Procedure
Leveling Notes
CEN 101 – Leveling Methods
DIFFERENTIAL
Definition of Terms
LEVELING
Definition of Terms
Definition of Terms
Bench Mark (BM).
A fixed point of reference whose elevation is
either known or assumed.
Permanent Bench Marks (PBM)
Established at intervals throughout the country by
the Philippine Coast and Geodetic Survey (PCGS)
or Bureau of Lands.
Temporary Bench Marks (TBM)
Set up by a surveyor for his own use in a particular
surveying project and may have assume elevations.
They should be stable and semi-permanent such as:
• Wooden peg set in concrete
• A nail or spike driven into a tree
• A X-mark on a bridge abutment
• A notch cut out in the root of a tree
• Top of a fire hydrant
Definition of Terms
Bench Mark (BM).
A fixed point of reference whose elevation is
either known or assumed.
Permanent Bench Marks (PBM)
Established at intervals throughout the country by
the Philippine Coast and Geodetic Survey (PCGS)
or Bureau of Lands.
Temporary Bench Marks (TBM)
Set up by a surveyor for his own use in a particular
surveying project and may have assume elevations.
They should be stable and semi-permanent such as:
• Wooden peg set in concrete
• A nail or spike driven into a tree
• A X-mark on a bridge abutment
• A notch cut out in the root of a tree
• Top of a fire hydrant
They serve as points of reference for levels in a given
locality, and their elevations are determined by precise
leveling methods. Permanent Bench Marks consist of
bronze or brass disks that are permanently set in
concrete foundations. They are marked with the
elevation above sea level, the year it was established, and
their reference number.
Definition of Terms
Backsight (BS).
➢ A reading taken on a rod held on a point of
know or assumed elevation.
➢ The measurement of the vertical distance from
the established line of sight to the point sighted
➢ Frequently referred to as plus sights (+S) since
they are added to the elevation of points being
sighted to determine the height of the
instrument.
Foresight (FS).
➢ A reading taken on a rod held on a point
whose elevation is to be determined.
➢ Represented as a vertical distance from the
line of sight of the instrument to the point
observed
➢ Referred to as minus sight (-S)
Definition of Terms
Backsight Distance (BSD).
➢ A measured distance from the center of the
instrument to the rod on which a backsight
is taken.
Foresight Distance (FSD).
➢ Horizontal distance from the center of the
instrument to the rod on which a foresight
is taken.
Definition of Terms
Turning Point (TP)
➢ An intervening point between two
benchmarks upon which point foresight and
backsight rod readings are taken to enable a
leveling operation to continue from a new
instrument position.
Height of the Instrument (HI)
➢ Also referred to as height of collimation
➢ The elevation of the line of sight of an
instrument above or below a selected
reference datum.
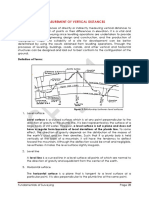
Definition of Terms
The different terms commonly used in
differential leveling works are shown in
this simple graph. As you can see, the
points along the leveling route all lie in a
straight line. It is important to
understand that this is not always the
case in actual leveling works. The points
and the instrument stations may in fact
be positioned in plan along a zigzagging
pattern.
Definition of Terms
As shown here, the route taken by the
surveying team follows a zigzagging
pattern possibly avoiding immovable
objects, ravines, bodies of water, or any
obstructions encountered on the site.
DIFFERENTIAL LEVELING
The process of determining the difference in elevation between
two or more points that are some distance apart.
It requires a series of setups of the instrument along a general
route and, for each set up, a rod reading back to the point of
known elevation.
It is commonly used to establish the elevation of a benchmark
referenced to an existing benchmark
It is also useful for comparing the elevation of several points or
objects.
Procedure
Leveling Notes
CEN 101 – Leveling Methods
DIFFERENTIAL
Definition of Terms
LEVELING
Procedure
1. Differential leveling can be done with at least two
people:
• the rodman » carries and holds the rod
• the instrument man » sets up the level and determines the
required rod readings.
• the recorder » records all data collected accurately in the
field notebook
• The chief of party » instructs and supervises all party
members
• A pacer » who measures the horizontal distance of the
route
• An axeman » clears away obstructions and disturbances in
the general route of the survey
• And utilitymen
Procedure
2. The leveling instrument is setup at any
convenient location along the level route.
3. After determining the location and elevation of
the benchmark, take a backsight reading on the
leveling rod placed atop the benchmark.
HI = Elev of BM1 + BS
4. A second rodman positions himself at a
convenient turning point (TP) and the
instrument man takes a foresight reading.
Elev of TP = HI - FS
Procedure
5. The level is then transferred and set up at
another convenient location beyond TP, but still
in the general route to BM2.
6. A backsight reading is taken to TP to establish a
new height of instrument (HI2)
HI2 = Elev of TP + BS
7. The rodman finally moves forward to the location
of BM2, and a foresight reading is taken.
Elev of BM2 = HI2 - FS
Procedure
Leveling Notes
CEN 101 – Leveling Methods
DIFFERENTIAL
Definition of Terms
LEVELING
Leveling Notes
Station BS HI FS Elevation
1 5.87 398.12 392.25 m
2 7.03 398.86 6.29 391.83 m
3 3.48 396.09 6.25 392.61 m
4 7.25 397.09 6.25 389.84 m
5 10.19 401.71 5.57 391.52 m
6 9.29 406.55 4.45 397.26 m
7 4.94 401.61 m
Leveling Notes
Station BS HI FS Elevation
1 5.87 398.12 392.25 m Elev @ 7 = Elev @ 1 + ∑BS - ∑FS
2 7.03 398.86 6.29 391.83 m
Elev @ 7 = 392.25 + 43.11 – 33.75
3 3.48 396.09 6.25 392.61 m
4 7.25 397.09 6.25 389.84 m Elev @ 7 = 401.61 meters
5 10.19 401.71 5.57 391.52 m
6 9.29 406.55 4.45 397.26 m
7 4.94 401.61 m
∑BS = 43.11 ∑FS = 33.75
Leveling Notes
Columns for STATIONINGS
used in the route, the
BACKSIGHT readings, the
FORESIGHT readings, and the
ELEVATIONS.
Arithmetic check. Serves as the
closing remarks signifying that
the data collected is accurate
and true.
Remarks on stations for
clarification and future usage.
Formulas used in the
computations.