Single-Row Functions
Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able
to do the following :
– Describe various types functions available in SQL
– Use character, number, and date functions in
SELECT statements.
– Describe the use of conversion functions.
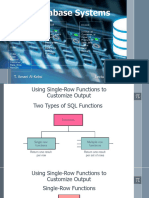
SQL Functions
Input Output
Function
arg 1 Function
performs action
arg 2 Result
Value
arg n
Two Types of SQL Functions
Functions
Single-row Multiple-row
Functions Functions
Single-Row Functions
• Manipulate data items
• Accept arguments and return one value
• Act on each row returned
• Return one result per row
• May modify the data type
• Can be nested
Function_name (column 1 expression, [arg1, arg2,…..])
Single-Row Functions
Character
Single-row
General Number
functions
Conversion Date
Character Functions
Character
functions
Case conversion Character manipulation
functions functions
LOWER CONCAT
UPPER SUBSTR
INITCAP LENGTH
INSTR
LPAD
Case Conversion Functions
Convert case for character strings
Function Result
LOWER (‘SQL Course’) sql sourse
UPPER (‘SQL Course’) SQL COURSE
INITCAP (‘SQL Course’) Sql Course
Using Case Conversion Functions
Display the employee number, name and department number
for employee Blake.
SQL> SELECT empno, ename, deptno
2 FROM emp
3 WHERE ename = ‘blake’;
no rows selected
SQL> SELECT empno, ename, deptno
2 FROM emp
3 WHERE LOWER(ename) = ‘blake’;
EMPNO ENAME DEPTNO
------------- ------------------- ---------------
7698 BLAKE 30
Character Manipulation Functions
Manipulate character strings
Function Result
CONCAT (‘Good’, ‘String’) GoodString
SUBSTR (‘String’, 1,3) Str
LENGTH (‘String’) 6
INSTR (‘String’, ‘r’) 3
LPAD (sal, 10, ‘*’) ******5000
Using the Character
Manipulation Functions
SQL> SELECT ename, CONCAT(ename, job), LENGTH(ename),
2 INSTR (ename, ‘A’)
3 FROM emp
4 WHERE SUBSTR (job, 1,5) = ‘SALES’;
ENAME CONCAT(ENAME,JOB) LENGTH(ENAME) INSTR(ENAME, ‘A’
---------------- ------------------------------- -------------------------- --------------------------
MARTIN MARTINSALESMAN 6 2
ALLEN ALLENSALESMAN1 5 1
TURNER TURNERSALESMAN 6 0
WARD WARDSALESMAN 4 2
Number Functions
• ROUND: Rounds value to specified decimal
ROUND (45.926,2) ------------> 45.93
• TRUNC: Truncates value to specified decimal
TRUNC (45.926,2) ------------> 45.92
• MOD: Returns remainder of division
MOD (1600,300) ------------> 100
Using the ROUND Function
SQL> SELECT ROUND (45.923,2), ROUND (45.923,0),
2 ROUND (45.923,-1)
3 FROM DUAL;
ROUND (45.923,2) ROUND (45.923,0) ROUND (45.923,-1)
------------------------ ------------------------ ------------------------
45.92 46 50
Using the TRUNC Function
SQL> SELECT TRUNC (45.923,2), TRUNC (45.923),
2 TRUNC (45.923,-1)
3 FROM DUAL;
TRUNC (45.923,2) TRUNC (45.923) TRUNC (45.923,-1)
------------------------ ------------------------ ------------------------
45.92 46 50
Using the MOD Function
Calculate the remainder of the ratio of
salary to commission for all employees
whose job title is a salesman
SQL> SELECT ename, sal, comm, MOD (sal, comm)
2 FROM emp
3 WHERE job = ‘SALESMAN’
ENAME SAL COMM MOD(SAL,COMM)
--------------------- ------- --------------- ------------------------
MARTIN 1250 1400 1250
ALLEN 1600 300 100
TURNER 1500 0 1500
WARD 1250 500 250
Working with Dates
• Oracle stores dates in an internal numeric
format: Century, year, month, day, hours,
minutes, seconds.
• The default date format is DD-MON-YY.
• SYSDATE is a function returning date and
time.
• DUAL is a dummy table used to view
SYSDATE.
Arithmetic with Dates
• Add or subtract a number to or from a date for
a resultant date value.
• Subtract two dates to find number of days
between those dates.
• Add hours to a date by dividing the number of
hours by 24.
Using Arithmetic Operators with
Dates
SQL> SELECT ename, (SYSDATE-hiredate) / 7 Weeks
2 FROM emp
3 WHERE deptno = 10;
ENAME WEEKS
------------ ----------------
KING 830.93709
CLARK 853.93709
MILLER 821.36566
Date Functions
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
Number of months
MONTHS_BETWEEN
between two dates
Add calendar
ADD_MONTHS
months to date
Next day of the date
NEXT_DAY
specified
LAST_DAY Last day of the month
ROUND Round the date
TRUNC Truncate the date
Using Date Functions
• MONTHS_BETWEEN (‘01-SEP-95’, ‘11-JAN-94’ -------> 19.6774194
• ADD_MONTHS (‘11-JAN-94’,6) -------> ‘11-JUL-94’
• NEXT_DAY (‘01-SEP-95’, ‘FRIDAY’) ----------> ‘08-SEP-95’
• LAST_DAY (‘01-SEP-95’) ----------> ‘30-SEP-95’
Using Date Functions
• ROUND (‘25-JUL-95’, ‘MONTH’) -------> 01-AUG-95
• ROUND (‘25-JUL-95’, ‘YEAR’) -------> 01-JAN-96
• TRUNC (‘25-JUL-95’, ‘MONTH’) -------> 01-JUL-95
• TRUNC (‘25-JUL-95’, ‘YEAR’) -------> 01-JAN-95
Conversion Functions
Datatype
conversion
Implicit datatype Explicit datatype
conversion conversion
Implicit Datatype Conversion
From To
VARCHAR2 or CHAR NUMBER
VARCHAR2 or CHAR DATE
NUMBER VARCHAR2
DATE VARCHAR2