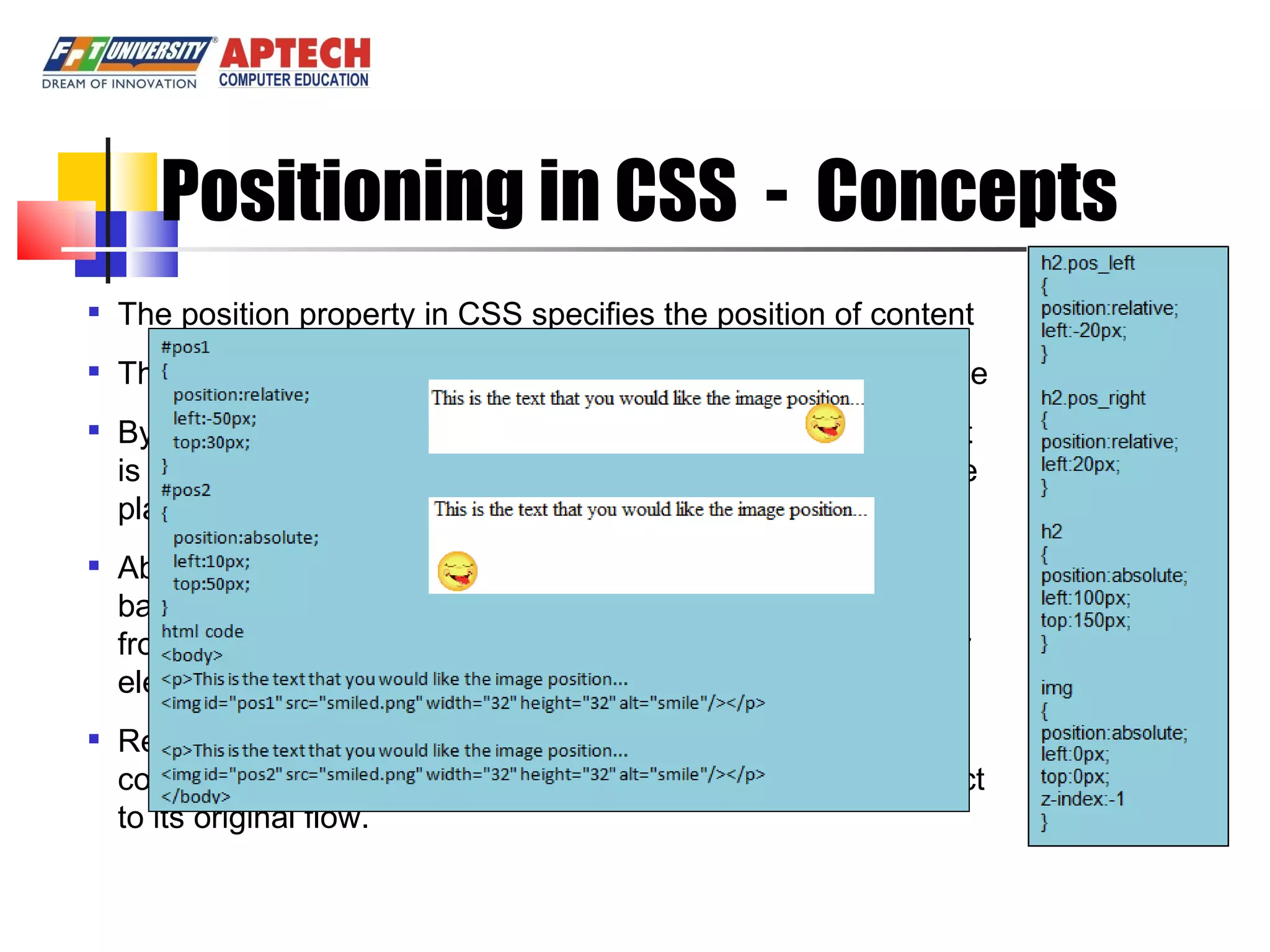
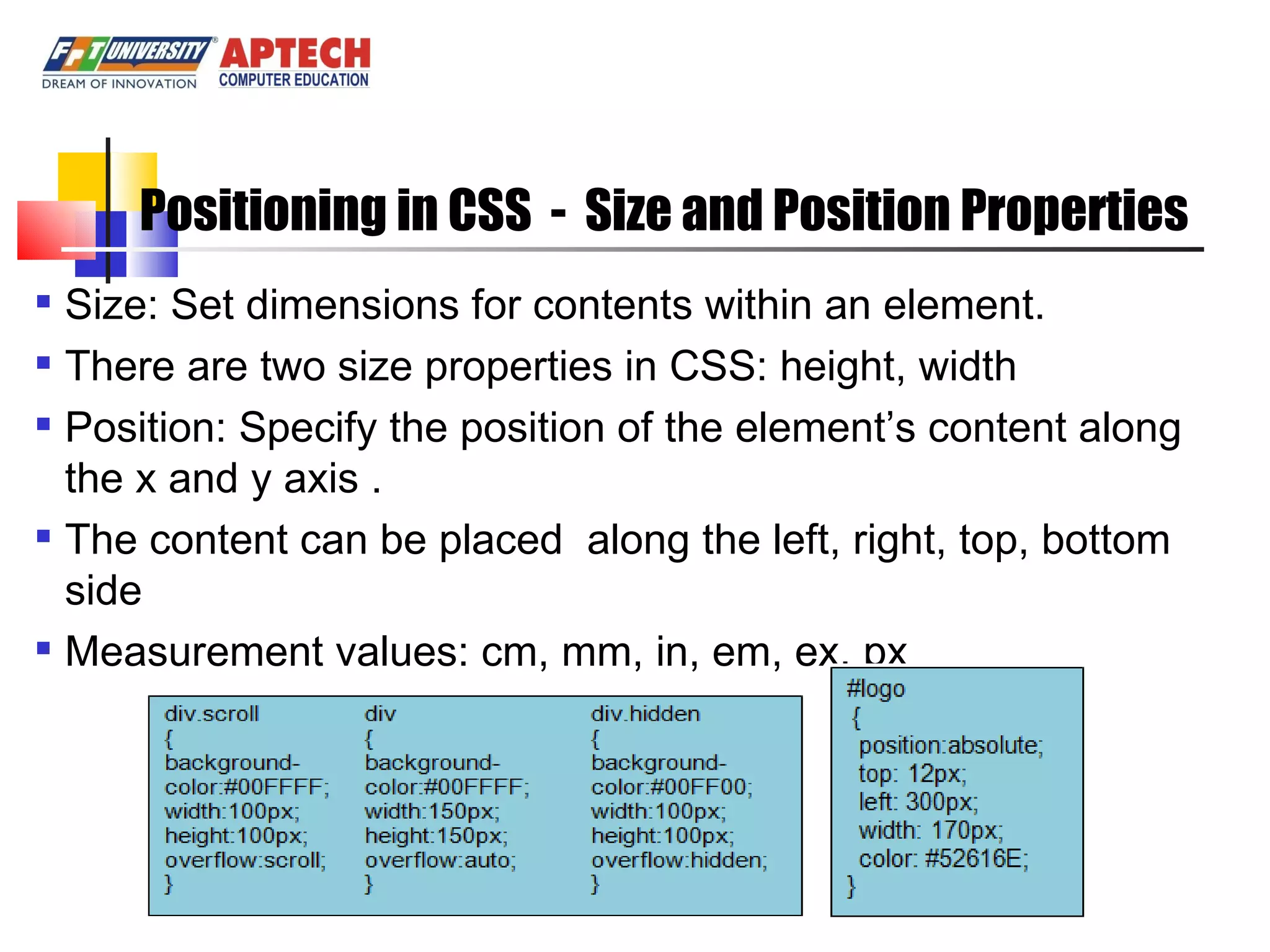
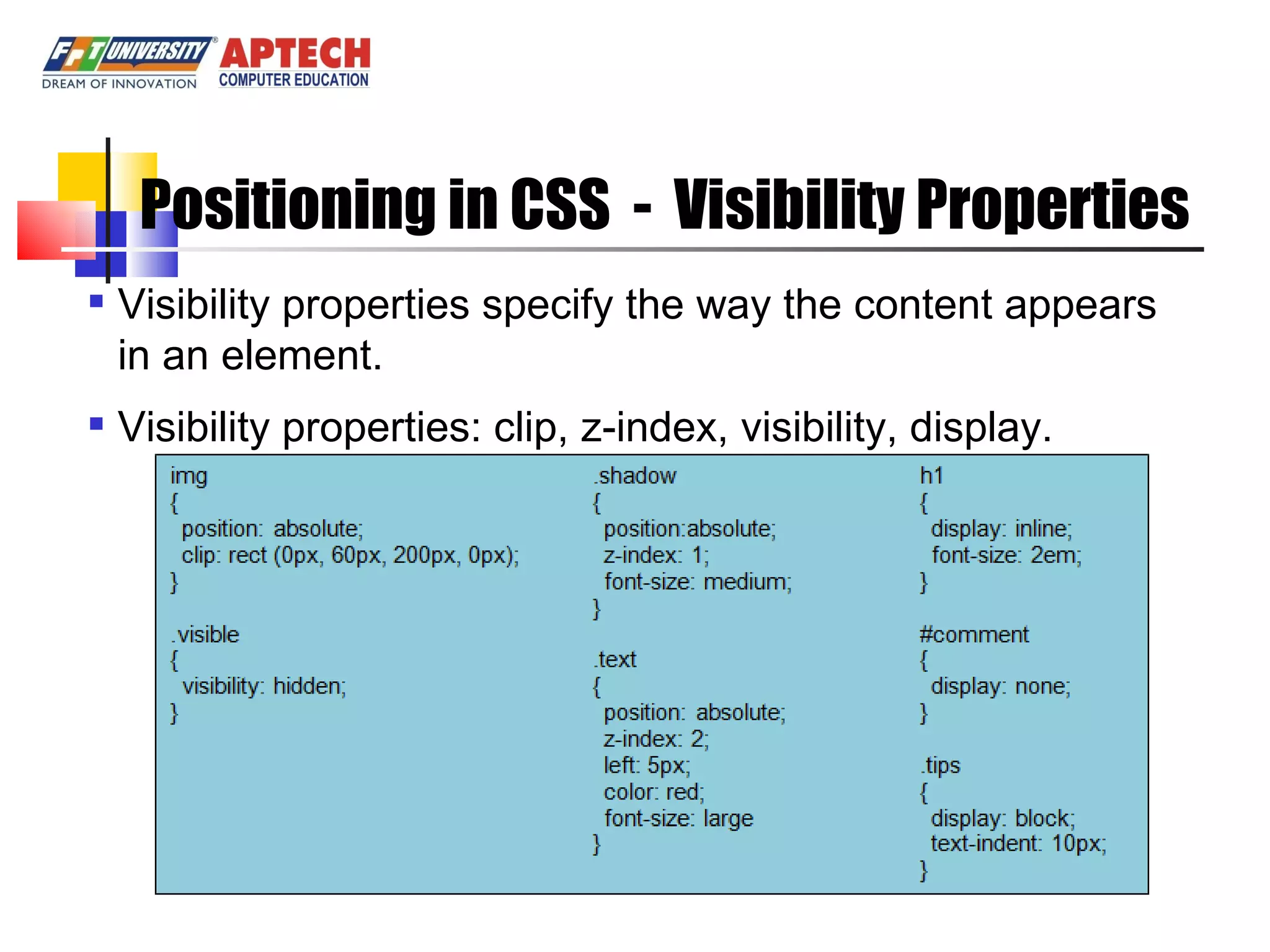
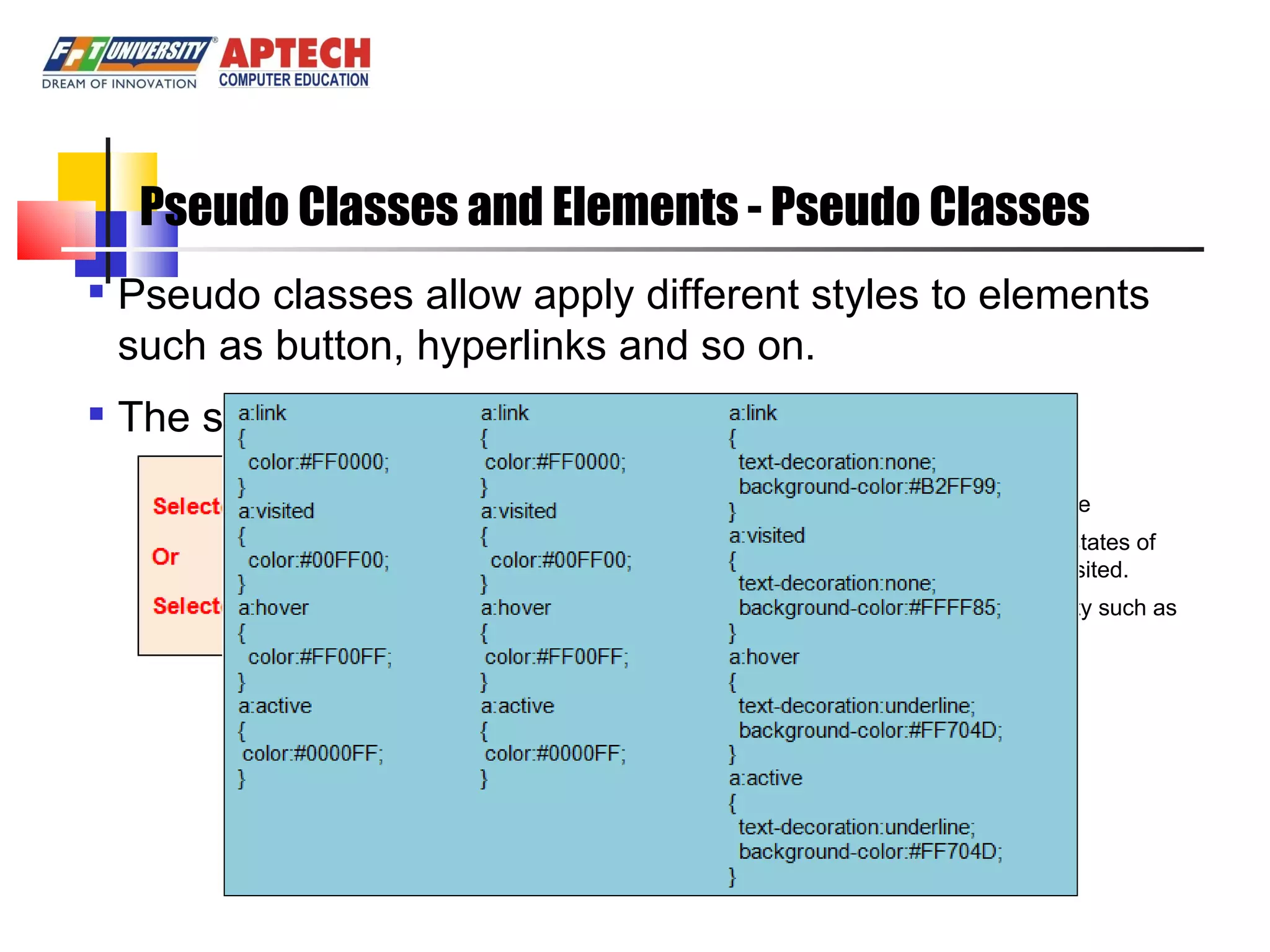
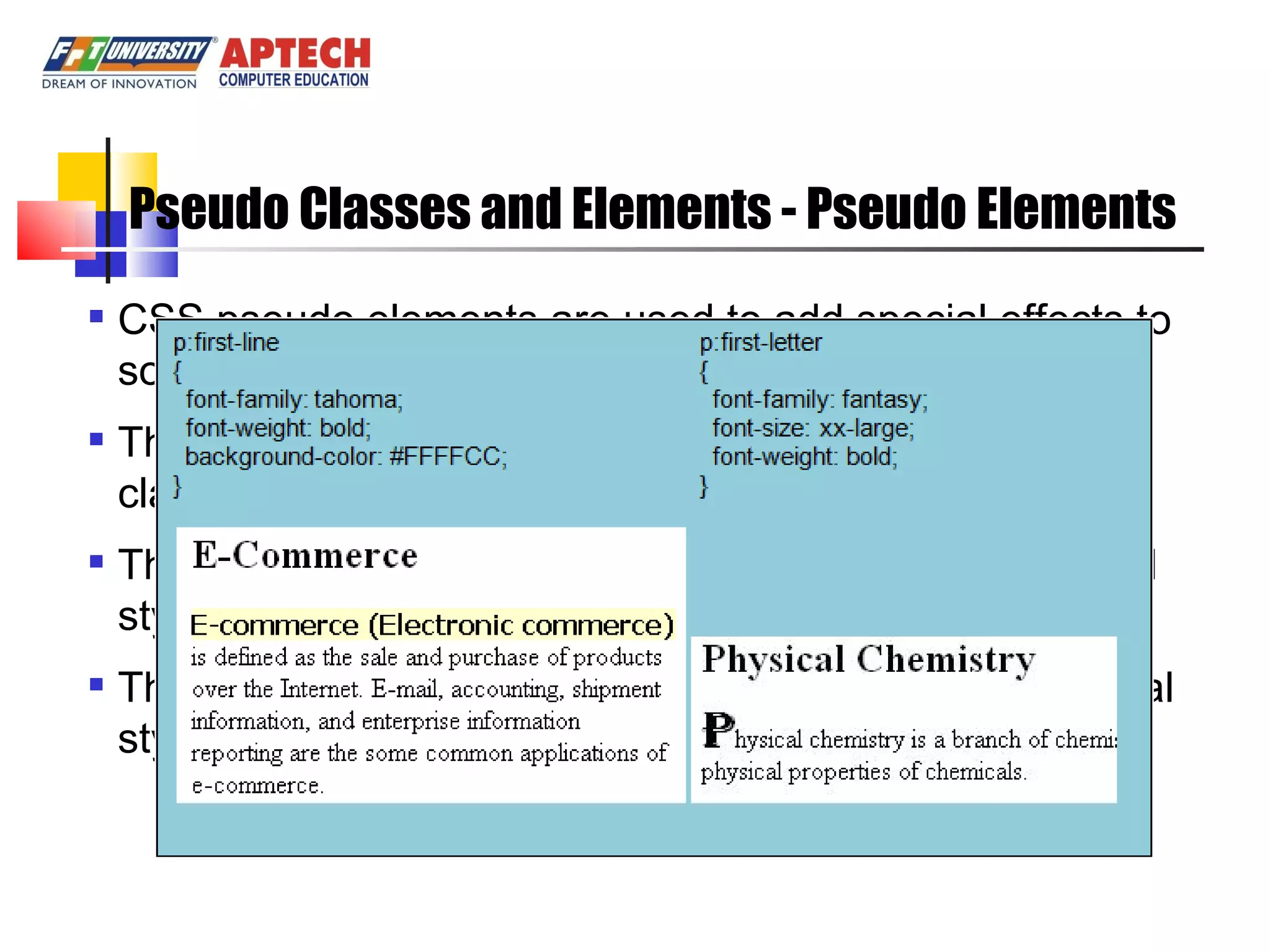
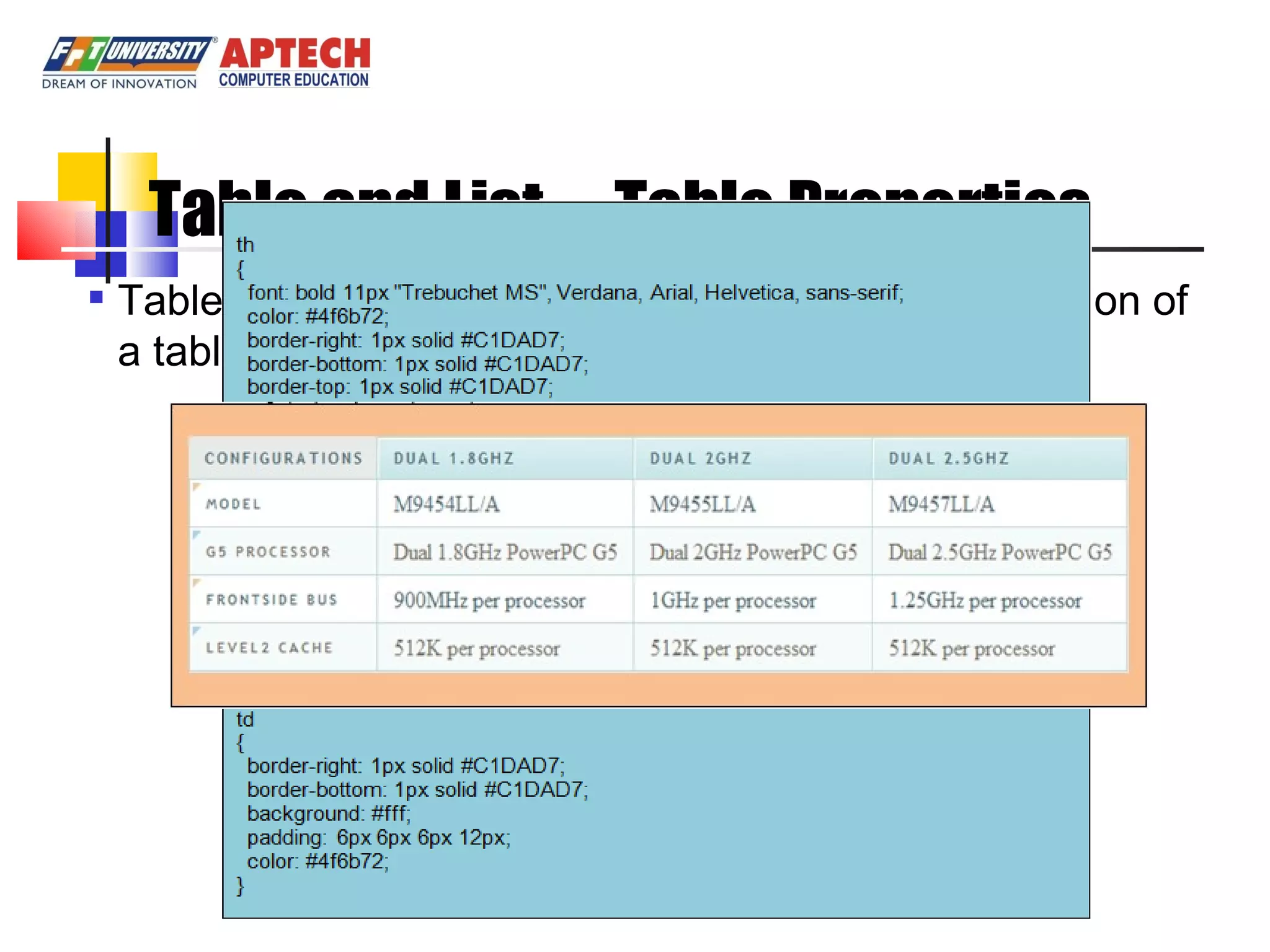
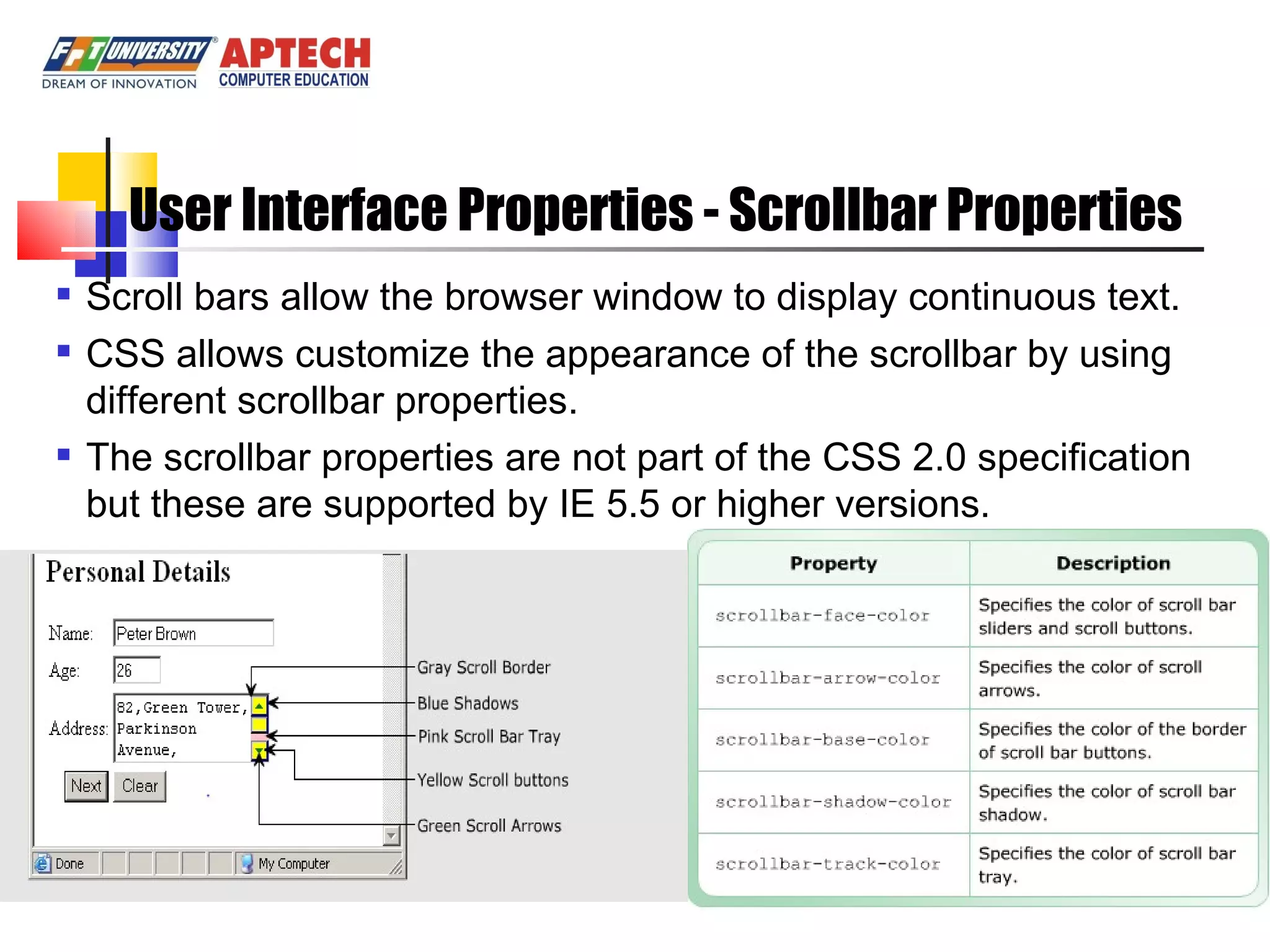
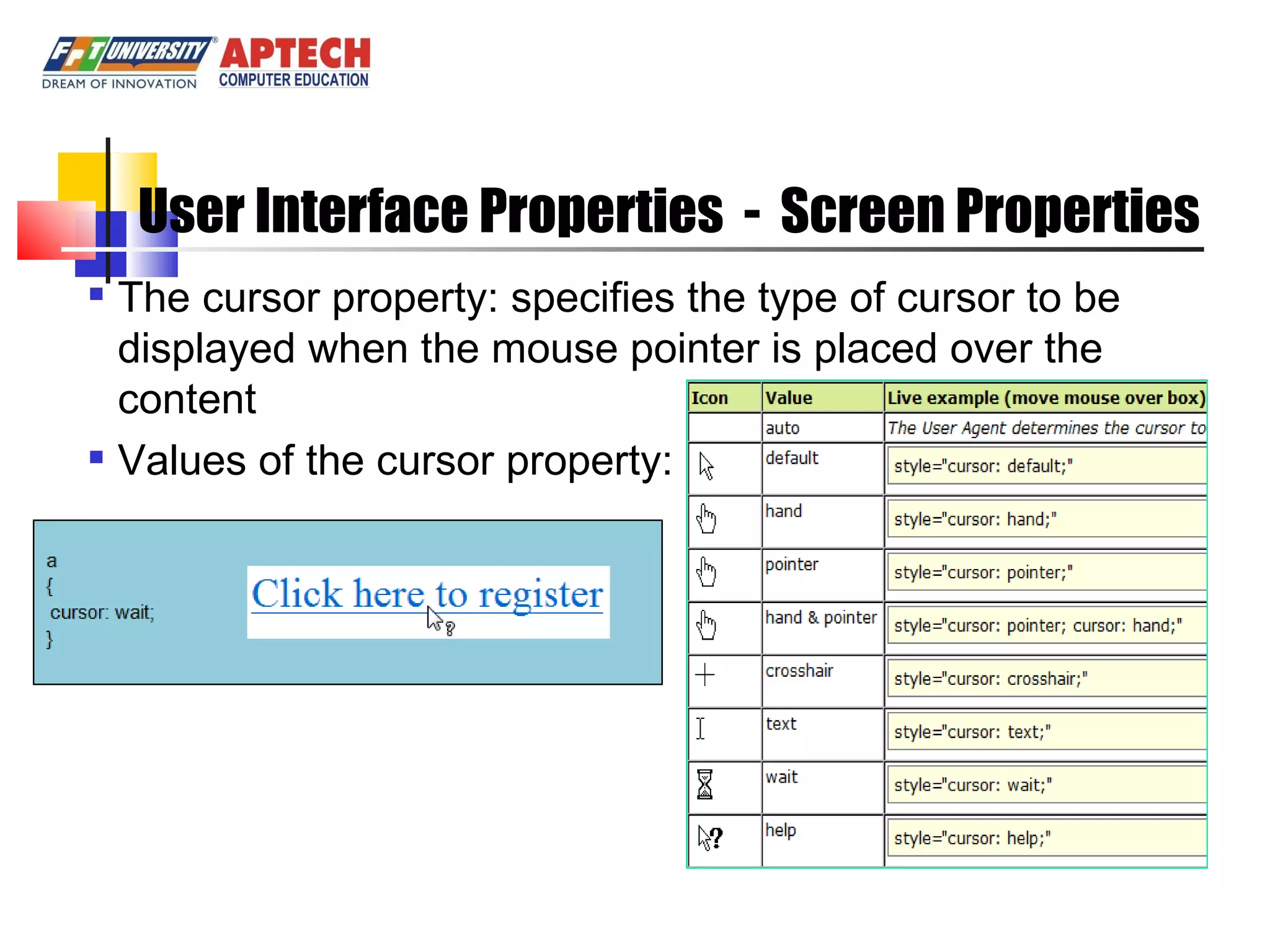
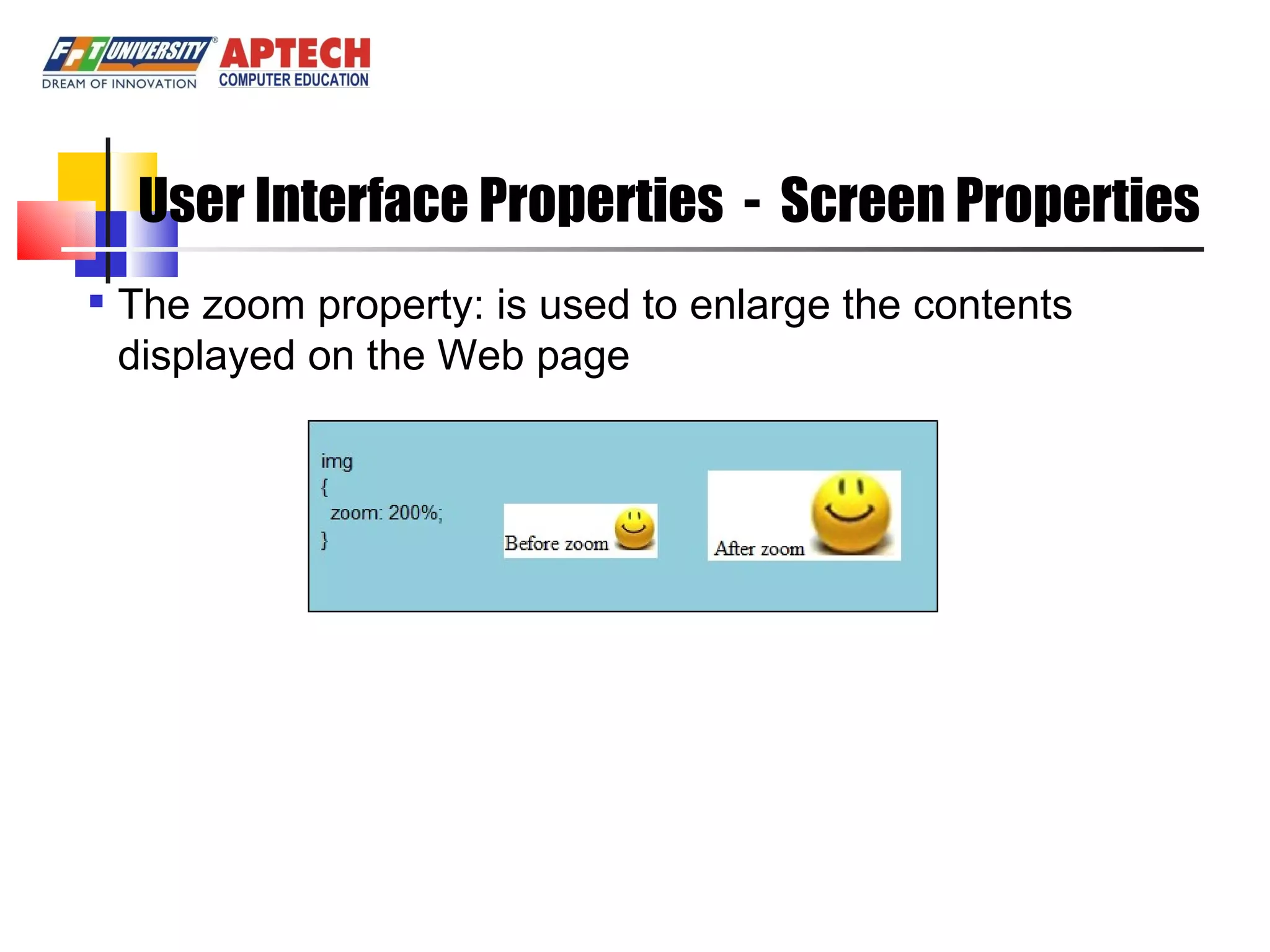
Positioning in CSS allows elements to be positioned using normal, absolute, or relative positioning. Size properties set dimensions, position properties specify placement, and visibility properties control appearance. Pseudo classes apply styles based on element states like hover, while pseudo elements add effects to selectors. Table properties structure tables and list properties format lists. Scrollbar properties customize scrollbars, and screen properties control the cursor and zoom level.