The pivot_table() function in Pandas allows us to create a spreadsheet-style pivot table making it easier to group and analyze our data.
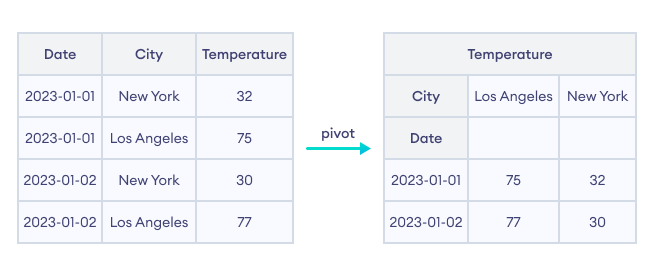
Let's look at an example.
import pandas as pd # create a dataframe data = {'Date': ['2023-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-02'], 'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles'], 'Temperature': [32, 75, 30, 77]} df = pd.DataFrame(data) print("Original DataFrame\n", df) print() # pivot the dataframe pivot_df = df.pivot_table(index='Date', columns='City', values='Temperature') print("Reshaped DataFrame\n", pivot_df) Output
Original DataFrame Date City Temperature 0 2023-01-01 New York 32 1 2023-01-01 Los Angeles 75 2 2023-01-02 New York 30 3 2023-01-02 Los Angeles 77 Reshaped DataFrame City Los Angeles New York Date 2023-01-01 75 32 2023-01-02 77 30
In this example, we reshaped the DataFrame with Date as index, City as columns and Temperature as values.
The pivot_df DataFrame is a multidimensional table that shows the temperature based on the city and the date.
Thus the pivot_table() operation reshapes the data to make it clearer for further analysis.
pivot_table() Syntax
The syntax of pivot_table() in Pandas is:
df.pivot_table(values=None, index=None, columns=None, aggfunc='mean', fill_value=None, dropna=True) Here,
index: the column to use as row labelscolumns: the column that will be reshaped as columnsvalues: the column(s) to use for the new DataFrame's valuesaggfunc: the function to use for aggregation, defaulting to'mean'fill_value: value to replace missing values withdropna: whether to exclude the columns whose entries are all NaN
Example: pivot_table() with Multiple Values
If we omit the values argument in pivot_table(), it selects all the remaining columns (besides the ones specified index and columns) as values for the pivot table.
import pandas as pd # create a dataframe data = {'Date': ['2023-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-02'], 'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles'], 'Temperature': [32, 75, 30, 77], 'Humidity': [80, 10, 85, 5]} df = pd.DataFrame(data) print('Original DataFrame') print(df) print() # pivot the dataframe pivot_df = df.pivot_table(index='Date', columns='City') print('Reshaped DataFrame') print(pivot_df) Output
Original DataFrame Date City Temperature Humidity 0 2023-01-01 New York 32 80 1 2023-01-01 Los Angeles 75 10 2 2023-01-02 New York 30 85 3 2023-01-02 Los Angeles 77 5 Reshaped DataFrame Humidity Temperature City Los Angeles New York Los Angeles New York Date 2023-01-01 10 80 75 32 2023-01-02 5 85 77 30
In this example, we created a pivot table for multiple values i.e. Temperature and Humidity.
pivot_table() With Aggregate Functions
We can use the pivot_table() method with different aggregate functions using the aggfunc parameter. We can set the value of aggfunc to functions such as 'sum', 'mean', 'count', 'max' or 'min'.
Let's see an example.
import pandas as pd data = {'Date': ['2023-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-03', '2023-01-03'], 'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles'], 'Temperature': [32, 75, 30, 77, 33, 78], 'Humidity': [80, 10, 85, 5, 81, 7]} df = pd.DataFrame(data) # calculate mean temperature for each city using pivot_table() mean_temperature = df.pivot_table(index='City', values='Temperature', aggfunc='mean') print(mean_temperature) Output
Temperature City Los Angeles 76.666667 New York 31.666667
In the above example, we calculated the mean temperature of each city using the aggfunc='mean' argument in pivot_table().
Pivot Table With MultiIndex
We can create a pivot table with MultiIndex using the pivot_table() function.
Let's look at an example.
import pandas as pd # create a dataframe data = {'Date': ['2023-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-02'], 'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles','Delhi', 'Chennai', 'Delhi', 'Chennai'], 'Country': ['USA', 'USA', 'USA', 'USA', 'India', 'India', 'India', 'India'], 'Temperature': [32, 75, 30, 77, 75, 80, 78, 79]} df = pd.DataFrame(data) print("Original DataFrame\n", df) print() # create a pivot table with multiindex pivot_df = df.pivot_table(index=['Country', 'City'], columns='Date', values='Temperature') print("Reshaped DataFrame\n", pivot_df) Output
Original DataFrame Date City Country Temperature 0 2023-01-01 New York USA 32 1 2023-01-01 Los Angeles USA 75 2 2023-01-02 New York USA 30 3 2023-01-02 Los Angeles USA 77 4 2023-01-01 Delhi India 75 5 2023-01-01 Chennai India 80 6 2023-01-02 Delhi India 78 7 2023-01-02 Chennai India 79 Reshaped DataFrame Date 2023-01-01 2023-01-02 Country City India Chennai 80 79 Delhi 75 78 USA Los Angeles 75 77 New York 32 30
In this example, we created a pivot table with a MultiIndex by passing a list of columns as an index argument.
A MultiIndex contains multiple levels of indexes with columns linked to one another through a parent/relationship. Here, Country is the parent column and City is the child column.
Handle Missing Values With pivot_table()
Sometimes while reshaping data using pivot_table(), missing values may occur in the pivot table. Such missing values or NaN values can be handled in a pivot_table() operation using the arguments fill_value and dropna.
The dropna argument specifies whether to remove the columns whose entries are all NaN. The default value of dropna is True.
Let's look at an example.
import pandas as pd import numpy as np # Creating the DataFrame data = {'Date': ['2023-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-03', '2023-01-03', '2023-01-03'], 'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago'], 'Temperature': [32, 75, 30, 77, np.nan, 76, np.nan]} df = pd.DataFrame(data) # create a pivot table pivot_df = df.pivot_table(index='Date', columns='City', values='Temperature') print("\nDefault Pivot Table\n", pivot_df) # create a pivot table with dropna=True pivot_df_dropna = df.pivot_table(index='Date', columns='City', values='Temperature', dropna=False) print("\nPivot Table with dropna=False:\n", pivot_df_dropna) Output
Default Pivot Table City Los Angeles New York Date 2023-01-01 75.0 32.0 2023-01-02 77.0 30.0 2023-01-03 76.0 NaN Pivot Table with dropna=False: City Chicago Los Angeles New York Date 2023-01-01 NaN 75.0 32.0 2023-01-02 NaN 77.0 30.0 2023-01-03 NaN 76.0 NaN
In this example, we used the dropna function to determine the handling of columns with entirely NaN entries. By default, the dropna parameter is set to True, resulting in the automatic removal of the Chicago column.
Notice that the New York column is not dropped despite having one NaN value. This is because dropna removes the columns whose entries are all NaN.
The fill_value argument on the other hand replaces all the NaN values with a specified value. For example,
import pandas as pd import numpy as np # Creating the DataFrame data = {'Date': ['2023-01-01', '2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-03', '2023-01-03'], 'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles', 'New York', 'Los Angeles'], 'Temperature': [32, np.nan, 30, 77, np.nan, 76]} df = pd.DataFrame(data) # create a pivot table pivot_df = df.pivot_table(index='Date', columns='City', values='Temperature') print("\nDefault Pivot Table\n", pivot_df) # create a pivot table with fill_value=0 pivot_df_dropna = df.pivot_table(index='Date', columns='City', values='Temperature', fill_value=0) print("\nPivot Table with fill_value=0:\n", pivot_df_dropna) Output
Default Pivot Table City Los Angeles New York Date 2023-01-01 NaN 32.0 2023-01-02 77.0 30.0 2023-01-03 76.0 NaN Pivot Table with fill_value=0: City Los Angeles New York Date 2023-01-01 0 32 2023-01-02 77 30 2023-01-03 76 0
In this example, we replaced the NaN values with 0 using the fill_value=0 argument.
pivot() vs pivot_table()
The pivot() and pivot_table() functions perform similar operations but with few key differences.
| Basis | pivot() | pivot_table() |
|---|---|---|
| Aggregation | Does not allow aggregation of data. | Allows aggregation (sum, mean, count, etc.). |
| Duplicate Index | Cannot handle duplicate index values. | Can handle duplicate index values. |
| MultiIndex | Only accepts a single-level index. | Accepts multi-level index for complex data. |
