📘 Premium Read: Access my best content on Medium member-only articles — deep dives into Java, Spring Boot, Microservices, backend architecture, interview preparation, career advice, and industry-standard best practices.
🎓 Top 15 Udemy Courses (80-90% Discount): My Udemy Courses - Ramesh Fadatare — All my Udemy courses are real-time and project oriented courses.
▶️ Subscribe to My YouTube Channel (176K+ subscribers): Java Guides on YouTube
▶️ For AI, ChatGPT, Web, Tech, and Generative AI, subscribe to another channel: Ramesh Fadatare on YouTube
In a previous couple of tutorials, we created a Spring boot project, built CRUD Restful web services with DTO, and used the ModelMapper library to convert the JPA entity into DTO and vice versa.
Refer to previous tutorials:
Spring Boot 3 CRUD RESTful WebServices with MySQL Database
Spring Boot DTO Example Tutorial
Spring Boot ModelMapper Example - Map Entity to DTO
In this tutorial, we will learn how to use the MapStruct library to map the JPA entity into DTO and vice versa in the Spring boot application.
MapStruct Library Overview
The MapStruct is an annotation-based code generator/mapper which greatly simplifies the mapping implementations of Java Beans. It follows convention over configuration and uses plain method invocations. MapStruct operations are very fast, type-safe, and easy to understand.
MapStruct automates the process of creating a mapper to map data objects with model objects using annotations. It creates a mapper implementation at compile time which helps the developer to figure out errors during development and makes it easy to understand.
Check the official doc to read more about MapStruct at https://mapstruct.org/
Prerequisites
This tutorial is a continuation of below three tutorials so first, create CRUD REST APIs using below tutorials:
Spring Boot 3 CRUD RESTful WebServices with MySQL Database
Spring Boot DTO Example Tutorial
Spring Boot ModelMapper Example - Map Entity to DTO
The complete source code of this tutorial is available on my GitHub repository at Spring Boot CRUD RESTful WebServices
Development Steps
If you want to use the MapStruct library in your existing Spring boot project then follow these simple steps:
1. Add Maven Dependencies
2. User and UserDto Classes
3. Create UserMapper
4. Use UserMapper in Service Class to map the JPA entity into DTO and vice versa.
5. Test CRUD REST APIs using the Postman client
1. Add Maven Dependencies
Open the pom.xml file and add below Maven dependency and plugin.
MapStruct maven dependency:
<dependency> <groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId> <artifactId>mapstruct</artifactId> <version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version> </dependency>
Let’s also add the annotationProcessorPaths section to the configuration part of the maven-compiler-plugin plugin.
The mapstruct-processor is used to generate the mapper implementation during the build:
<plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <configuration> <source>17</source> <target>17</target> <annotationProcessorPaths> <path> <groupId>org.mapstruct</groupId> <artifactId>mapstruct-processor</artifactId> <version>${org.mapstruct.version}</version> </path> <path> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>${org.projectlombok.version}</version> </path> <path> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok-mapstruct-binding</artifactId> <version>${lombok-mapstruct-binding.version}</version> </path> </annotationProcessorPaths> </configuration> </plugin>
Note that we have added below annotation processor path to the above plugin to support MapStruct annotations with Lombok annotations:
<path> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>${org.projectlombok.version}</version> </path> <path> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok-mapstruct-binding</artifactId> <version>${lombok-mapstruct-binding.version}</version> </path>
Next, add the version properties to the properties section:
<properties> <java.version>17</java.version> <org.mapstruct.version>1.5.3.Final</org.mapstruct.version> <org.projectlombok.version>1.18.20</org.projectlombok.version> <lombok-mapstruct-binding.version>0.2.0</lombok-mapstruct-binding.version> </properties>
2. User JPA Entity and UserDto
Here is our User JPA entity:
package net.javaguides.springboot.entity; import jakarta.persistence.*; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import lombok.Setter; @Getter @Setter @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Entity @Table(name = "users") public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; @Column(nullable = false) private String firstName; @Column(nullable = false) private String lastName; @Column(nullable = false, unique = true) private String email; }
Here is our UserDto class:
package net.javaguides.springboot.dto; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import lombok.Setter; @Setter @Getter @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class UserDto { private Long id; private String firstName; private String lastName; private String email; }
3. Create UserMapper
Next, let's create a Mapper using MapStruct. Let's create an AutoUserMapper interface and define the mapping methods to map Entity to DTO and vice versa.
package net.javaguides.springboot.mapper; import net.javaguides.springboot.dto.UserDto; import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.User; import org.mapstruct.Mapper; import org.mapstruct.factory.Mappers; @Mapper public interface AutoUserMapper { AutoUserMapper MAPPER = Mappers.getMapper(AutoUserMapper.class); UserDto mapToUserDto(User user); User mapToUser(UserDto userDto); }
Notice we did not create an implementation class for our AutoUserMapper interface because MapStruct creates it for us during compilation time.
The @Mapper annotation marks the interface as a mapping interface and lets the MapStruct processor kick in during compilation.
We defined two mapping methods to convert JPA entity into DTO and vice versa:
UserDto mapToUserDto(User user); User mapToUser(UserDto userDto);
An instance of the interface implementation can be retrieved from the Mappers class:
AutoUserMapper MAPPER = Mappers.getMapper(AutoUserMapper.class);
Mapping Fields With Different Field Names
From our previous example, MapStruct was able to map our beans automatically because they have the same field names. So, what if a bean we are about to map has a different field name?.
Consider email field name is different in both User and UserDto. For example:
@Getter @Setter @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor @Entity @Table(name = "users") public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; @Column(nullable = false) private String firstName; @Column(nullable = false) private String lastName; @Column(nullable = false, unique = true) private String email; }
The email field name in UserDto is emailAddress:
@Setter @Getter @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class UserDto { private Long id; private String firstName; private String lastName; private String emailAddress; }
When mapping different field names, we will need to configure its source field to its target field, and to do that, we will need to add @Mapping annotation for each field.
For example:
@Mapper public interface AutoUserMapper { AutoUserMapper MAPPER = Mappers.getMapper(AutoUserMapper.class); @Mapping(source = "email", target = "emailAddress") UserDto mapToUserDto(User user); @Mapping(source = "emailAddress", target = "email") User mapToUser(UserDto userDto); }
3. Use UserMapper in Service Class to map the JPA entity into DTO and vice versa
package net.javaguides.springboot.service.impl; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import net.javaguides.springboot.dto.UserDto; import net.javaguides.springboot.entity.User; import net.javaguides.springboot.mapper.AutoUserMapper; import net.javaguides.springboot.mapper.UserMapper; import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.UserRepository; import net.javaguides.springboot.service.UserService; import org.apache.logging.log4j.util.Strings; import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.util.List; import java.util.Objects; import java.util.Optional; import java.util.stream.Collectors; @Service @AllArgsConstructor public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private UserRepository userRepository; private ModelMapper modelMapper; @Override public UserDto createUser(UserDto userDto) { // Convert UserDto into User JPA Entity // User user = UserMapper.mapToUser(userDto); //User user = modelMapper.map(userDto, User.class); User user = AutoUserMapper.MAPPER.mapToUser(userDto); User savedUser = userRepository.save(user); // Convert User JPA entity to UserDto //UserDto savedUserDto = UserMapper.mapToUserDto(savedUser); //UserDto savedUserDto = modelMapper.map(savedUser, UserDto.class); UserDto savedUserDto = AutoUserMapper.MAPPER.mapToUserDto(savedUser); return savedUserDto; } @Override public UserDto getUserById(Long userId) { User user = userRepository.findById(userId).get(); //return UserMapper.mapToUserDto(user); //return modelMapper.map(user, UserDto.class); return AutoUserMapper.MAPPER.mapToUserDto(user); } @Override public List<UserDto> getAllUsers() { List<User> users = userRepository.findAll(); // return users.stream().map(UserMapper::mapToUserDto) // .collect(Collectors.toList()); // return users.stream().map((user) -> modelMapper.map(user, UserDto.class)) // .collect(Collectors.toList()); return users.stream().map((user) -> AutoUserMapper.MAPPER.mapToUserDto(user)) .collect(Collectors.toList()); } @Override public UserDto updateUser(UserDto user) { User existingUser = userRepository.findById(user.getId()).get() existingUser.setFirstName(user.getFirstName()); existingUser.setLastName(user.getLastName()); existingUser.setEmail(user.getEmail()); User updatedUser = userRepository.save(existingUser); //return UserMapper.mapToUserDto(updatedUser); //return modelMapper.map(updatedUser, UserDto.class); return AutoUserMapper.MAPPER.mapToUserDto(updatedUser); } @Override public void deleteUser(Long userId) { userRepository.deleteById(userId); } }
4. Test CRUD REST APIs using the Postman Client
Create User REST API:
HTTP Method: POST
Request Body:
{ "firstName": "ramesh", "lastName":"fadatare", "email": "ramesh@gmail.com" }
Refer to this screenshot to test Create User REST API:Get User REST API:
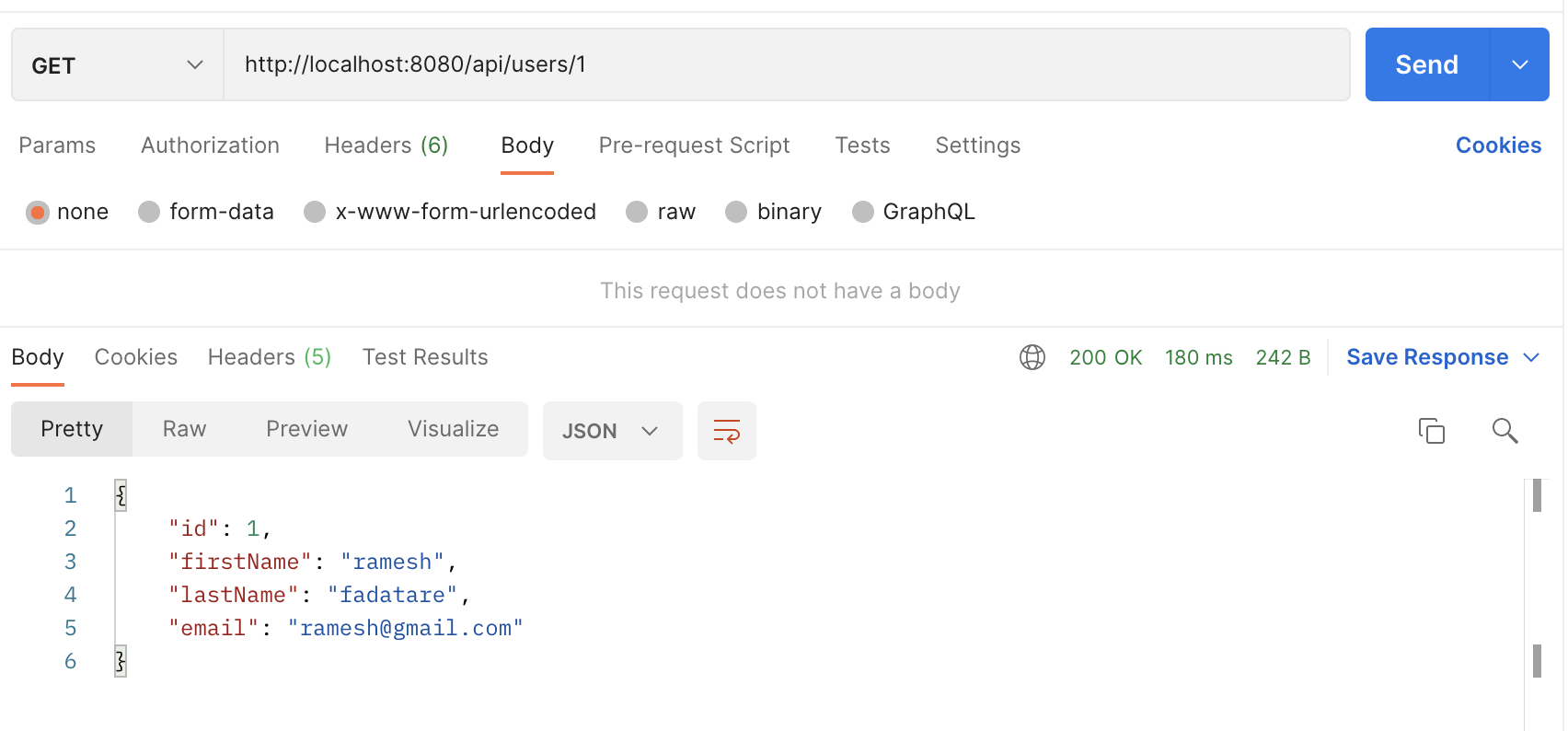
HTTP Method: GET
Refer to this screenshot to test GET User REST API: Update User REST API:
HTTP Method: PUT
Request Body:
{ "firstName": "ram", "lastName":"fadatare", "email": "ram@gmail.com" }
Refer to this screenshot to test the Update User REST API:Get All Users REST API:
HTTP Method: GET
Refer to this screenshot to test GET All User REST API:
DELETE User REST API:
HTTP Method: DELETE
Refer to this screenshot to test Delete User REST API:
Source Code on GitHub
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have seen how to use the MapStruct library to map the JPA entity into DTO and vice versa in the Spring boot application.
Related Spring Boot and Microservices Tutorials/Guides:
The Hidden Magic of Spring Boot: Secrets Every Developer Should Know What Happens When You Hit a Spring Boot REST API Endpoint (Behind the Scenes) Spring Boot Exception Handling Build CRUD REST API with Spring Boot, Spring Data JPA, Hibernate, and MySQL Spring Boot DELETE REST API: @DeleteMapping Annotation Spring Boot PUT REST API — @PutMapping Annotation Spring Boot POST REST API Spring Boot GET REST API — @GetMapping Annotation Spring Boot REST API with Request Param | Spring Boot Course Spring Boot REST API with Path Variable — @PathVariable Chapter 13: Understanding @SpringBootApplication Annotation | Spring Boot Course Chapter 5: Create Spring Boot Project and Build Hello World REST API | Spring Boot Course 10 Real-World Spring Boot Architecture Tips Every Developer Should Follow Top 10 Spring Boot Tricks Every Java Developer Should Know Debugging Spring Dependency Injection Issues - Very Important Common Code Smells in Spring Applications — How to Fix Them Spring Boot + OpenAI ChatGPT API Integration Tutorial Spring Boot Course -> New Series on Medium ❤️ Spring Boot Microservices with RabbitMQ Example React JS + Spring Boot Microservices Dockerizing a Spring Boot Application How to Change the Default Port in Spring Boot How to Change Context Path in Spring Boot Top 10 Spring Boot REST API Mistakes and How to Avoid Them (2025 Update) Spring Boot REST API Best Practices Spring Boot Security Database Authentication Example Tutorial Spring Boot Security Form-Based Authentication Spring Boot Security In-Memory Authentication What is Spring Boot Really All About? Why Spring Boot over Spring? Top 10 Spring Boot Key Features That You Should Know Spring vs Spring Boot Setting Up the Development Environment for Spring Boot Spring Boot Auto-Configuration: A Quick Guide Spring Boot Starters Quick Guide to Spring Boot Parent Starter Spring Boot Embedded Servers Spring Boot Thymeleaf Hello World Example Chapter 10: Spring Boot DevTools | Spring Boot Course Chapter 13: Spring Boot REST API That Returns JSON | Spring Boot Course Spring Boot REST API That Returns List of Java Objects in JSON Format Top 10 Spring Boot Mistakes and How to Avoid Them Advanced Spring Boot Concepts that Every Java Developer Should Know What Are Microservices in Spring Boot? Integrating React Frontend with Spring Boot ChatGPT API (Step-by-Step Guide) Build a Chatbot Using Spring Boot, React JS, and ChatGPT API Top 10 Mistakes in Spring Boot Microservices and How to Avoid Them (With Examples) Spring Boot Security Best Practices: Protecting Your Application from Attacks 🔄 Dependency Injection in Spring (Explained with Coding Examples) ⚙️ How Spring Container Works Behind the Scenes How Spring Container Works Behind the Scenes (Spring Container Secrets Revealed!) Spring @Component vs @Bean vs @Service vs @Repository Explained How Component Scanning Works Behind the Scenes in Spring How Spring Autowiring Works Internally Top 20 Spring Boot Best Practices for Java Developers Build Spring Boot React Full Stack Project — Todo App [2025 Update] Spring vs Spring MVC vs Spring Boot Spring Boot Best Practices: Use DTOs Instead of Entities in API Responses Spring Boot DTO Tutorial (Using Java record) – Complete CRUD REST API Implementation Spring Boot Architecture: Controller, Service, Repository, Database and Architecture Flow Java Stream filter() Method with Real-World Examples Spring Boot Auto Configuration Explained | How It Works Spring Boot Profiles: How to Manage Environment-Based Configurations Create a Custom Spring Boot Starter | Step-by-Step Guide Spring Boot Starter Modules Explained | Auto-Configuration Guide Deploy Spring Boot Applications with Profile-Based Settings | Step-by-Step Guide Spring Boot Performance Tuning: 10 Best Practices for High Performance Spring Boot @ComponentScan Annotation | Customizing Component Scanning Difference Between @RestController and @RequestMapping in Spring Boot Spring Boot @Cacheable Annotation – Improve Performance with Caching Spring Boot Redis Cache — @Cacheable Complete Guide When to Use @Service, @Repository, @Controller, and @Component Annotations in Spring Boot Why, When, and How to Use @Bean Annotation in Spring Boot App Java Spring Boot vs. Go (Golang) for Backend Development in 2025 Is Autowired Annotation Deprecated in Spring Boot? Everything You Need to Know 🚫 Stop Making These Common Mistakes in Spring Boot Projects Top 10 Mind-Blowing Spring Boot Tricks for Beginners Why Choose Spring Boot Over Spring Framework? | Key Differences and Benefits How to Run a Spring Boot Application | 5 Easy Ways for Developers What is AutoConfiguration in Spring Boot? | Explained with Example Customize Default Configuration in Spring Boot | 5 Proven Ways Chapter 12: Understanding SpringApplication.run() Method Internals | Spring Boot Course What is CommandLineRunner in Spring Boot? How to Create Custom Bean Validation in Spring Boot Can You Build a Non-Web Application with Spring Boot? How to Disable Auto-Configuration in Spring Boot (Step-by-Step Guide) Top 25 Spring Boot Interview Questions and Answers for Beginners How to Use Java Records with Spring Boot Spring Boot Constructor Injection Explained with Step-by-Step Example 🚫 Stop Using @Transactional Everywhere: Understand When You Actually Need It 🚫 Stop Writing Fat Controllers: Follow the Controller-Service-Repository Pattern 🚫 Stop Using Field Injection in Spring Boot: Use Constructor Injection 🚫 Stop Sharing Databases Between Microservices: Use Database Per Service Pattern 10 Java Microservices Best Practices Every Developer Should Follow How to Choose the Right Java Microservices Communication Style (Sync vs Async) How to Implement Event-Driven Communication in Java Microservices (Step-by-Step Guide with Kafka) Stop Building Tight-Coupled Microservices: Aim for Loose Coupling Spring Boot Microservices E-Commerce Project: Step-by-Step Guide Spring Boot Microservices with RabbitMQ Example React JS + Spring Boot Microservices The Ultimate Microservices Roadmap for Beginners: Building Modern Scalable Systems What Are Microservices in Spring Boot? Top 5 Message Brokers Every Developer Should Know Top 10 Spring Cloud Microservices Best Practices [Removed Deprecated Features] Best Tools for Microservices Development in 2025 How to Break a Monolithic Application into Microservices (E-Commerce Use Case) Monoliths Aren’t Dead — Microservices Are Just Overused When to Break a Monolith: A Developer’s Checklist 👑 Java Is Still the King of Microservices — And Here’s the Proof 5 Microservices Design Patterns You Must Know in 2025 Bulkhead Pattern in Microservices — Improve Resilience and Fault Isolation Strangler Fig Pattern in Microservices — Migrate Monolith to Microservices Event Sourcing Pattern in Microservices (With Real-World Example) Circuit Breaker Pattern in Microservices using Spring Boot 3, WebClient and Resilience4j CQRS Pattern in Microservices Aggregator Design Pattern in Microservices — A Complete Guide Database Per Service Pattern in Microservices API Gateway Pattern in Microservices — A Complete Guide Saga Pattern in Microservices: A Step-by-Step Guide Microservices Are a Mess Without These Java Design Patterns️ Java Microservices Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers Top Microservices Interview Questions and Answers for Experienced Professionals Top 10 Microservices Design Pattern Interview Questions and Answers Top Microservices Tricky Interview Questions You Should Know (With Answers) Microservices Best Practices: Building Scalable and Resilient Systems Why Microservices Are the Future of Software Architecture Microservices with Spring Cloud: Simplify Your Architecture Spring Boot and Microservices Roadmap for Beginners [2025 Update] Best Programming Language for Microservices Project Development in 2025 My 50+ Must-Read Microservices Tutorials, Articles and Guides on the Medium Platform 



![[NEW] Full-Stack Java Development with Spring Boot 3 & React Build 5 Spring Boot Projects with Java: Line-by-Line Coding](https://img-c.udemycdn.com/course/750x422/5338984_4d3a_5.jpg)














Comments
Post a Comment
Leave Comment