Spring Boot集成Spring Batch快速入门Demo
1.什么是Spring Batch?
Spring Batch 是一个轻量级的开源框架,它提供了一种简单的方式来处理大量的数据。它基于Spring框架,提供了一套批处理框架,可以处理各种类型的批处理任务,如ETL、数据导入/导出、报表生成等。Spring Batch提供了一些重要的概念,如Job、Step、ItemReader、ItemProcessor、ItemWriter等,这些概念可以帮助我们构建可重用的批处理应用程序。通过Spring Batch,我们可以轻松地实现批处理的并发、容错、重试等功能,同时也可以方便地与其他Spring组件集成,如Spring Boot、Spring Data等。总之,Spring Batch是一个非常强大、灵活、易于使用的批处理框架,可以帮助我们快速构建高效、可靠的批处理应用程序。
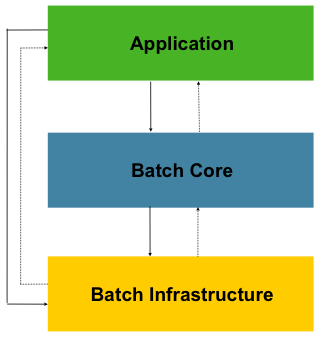
可以看到它分为三层,分别是:
Application应用层:包含了所有任务batch jobs和开发人员自定义的代码,主要是根据项目需要开发的业务流程等。Batch Core核心层:包含启动和管理任务的运行环境类,如JobLauncher等。Batch Infrastructure基础层:上面两层是建立在基础层之上的,包含基础的读入reader和写出writer、重试框架等。
主要概念
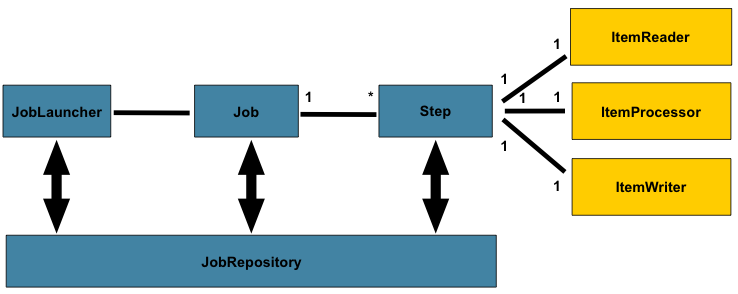
2.2.1 JobRepository
专门负责与数据库打交道,对整个批处理的新增、更新、执行进行记录。所以Spring Batch是需要依赖数据库来管理的。 2.2.2 任务启动器JobLauncher
负责启动任务Job。 2.2.3 任务Job
Job是封装整个批处理过程的单位,跑一个批处理任务,就是跑一个Job所定义的内容。 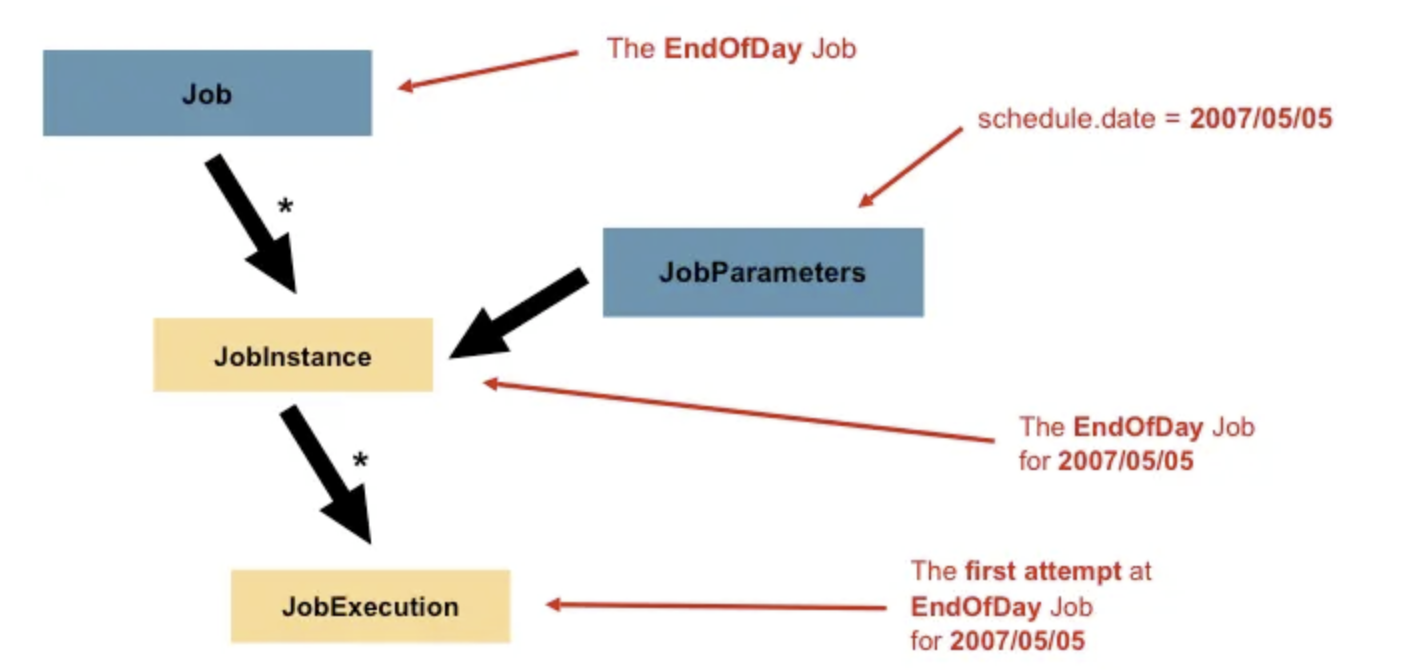 上图介绍了
上图介绍了Job的一些相关概念: Job:封装处理实体,定义过程逻辑。JobInstance:Job的运行实例,不同的实例,参数不同,所以定义好一个Job后可以通过不同参数运行多次。JobParameters:与JobInstance相关联的参数。JobExecution:代表Job的一次实际执行,可能成功、可能失败。
Job。 2.2.4 步骤Step
Step是对Job某个过程的封装,一个Job可以包含一个或多个Step,一步步的Step按特定逻辑执行,才代表Job执行完成。 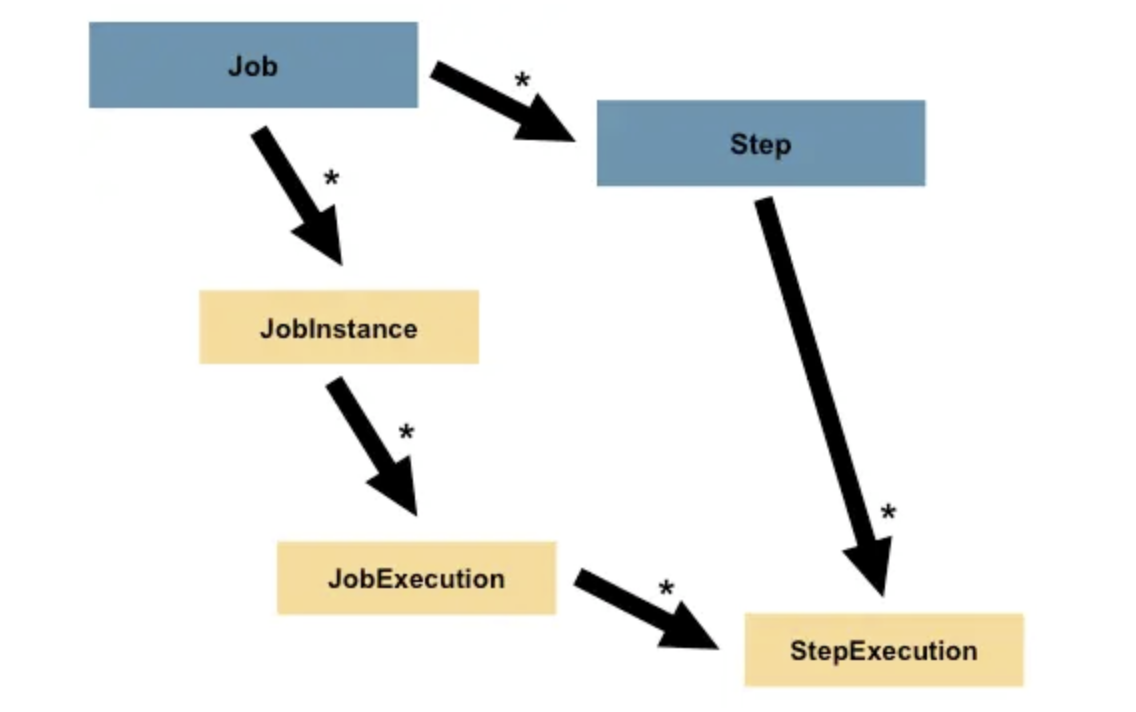 通过定义
通过定义Step来组装Job可以更灵活地实现复杂的业务逻辑。 2.2.5 输入——处理——输出
所以,定义一个Job关键是定义好一个或多个Step,然后把它们组装好即可。而定义Step有多种方法,但有一种常用的模型就是输入——处理——输出,即Item Reader、Item Processor和Item Writer。比如通过Item Reader从文件输入数据,然后通过Item Processor进行业务处理和数据转换,最后通过Item Writer写到数据库中去。 Spring Batch为我们提供了许多开箱即用的Reader和Writer,非常方便。 2.环境搭建
参照代码仓库mysql模块里面docker目录搭建3.代码工程
实验目标
如何使用 Spring Boot 创建各种不同类型 Spring Batch Jobpom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <parent> <artifactId>springboot-demo</artifactId> <groupId>com.et</groupId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> </parent> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <artifactId>SpringBatch</artifactId> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-batch</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>job
第一个简单的任务package com.et.batch.job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Step; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.repeat.RepeatStatus; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class FirstJobDemo { @Autowired private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory; @Autowired private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory; @Bean public Job firstJob() { return jobBuilderFactory.get("firstJob") .start(step()) .build(); } private Step step() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step") .tasklet((contribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step...."); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } }package com.et.batch.job; import org.springframework.batch.core.ExitStatus; import org.springframework.batch.core.Job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Step; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.repeat.RepeatStatus; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class MultiStepJobDemo { @Autowired private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory; @Autowired private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory; @Bean public Job multiStepJob() { /*return jobBuilderFactory.get("multiStepJob") .start(step1()) .next(step2()) .next(step3()) .build();*/ // control the next step by last Status return jobBuilderFactory.get("multiStepJob2") .start(step1()) .on(ExitStatus.COMPLETED.getExitCode()).to(step2()) .from(step2()) .on(ExitStatus.COMPLETED.getExitCode()).to(step3()) .from(step3()).end() .build(); } private Step step1() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step1。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Step step2() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step2") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step2。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Step step3() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step3") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step3。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } }package com.et.batch.job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Step; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.job.builder.FlowBuilder; import org.springframework.batch.core.job.flow.Flow; import org.springframework.batch.repeat.RepeatStatus; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class FlowJobDemo { @Autowired private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory; @Autowired private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory; @Bean public Job flowJob() { return jobBuilderFactory.get("flowJob") .start(flow()) .next(step3()) .end() .build(); } private Step step1() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step1。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Step step2() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step2") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step2。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Step step3() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step3") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step3。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Flow flow() { return new FlowBuilder<Flow>("flow") .start(step1()) .next(step2()) .build(); } }package com.et.batch.job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Step; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.job.builder.FlowBuilder; import org.springframework.batch.core.job.flow.Flow; import org.springframework.batch.repeat.RepeatStatus; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.core.task.SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class SplitJobDemo { @Autowired private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory; @Autowired private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory; @Bean public Job splitJob() { return jobBuilderFactory.get("splitJob") .start(flow1()) .split(new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor()).add(flow2()) .end() .build(); } private Step step1() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step1。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Step step2() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step2") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step2。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Step step3() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step3") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step3。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Flow flow1() { return new FlowBuilder<Flow>("flow1") .start(step1()) .next(step2()) .build(); } private Flow flow2() { return new FlowBuilder<Flow>("flow2") .start(step3()) .build(); } }package com.et.batch.job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Step; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.repeat.RepeatStatus; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class DeciderJobDemo { @Autowired private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory; @Autowired private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory; @Autowired private MyDecider myDecider; @Bean public Job deciderJob() { return jobBuilderFactory.get("deciderJob") .start(step1()) .next(myDecider) .from(myDecider).on("weekend").to(step2()) .from(myDecider).on("workingDay").to(step3()) .from(step3()).on("*").to(step4()) .end() .build(); } private Step step1() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step1") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step1。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Step step2() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step2") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step2。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Step step3() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step3") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step3。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } private Step step4() { return stepBuilderFactory.get("step4") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("execute step4。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build(); } }package com.et.batch.job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Job; import org.springframework.batch.core.Step; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.JobBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.configuration.annotation.StepBuilderFactory; import org.springframework.batch.core.launch.JobLauncher; import org.springframework.batch.core.repository.JobRepository; import org.springframework.batch.core.step.builder.JobStepBuilder; import org.springframework.batch.core.step.builder.StepBuilder; import org.springframework.batch.repeat.RepeatStatus; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager; @Component public class NestedJobDemo { @Autowired private JobBuilderFactory jobBuilderFactory; @Autowired private StepBuilderFactory stepBuilderFactory; @Autowired private JobLauncher jobLauncher; @Autowired private JobRepository jobRepository; @Autowired private PlatformTransactionManager platformTransactionManager; @Bean public Job parentJob() { return jobBuilderFactory.get("parentJob") .start(childJobOneStep()) .next(childJobTwoStep()) .build(); } private Step childJobOneStep() { return new JobStepBuilder(new StepBuilder("childJobOneStep")) .job(childJobOne()) .launcher(jobLauncher) .repository(jobRepository) .transactionManager(platformTransactionManager) .build(); } private Step childJobTwoStep() { return new JobStepBuilder(new StepBuilder("childJobTwoStep")) .job(childJobTwo()) .launcher(jobLauncher) .repository(jobRepository) .transactionManager(platformTransactionManager) .build(); } private Job childJobOne() { return jobBuilderFactory.get("childJobOne") .start( stepBuilderFactory.get("childJobOneStep") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("subtask1。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build() ).build(); } private Job childJobTwo() { return jobBuilderFactory.get("childJobTwo") .start( stepBuilderFactory.get("childJobTwoStep") .tasklet((stepContribution, chunkContext) -> { System.out.println("subtask2。。。"); return RepeatStatus.FINISHED; }).build() ).build(); } }application.yaml
自动会初始化脚本,只需要建立以恶搞空库就行spring: datasource: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springbatch username: root password: 123456 batch: jdbc: schema: classpath:org/springframework/batch/core/schema-mysql.sql initialize-schema: always #Since Spring Boot 2.5.0 use spring.batch.jdbc.initialize-schema=never job: enabled: true
代码仓库
4.测试
- 启动Spring Boot应用程序,系统会自动运行job,跑过一次,下次启动不会继续执行
- 如果要执行定时任务,可以利用spring提供的scheduledTaskRegistrar注册一个定时任务,扫描最新的定时任务,将这些定时任务注册到scheduleFuture中从而实现动态定时任务。
5.引用
正文到此结束
- 本文标签: Spring Boot Spring Batch
- 版权声明: 本文由HARRIES原创发布,转载请遵循《署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)》许可协议授权
- 本文海报: 生成海报一 生成海报二
热门推荐
相关文章
Loading...











![[HBLOG]公众号](https://www.liuhaihua.cn/img/qrcode_gzh.jpg)

