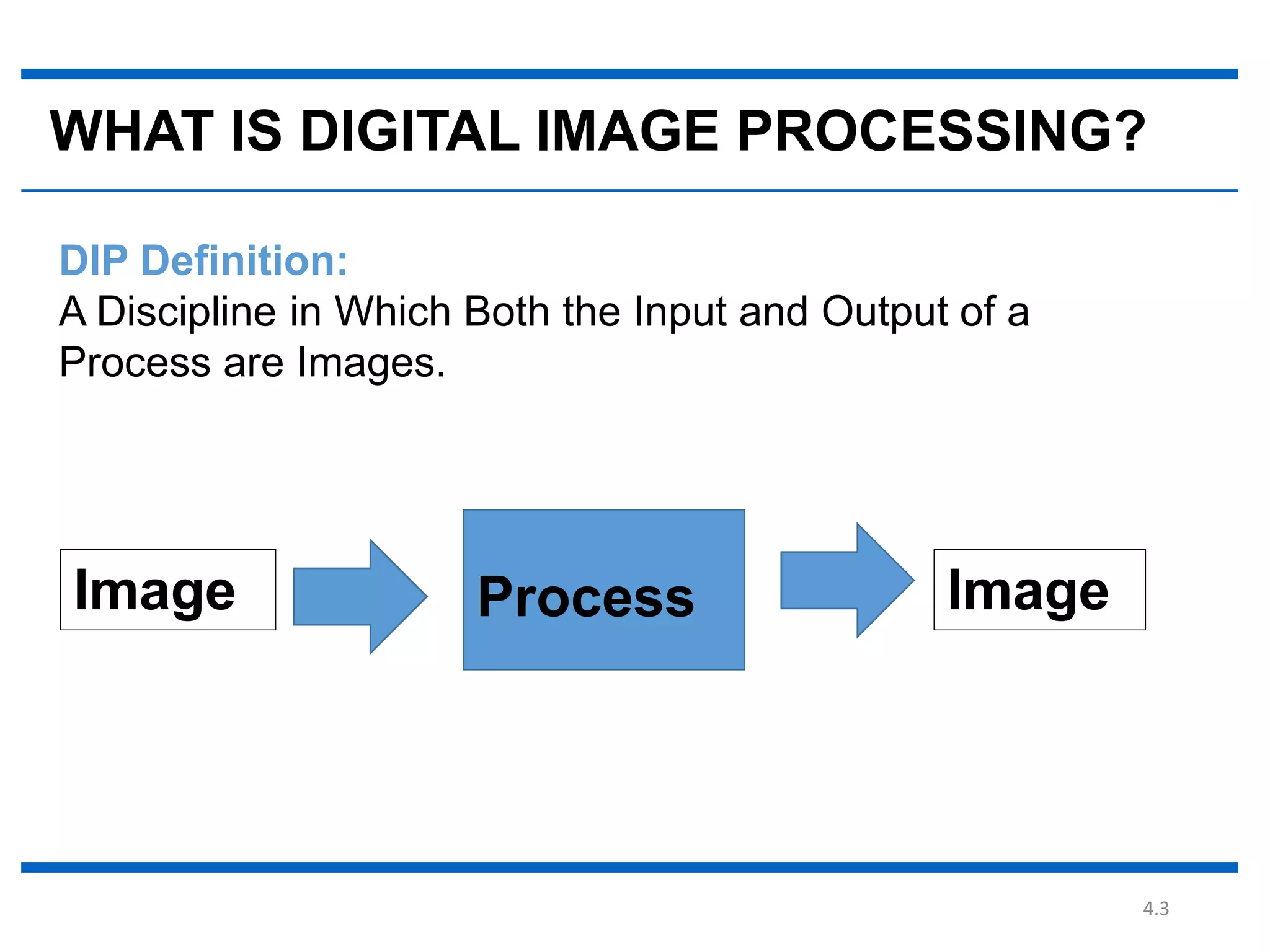
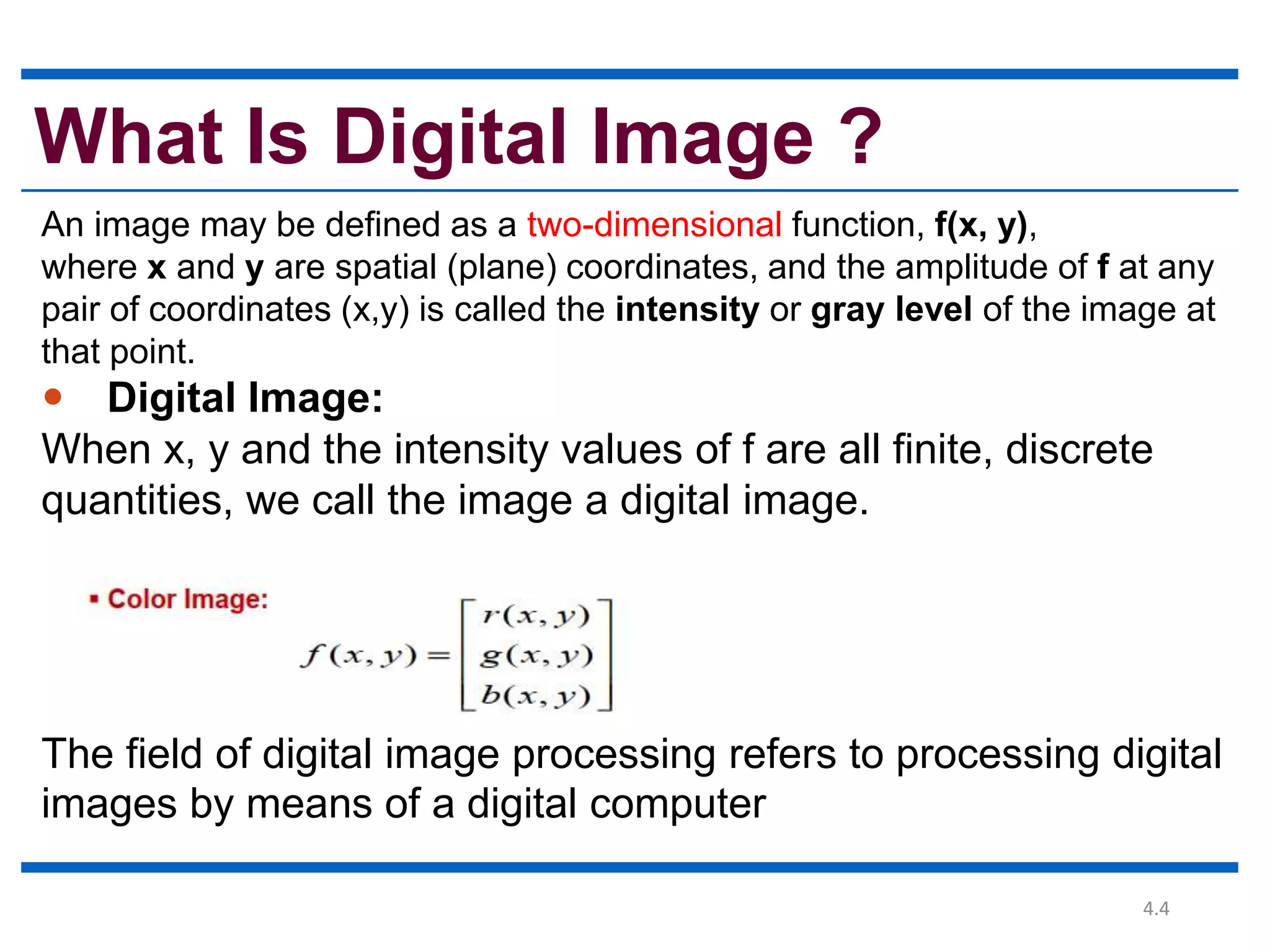
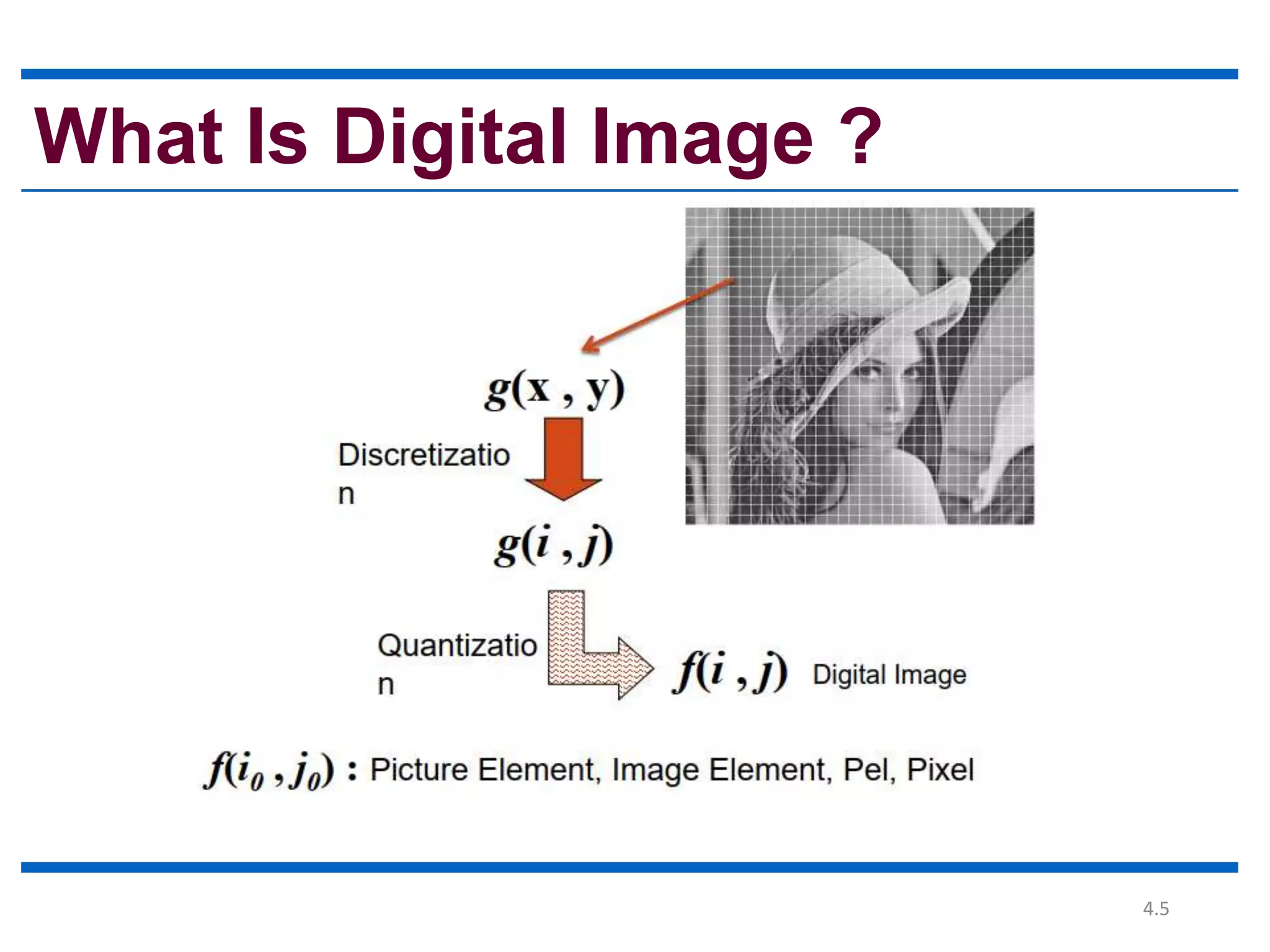
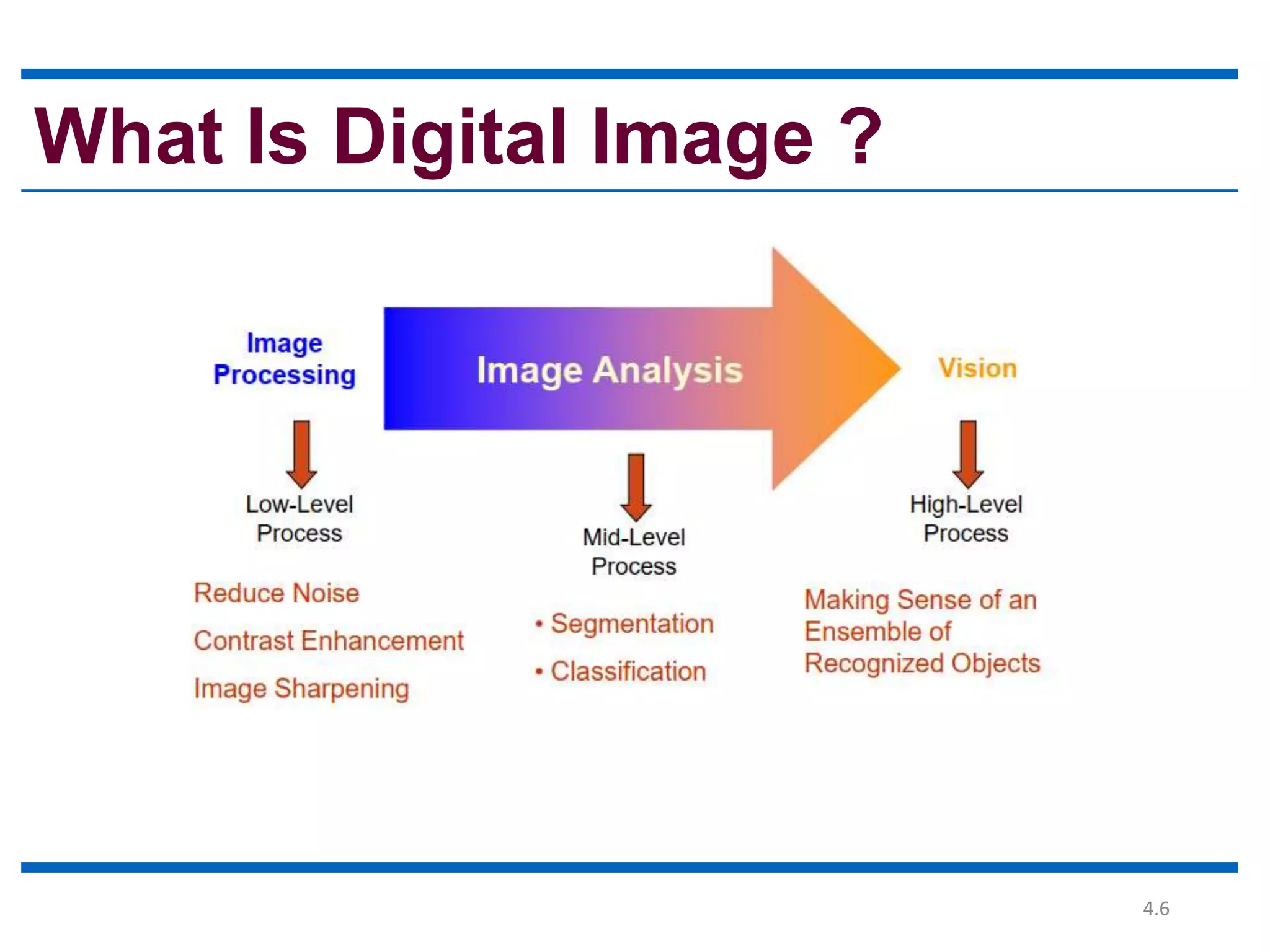
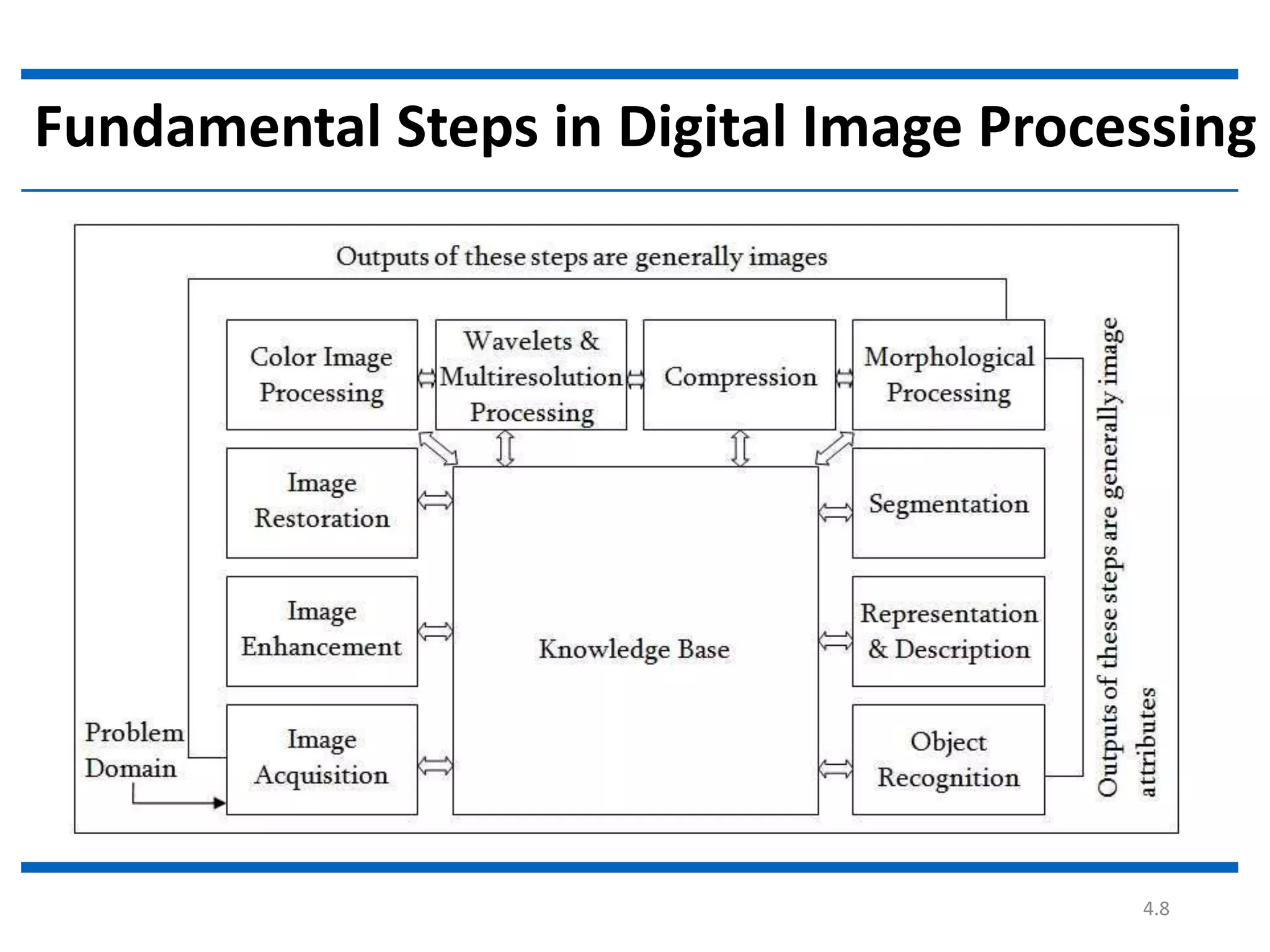
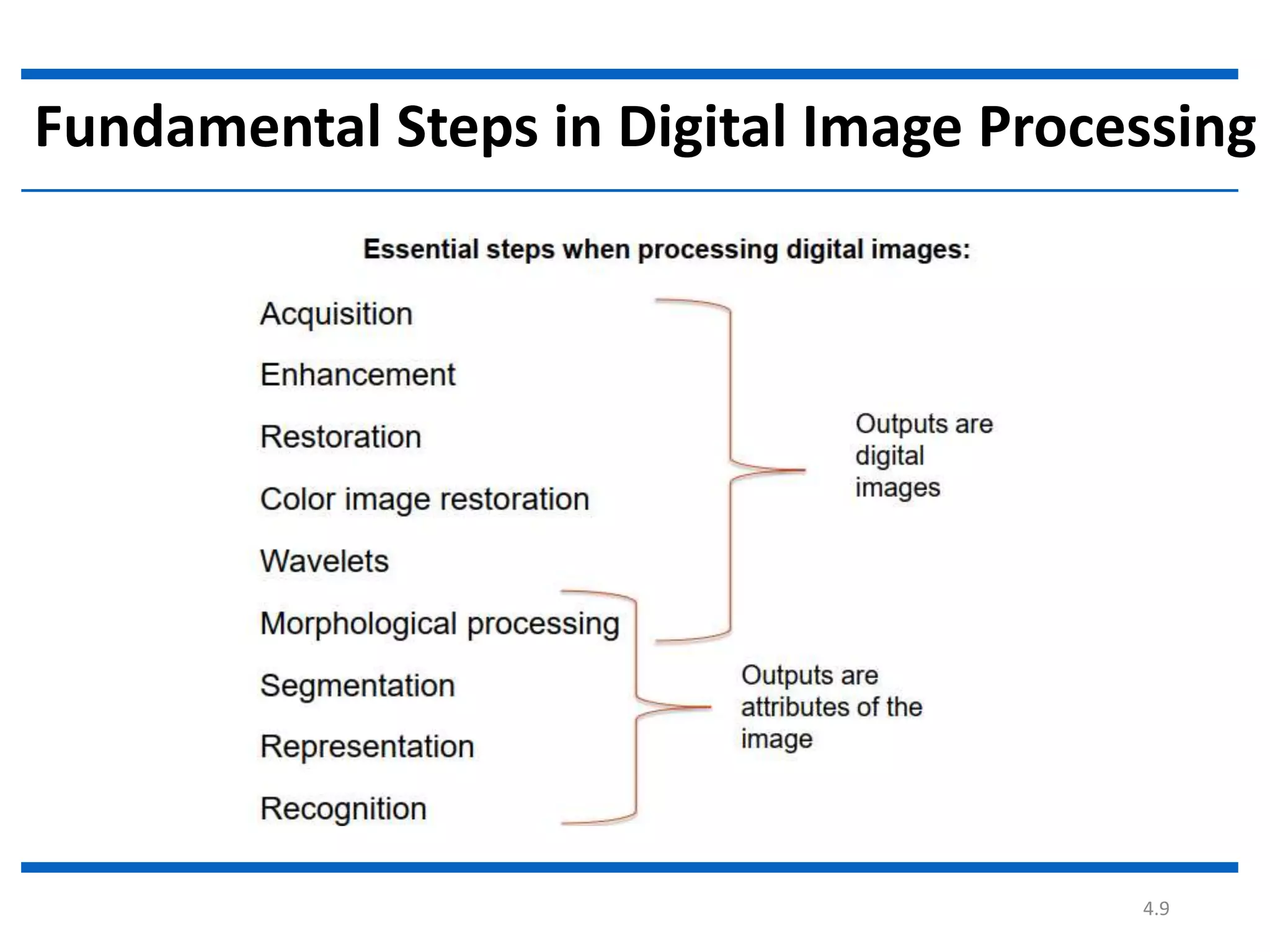
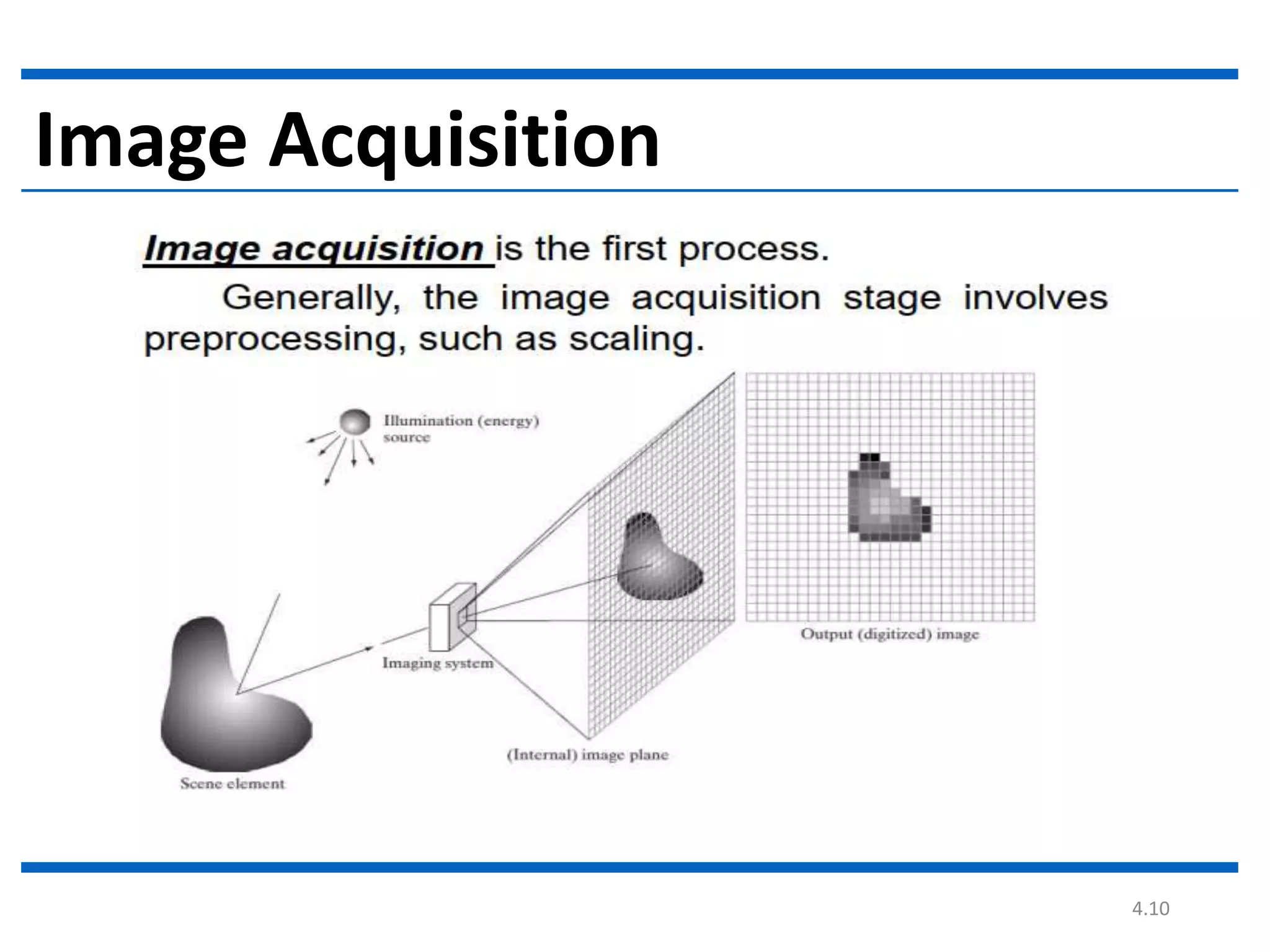
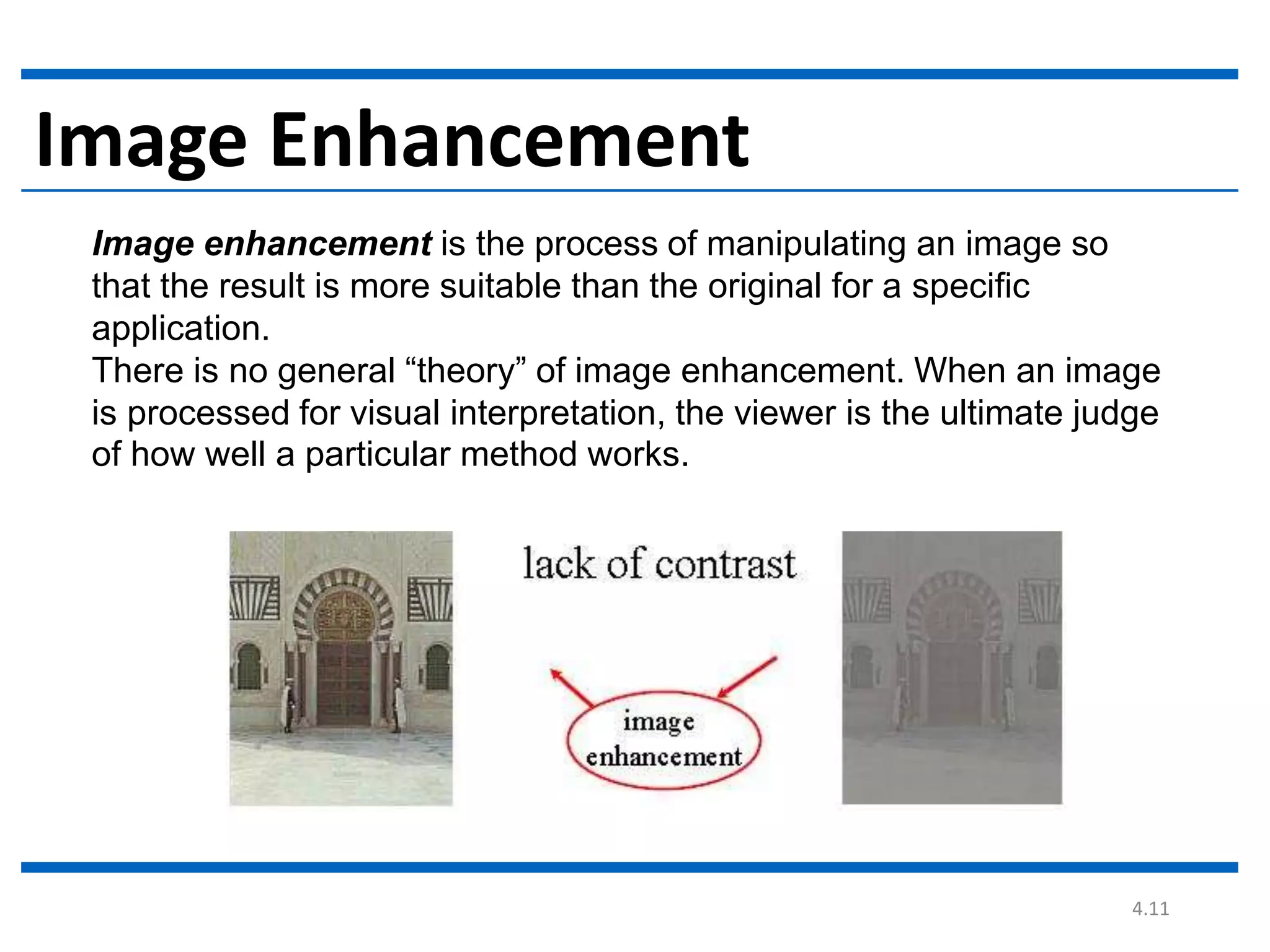
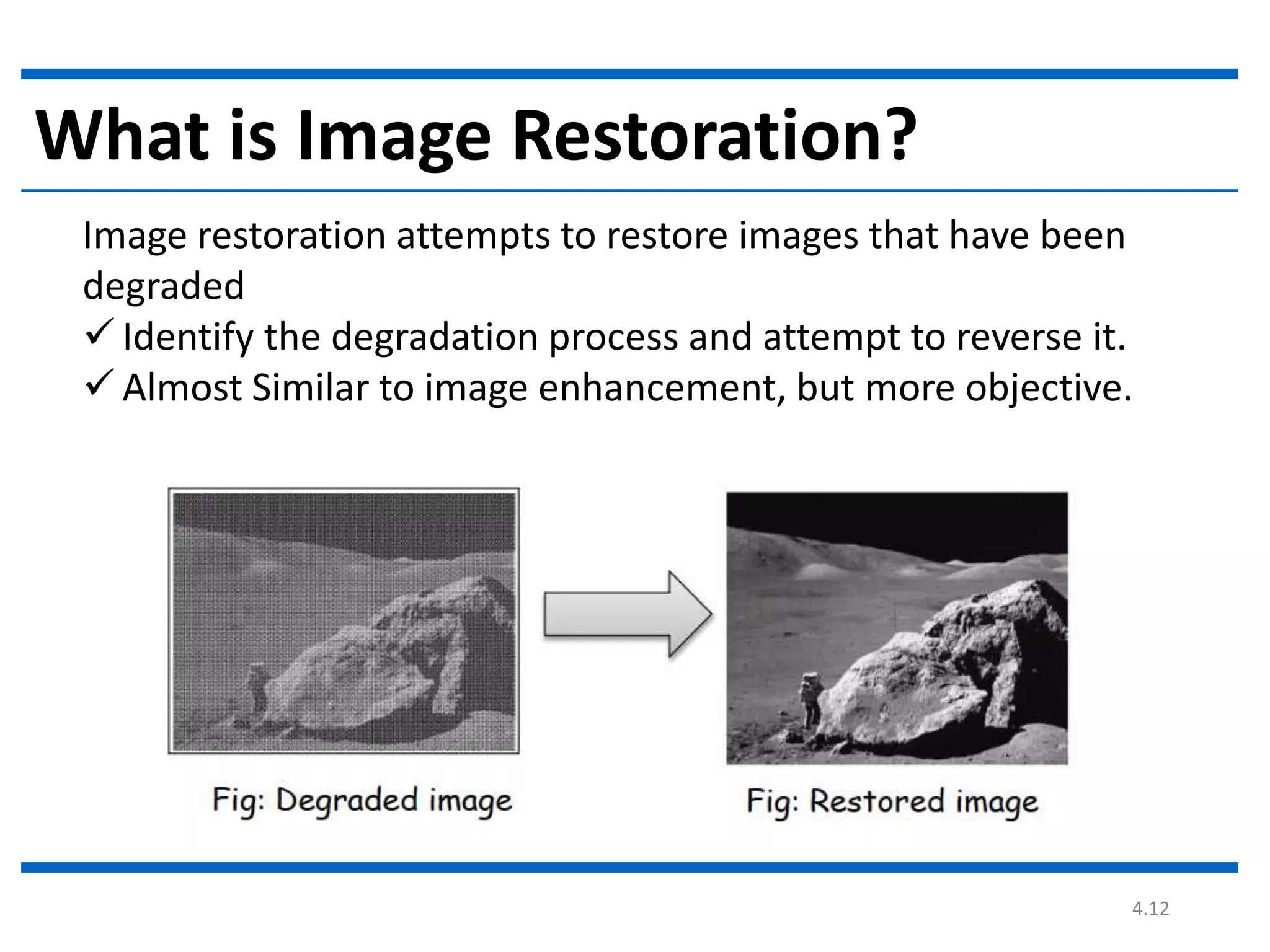
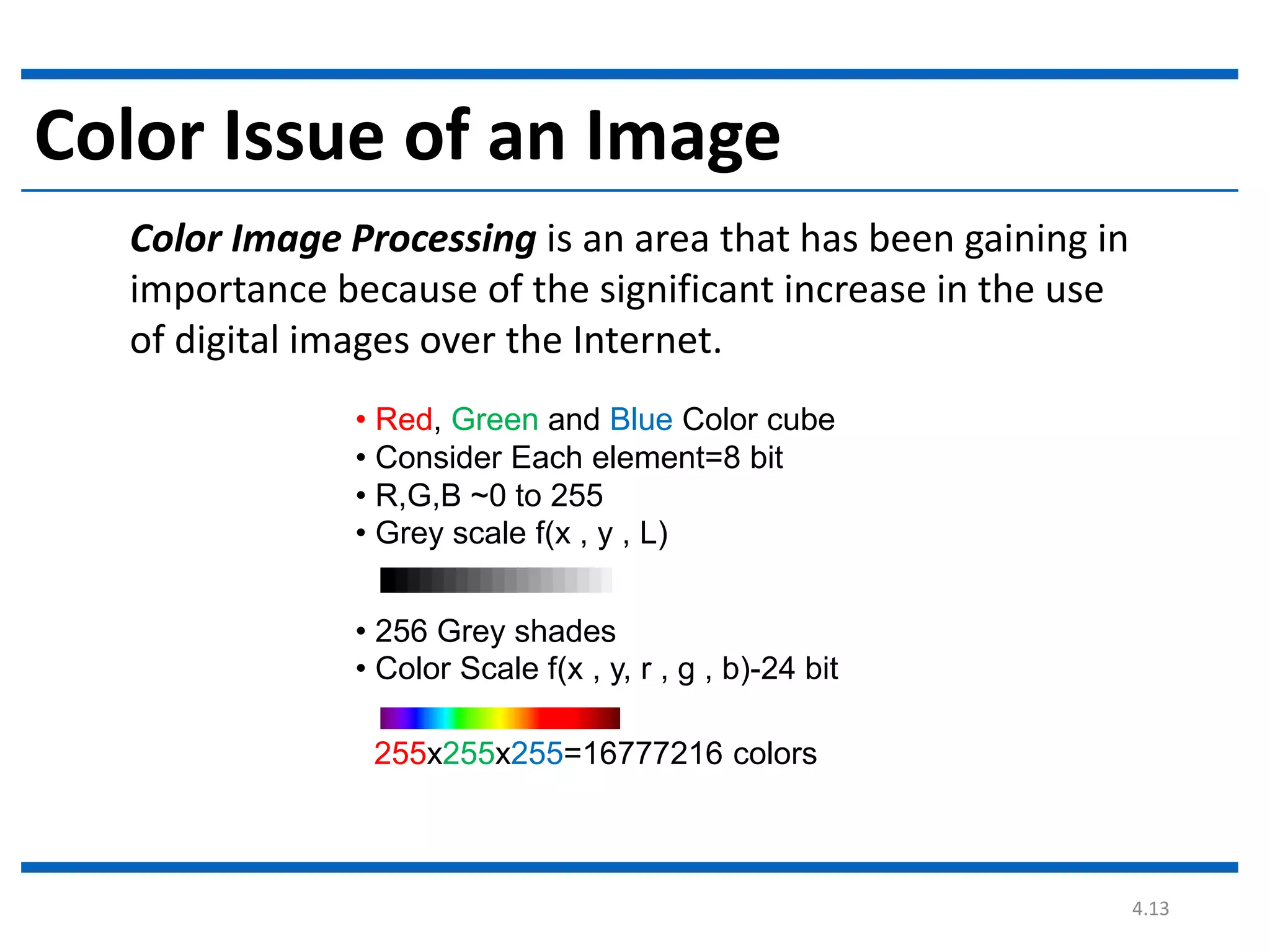
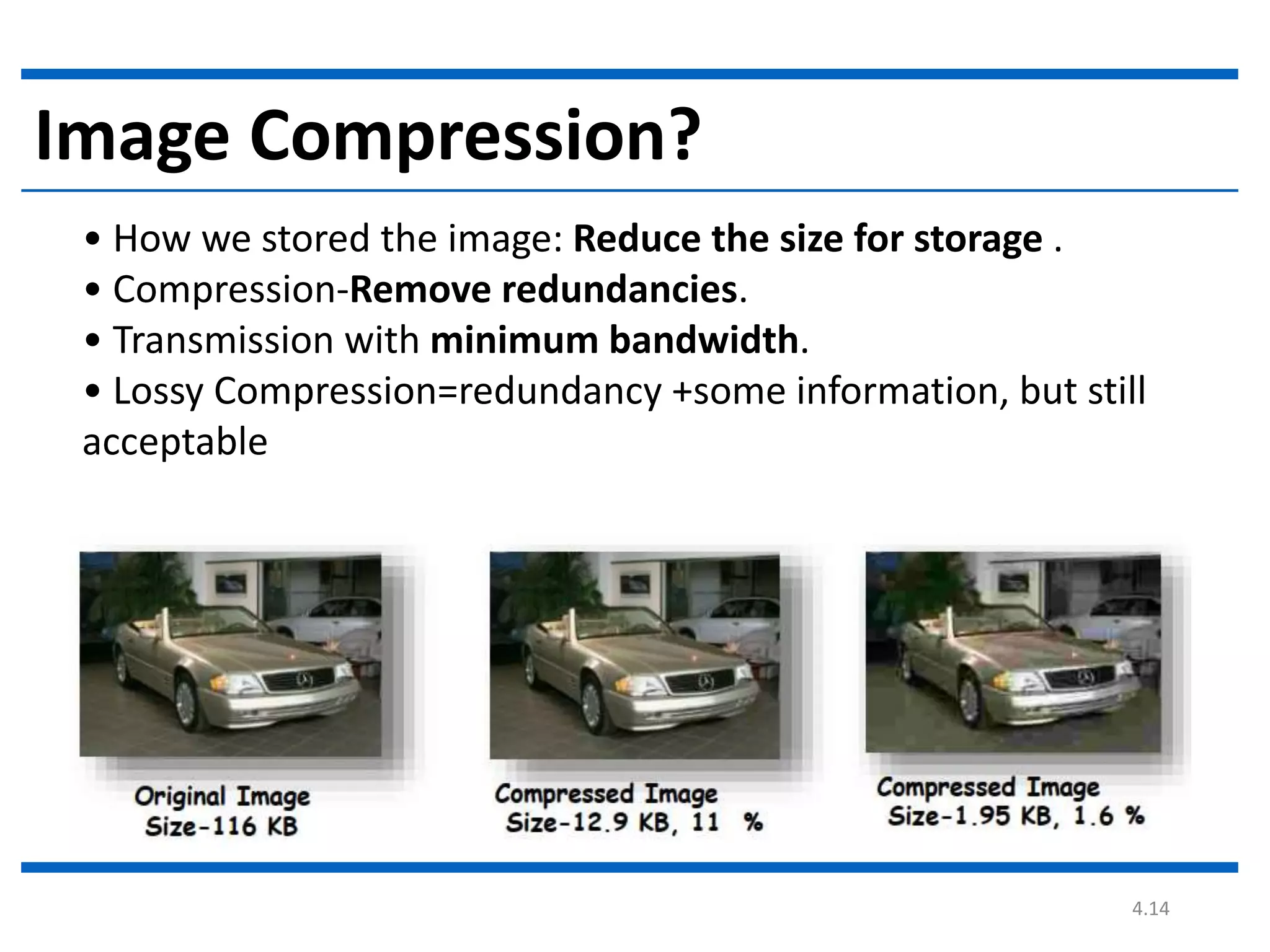
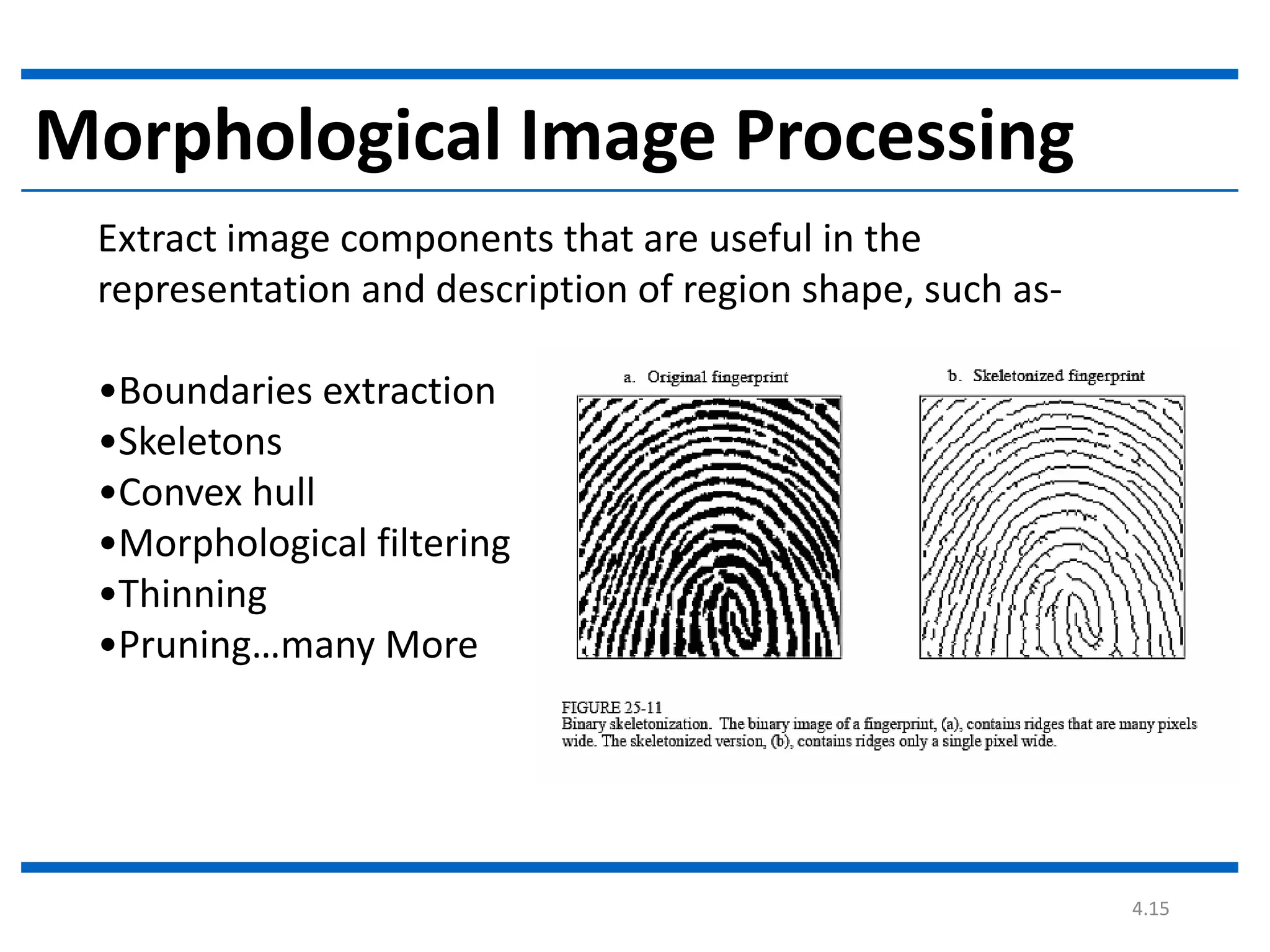
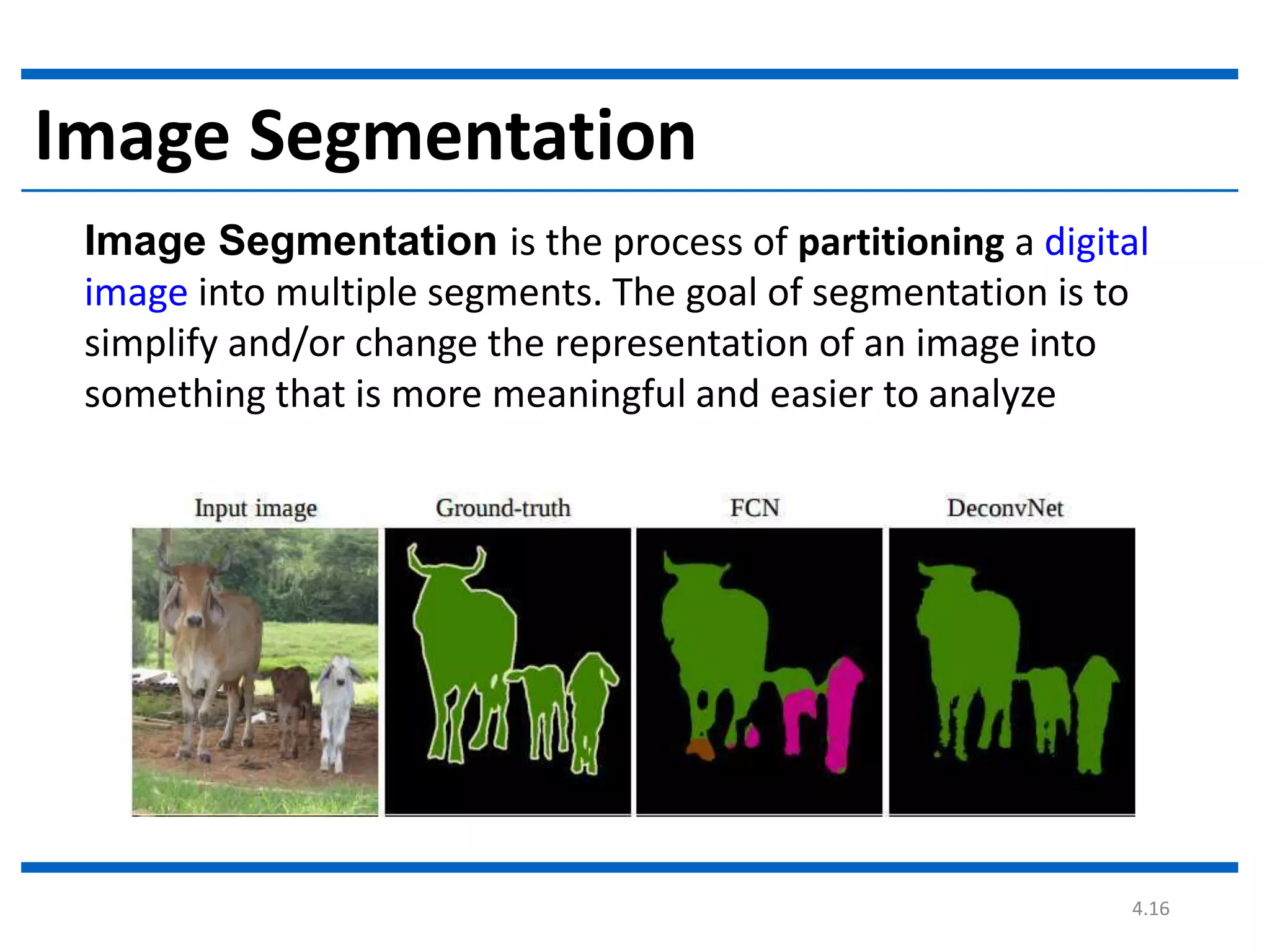
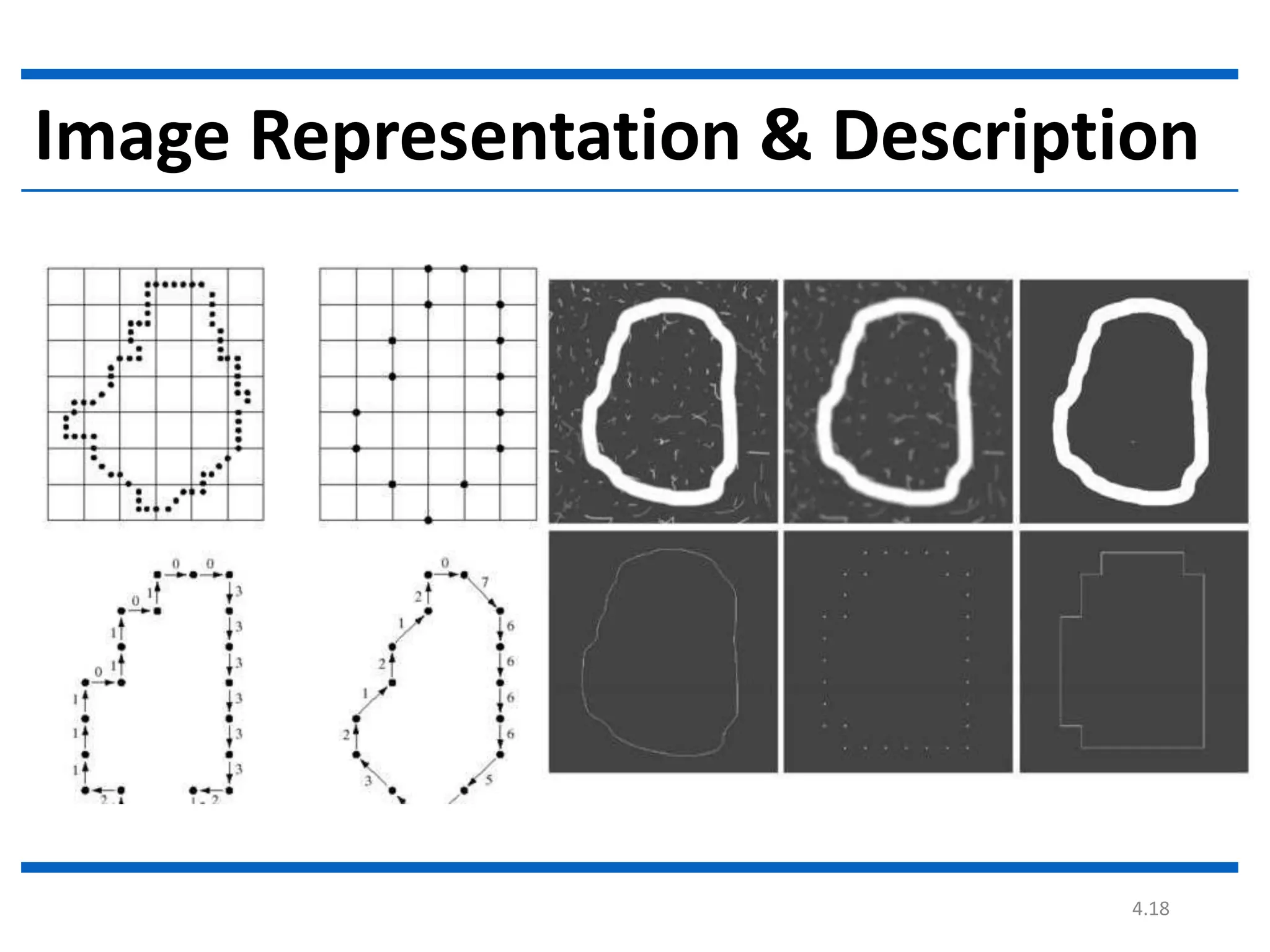
Digital image processing involves processing digital images using a computer. It defines a digital image as a two-dimensional function where intensity values are discrete quantities. The fundamental steps in digital image processing are image acquisition, enhancement, restoration, compression, morphological operations, segmentation, and representation and description. Image enhancement improves image quality, restoration fixes degraded images, and compression reduces file size for storage and transmission with minimal information loss.