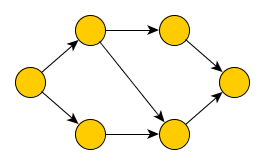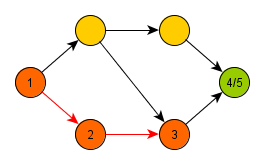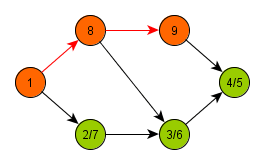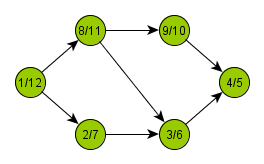
Depth-first search is a graph traversal algorithm, which has a very wide application area. This algorithm may be used for finding out number of components of a graph, topological order of its nodes or detection of cycles.
Description
In its recursive form, the algorithm starts at an arbitrary node and marks it as open, processes it, and then calls itself on all newly discovered descendants of
. After returning back from recursion, the algorithm marks the node
as closed.
Using this simple procedure, all branches of the graph are processed to their maximum depth.
Complexity
Provided all nodes and edges can be accessed randomly, the asymptotic complexity of depth-first search is , because all edges and vertices are visited exactly once.
Code
/** * Not discovered node */ private static final int FRESH = 0; /** * Open node */ private static final int OPEN = 1; /** * Closed node */ private static final int CLOSED = 2; /** * Recursive form of depth-first search * * @param graph */ public static void depthFirstSearch(GraphIface graph) { //node states int[] state = new int[graph.getVertexCount()]; for (int i = 0; i < state.length; i++) { state[i] = FRESH; } //perform depth first search of all connected components for (int i = 0; i < graph.getVertexCount(); i++) { if (state[i] == FRESH) { doDFS(graph, i, state); } } } /** * Perform depth-first search * * @param graph graph * @param vertexNr node identifier * @param state array of node states */ private static void doDFS(GraphIface graph, int vertexNr, int[] state) { state[vertexNr] = OPEN; List<GraphNodeIface> succ = graph.getNode(vertexNr).getSuccessors(); for (GraphNodeIface n : succ) { if (state[n.getId()] == FRESH) { doDFS(graph, n.getId(), state); } } state[vertexNr] = CLOSED; } /** * Defines basic interface for a generic graph * * @author Pavel Micka */ public interface GraphIface<ENTITY> { /** * Add an edge to a graph * * @param from source node * @param to target node */ public void addEdge(int from, int to); /** * Get number of edges in the graph * * @return number of edges in the graph */ public int getEdgeCount(); /** * Return vertex (node) with the given identifier * * @param id * @return */ public GraphNodeIface getNode(int id); /** * Return total number of nodes (vertices) * * @return total number of nodes (vertices) */ public int getVertexCount(); /** * Remove the edge * * @param from source node * @param to target node */ public void removeEdge(int from, int to); /** * Defines basic interface for a node of a graph * * @param <ENTITY> */ public interface GraphNodeIfac<ENTITY> { /** * @return the id */ public int getId(); /** * @return the successors */ public List<GraphNodeIface> getSuccessors(); /** * @return the value */ public ENTITY getValue(); /** * @param value the value to set */ public void setValue(ENTITY value); } } Sources
- KOLÁŘ, Josef. Teoretická informatika. 2nd edition. Praha : Česká informatická společnost, 2004. 205 p. ISBN 80-900853-8-5.