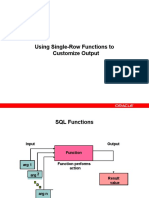
Sql Functions
FUNCTION PERFORMS
ACTIONS
FUNCTIONS
-Functions are a very powerful feature of SQL
and can be used to do the following:
- Perform calculations on data
- Modify individual data items
- Manipulate output for group of rows
- Format dates and numbers for display
- Convert column data types
SQL functions sometimes take arguments and
always return a value. Functions are reusable
programs.
TWO TYPES OF SQL FUNCTIONS
SINGLE-ROW FUNCTIONS
Single-Row Functions:
Manipulate data items
Accept arguments and return one value
Act on each row returned
Return one result per row
May modify the data type
Can be nested
Accept arguments which can be a column or
an expression
SINGLE ROW FUNCTIONS
Character
Number
General
Conversion Date
CHARACTER FUNCTION
LOWER CONCAT
UPPER SUBSTR
INITCAP LENGTH
INSTR
REPLACE
CASE MANIPULATION
These functions convert case for character strings.
USING CASE MANIPULATION FUNCTIONS
Display the employee number, name, and department
number for employee KIRAN:
CHARACTER MANIPULATION FUNCTIONS
These Functions manipulate character strings:
Functions Result
CONCAT(‘HELLO’ , ‘WORLD’) HELLOWORLD
SUBSTR(‘HELLOWORLD’ , 5 , 5) OWORL
LENGTH(‘HELLOWORLD’) 10
REPLACE(‘HELLOWORLD’ , ‘W’ , ‘S’) HELLOSORLD
INSTR(‘HELLOWORLD’ , ‘W’ , 1 , 1) 6
USING CHARACTER-MANIPULATION
FUNCTIONS
1
2
3
1 2 3
NUMBER FUNCTIONS
ROUND: Rounds value to specified decimal
e.g ROUND (45.926,2) 46.93
TRUNC : Truncates value to specified decimal
e.g TRUNC(45.926,2) 45.92
MOD : Returns remainder of division
e.g MOD(1600,300) 100
Q: Calculate the remainder of a salary after its divided by 5000 for all emp
whose job title is sales representative.
WORKING WITH DATES
Oracle database stores dates in an internal numeric
format: century, year, month, day, hours, minutes,
seconds.
The default date display format is DD-MON-YY
SELECT ename, hiredate
FROM emp
WHERE ename like ‘A%’ ;
WORKING WITH DATES
SYSDATE is a function that returns:
Date
SYSTIMESTAMP is a function that returns:
Date
Time including milliseconds
Time zone
ARITHMETIC WITH DATES
Add or subtract a number to or from a date for a
resultant date value.
Subtract two dates to find the number of days
between those dates
USING ARITHMETIC OPERATORS
DATE FUNCTIONS
USING DATE FUNCTIONS
MONTHS_BETWEEN (‘01-SEP-95’ , ‘11-JAN-94’)
ADD_MONTHS (‘11-JAN-94’, 6)
NEXT_DAY ( ’01-SEP-95’ , ‘FRIDAY’)
LAST_DAY (‘01-FEB-95’)
USING DATE FUNCTIONS
Assume SYSDATE
ROUND(SYSDATE, ‘MONTH’) ===
ROUND(SYSDATE,’YEAR’) ===
TRUNC(SYSDATE,’MONTH’) ===
TRUNC(SYSDATE,’YEAR’) ===
DATA TYPES
A data type signifies type of data stored in a column of
the table
CONVERSION FUNCTIONS
Data type
Conversion
Implicit data type Explicit data type
conversion conversion
Oracle server can automatically convert the data to the
expected data type. This data type conversion can be
done implicitly by Oracle server, or explicitly by the
user.
EXPLICIT DATA TYPE CONVERSION
TO_CHAR
Number CHARACTER Date
TO_CHAR
CONTINUATION…
Explicit data type conversions are done by using the
conversion functions. Conversion functions convert a
value from one data type to another.
USING THE TO_CHAR FUNCTION WITH DATES.
The format model :
Must be enclosed in single quotation marks and is
case sensitive
Can include any valid date format element
Has an fm element to remove padded blanks or
suppress leading zeros.
Is separated from the data value by a comma.
ELEMENTS OF THE DATA FORMAT MODEL
ELEMENTS OF THE DATE FORMAT MODEL
Time elements format the time portion of the date.
Add character strings by enclosing them in double
quotation marks.
Number suffixes spell out numbers.
USING THE TO_CHAR FUNCTION WITH DATES
Q: Display result as follows,
Seventh of June 1994 12:00:00 AM
USING THE TO_CHAR FUNCTION WITH
NUMBERS
These are some of the format elements you can
use with TO_CHAR function to display a number
value as a character:
USING THE TO_CHAR FUNCTION WITH
NUMBERS
GENERAL FUNCTIONS
These functions work with any data type and
pertain to using nulls.
• NVL (expr1,expr2)
• NVL2 (expr1, expr2, expr3)
NVL FUNCTION
Converts a null to an actual value.
Data types that can be used are date, character, and
number.
Data types must match:
NVL(comm,0)
NVL(hiredate,’01-JAN-97’)
USING NVL FUNCTION
Calculate annual salary for all employees?
SELECT ename, sal, NVL(comm,0),
((sal*12) + NVL(comm,0)) AN_SAL
FROM emp;
USING NVL2 FUNCTION
SELECT ename, sal, comm,
NVL2(comm, ‘SAL+COMM’, ‘SAL’) income
FROM emp WHERE deptno IN (10, 30);