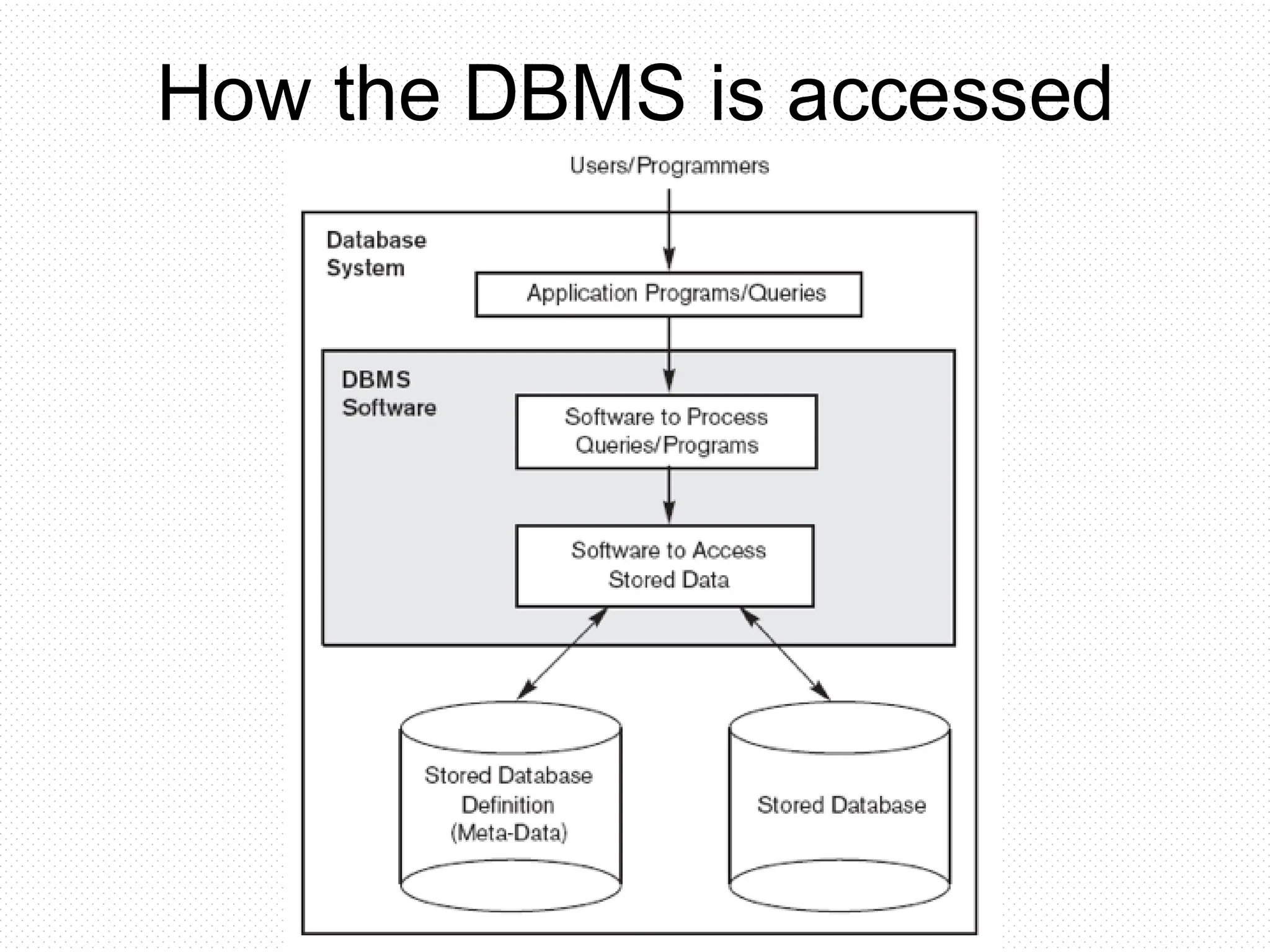
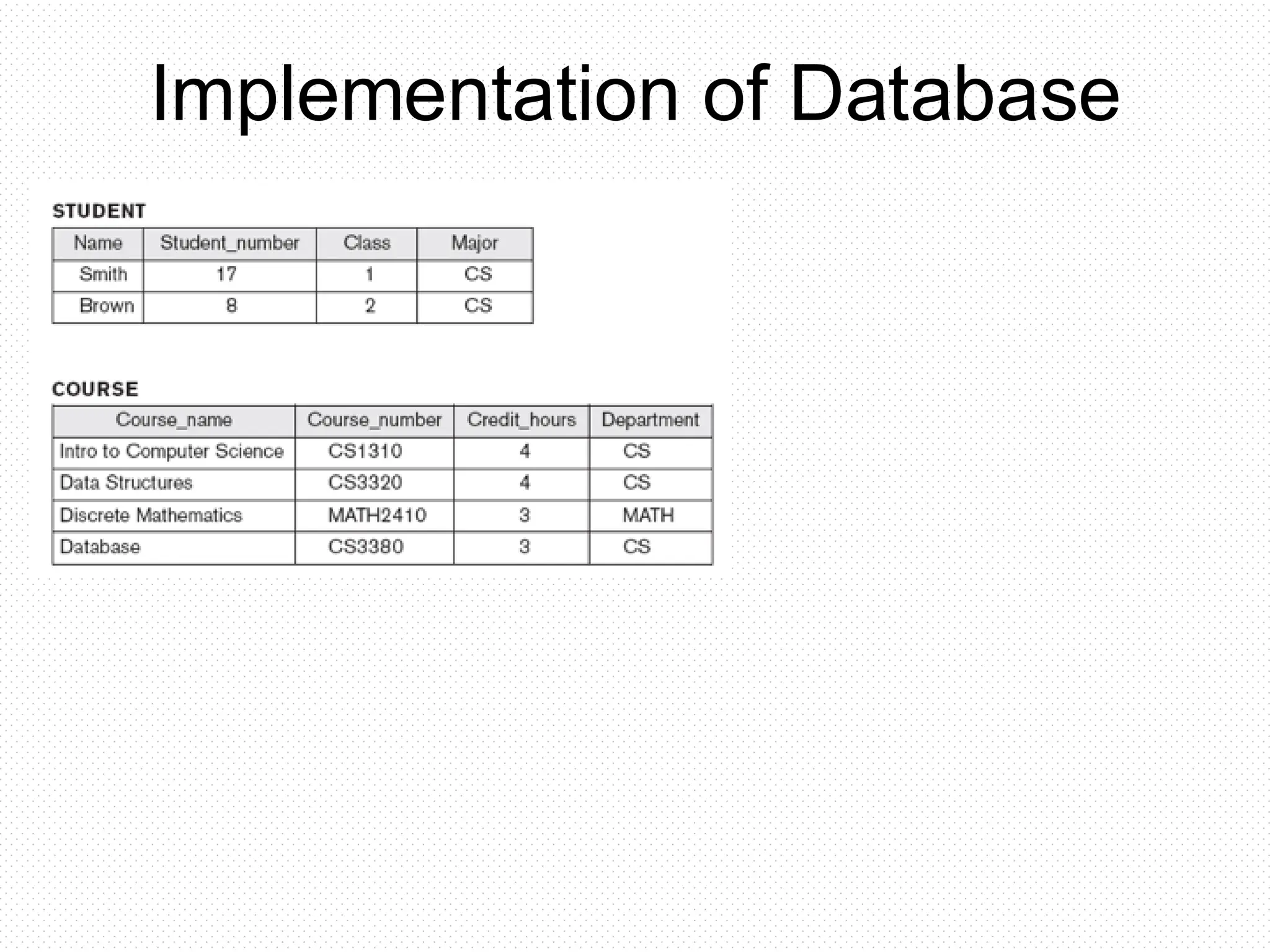
The document provides an overview of database management systems, defining key terms such as database, DBMS, and SQL, while outlining the functions and roles involved in managing databases. It explains the operations a DBMS can perform, such as data creation, updating, retrieval, and security management. Additionally, it highlights the different actors involved in the database system and outlines the steps in database design.