This topic describes Simple Log Service (SLS) Processing Language (SPL), including its implementation, syntax, and instruction expressions.
SPL overview
SLS uses SPL statements to extract structured information, manipulate fields, and filter data from raw data. It also offers a multi-level pipeline feature, where the first pipeline is for index filter conditions and subsequent pipelines are for SPL instructions. The final output is the data processed by SPL. If you are familiar with SQL, see Comparison of use cases for SPL and SQL to learn how to use SPL for various data processing tasks.
How it works
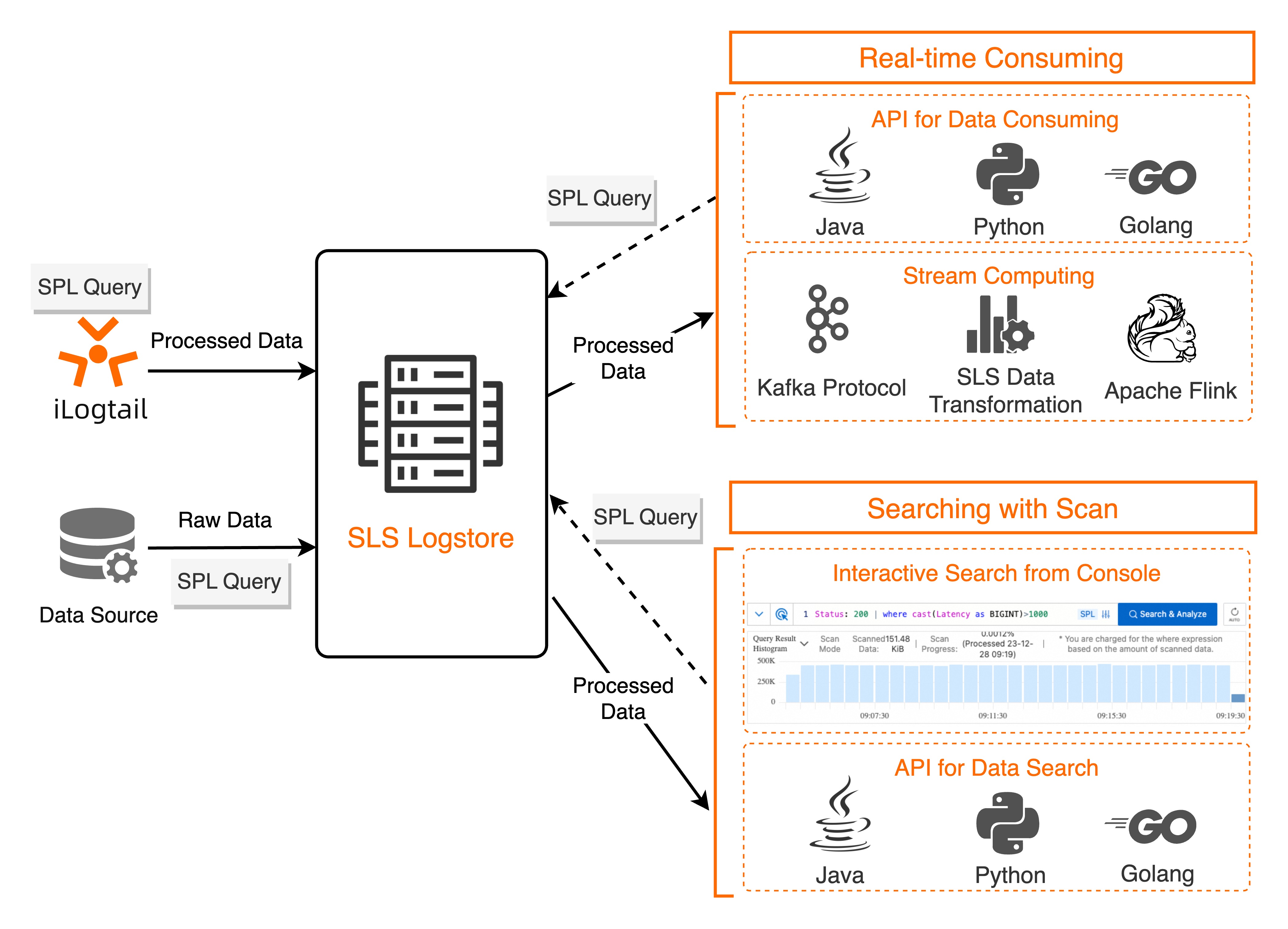
SLS SPL works with features such as Logtail data collection, ingest processor, rule-based data consumption, data transformation (new version), and Scan-based query and analysis. The following figure shows how it works.
For more information about the SPL functions in each use case, see General reference.
Limitations
Category | Limit | Logtail data collection | Write Processor | Real-time consumption | Data Transformation (New) | Scan query |
SPL complexity | Number of script pipeline levels | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
Script length | 64 KB | 64 KB | 10 KB | 10 KB | 64 KB | |
SPL runtime | Runtime memory size Important For solutions, see Fault handling. | 50 MB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 1 GB | 2 GB |
Runtime timeout Important For solutions, see Fault handling. | 1 second | 5 seconds | 5 seconds | 5 seconds | 2 seconds |