The Java substring() method extracts a part of the string (substring) and returns it.
Example
class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "java is fun"; // extract substring from index 0 to 3 System.out.println(str1.substring(0, 4)); } } // Output: java substring() Syntax
string.substring(int startIndex, int endIndex) substring() Parameters
The substring() method can take a maximum of two arguments.
- startIndex - the beginning index
- endIndex (optional) - the ending index
substring() Return Value
The substring() method returns a substring from the given string.
- The substring begins with the character at the startIndex and extends to the character at index
endIndex - 1 - If the endIndex is not passed, the substring begins with the character at the specified index and extends to the end of the string
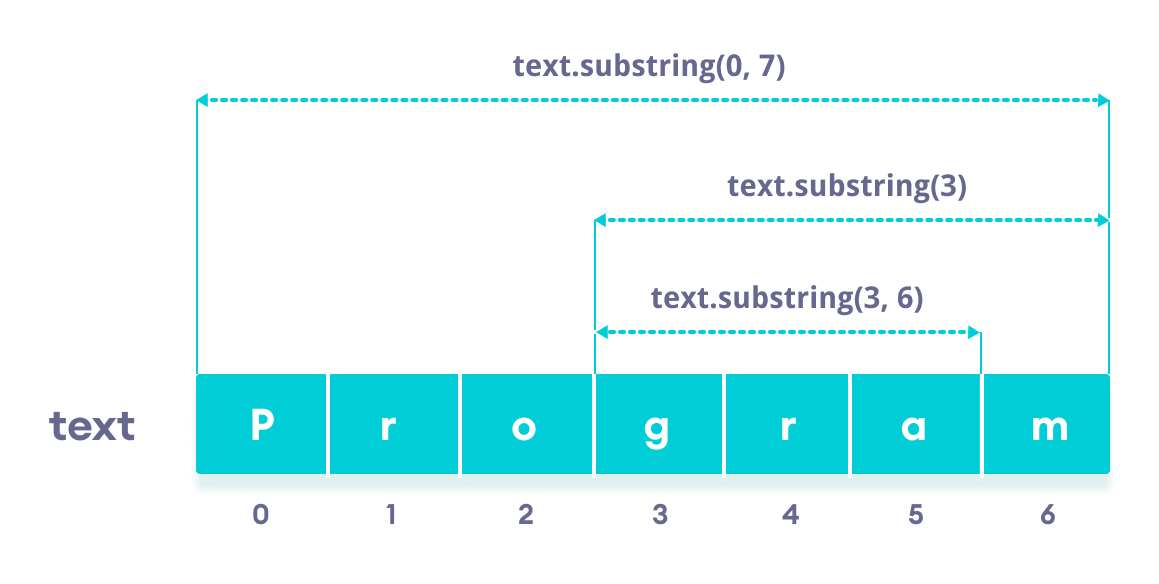
Note: You will get an error if
- startIndex/endIndex is negative or greater than string's length
- startIndex is greater than endIndex
Example 1: Java substring() With Only Start Index
class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "program"; // 1st character to the last character System.out.println(str1.substring(0)); // program // 4th character to the last character System.out.println(str1.substring(3)); // gram } } Example 2: Java substring() With Start and End Index
class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { String str1 = "program"; // 1st to the 7th character System.out.println(str1.substring(0, 7)); // program // 1st to the 5th character System.out.println(str1.substring(0, 5)); // progr // 4th to the 5th character System.out.println(str1.substring(3, 5)); // gr } } Also Read: