This topic describes the basic syntax and examples of string functions.
Simple Log Service supports the following string functions.
Function name | Syntax | Description | SQL supported | SPL supported |
chr(x) | Converts an ASCII code to a character. | √ | √ | |
codepoint(x) | Converts a character to an ASCII code. | √ | √ | |
concat(x, y...) | Concatenates multiple strings into a single string. | √ | √ | |
from_utf8(x) | Decodes a binary string into the UTF-8 encoding format and replaces invalid UTF-8 characters with the default character U+FFFD. | √ | √ | |
from_utf8(x, replace_string) | Decodes a binary string into the UTF-8 encoding format and replaces invalid UTF-8 characters with a custom string. | √ | √ | |
length(x) | Calculates the length of a string. | √ | √ | |
levenshtein_distance(x, y) | Calculates the minimum edit distance between x and y. | √ | × | |
lower(x) | Converts a string to lowercase. | √ | √ | |
lpad(x, length, lpad_string) | Pads the beginning of a string with a specified character to a specified length and returns the result string. | √ | √ | |
ltrim(x) | Removes the spaces from the beginning of a string. | √ | √ | |
normalize(x) | Formats a string in the NFC format. | √ | × | |
position(sub_string in x) | Returns the position of a substring in a string. | √ | × | |
replace(x, sub_string ) | Deletes the matched characters from a string. | √ | √ | |
replace(x, sub_string, replace_string) | Replaces the matched characters in a string with specified characters. | √ | √ | |
reverse(x) | Returns a string in reverse order. | √ | √ | |
rpad(x, length, rpad_string) | Pads the end of a string with a specified character to a specified length and returns the result string. | √ | √ | |
rtrim(x) | Removes the spaces from the end of a string. | √ | √ | |
split(x, delimeter) | Splits a string using a specified separator and returns a collection of substrings. | √ | √ | |
split(x, delimeter, limit) | Splits a string using a specified separator, limits the number of splits using limit, and then returns a collection of the split substrings. | √ | √ | |
split_part(x, delimeter, part) | Splits a string using a specified separator and returns the content at a specified position. | √ | √ | |
split_to_map(x, delimiter01, delimiter02) | Splits a string using a specified first separator and then splits the string again using a specified second separator. | √ | √ | |
strpos(x, sub_string) | Returns the position of a substring in a string. This function is equivalent to the position(sub_string in x) function. | √ | √ | |
substr(x, start) | Returns a substring from a specified position in a string. | √ | √ | |
substr(x, start, length) | Returns a substring of a specified length from a specified position in a string. | √ | √ | |
to_utf8(x) | Converts a string to the UTF-8 encoding format. | √ | √ | |
trim(x) | Removes the spaces from the beginning and end of a string. | √ | √ | |
upper(x) | Converts a string to uppercase. | √ | √ | |
csv_extract_map(x, delimeter, quote, keys) | Extracts single-line CSV information from a target string. | √ | × | |
ilike(x, pattern) | Checks whether a string matches a specified character pattern. The check is case-insensitive. | √ | √ |
chr function
The chr function converts an ASCII code to a character.
Syntax
chr(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The ASCII code. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
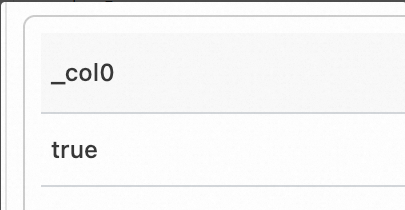
Check whether the value of the region field starts with c. The ASCII code 99 represents the lowercase letter c.
Sample field
region:cn-shanghaiQuery statement (Test)
* | SELECT substr(region, 1, 1) = chr(99)Query and analysis results

codepoint function
The codepoint function converts a character to an ASCII code.
Syntax
codepoint(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
integer.
Examples
Check whether the value of the region field starts with c. The ASCII code 99 represents the lowercase letter c.
Sample field
upstream_status:200Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT codepoint(cast (substr(region, 1, 1) AS char(1))) = 99Query and analysis results
concat function
The concat function concatenates multiple strings into a single string.
Syntax
concat(x, y...)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
y | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
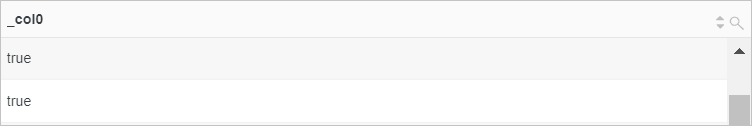
Concatenate the values of the region field and the request_method field.
Sample field
region:cn-shanghai time:14/Jul/2021:02:19:40Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT concat(region, '-', time)Query and analysis results
from_utf8 function
The from_utf8 function decodes a binary string into the UTF-8 encoding format.
Syntax
Replace invalid UTF-8 characters with the default character U+FFFD.
from_utf8(x)Replace invalid UTF-8 characters with a custom character.
from_utf8(x,replace_string)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the binary type. |
replace_string | The string that is used for replacement. The string can be only a single character or a space. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
Decode the binary string 0x80 into the UTF-8 encoding format and replace invalid UTF-8 characters with the default character U+FFFD.
Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT from_utf8(from_base64('0x80'))Query and analysis results

Decode the binary string 0x80 into the UTF-8 encoding format and replace invalid UTF-8 characters with 0.
Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT from_utf8(from_base64('0x80'), '0')Query and analysis results

length function
The length function calculates the length of a string.
Syntax
length(x)Parameters
Parameter | |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
bigint.
Examples
Calculate the length of the value of the http_user_agent field.
Sample field
http_user_agent:Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.2 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/22.0.1216.0 Safari/537.2Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT length(http_user_agent)Query and analysis results

levenshtein_distance function
The levenshtein_distance function calculates the minimum edit distance between two strings.
Syntax
levenshtein_distance(x, y)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
y | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
bigint.
Examples
Calculate the minimum edit distance between the value of the instance_id field and the value of the owner_id field.
Example
instance_id:i-01 owner_id:owner-01Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT levenshtein_distance(owner_id, instance_id)Query and analysis results

lower function
The lower function converts a string to lowercase.
Syntax
lower(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
Convert the value of the request_method field to lowercase.
Sample field
request_method:GETQuery statement (Test)
* | SELECT lower(request_method)Query and analysis results

lpad function
The lpad function pads the beginning of a target string with a specified character to a specified length.
Syntax
lpad(x, length, lpad_string)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
length | An integer that specifies the length of the result string.
|
lpad_string | The new character for padding. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
Pad the beginning of the value of the instance_id field with 0 to a total length of 10 characters.
Sample field
instance_id:i-01Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT lpad(instance_id, 10, '0')Query and analysis results

ltrim function
The ltrim function removes leading spaces from a string.
Syntax
ltrim(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
Remove the leading spaces from the value of the region field.
Sample field
region: cn-shanghaiQuery statement (Test)
* | SELECT ltrim(region)Query and analysis results

normalize function
The normalize function formats a string in the Normalization Form C (NFC) format.
Syntax
normalize(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
Format the string schön in the NFC format.
Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT normalize('schön')Query and analysis results

position function
The position function returns the position of a target substring in a string.
Syntax
position(sub_string in x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
sub_string | The target substring. |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
int. The value is 1-based. If the target substring is not found, the function returns 0.
Examples
Find the position of the substring cn in the value of the region field.
Sample field
region:cn-shanghaiQuery statement (Test)
* | SELECT position('cn' in region)Query and analysis results

replace function
The replace function deletes characters from a string or replaces them with other characters.
Syntax
Deletes all occurrences of a substring.
replace(x, sub_string)Replaces all occurrences of a substring with another string.
replace(x, sub_string, replace_string)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
sub_string | The target substring. |
replace_string | The substring that is used for replacement. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
Example 1: Replace
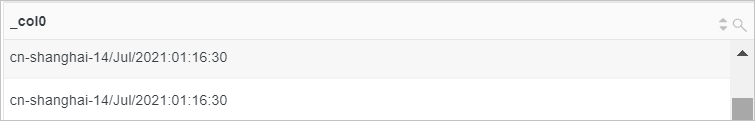
cnin the value of theregionfield withChina.Sample field
region:cn-shanghaiQuery statement (Test)
* | select replace(region, 'cn', 'China')Query and analysis results
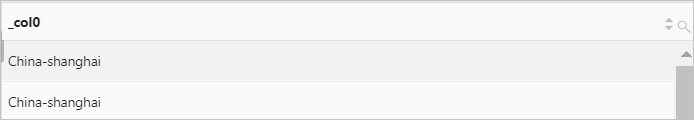
Example 2: Remove
cn-from the value of theregionfield.Sample field
region:cn-shanghaiQuery statement (Test)
* | select replace(region, 'cn-')Query and analysis results

reverse function
The reverse function returns a string in reverse order.
Syntax
reverse(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
Reverse the value of the request_method field.
Sample field
request_method:GETQuery statement (Test)
* | SELECT reverse(request_method)Query and analysis results
rpad function
The rpad function pads the end of a string with a specified character to a specified length.
Syntax
rpad(x, length, rpad_string)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
length | An integer that specifies the length of the result string.
|
rpad_string | The new character for padding. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
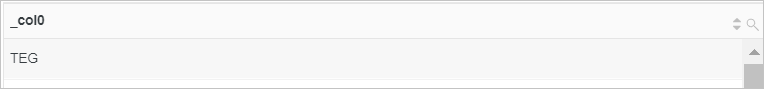
Pad the end of the value of the instance_id field with 0 to a total length of 10 characters.
Sample field
instance_id:i-01Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT rpad(instance_id, 10, '0')Query and analysis results
rtrim function
The rtrim function removes trailing spaces from a string.
Syntax
rtrim(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
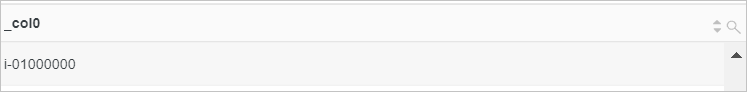
Remove the trailing spaces from the value of the instance_id field.
Sample field
instance_id:i-01Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT rtrim(instance_id)Query and analysis results
split function
The split function splits a string using a specified separator and returns an array of the resulting substrings.
Syntax
Splits a string using a specified separator.
split(x, delimeter)Splits a string using a specified separator into a specified number of substrings.
split(x,delimeter,limit)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
delimeter | The separator. |
limit | The number of splits. The value must be an integer greater than 0. |
Return value type
array.
Examples
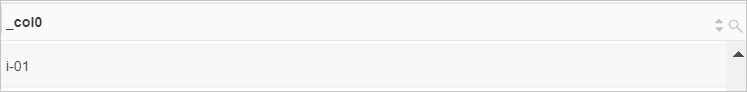
Example 1: Split the value of the
request_urifield using a forward slash (/) as the separator.Sample field
request_uri:/request/path-1/file-9Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT split(request_uri, '/')Query and analysis results

Example 2: Split the value of the
request_urifield using a forward slash (/) as the separator, with a limit of three substrings.Sample field
request_uri:/request/path-1/file-9Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT split(request_uri, '/', 3)Query and analysis results

split_part function
The split_part function splits a string using a specified separator and returns the substring at a specified position.
Syntax
split_part(x, delimeter, part)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
delimeter | The separator. |
part | An integer greater than 0. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
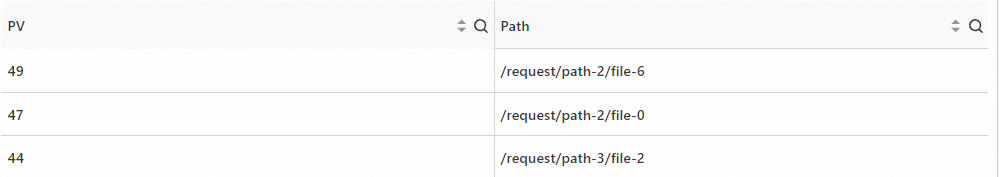
Split the value of the request_uri field using a question mark (?) as the separator and return the first substring, which is the file path. Then, count the number of requests for each path.
Sample field
request_uri: /request/path-2/file-6?name=value&age=18 request_uri: /request/path-2/file-0?name=value&age=18 request_uri: /request/path-3/file-2?name=value&age=18Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT count(*) AS PV, split_part(request_uri, '?', 1) AS Path GROUP BY Path ORDER BY pv DESCQuery and analysis results
split_to_map function
The split_to_map function splits a string into key-value pairs using two specified separators.
Syntax
split_to_map(x, delimiter01, delimiter02)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
delimeter01 | The separator. |
delimeter02 | The separator. |
Return value type
map.
Examples
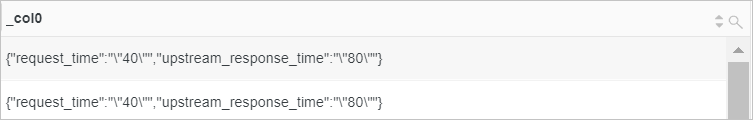
Split the value of the time field using a comma (,) as the pair separator and a colon (:) as the key-value separator. The result is a map.
Sample field
time:upstream_response_time:"80", request_time:"40"Query statement
* | SELECT split_to_map(time, ',', ':')Query and analysis results
strpos function
The strpos function returns the position of a target substring in a string. This function is equivalent to the position function.
Syntax
strpos(x, sub_string)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
sub_string | The target substring. |
Return value type
int. The value is 1-based. If the target substring is not found, the function returns 0.
Examples
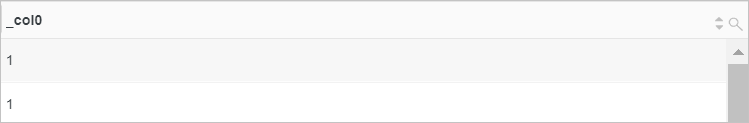
Find the position of the letter H in the value of the server_protocol field.
Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT strpos(server_protocol, 'H')Query and analysis results
substr function
The substr function returns a substring from a specified position in a string.
Syntax
Returns a substring from a specified starting position to the end of the string.
substr(x, start)Returns a substring of a specified length from a specified starting position.
substr(x,start,length)
Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
start | The position from which the substring starts to be extracted. The value starts from 1. |
length | The length of the substring. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
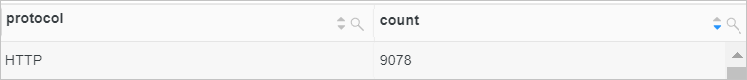
Extract the first four characters (HTTP) from the value of the server_protocol field. Then, count the number of requests that use the HTTP protocol.
Sample field
server_protocol:HTTP/2.0Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT substr(server_protocol, 1, 4) AS protocol, count(*) AS count GROUP BY server_protocolQuery and analysis results
to_utf8 function
The to_utf8 function encodes a string into a UTF-8 binary representation.
Syntax
to_utf8(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
varbinary.
Examples
Encode the string 'log' into the UTF-8 format.
Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT to_utf8('log')Query and analysis results

trim function
The trim function removes leading and trailing spaces from a string.
Syntax
trim(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
Remove the leading and trailing spaces from the value of the instance_id field.
Sample field
instance_id: i-01Query statement (Test)
* | SELECT trim(instance_id)Query and analysis results

upper function
The upper function converts a target string to uppercase.
Syntax
upper(x)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
Return value type
varchar.
Examples
Convert the value of the region field to uppercase.
Sample field
region:cn-shanghaiQuery statement (Test)
* | SELECT upper(region)Query and analysis results

csv_extract_map function
The csv_extract_map function extracts single-line CSV information from a target string.
Syntax
csv_extract_map(x, delimeter, quote, keys)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
delimeter | The CSV separator. The value is of the varchar type and the length is 1. |
quote | The CSV quote. The value is of the varchar type and the length is 1. |
keys | The key name for the output of the CSV information. The value is of the array type. If the number of elements is different from the number of pieces of CSV information in the data, null is returned. |
Return value type
map(varchar, varchar).
Examples
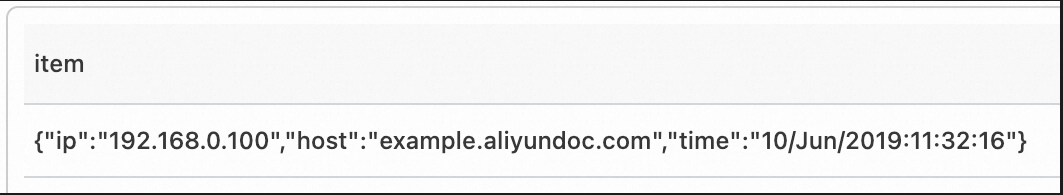
Extract the CSV information from the content field.
Sample field
content: '192.168.0.100,"10/Jun/2019:11:32:16,127 +0800",example.aliyundoc.com'Query statement
select csv_extract_map(content, ',', '"', array['ip', 'time', 'host']) as itemOutput data
ilike function
The ilike function checks whether an input string matches a specified character pattern. The check is case-insensitive.
Syntax
ilike(x, pattern)Parameters
Parameter | Description |
x | The value is of the varchar type. |
pattern | The character pattern, which includes strings and wildcard characters. The following table describes the wildcard characters.
|
Return value type
boolean
Examples
Check whether request_uri ends with file-6.
Sample field
request_uri: '/request/path-2/File-6'Query statement
select ilike(request_uri, '%file-6')Output data