MQL5交易策略自动化(第十二部分):实现缓解型订单块(MOB)策略
概述
在前一篇文章(第十一部分)中,我们使用MetaQuotes Language 5(MQL5)构建了一个多层级网格交易系统,以利用市场波动获利。现在,在第十二部分中,我们将重点实现缓解型订单块(MOB) 策略,这是一种“聪明资金”概念,用于识别在市场出现重大波动之前机构订单得到缓解的关键价格区域。我们将涵盖以下主题:
在本文结束前,您将拥有一个可随时用于交易的完全自动化的缓解型订单块交易系统。让我们开始吧!
策略设计方案
为了实现缓解型订单块策略,我们将开发一个自动化系统,该系统能够基于订单块缓解事件来检测、验证并执行交易。该策略将侧重于识别在趋势延续前吸收流动性的机构价格区域。我们的系统将纳入精确的入场条件、止损设置和交易管理规则,以确保高效性和准确性。我们将按以下结构进行开发:
- 订单块识别——系统将扫描历史价格走势,以检测多头和空头订单块,并根据波动性、流动性捕捉和价格失衡过滤掉弱势区域。
- 缓解验证——我们将编程设定条件,以确认有效的缓解事件,确保价格重新触及订单块并出现拒绝信号,如影线或动量转变。
- 市场结构确认——智能交易系统(EA)将分析更高时间框架的趋势和流动性扫荡,以确保所识别的缓解块与整体市场流向保持一致。
- 交易执行规则——一旦缓解得到确认,系统将确定精确的入场点,根据订单块结构动态计算止损水平,并根据风险回报参数设置止盈目标。
- 风险与资金管理——该策略将整合头寸规模设定、回撤保护和退出策略,以便有效管理交易风险。
简言之,以下是该策略的整体图示:
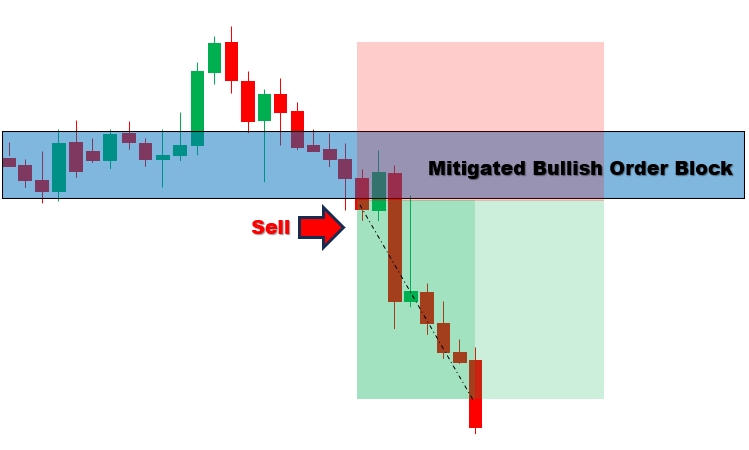
在MQL5中的实现
要在MQL5中创建该程序,请打开MetaEditor,进入导航器,找到“指标”文件夹,点击“新建”选项卡,并按照提示创建文件。文件创建完成后,在编码环境中,我们需要声明一些将在整个程序中使用到的全局变量。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Copyright 2025, Forex Algo-Trader, Allan. | //| "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ #property copyright "Forex Algo-Trader, Allan" #property link "https://t.me/Forex_Algo_Trader" #property version "1.00" #property description "This EA trades based on Mitigation Order Blocks Strategy" #property strict //--- Include the trade library for managing positions #include <Trade/Trade.mqh> CTrade obj_Trade;
我们首先通过“#include<Trade/Trade.mqh>”引入交易库,该库提供用于管理交易操作的内置函数。接下来,我们使用“CTrade”类初始化交易对象“obj_Trade”,允许EA能够以编程方式执行买入和卖出订单。这样的设置将确保交易执行能够高效处理,无需人工干预。然后,我们可以提供一些输入参数,以便用户能够通过用户界面(UI)更改并控制系统的行为。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Input Parameters | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ input double tradeLotSize = 0.01; // Trade size for each position input bool enableTrading = true; // Toggle to allow or disable trading input bool enableTrailingStop = true; // Toggle to enable or disable trailing stop input double trailingStopPoints = 30; // Distance in points for trailing stop input double minProfitToTrail = 50; // Minimum profit in points before trailing starts (not used yet) input int uniqueMagicNumber = 12345; // Unique identifier for EA trades input int consolidationBars = 7; // Number of bars to check for consolidation input double maxConsolidationSpread = 50; // Maximum allowed spread in points for consolidation input int barsToWaitAfterBreakout = 3; // Bars to wait after breakout before checking impulse input double impulseMultiplier = 1.0; // Multiplier for detecting impulsive moves input double stopLossDistance = 1500; // Stop loss distance in points input double takeProfitDistance = 1500; // Take profit distance in points input color bullishOrderBlockColor = clrGreen; // Color for bullish order blocks input color bearishOrderBlockColor = clrRed; // Color for bearish order blocks input color mitigatedOrderBlockColor = clrGray; // Color for mitigated order blocks input color labelTextColor = clrBlack; // Color for text labels
这部分中,我们定义了输入参数,用于配置程序的运行方式。“tradeLotSize”用于设置仓位大小,而“enableTrading”和“enableTrailingStop”则分别控制交易执行和追踪止损功能,其中“trailingStopPoints”和“minProfitToTrail”进一步细化了止损逻辑。“uniqueMagicNumber”用于识别交易,“consolidationBars”和“maxConsolidationSpread”则用于检测价格盘整区间。突破行情通过“barsToWaitAfterBreakout”和“impulseMultiplier”进行确认。“stopLossDistance”和“takeProfitDistance”用于管理风险,而“bullishOrderBlockColor”、“bearishOrderBlockColor”、“mitigatedOrderBlockColor”和“labelTextColor”则用于处理图表的可视化效果。
最后,我们需要定义一些全局变量,这些变量将用于控制整个系统。
//--- Struct to store price and index for highs and lows struct PriceAndIndex { double price; // Price value int index; // Bar index where this price occurs }; //--- Global variables for tracking market state PriceAndIndex rangeHighestHigh = {0, 0}; // Highest high in the consolidation range PriceAndIndex rangeLowestLow = {0, 0}; // Lowest low in the consolidation range bool isBreakoutDetected = false; // Flag for when a breakout occurs double lastImpulseLow = 0.0; // Low price after breakout for impulse check double lastImpulseHigh = 0.0; // High price after breakout for impulse check int breakoutBarNumber = -1; // Bar index where breakout happened datetime breakoutTimestamp = 0; // Time of the breakout string orderBlockNames[]; // Array of order block object names datetime orderBlockEndTimes[]; // Array of order block end times bool orderBlockMitigatedStatus[]; // Array tracking if order blocks are mitigated bool isBullishImpulse = false; // Flag for bullish impulsive move bool isBearishImpulse = false; // Flag for bearish impulsive move #define OB_Prefix "OB REC " // Prefix for order block object names
我们首先定义“PriceAndIndex”结构体,用于存储一个“价格”值以及该价格所在的K线“索引”。这一结构对于在特定范围内追踪特定价格点非常有用。全局变量用于管理市场结构和突破行情检测的关键方面。“rangeHighestHigh”和“rangeLowestLow”将分别存储盘整区间内的最高价和最低价,有助于界定潜在订单块的边界。“isBreakoutDetected”将作为标识,用于指示何时发生了突破行情,而“lastImpulseLow”和“lastImpulseHigh”将存储突破行情后的第一个低点和高点,用于确认强劲的走势。
“breakoutBarNumber”将记录突破行情发生的K线索引,“breakoutTimestamp”将存储突破行情事件的确切时间。数组“orderBlockNames”、“orderBlockEndTimes”和“orderBlockMitigatedStatus”将处理订单块的识别、生命周期以及缓解情况的追踪。布尔标识“isBullishImpulse”和“isBearishImpulse”用于确定突破行情走势是否符合多头或空头强劲走势的条件。最后,“OB_Prefix”是一个由宏#define定义的预定义字符串前缀,在命名订单块对象时使用,确保图形表示的一致性。基于这些变量,我们开始编写程序逻辑。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert initialization function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ int OnInit() { //--- Set the magic number for the trade object to identify EA trades obj_Trade.SetExpertMagicNumber(uniqueMagicNumber); return(INIT_SUCCEEDED); }
这部分中,我们在OnInit事件处理程序中初始化EA。我们使用“SetExpertMagicNumber”方法设置专家magic数字,确保我们EA执行的所有交易均被唯一标记,避免与其他交易产生冲突。这一步骤对于仅跟踪和管理由我们策略开启的交易至关重要。初始化完成后,我们返回INIT_SUCCEEDED,确认我们的程序已准备好运行。随后,我们可以进入主要的OnTick事件处理程序,开始编写主要控制逻辑。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Expert OnTick function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void OnTick() { //--- Check for a new bar to process logic only once per bar static bool isNewBar = false; int currentBarCount = iBars(_Symbol, _Period); static int previousBarCount = currentBarCount; if (previousBarCount == currentBarCount) { isNewBar = false; } else if (previousBarCount != currentBarCount) { isNewBar = true; previousBarCount = currentBarCount; } //--- Exit if not a new bar to avoid redundant processing if (!isNewBar) return; //--- }
为确保我们在每根K线(而非每个价格变动tick)上进行数据处理,在OnTick函数(该函数在收到每个新tick时执行)中,我们使用iBars函数获取图表上的K线总数,并将其存储在“currentBarCount”变量中。随后,我们将它与“previousBarCount”进行比较,如果两者相等,则“isNewBar”仍保持false,从而避免重复处理。如果检测到新K线,我们会更新“previousBarCount”并将“isNewBar”设置为true,以允许策略逻辑执行。最后,如果“isNewBar”为false,我们提前返回,通过跳过不必要的计算来优化性能。如果出现了新K线,我们则继续寻找盘整区间。
//--- Define the starting bar index for consolidation checks int startBarIndex = 1; //--- Check for consolidation or extend the existing range if (!isBreakoutDetected) { if (rangeHighestHigh.price == 0 && rangeLowestLow.price == 0) { //--- Check if bars are in a tight consolidation range bool isConsolidated = true; for (int i = startBarIndex; i < startBarIndex + consolidationBars - 1; i++) { if (MathAbs(high(i) - high(i + 1)) > maxConsolidationSpread * Point()) { isConsolidated = false; break; } if (MathAbs(low(i) - low(i + 1)) > maxConsolidationSpread * Point()) { isConsolidated = false; break; } } if (isConsolidated) { //--- Find the highest high in the consolidation range rangeHighestHigh.price = high(startBarIndex); rangeHighestHigh.index = startBarIndex; for (int i = startBarIndex + 1; i < startBarIndex + consolidationBars; i++) { if (high(i) > rangeHighestHigh.price) { rangeHighestHigh.price = high(i); rangeHighestHigh.index = i; } } //--- Find the lowest low in the consolidation range rangeLowestLow.price = low(startBarIndex); rangeLowestLow.index = startBarIndex; for (int i = startBarIndex + 1; i < startBarIndex + consolidationBars; i++) { if (low(i) < rangeLowestLow.price) { rangeLowestLow.price = low(i); rangeLowestLow.index = i; } } //--- Log the established consolidation range Print("Consolidation range established: Highest High = ", rangeHighestHigh.price, " at index ", rangeHighestHigh.index, " and Lowest Low = ", rangeLowestLow.price, " at index ", rangeLowestLow.index); } } else { //--- Check if the current bar extends the existing range double currentHigh = high(1); double currentLow = low(1); if (currentHigh <= rangeHighestHigh.price && currentLow >= rangeLowestLow.price) { Print("Range extended: High = ", currentHigh, ", Low = ", currentLow); } else { Print("No extension: Bar outside range."); } } }
这部分中,我们通过分析近期价格走势来定义并确定盘整区间。首先,我们将“startBarIndex”设置为1,以此确定盘整区间检验的起始点。如果尚未检测到突破行情(由“isBreakoutDetected”指示),我们将继续评估市场是否处于严格的盘整阶段。我们遍历最近“consolidationBars”数量的K线,使用MathAbs函数测量连续高点和低点之间的绝对差值。如果所有差值均保持在“maxConsolidationSpread”范围内,我们确认市场处于盘整阶段。
一旦检测到盘整区间,我们确定该区间内的最高价和最低价。我们将“rangeHighestHigh”和“rangeLowestLow”初始化为“startBarIndex”对应K线的高点和低点,然后遍历整个区间,每当遇到新的最高价或最低价时,便更新这些值。这些值定义了我们的盘整区间边界。
如果盘整区间已经确定,则检查当前K线是否扩展了现有区间。我们使用“high”和“low”函数获取“currentHigh”和“currentLow”,并将其与“rangeHighestHigh.price”和“rangeLowestLow.price”进行比较。如果价格仍处于区间内,我们使用Print函数打印一条消息,显示区间扩展。否则,我们打印未发生扩展的消息,表明可能出现了突破行情。自定义价格函数如下:
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Price data accessors | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ double high(int index) { return iHigh(_Symbol, _Period, index); } //--- Get high price of a bar double low(int index) { return iLow(_Symbol, _Period, index); } //--- Get low price of a bar double open(int index) { return iOpen(_Symbol, _Period, index); } //--- Get open price of a bar double close(int index) { return iClose(_Symbol, _Period, index); } //--- Get close price of a bar datetime time(int index) { return iTime(_Symbol, _Period, index); } //--- Get time of a bar
这些自定义函数有助于我们获取价格数据。“high”函数使用iHigh返回指定“索引”处K线的最高价,而“low”函数调用iLow获取相应K线的最低价。“open”函数使用iOpen获取开盘价,“close”函数则通过iClose获取收盘价。此外,“time”函数采用iTime返回给定K线的时间戳。运行程序后,我们得到以下结果。
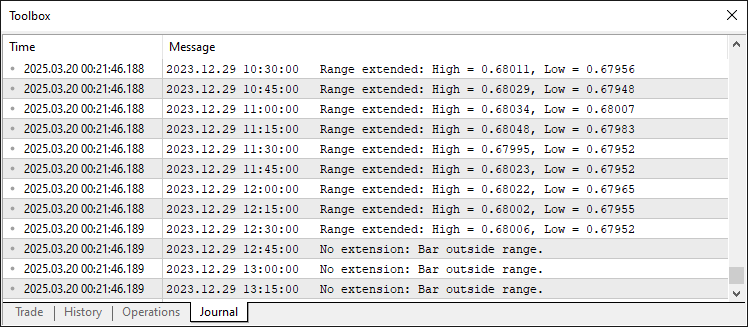
由图可见,一旦价格区间确定,且价格在该区间内波动,我们会持续扩展该区间,直至出现区间突破。因此,现在需要检测已确认价格区间内的突破行情。我们通过以下逻辑来实现这一目标:
//--- Detect a breakout from the consolidation range if (rangeHighestHigh.price > 0 && rangeLowestLow.price > 0) { double currentClosePrice = close(1); if (currentClosePrice > rangeHighestHigh.price) { Print("Upward breakout at ", currentClosePrice, " > ", rangeHighestHigh.price); isBreakoutDetected = true; } else if (currentClosePrice < rangeLowestLow.price) { Print("Downward breakout at ", currentClosePrice, " < ", rangeLowestLow.price); isBreakoutDetected = true; } } //--- Reset state after a breakout is detected if (isBreakoutDetected) { Print("Breakout detected. Resetting for the next range."); breakoutBarNumber = 1; breakoutTimestamp = TimeCurrent(); lastImpulseHigh = rangeHighestHigh.price; lastImpulseLow = rangeLowestLow.price; isBreakoutDetected = false; rangeHighestHigh.price = 0; rangeHighestHigh.index = 0; rangeLowestLow.price = 0; rangeLowestLow.index = 0; }
为了检测并处理先前确定的盘整区间内的突破行情,我们首先验证“rangeHighestHigh.price”和“rangeLowestLow.price”值是否有效,确保已确定盘整区间。然后,我们使用“close”函数获取“currentClosePrice”(当前收盘价),并将其与区间边界进行比较。如果收盘价超过“rangeHighestHigh.price”,我们确认出现向上突破行情,记录该事件并将“isBreakoutDetected”设置为true。同样,如果收盘价低于“rangeLowestLow.price”,我们确认出现向下突破行情,并相应地标记该事件。
一旦确认突破行情,我们重置必要的状态变量,为跟踪新的盘整阶段做好准备。我们记录突破行情的发生情况,并将“breakoutBarNumber”设置为1,标记突破行情序列的第一根K线。使用TimeCurrent记录“breakoutTimestamp”(突破时间戳),以注明突破行情的确切时间。另外,我们存储“lastImpulseHigh”(最后强劲走势高点)和“lastImpulseLow”(最后强劲走势低点),以跟踪突破行情后的价格走势。最后,我们将“isBreakoutDetected”重置为false,并通过将“rangeHighestHigh.price”和“rangeLowestLow.price”设置为0来清除之前的盘整区间,确保系统已准备好检测下一个交易机会。
如果确认出现突破行情,我们会等待并通过强劲走势进行验证,然后将其绘制在图表上。
//--- Check for impulsive movement after breakout and create order blocks if (breakoutBarNumber >= 0 && TimeCurrent() > breakoutTimestamp + barsToWaitAfterBreakout * PeriodSeconds()) { double impulseRange = lastImpulseHigh - lastImpulseLow; double impulseThresholdPrice = impulseRange * impulseMultiplier; isBullishImpulse = false; isBearishImpulse = false; for (int i = 1; i <= barsToWaitAfterBreakout; i++) { double closePrice = close(i); if (closePrice >= lastImpulseHigh + impulseThresholdPrice) { isBullishImpulse = true; Print("Impulsive upward move: ", closePrice, " >= ", lastImpulseHigh + impulseThresholdPrice); break; } else if (closePrice <= lastImpulseLow - impulseThresholdPrice) { isBearishImpulse = true; Print("Impulsive downward move: ", closePrice, " <= ", lastImpulseLow - impulseThresholdPrice); break; } } if (!isBullishImpulse && !isBearishImpulse) { Print("No impulsive movement detected."); } //--- }
这部分中,我们分析突破行情后的价格走势,以判断是否出现强劲走势,这对于识别有效的订单块至关重要。我们首先检查“breakoutBarNumber”是否有效,并通过TimeCurrent获取当前时间,确认其是否已超过“breakoutTimestamp”加上“barsToWaitAfterBreakout”乘以PeriodSeconds,从而确保已度过足够的等待期。随后,我们计算“impulseRange”,即“lastImpulseHigh”与“lastImpulseLow”、之间的差值,该值代表突破后的价格波动范围。利用这一数值,我们通过将“impulseRange”乘以“impulseMultiplier”来计算“impulseThresholdPrice”(强劲走势阈值价格),以此定义强劲走势所需的最小价格延伸幅度。
接下来,我们将“isBullishImpulse”(多头强劲走势标识)和“isBearishImpulse”(空头强劲走势标识)初始化为false,为评估最近“barsToWaitAfterBreakout”根K线的价格走势做好准备。我们使用for loop循环遍历这些K线,并通过“close”函数获取每根K线的收盘价。如果“closePrice”大于或等于“lastImpulseHigh + impulseThresholdPrice”,我们检测到多头强劲走势,将“isBullishImpulse”设置为true,并记录该事件。如果“closePrice”小于或等于“lastImpulseLow - impulseThresholdPrice”,我们识别出空头强劲走势,将“isBearishImpulse”设置为true,并记录该事件。如果上述条件均不满足,我们打印一条消息,表明未检测到强劲走势。这一逻辑确保只有突破后的强劲延续走势才被视为有效的订单块,以供后续处理。为了呈现可视化效果,我们采用以下逻辑:
bool isOrderBlockValid = isBearishImpulse || isBullishImpulse; if (isOrderBlockValid) { datetime blockStartTime = iTime(_Symbol, _Period, consolidationBars + barsToWaitAfterBreakout + 1); double blockTopPrice = lastImpulseHigh; int visibleBarsOnChart = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_VISIBLE_BARS); datetime blockEndTime = blockStartTime + (visibleBarsOnChart / 1) * PeriodSeconds(); double blockBottomPrice = lastImpulseLow; string orderBlockName = OB_Prefix + "(" + TimeToString(blockStartTime) + ")"; color orderBlockColor = isBullishImpulse ? bullishOrderBlockColor : bearishOrderBlockColor; string orderBlockLabel = isBullishImpulse ? "Bullish OB" : "Bearish OB"; if (ObjectFind(0, orderBlockName) < 0) { //--- Create a rectangle for the order block ObjectCreate(0, orderBlockName, OBJ_RECTANGLE, 0, blockStartTime, blockTopPrice, blockEndTime, blockBottomPrice); ObjectSetInteger(0, orderBlockName, OBJPROP_TIME, 0, blockStartTime); ObjectSetDouble(0, orderBlockName, OBJPROP_PRICE, 0, blockTopPrice); ObjectSetInteger(0, orderBlockName, OBJPROP_TIME, 1, blockEndTime); ObjectSetDouble(0, orderBlockName, OBJPROP_PRICE, 1, blockBottomPrice); ObjectSetInteger(0, orderBlockName, OBJPROP_FILL, true); ObjectSetInteger(0, orderBlockName, OBJPROP_COLOR, orderBlockColor); ObjectSetInteger(0, orderBlockName, OBJPROP_BACK, false); //--- Add a text label in the middle of the order block with dynamic font size datetime labelTime = blockStartTime + (blockEndTime - blockStartTime) / 2; double labelPrice = (blockTopPrice + blockBottomPrice) / 2; string labelObjectName = orderBlockName + orderBlockLabel; if (ObjectFind(0, labelObjectName) < 0) { ObjectCreate(0, labelObjectName, OBJ_TEXT, 0, labelTime, labelPrice); ObjectSetString(0, labelObjectName, OBJPROP_TEXT, orderBlockLabel); ObjectSetInteger(0, labelObjectName, OBJPROP_COLOR, labelTextColor); ObjectSetInteger(0, labelObjectName, OBJPROP_FONTSIZE, dynamicFontSize); ObjectSetInteger(0, labelObjectName, OBJPROP_ANCHOR, ANCHOR_CENTER); } ChartRedraw(0); //--- Store the order block details in arrays ArrayResize(orderBlockNames, ArraySize(orderBlockNames) + 1); orderBlockNames[ArraySize(orderBlockNames) - 1] = orderBlockName; ArrayResize(orderBlockEndTimes, ArraySize(orderBlockEndTimes) + 1); orderBlockEndTimes[ArraySize(orderBlockEndTimes) - 1] = blockEndTime; ArrayResize(orderBlockMitigatedStatus, ArraySize(orderBlockMitigatedStatus) + 1); orderBlockMitigatedStatus[ArraySize(orderBlockMitigatedStatus) - 1] = false; Print("Order Block created: ", orderBlockName); } }
这部分中,我们根据是否检测到强劲走势来决定是否创建订单块。我们首先通过检查“isBearishImpulse”或“isBullishImpulse”是否为true,来评估“isOrderBlockValid”。如果有效,我们为订单块定义关键参数:“blockStartTime”通过iTime函数获取,引用“consolidationBars + barsToWaitAfterBreakout + 1”对应的K线时间,确保其与已识别的结构对齐。将“blockTopPrice”设置为“lastImpulseHigh”,“blockBottomPrice”设置为“lastImpulseLow”,以标记订单块的价格范围。我们使用ChartGetInteger函数确定“visibleBarsOnChart”,并根据PeriodSeconds动态计算“blockEndTime”,确保矩形在图表当前范围内保持可见。
订单块的名称使用“OB_Prefix”(订单块前缀)和TimeToString函数构建,以包含时间戳以确保唯一性。订单块的颜色和标签根据强劲走势是多头还是空头来确定,选择“bullishOrderBlockColor”或“bearishOrderBlockColor”,并分配相应的标签。
随后,我们使用ObjectFind函数检查该订单块是否已存在。如果不存在,则使用ObjectCreate函数绘制一个矩形(OBJ_RECTANGLE)来表示订单块,并通过ObjectSetInteger和ObjectSetDouble函数分别设置其时间边界和价格边界。该矩形设置为填充模式(OBJPROP_FILL = true),应用指定颜色(OBJPROP_COLOR),并绘制在图表前景层(OBJPROP_BACK = false)。
接下来,我们在订单块内部新建一个标签以优化可视化效果。标签的时间("labelTime")设置为"blockStartTime"与"blockEndTime"的中点,而"labelPrice"则计算为"blockTopPrice"与"blockBottomPrice"的中点。我们通过将"orderBlockLabel"附加到"orderBlockName"后,生成唯一的标签名称。如果该标签不存在,则使用"ObjectCreate"函数创建一个文本对象(OBJ_TEXT),并通过设置文本内容(OBJPROP_TEXT)、颜色(OBJPROP_COLOR)、字体大小(OBJPROP_FONTSIZE),并将其锚点设置为居中(OBJPROP_ANCHOR = ANCHOR_CENTER)来完成配置。ChartRedraw函数确保新创建的元素能够立即显示。由于字体大小会因图表比例的不同而产生显著变化,因此我们按以下方式动态计算字体大小:
//--- Calculate dynamic font size based on chart scale (0 = zoomed out, 5 = zoomed in) int chartScale = (int)ChartGetInteger(0, CHART_SCALE); // Scale ranges from 0 to 5 int dynamicFontSize = 8 + (chartScale * 2); // Font size: 8 (min) to 18 (max)
最后,我们将订单块的详细信息存储至数组中:"orderBlockNames"(存储订单块对象名称)、"orderBlockEndTimes"(存储订单块到期时间)、"orderBlockMitigatedStatus"(跟踪订单块是否已失效)。我们使用 ArrayResize函数动态调整每个数组的大小,以容纳新增条目,确保订单块管理具备灵活性。系统会打印确认消息,表明订单块已成功创建。最后,我们只需重置突破行情跟踪变量即可。
//--- Reset breakout tracking variables breakoutBarNumber = -1; breakoutTimestamp = 0; lastImpulseHigh = 0; lastImpulseLow = 0; isBullishImpulse = false; isBearishImpulse = false;
程序编译并运行后,我们得到以下结果:
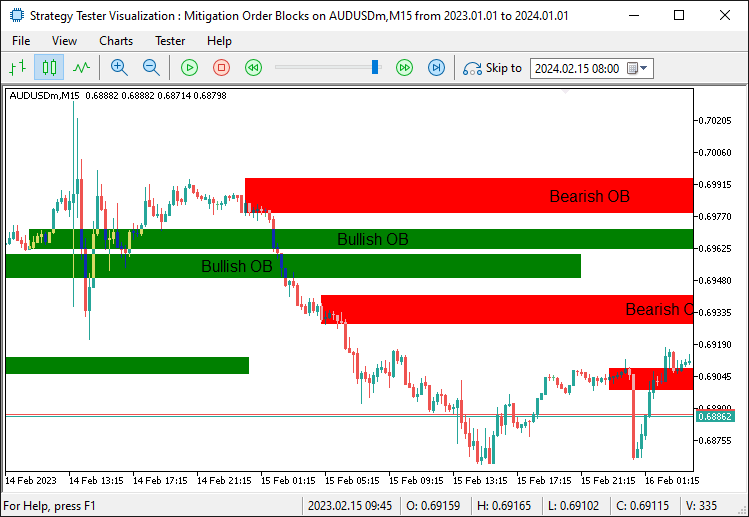
由图可见,我们已确认并标注了因强劲突破走势而形成的订单块。接下来,我们只需通过持续管理图表范围内的交易设置,来验证这些订单块是否已失效(即价格是否已突破或回踩订单块区域)。
//--- Process existing order blocks for mitigation and trading for (int j = ArraySize(orderBlockNames) - 1; j >= 0; j--) { string currentOrderBlockName = orderBlockNames[j]; bool doesOrderBlockExist = false; //--- Retrieve order block properties double orderBlockHigh = ObjectGetDouble(0, currentOrderBlockName, OBJPROP_PRICE, 0); double orderBlockLow = ObjectGetDouble(0, currentOrderBlockName, OBJPROP_PRICE, 1); datetime orderBlockStartTime = (datetime)ObjectGetInteger(0, currentOrderBlockName, OBJPROP_TIME, 0); datetime orderBlockEndTime = (datetime)ObjectGetInteger(0, currentOrderBlockName, OBJPROP_TIME, 1); color orderBlockCurrentColor = (color)ObjectGetInteger(0, currentOrderBlockName, OBJPROP_COLOR); //--- Check if the order block is still valid (not expired) if (time(1) < orderBlockEndTime) { doesOrderBlockExist = true; } //--- }
我们逆向遍历“orderBlockNames”数组,逐个处理每个订单块的失效判定及交易逻辑。“currentOrderBlockName”用于存储当前正在检查的订单块名称。通过ObjectGetDouble和ObjectGetInteger函数,我们分别获取订单块的“orderBlockHigh”、“orderBlockLow”、“orderBlockStartTime”、“orderBlockEndTime”及“orderBlockCurrentColor”,确保精准处理每个订单块的属性。
为了验证订单块是否仍然有效,我们将“time(1)”(通过“time”函数获取的当前K线时间)与“orderBlockEndTime”进行比较。如果当前时间仍在订单块的有效期内,“doesOrderBlockExist”被设置为true,表明该订单块仍处于活跃状态,可继续后续处理及交易逻辑。一旦满足条件,我们则执行对应的处理及交易操作。
//--- Get current market prices double currentAskPrice = NormalizeDouble(SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK), _Digits); double currentBidPrice = NormalizeDouble(SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_BID), _Digits); //--- Check for mitigation and execute trades if trading is enabled if (enableTrading && orderBlockCurrentColor == bullishOrderBlockColor && close(1) < orderBlockLow && !orderBlockMitigatedStatus[j]) { //--- Sell trade when price breaks below a bullish order block double entryPrice = currentBidPrice; double stopLossPrice = entryPrice + stopLossDistance * _Point; double takeProfitPrice = entryPrice - takeProfitDistance * _Point; obj_Trade.Sell(tradeLotSize, _Symbol, entryPrice, stopLossPrice, takeProfitPrice); orderBlockMitigatedStatus[j] = true; ObjectSetInteger(0, currentOrderBlockName, OBJPROP_COLOR, mitigatedOrderBlockColor); string blockDescription = "Bullish Order Block"; string textObjectName = currentOrderBlockName + blockDescription; if (ObjectFind(0, textObjectName) >= 0) { ObjectSetString(0, textObjectName, OBJPROP_TEXT, "Mitigated " + blockDescription); } Print("Sell trade entered upon mitigation of bullish OB: ", currentOrderBlockName); } else if (enableTrading && orderBlockCurrentColor == bearishOrderBlockColor && close(1) > orderBlockHigh && !orderBlockMitigatedStatus[j]) { //--- Buy trade when price breaks above a bearish order block double entryPrice = currentAskPrice; double stopLossPrice = entryPrice - stopLossDistance * _Point; double takeProfitPrice = entryPrice + takeProfitDistance * _Point; obj_Trade.Buy(tradeLotSize, _Symbol, entryPrice, stopLossPrice, takeProfitPrice); orderBlockMitigatedStatus[j] = true; ObjectSetInteger(0, currentOrderBlockName, OBJPROP_COLOR, mitigatedOrderBlockColor); string blockDescription = "Bearish Order Block"; string textObjectName = currentOrderBlockName + blockDescription; if (ObjectFind(0, textObjectName) >= 0) { ObjectSetString(0, textObjectName, OBJPROP_TEXT, "Mitigated " + blockDescription); } Print("Buy trade entered upon mitigation of bearish OB: ", currentOrderBlockName); }
我们首先使用SymbolInfoDouble函数获取当前市场价格,并通过_Digits将“currentAskPrice”和“currentBidPrice”标准化为适当的小数位数。这一步骤确保交易下单时的价格精度。接下来,我们检查“enableTrading”是否处于激活状态,并判断订单块的失效条件是否已经满足。当价格突破订单块边界(即价格向上突破订单块顶部或向下突破订单块底部)时,表明其支撑/阻力结构失效,此时判定订单块已失效。
对于多头订单块,我们需验证上一根K线的收盘价(通过“close”函数获取)是否已跌破订单块底部价格“orderBlockLow”,并确保该订单块尚未失效(即“orderBlockMitigatedStatus[j] = false”)。如果上述条件均满足,则通过“obj_Trade”对象的“Sell”函数执行卖出交易。交易以当前“currentBidPrice”成交,止损价(“stopLossPrice”)设置在入场价上方,距离为“stopLossDistance * _Point”,止盈价(“takeProfitPrice”)设置在入场价下方,距离为“takeProfitDistance * __Point”。
交易执行后,订单块会被标记为已失效:将“orderBlockMitigatedStatus[j]”更新为 true,并通过ObjectSetInteger修改其颜色,以直观显示失效状态。如果该订单块存在文本标签(通过ObjectFind函数检查),则使用ObjectSetString更新标签内容,显示为"Mitigated Bullish Order Block"。最后,通过Print语句记录交易执行信息,便于后续跟踪与调试。
对于空头订单块,处理逻辑类似:我们检查当前K线的“收盘价”是否已上破订单块顶部价格“orderBlockHigh”,这表明空头订单块失效。如果条件满足,则通过“Buy”函数执行买入交易,以当前“currentAskPrice”作为入场价。止损价(“stopLossPrice”)设置在入场价下方,止盈价(“takeProfitPrice”)设置在入场价上方,确保风险控制合理。买入交易执行后,我们更新“orderBlockMitigatedStatus[j]”为 true,使用ObjectSetInteger修改订单块颜色以标识其已失效状态,如果存在文本标签,则通过ObjectSetString将标签内容更新为 "Mitigated Bearish Order Block"。最后,通过“Print”语句记录买入交易执行信息,便于监控。实现效果如下:
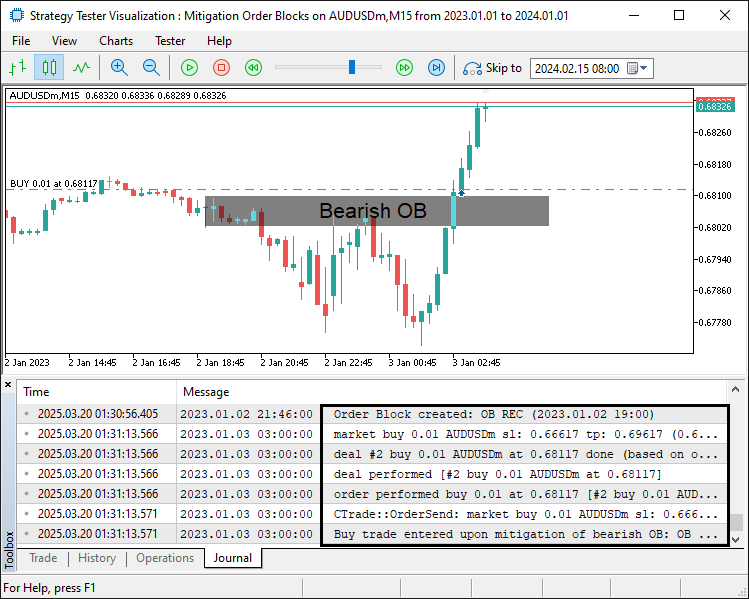
最后,当订单块超出有效范围(或失效)时,我们将其从存储数组中移除。
//--- Remove expired order blocks from arrays if (!doesOrderBlockExist) { bool removedName = ArrayRemove(orderBlockNames, j, 1); bool removedTime = ArrayRemove(orderBlockEndTimes, j, 1); bool removedStatus = ArrayRemove(orderBlockMitigatedStatus, j, 1); if (removedName && removedTime && removedStatus) { Print("Success removing OB DATA from arrays at index ", j); } }
如果订单块已经不存在,我们使用ArrayRemove函数从对应数组中移除其名称、结束时间及失效状态。一旦所有移除操作均成功完成,则通过Print 语句记录清理动作,确认数据已清理完成。以下是清理确认示例:
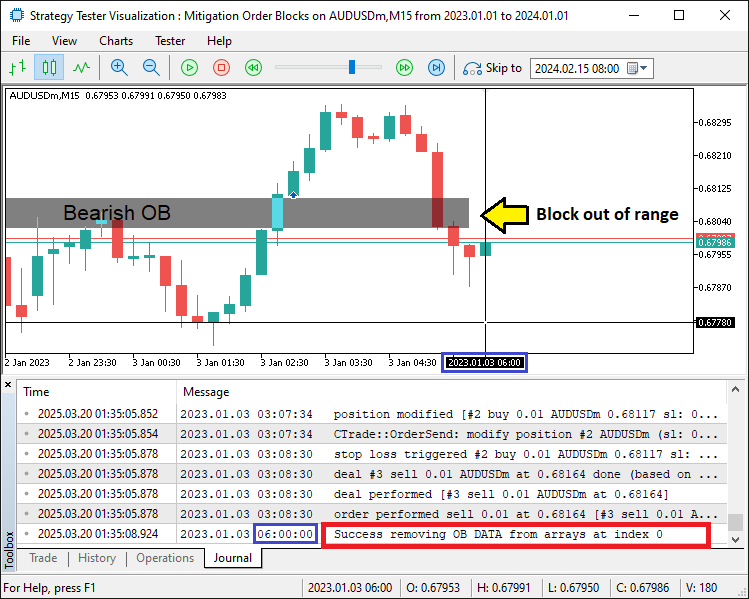
由图可见,我们已经成功地完成了订单块的清理工作。接下来,我们只需添加追踪止损逻辑,为此将通过一个函数封装相关功能。
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+ //| Trailing stop function | //+------------------------------------------------------------------+ void applyTrailingStop(double trailingPoints, CTrade &trade_object, int magicNo = 0) { //--- Calculate trailing stop levels based on current market prices double buyStopLoss = NormalizeDouble(SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_BID) - trailingPoints * _Point, _Digits); double sellStopLoss = NormalizeDouble(SymbolInfoDouble(_Symbol, SYMBOL_ASK) + trailingPoints * _Point, _Digits); //--- Loop through all open positions for (int i = PositionsTotal() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { ulong ticket = PositionGetTicket(i); if (ticket > 0) { if (PositionGetString(POSITION_SYMBOL) == _Symbol && (magicNo == 0 || PositionGetInteger(POSITION_MAGIC) == magicNo)) { //--- Adjust stop loss for buy positions if (PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE) == POSITION_TYPE_BUY && buyStopLoss > PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PRICE_OPEN) && (buyStopLoss > PositionGetDouble(POSITION_SL) || PositionGetDouble(POSITION_SL) == 0)) { trade_object.PositionModify(ticket, buyStopLoss, PositionGetDouble(POSITION_TP)); } //--- Adjust stop loss for sell positions else if (PositionGetInteger(POSITION_TYPE) == POSITION_TYPE_SELL && sellStopLoss < PositionGetDouble(POSITION_PRICE_OPEN) && (sellStopLoss < PositionGetDouble(POSITION_SL) || PositionGetDouble(POSITION_SL) == 0)) { trade_object.PositionModify(ticket, sellStopLoss, PositionGetDouble(POSITION_TP)); } } } } }
在此,我们定义了"applyTrailingStop"函数,用于动态调整持仓的止损价位。首先,根据当前买入价/卖出价以及预设的“追踪点数(trailingPoints)”,分别计算买入止损("buyStopLoss")和卖出止损("sellStopLoss")。接下来,遍历所有未平仓头寸,按交易品种和magic数字(如已指定)进行筛选。对于买入头寸,如果新的有效止损价高于入场价,并且超过当前止损价或者未设置止损,则更新止损。相类似地,对于卖出头寸,需确保新止损价低于入场价后再进行修改。
随后,我们在 OnTick事件处理器中调用该函数,使其在每个价格变动tick而非每根K线上运行,从而实现实时价格检验,具体如下:
//--- Apply trailing stop to open positions if enabled if (enableTrailingStop) { applyTrailingStop(trailingStopPoints, obj_Trade, uniqueMagicNumber); }
程序编译并运行后,我们得到以下结果:
由可视化结果可见,该程序能够识别并验证所有入场条件,如果条件成立,则会按照预设参数开立相应的头寸,从而实现我们的目标。接下来需完成的工作是程序回测,相关内容将在下一章节详细阐述。
回测
经过全面回测后,我们得到以下结果:
回测图:
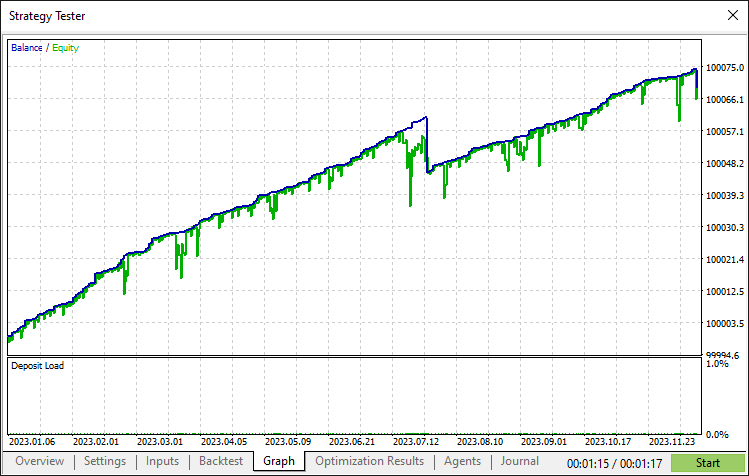
回测报告:
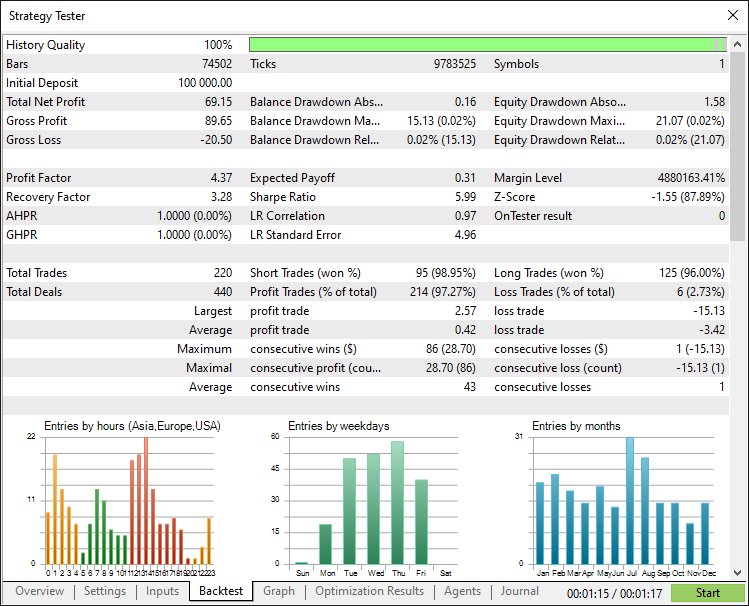
结论
综上所述,我们已在MQL5中成功实现缓解型订单块策略 (MOB),该策略基于主力资金行为逻辑,实现了订单块的精准识别、可视化呈现及自动化交易。通过整合突破验证、趋势脉冲识别与化解逻辑的交易执行模块,系统可高效捕捉并处理订单块,同时动态适应市场变化。另外,我们引入追踪止损与风险管理机制,进一步优化交易表现并提升策略稳健性。
免责声明:本文仅用于教学目的。交易涉及重大财务风险,且市场行情具有不可预测性。在实盘操作前,必须进行充分的回测与风险管理。
通过运用这些技术,您可以优化算法交易策略,并提升基于订单块的交易效率。持续测试、优化并且灵活调整策略,方能实现长期稳健收益。祝您好运!