
This page walks you through a simple demonstration of how CockroachDB replicates and distributes data. Starting with a 1-node local cluster, you'll write some data, add 2 nodes, and watch how the data is replicated automatically. You'll then update the cluster to replicate 5 ways, add 2 more nodes, and again watch how all existing replicas are re-replicated to the new nodes.
Before you begin
Make sure you have already installed CockroachDB.
Step 1. Start a 1-node cluster
$ cockroach start \ --insecure \ --store=repdemo-node1 \ --listen-addr=localhost:26257 \ --http-addr=localhost:8080 Step 2. Write data
In a new terminal, use cockroach workload command to generate an example intro database:
$ cockroach workload init intro \ 'postgresql://root@localhost:26257?sslmode=disable' In the same terminal, open the built-in SQL shell and verify that the new intro database was added with one table, mytable:
$ cockroach sql --insecure --host=localhost:26257 > SHOW DATABASES; database_name +---------------+ defaultdb intro postgres system (4 rows) > SHOW TABLES FROM intro; table_name +------------+ mytable (1 row) > SELECT * FROM intro.mytable WHERE (l % 2) = 0; l | v +----+------------------------------------------------------+ 0 | !__aaawwmqmqmwwwaas,,_ .__aaawwwmqmqmwwaaa,, 2 | !"VT?!"""^~~^"""??T$Wmqaa,_auqmWBT?!"""^~~^^""??YV^ 4 | ! "?##mW##?"- 6 | ! C O N G R A T S _am#Z??A#ma, Y 8 | ! _ummY" "9#ma, A 10 | ! vm#Z( )Xmms Y 12 | ! .j####mmm#####mm#m##6. 14 | ! W O W ! jmm###mm######m#mmm##6 16 | ! ]#me*Xm#m#mm##m#m##SX##c 18 | ! dm#||+*$##m#mm#m#Svvn##m 20 | ! :mmE=|+||S##m##m#1nvnnX##; A 22 | ! :m#h+|+++=Xmm#m#1nvnnvdmm; M 24 | ! Y $#m>+|+|||##m#1nvnnnnmm# A 26 | ! O ]##z+|+|+|3#mEnnnnvnd##f Z 28 | ! U D 4##c|+|+|]m#kvnvnno##P E 30 | ! I 4#ma+|++]mmhvnnvq##P` ! 32 | ! D I ?$#q%+|dmmmvnnm##! 34 | ! T -4##wu#mm#pw##7' 36 | ! -?$##m####Y' 38 | ! !! "Y##Y"- 40 | ! (21 rows) Exit the SQL shell:
> \q Step 3. Add two nodes
In a new terminal, add node 2:
$ cockroach start \ --insecure \ --store=repdemo-node2 \ --listen-addr=localhost:26258 \ --http-addr=localhost:8081 \ --join=localhost:26257 In a new terminal, add node 3:
$ cockroach start \ --insecure \ --store=repdemo-node3 \ --listen-addr=localhost:26259 \ --http-addr=localhost:8082 \ --join=localhost:26257 Step 4. Watch data replicate to the new nodes
Open the Admin UI at http://localhost:8080 to see that all three nodes are listed. At first, the replica count will be lower for nodes 2 and 3. Very soon, the replica count will be identical across all three nodes, indicating that all data in the cluster has been replicated 3 times; there's a copy of every piece of data on each node.
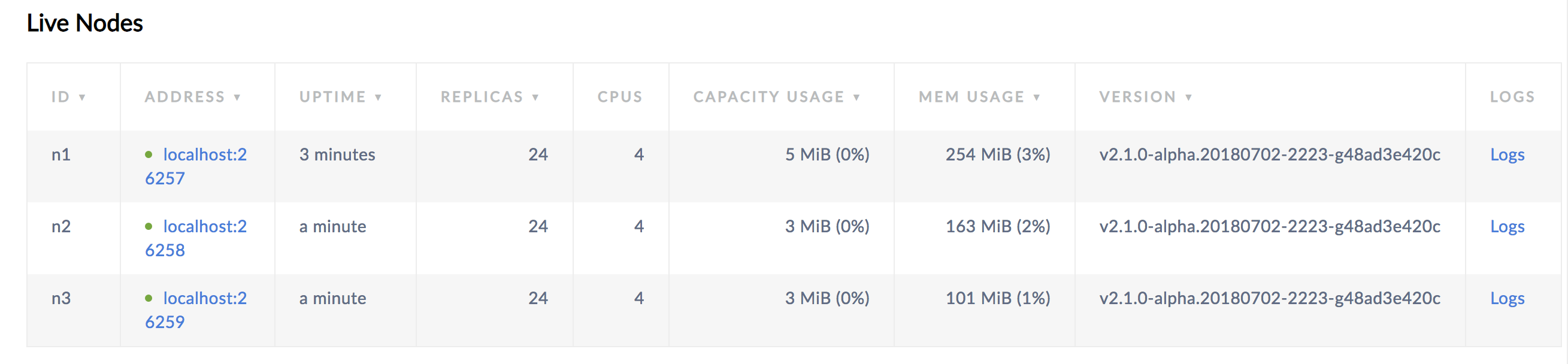
Step 5. Increase the replication factor
As you just saw, CockroachDB replicates data 3 times by default. Now, in the terminal you used for the built-in SQL shell or in a new terminal, use the ALTER RANGE ... CONFIGURE ZONE statement to change the cluster's .default replication factor to 5:
$ cockroach sql --execute="ALTER RANGE default CONFIGURE ZONE USING num_replicas=5;" --insecure --host=localhost:26257 Step 6. Add two more nodes
In a new terminal, add node 4:
$ cockroach start \ --insecure \ --store=repdemo-node4 \ --listen-addr=localhost:26260 \ --http-addr=localhost:8083 \ --join=localhost:26257 In a new terminal, add node 5:
$ cockroach start \ --insecure \ --store=repdemo-node5 \ --listen-addr=localhost:26261 \ --http-addr=localhost:8084 \ --join=localhost:26257 Step 7. Watch data replicate to the new nodes
Back in the Admin UI, you'll see that there are now 5 nodes listed. Again, at first, the replica count will be lower for nodes 4 and 5. But because you changed the default replication factor to 5, very soon, the replica count will be identical across all 5 nodes, indicating that all data in the cluster has been replicated 5 times.
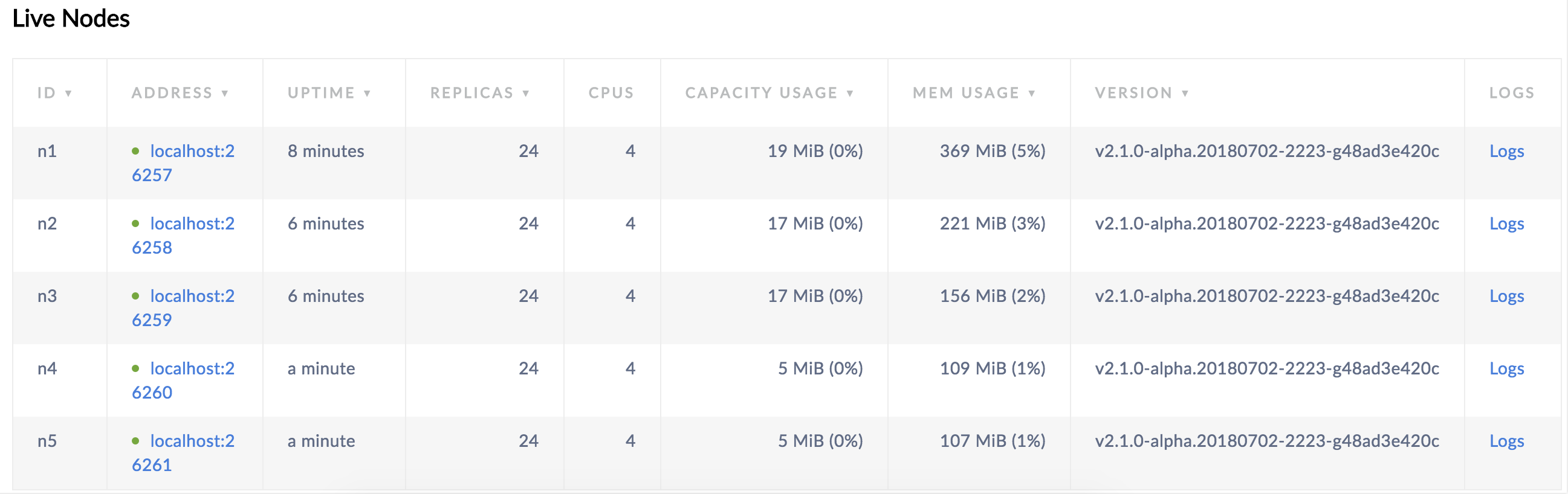
Step 8. Stop the cluster
Once you're done with your test cluster, stop each node by switching to its terminal and pressing CTRL-C.
For the last 2 nodes, the shutdown process will take longer (about a minute) and will eventually force stop the nodes. This is because, with only 2 nodes still online, a majority of replicas are no longer available (3 of 5), and so the cluster is not operational. To speed up the process, press CTRL-C a second time in the nodes' terminals.
If you do not plan to restart the cluster, you may want to remove the nodes' data stores:
$ rm -rf repdemo-node1 repdemo-node2 repdemo-node3 repdemo-node4 repdemo-node5 What's next?
Explore other core CockroachDB benefits and features: