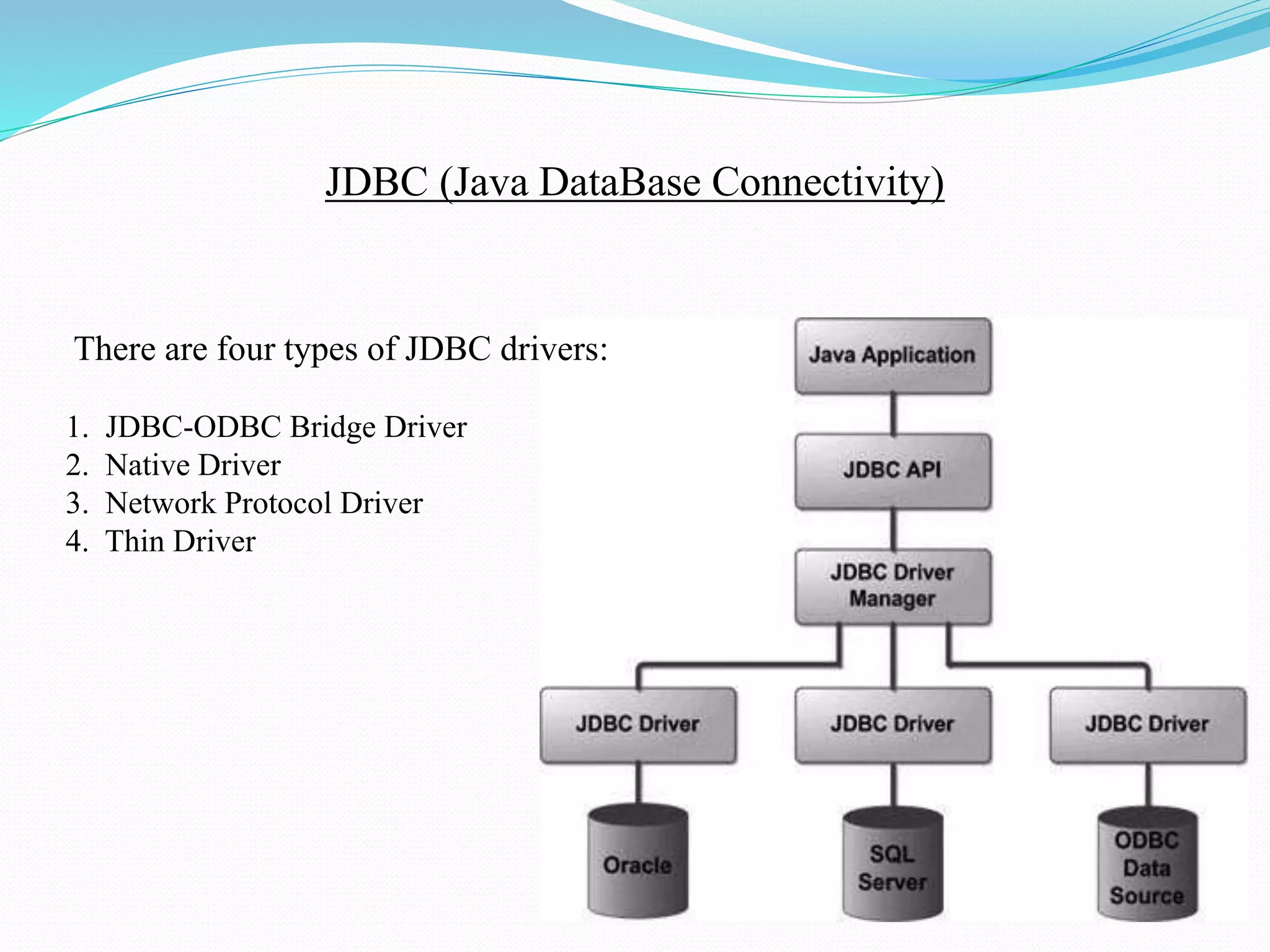
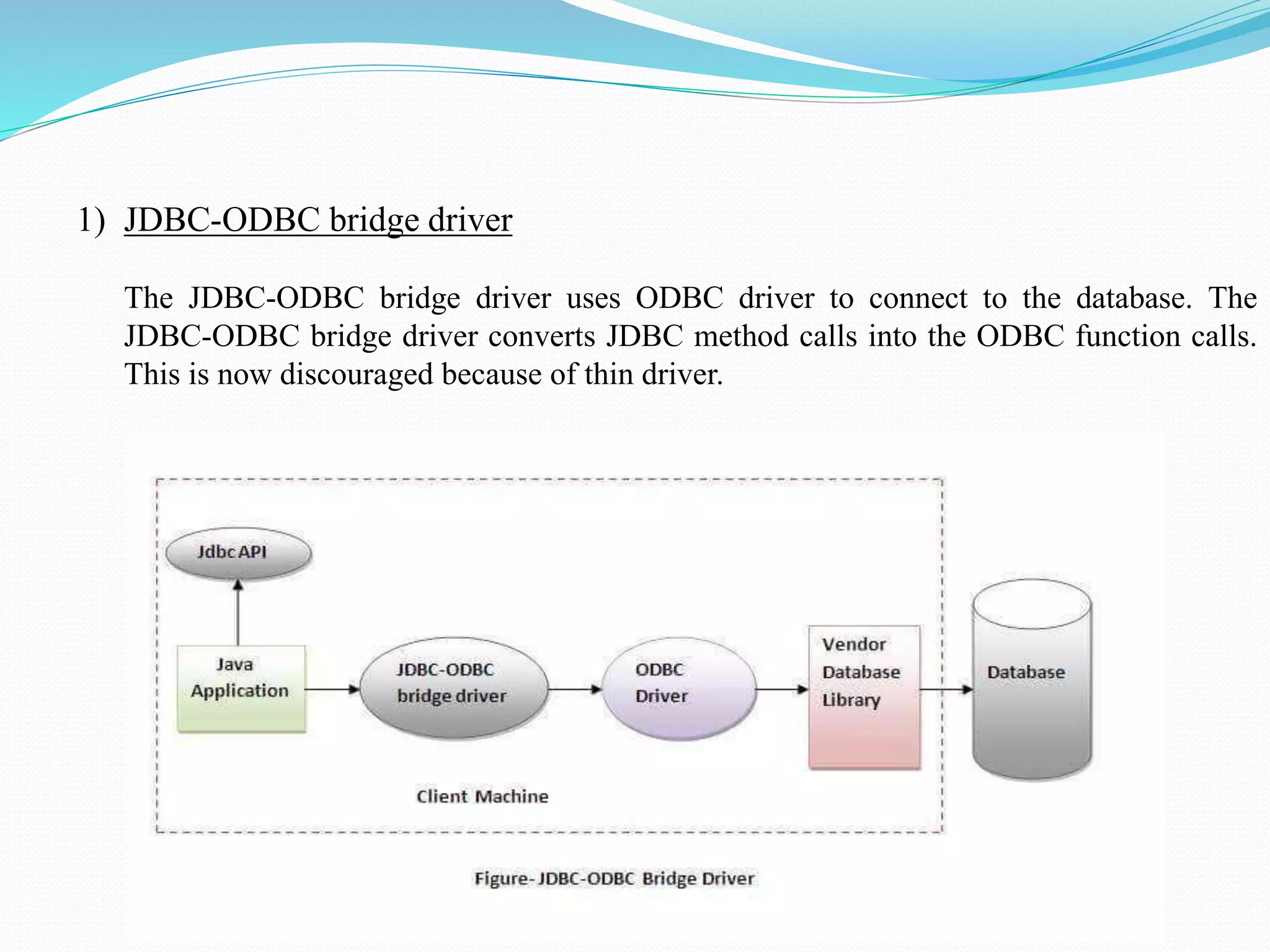
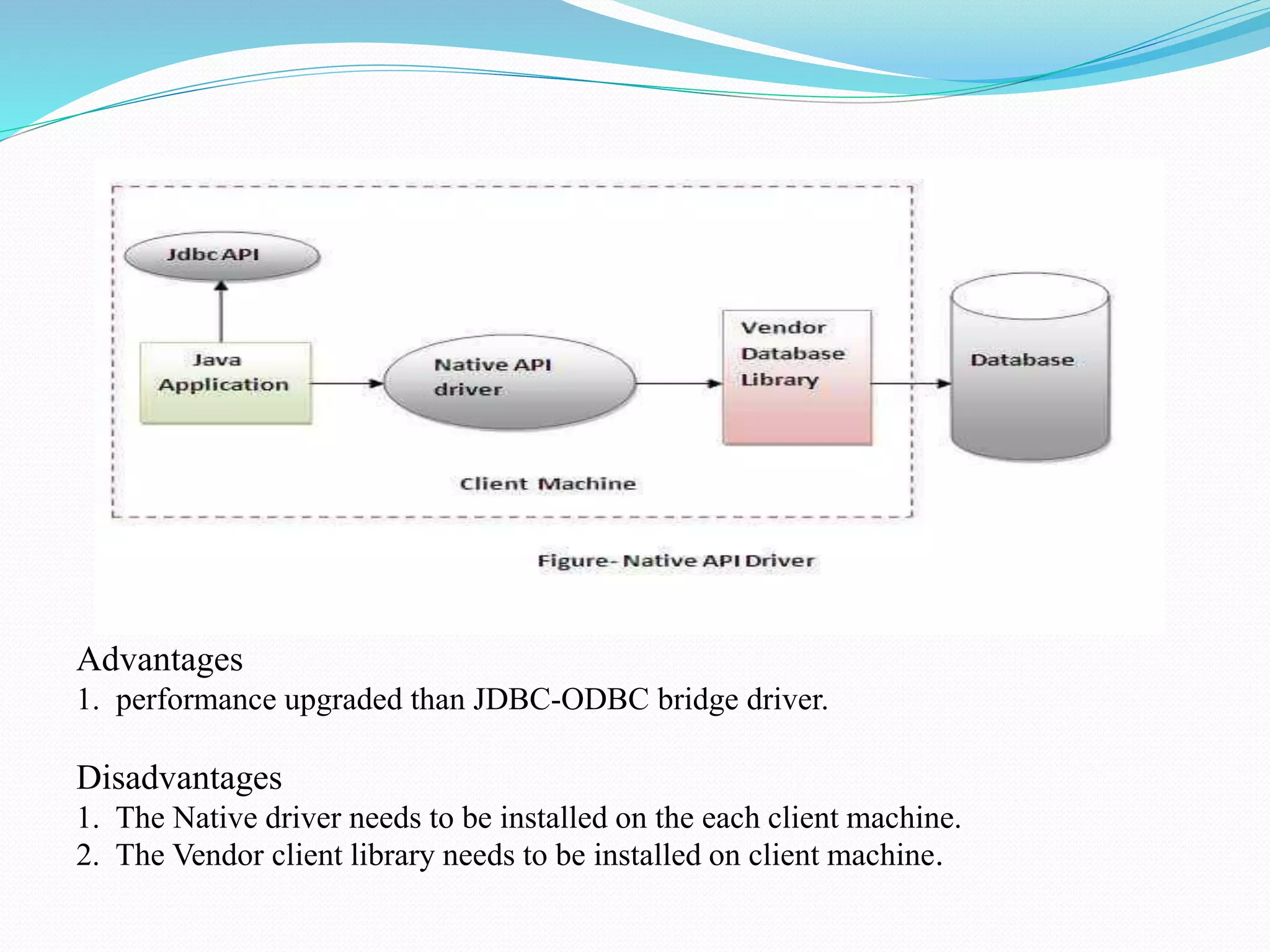
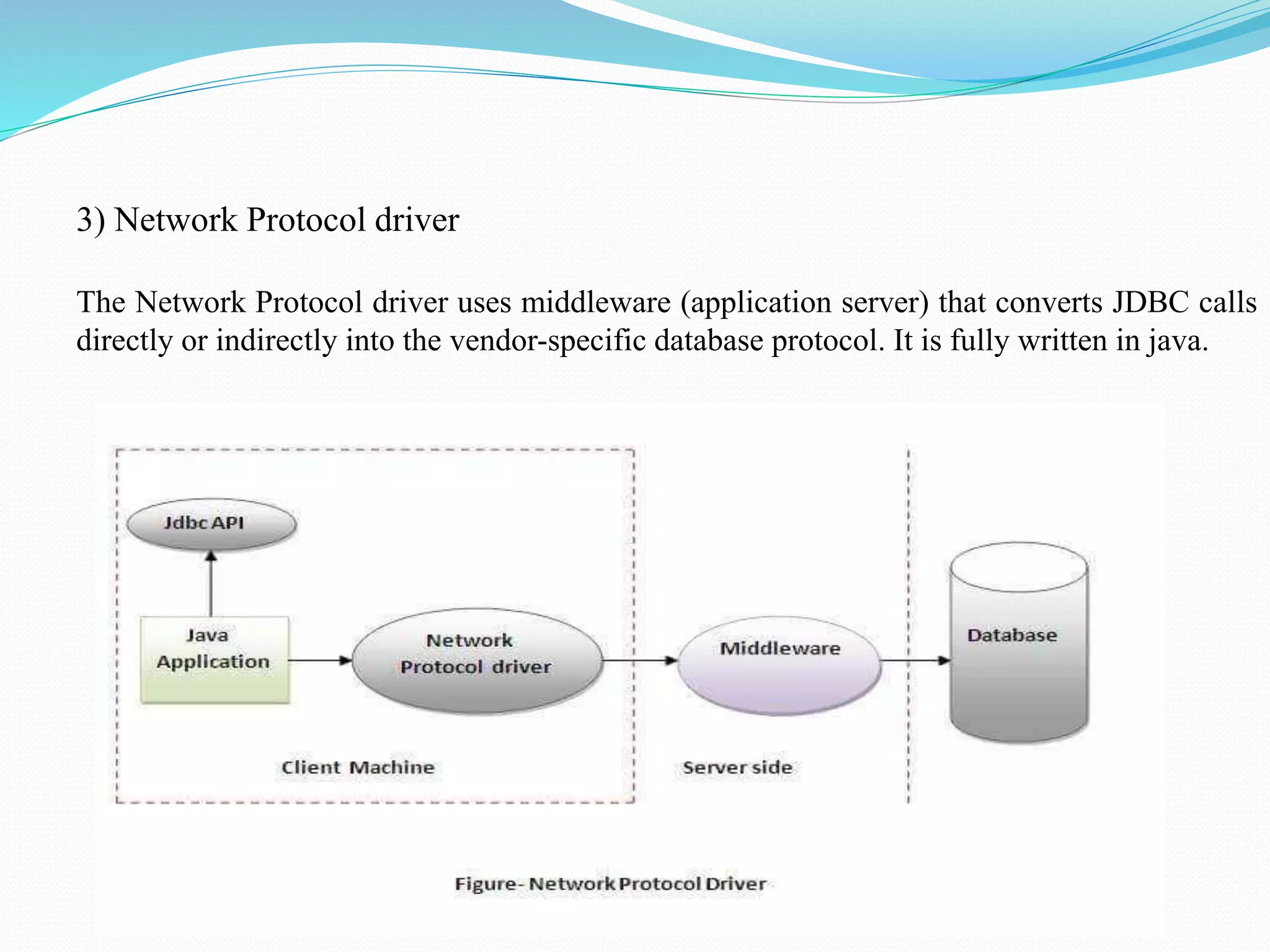
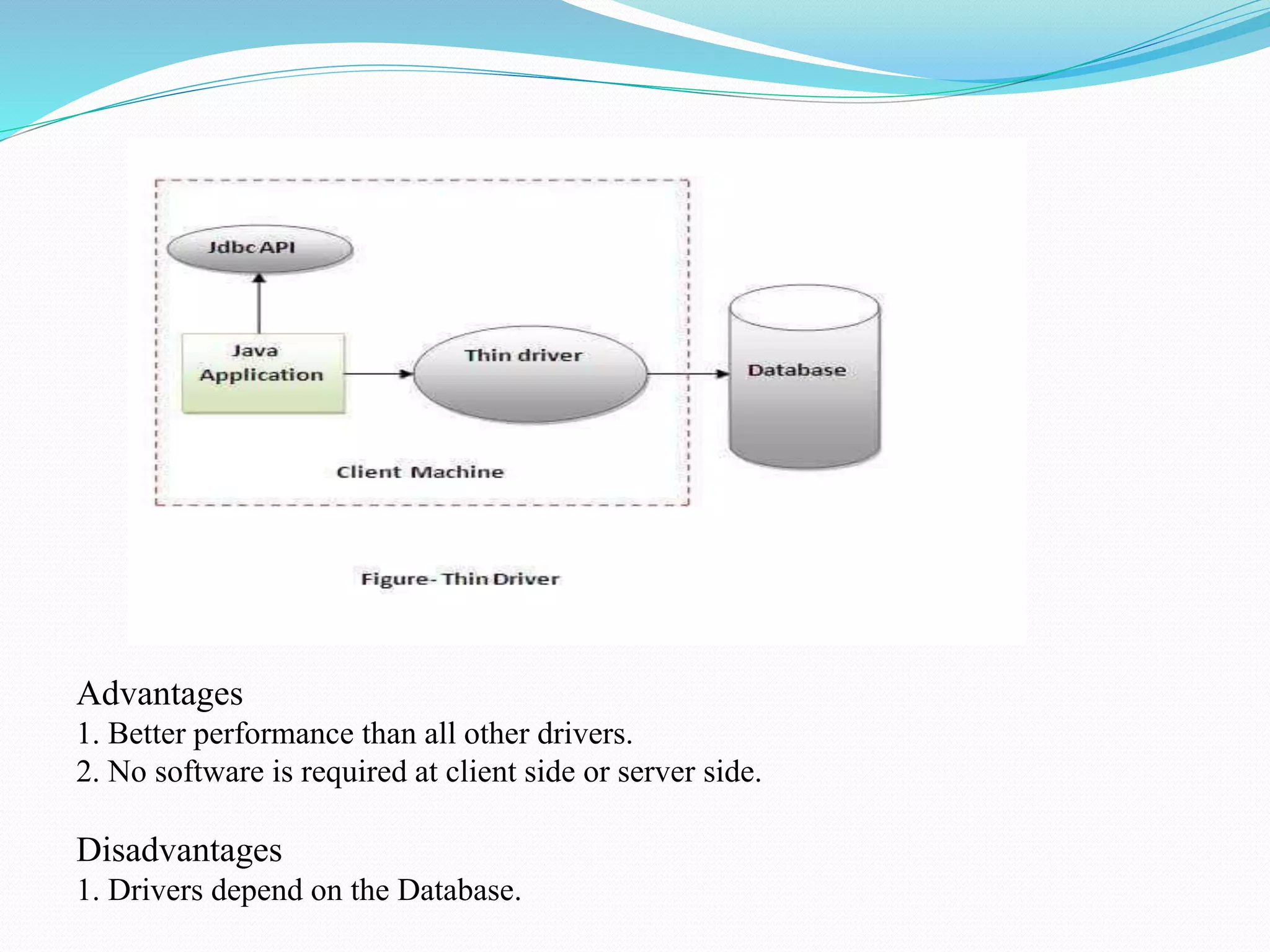
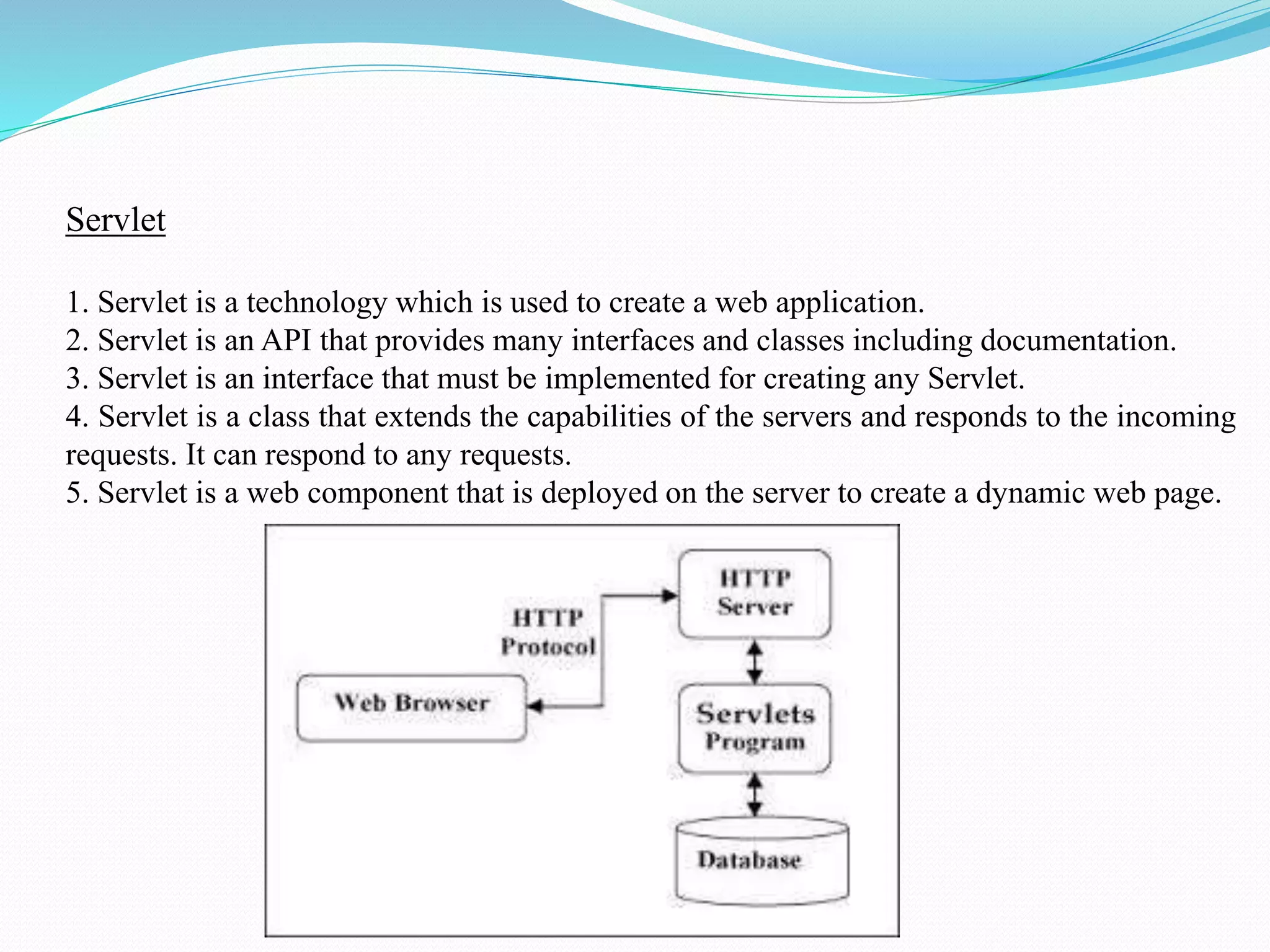
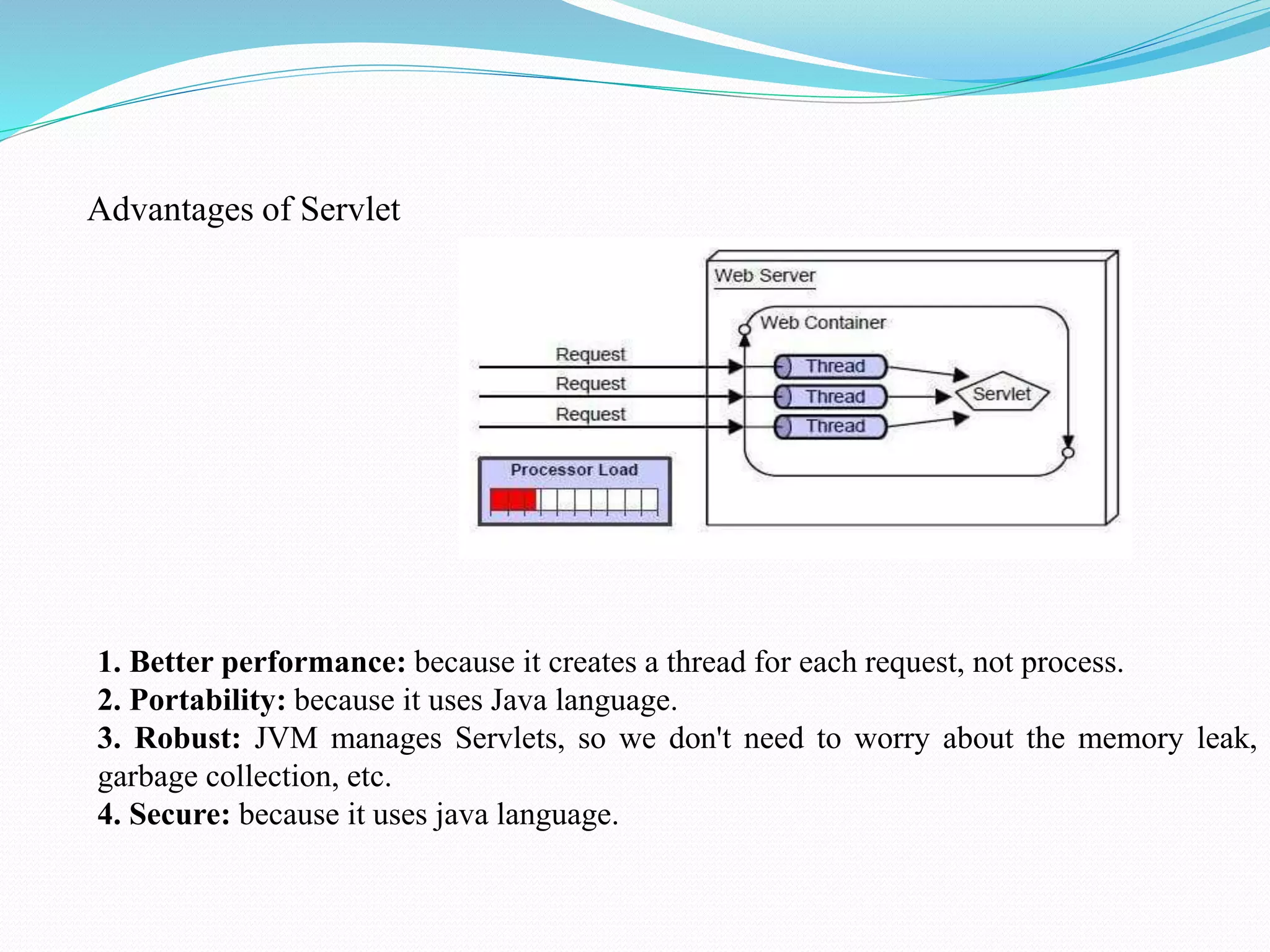
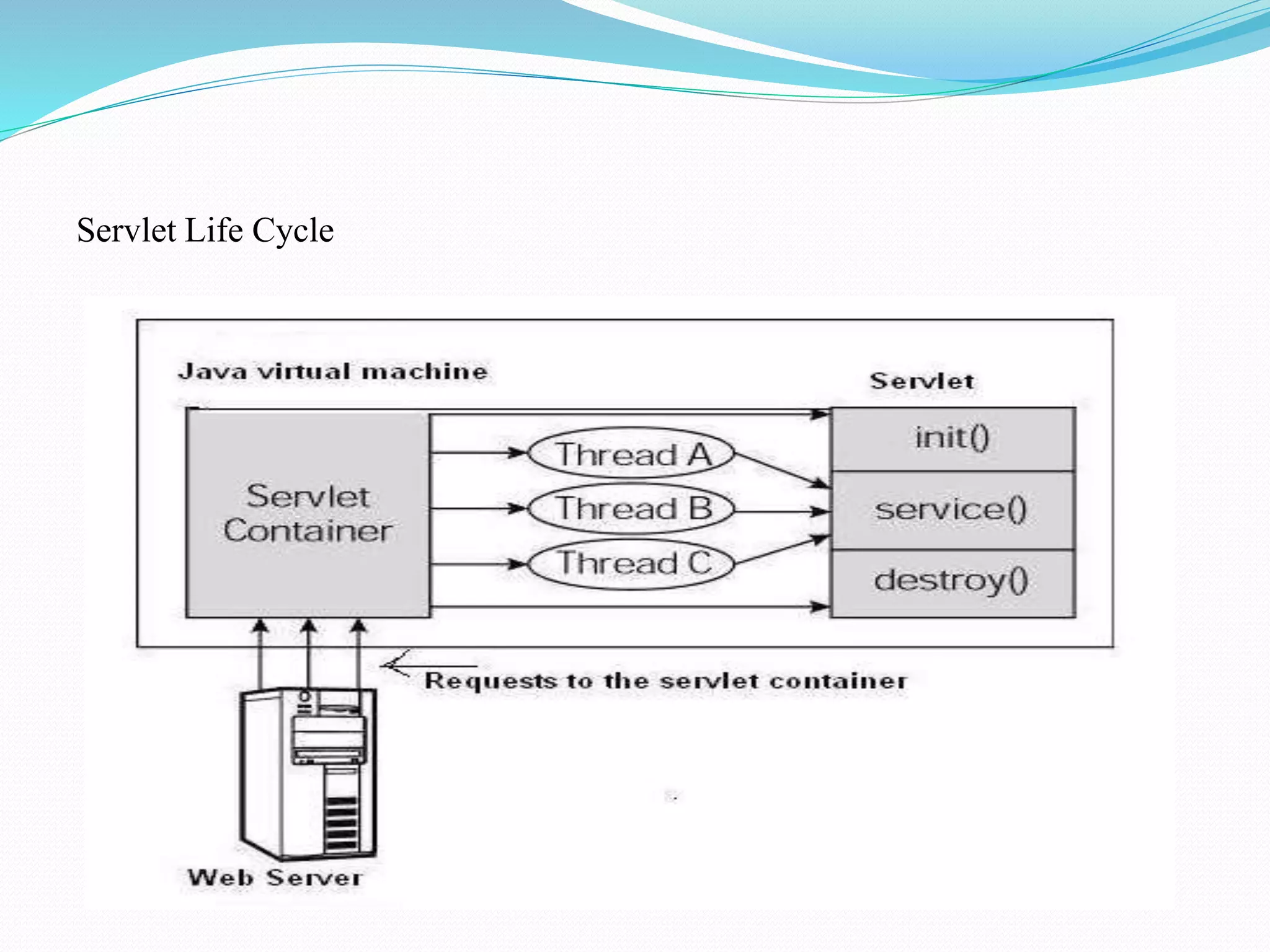
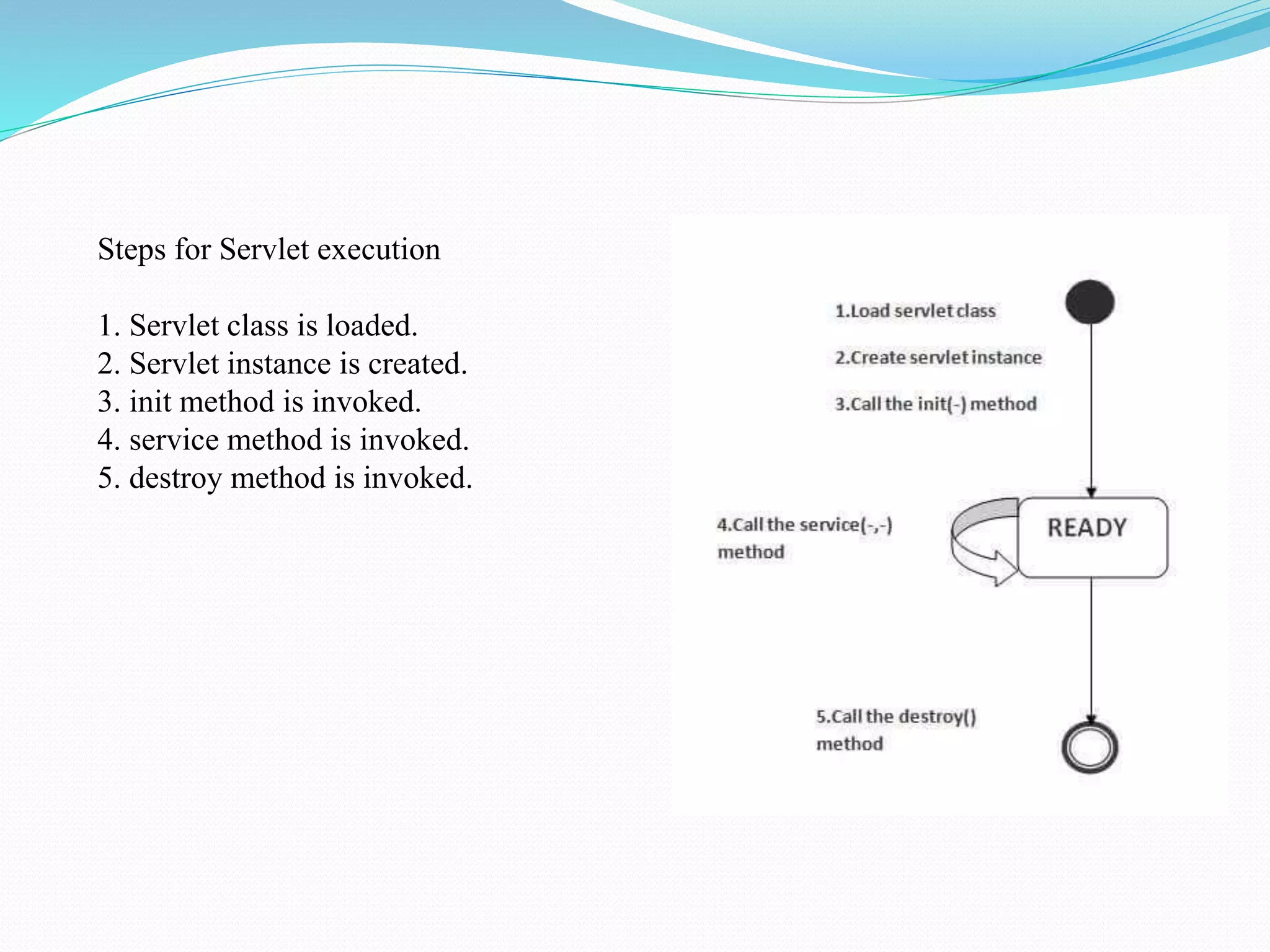
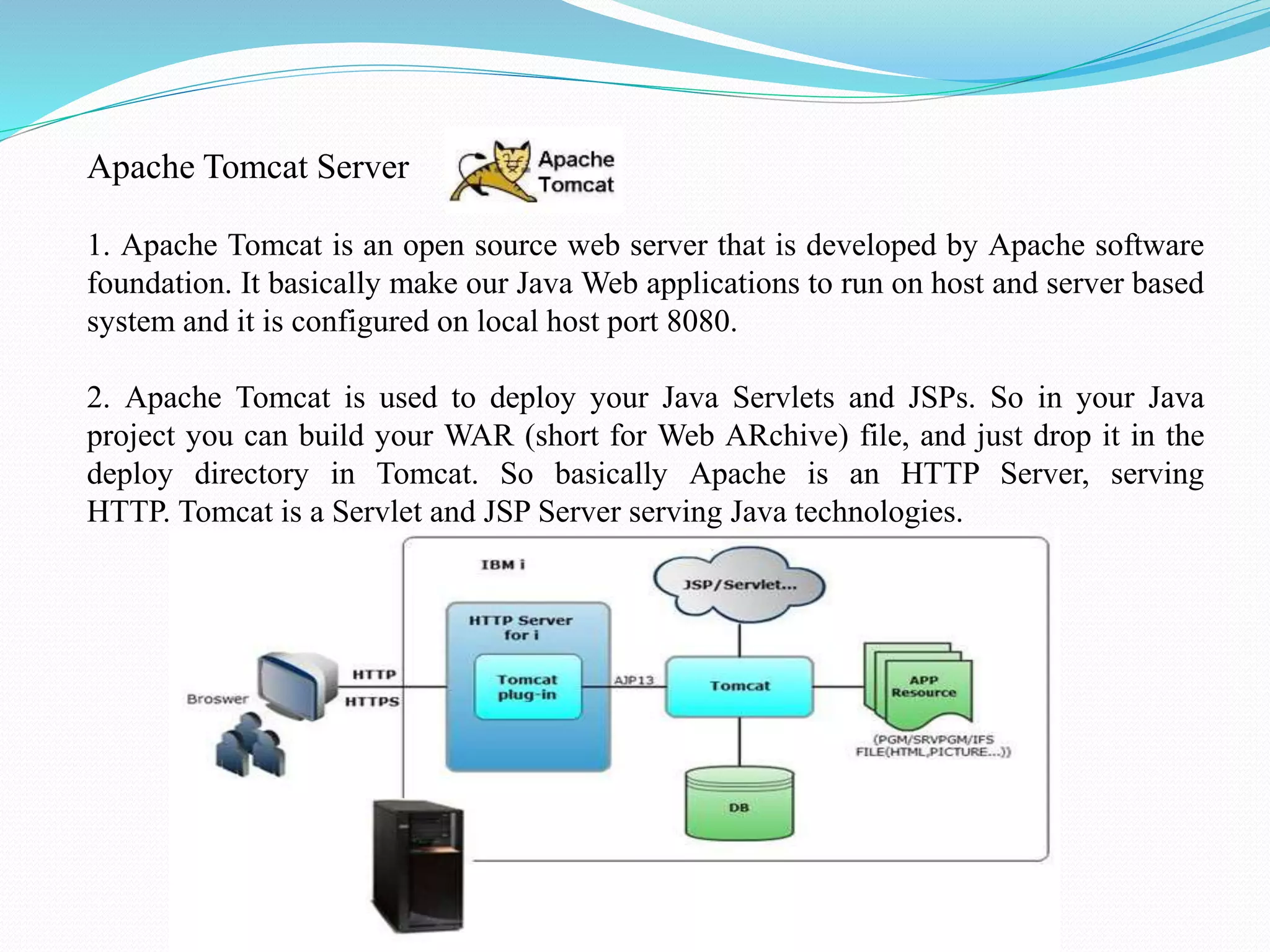
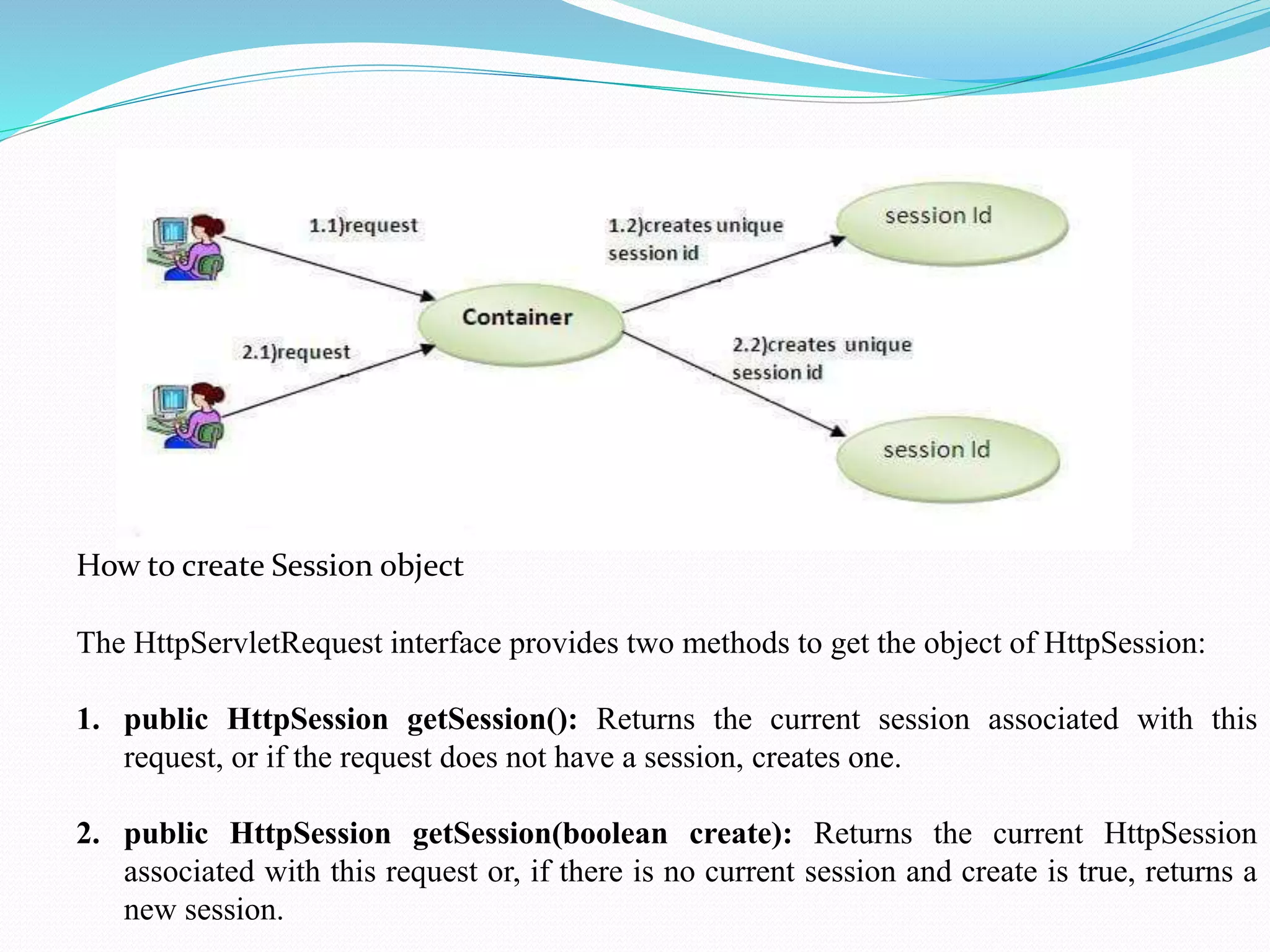
The document provides an overview of JDBC drivers, including the JDBC-ODBC bridge, native API driver, network protocol driver, and thin driver, detailing their advantages and disadvantages. It also covers servlets in Java, their lifecycle, and functionalities, as well as important components like the HttpServlet class and Apache Tomcat server. Additionally, it explains cookie management and session tracking in servlets/JSP, including types of cookies, session creation, and commonly used methods of the HttpSession interface.