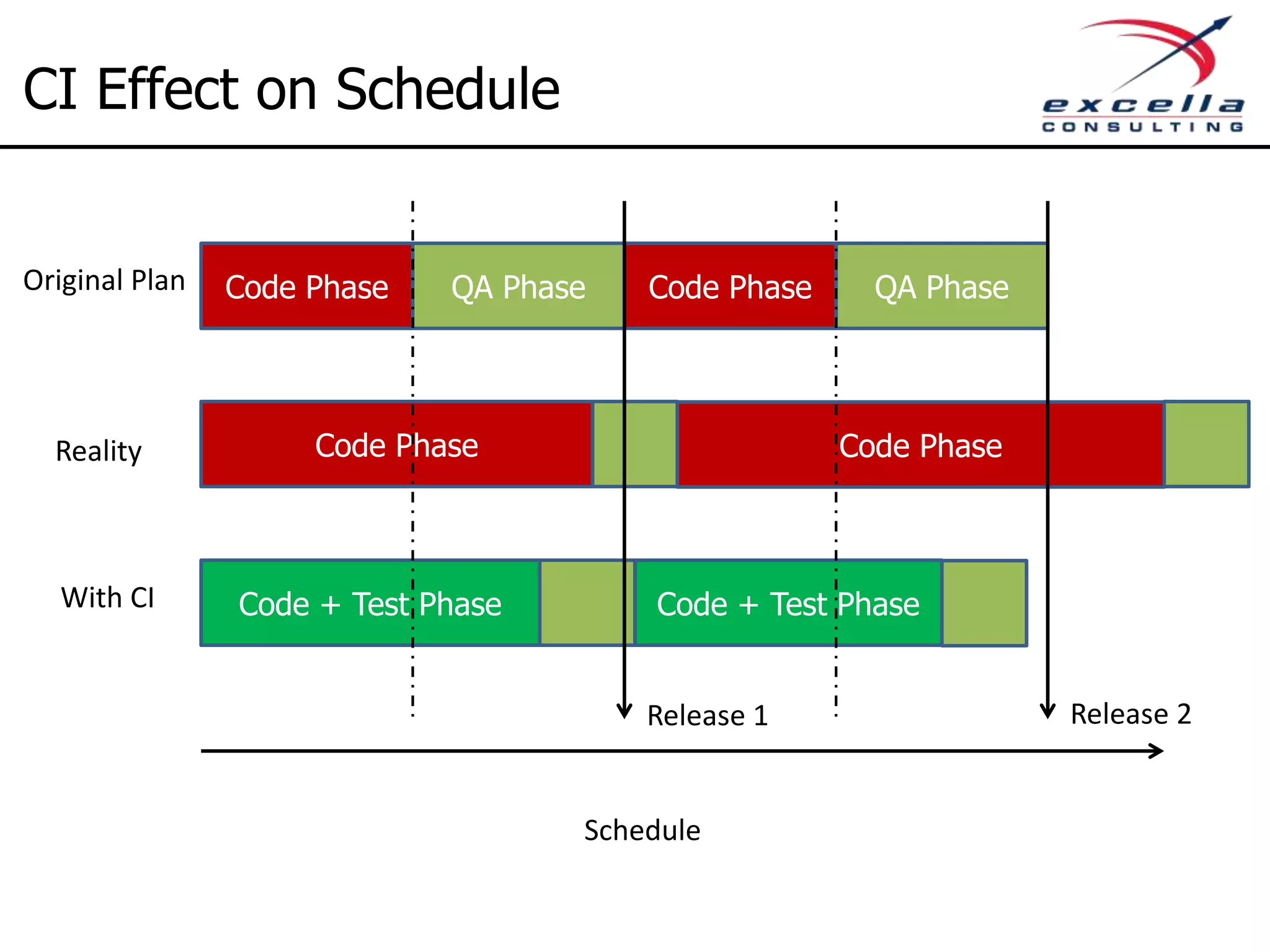
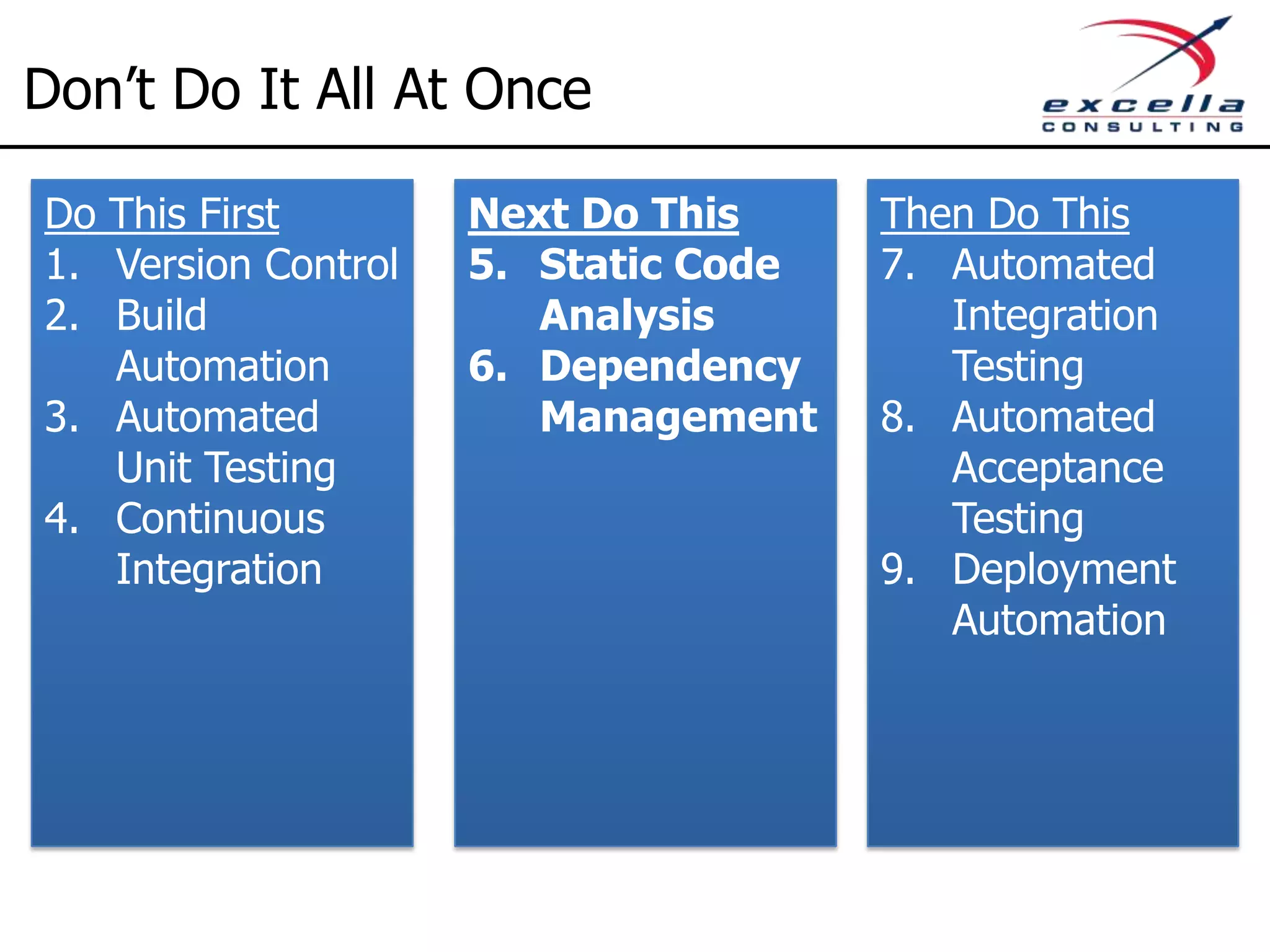
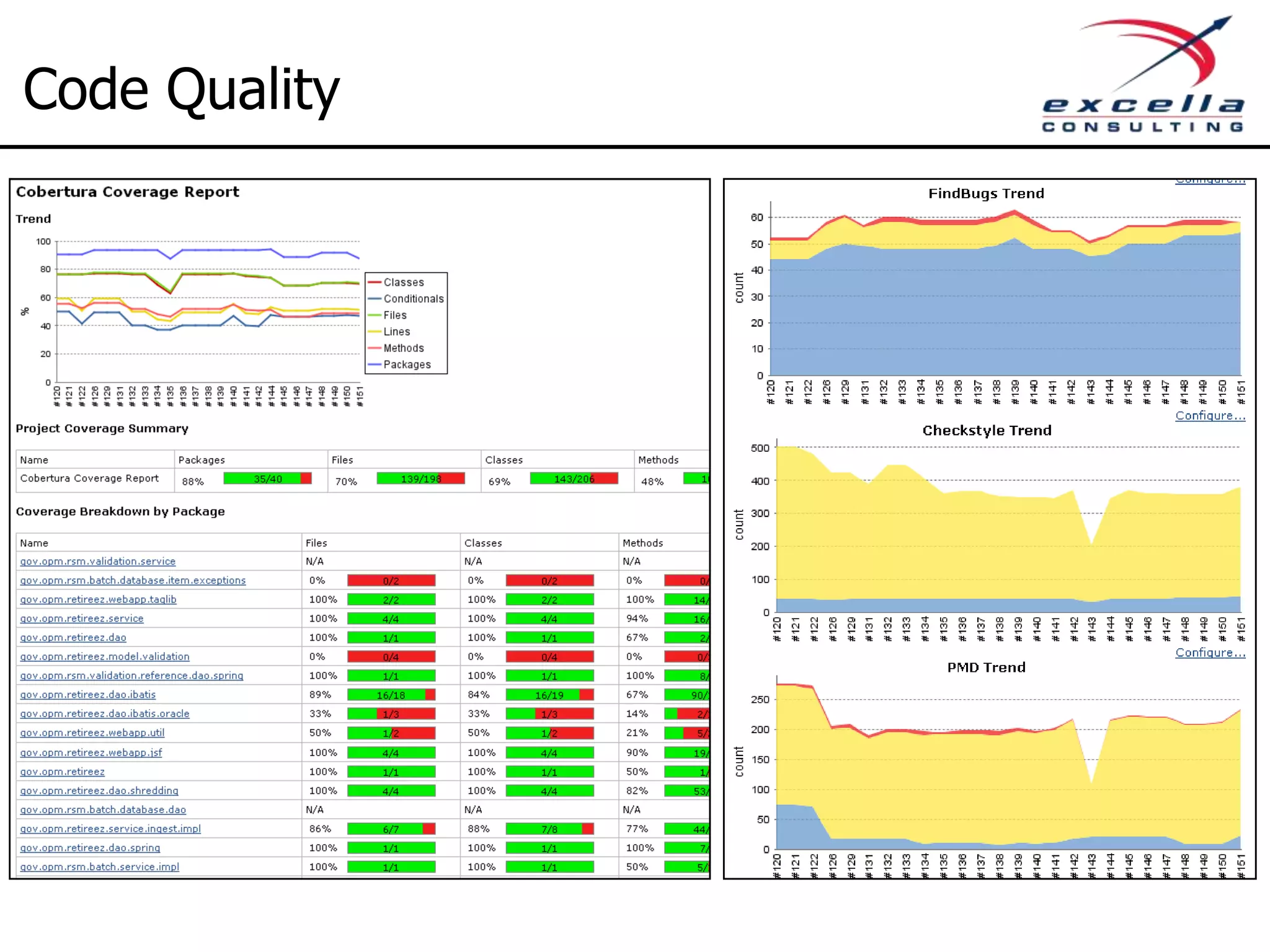
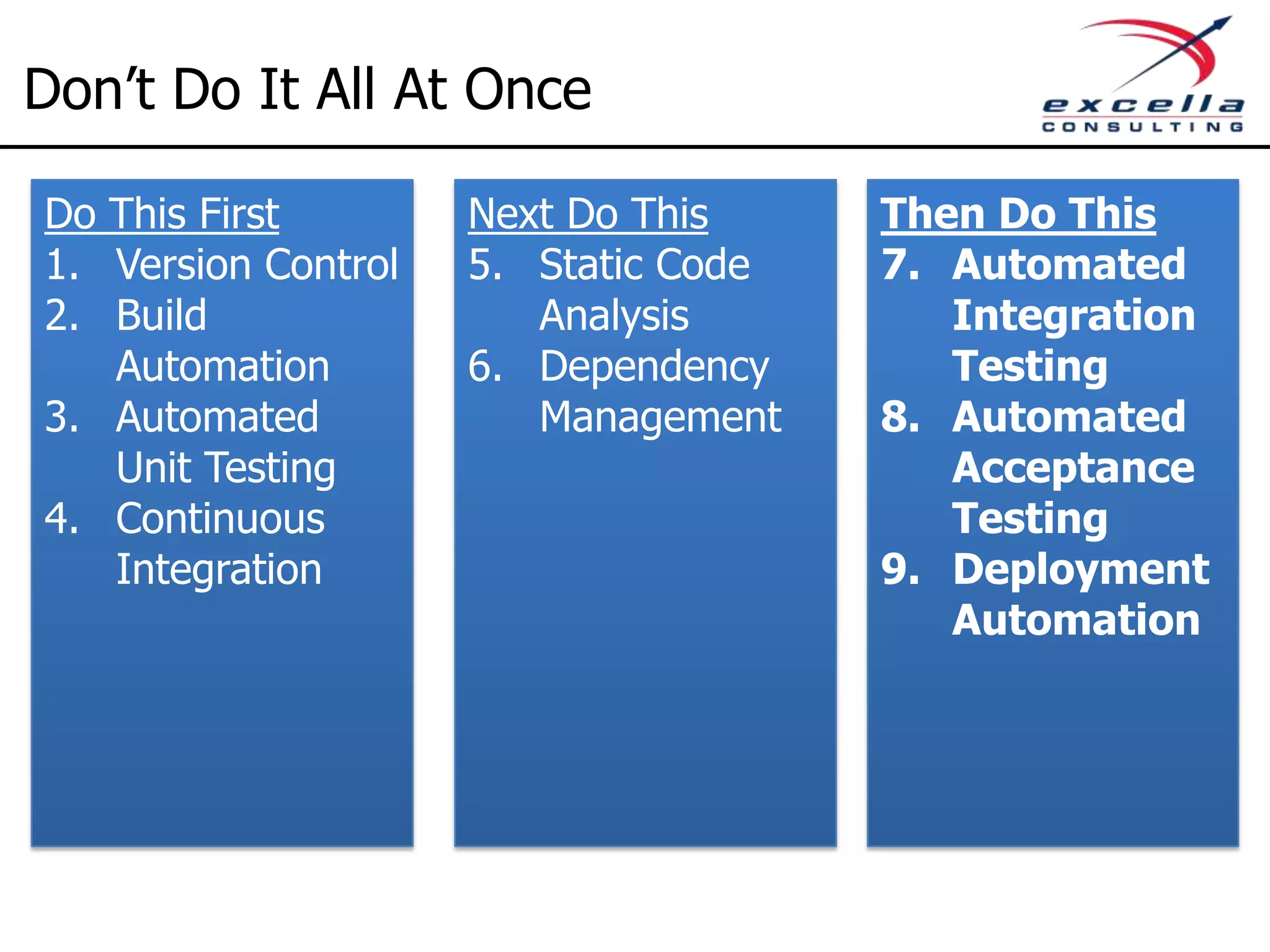
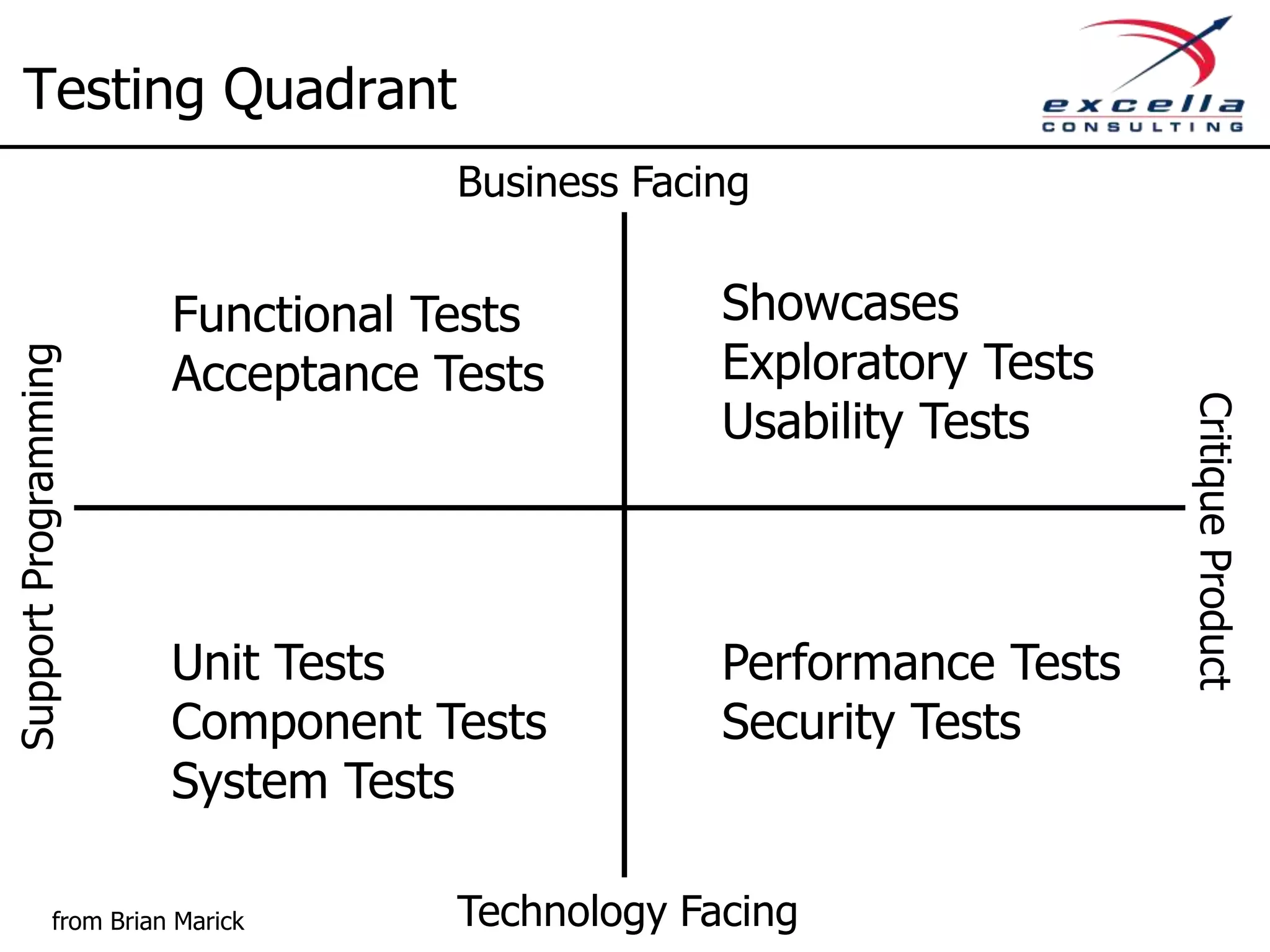
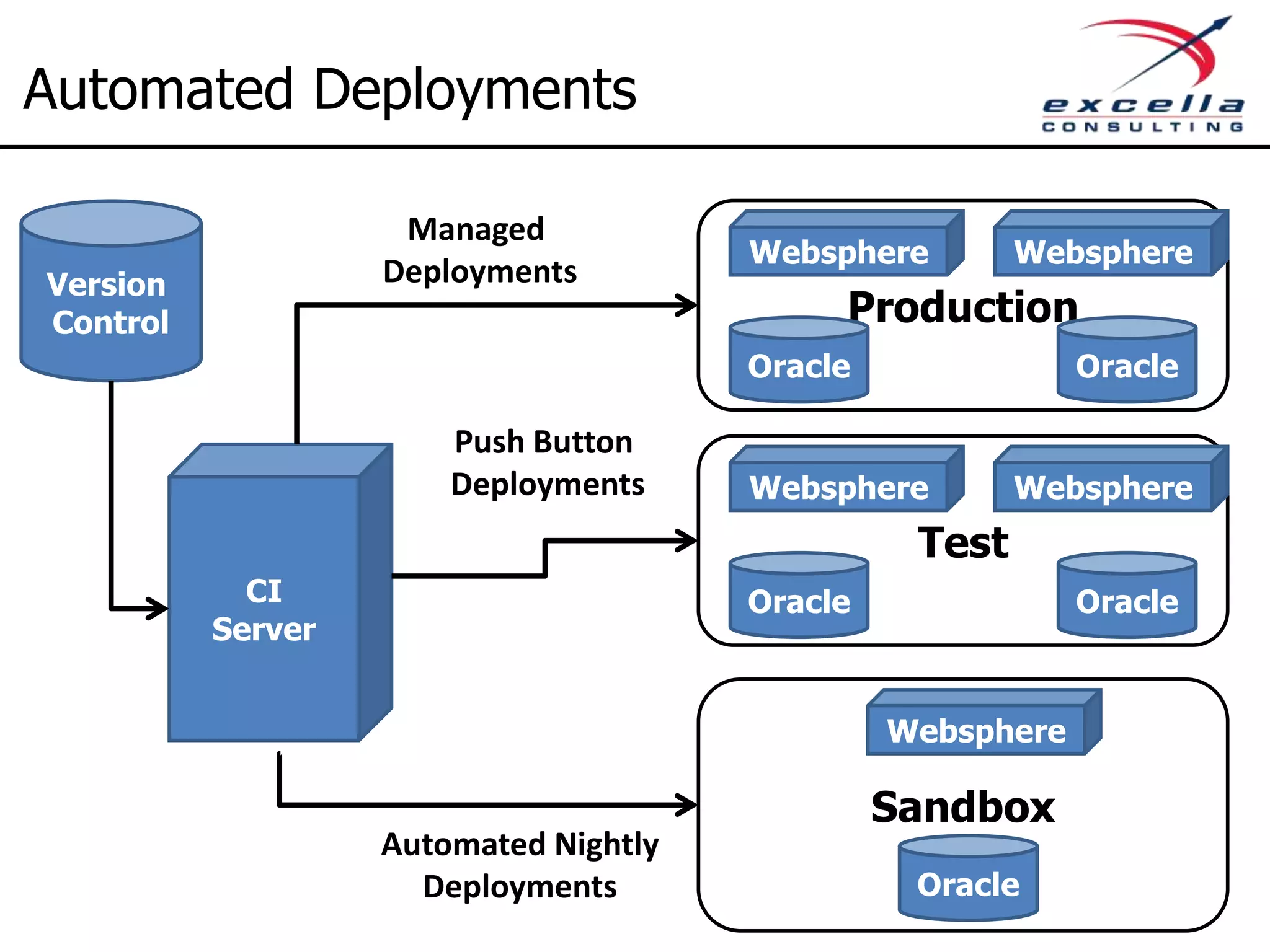
The document outlines best practices for implementing Agile methodologies, emphasizing the importance of continuous integration, automated testing, and build automation to improve software quality and reduce defect rates. It details a step-by-step approach for developers to adopt various technologies and practices, including version control and integration testing. The document also includes benefits of Agile practices, references to further reading, and contact information for coaching and training services at Excella Consulting.