Simple Log Service provides a managed, scalable, and high-availability data transformation (new version) service. Use this service for data processing scenarios such as data standardization, information extraction, data cleansing, data filtering, and data distribution to multiple destination Logstores.
How it works
The data transformation (new version) feature in Simple Log Service processes log data in real time. It works by managing real-time data consumption jobs and using the Structured Process Language (SPL) rule consumption feature. For more information about SPL rules, see SPL syntax. For more information about SPL real-time consumption scenarios, see Overview of real-time consumption.
The data transformation feature is based on the real-time consumption API of Simple Log Service and does not depend on the index configuration of the source Logstore.
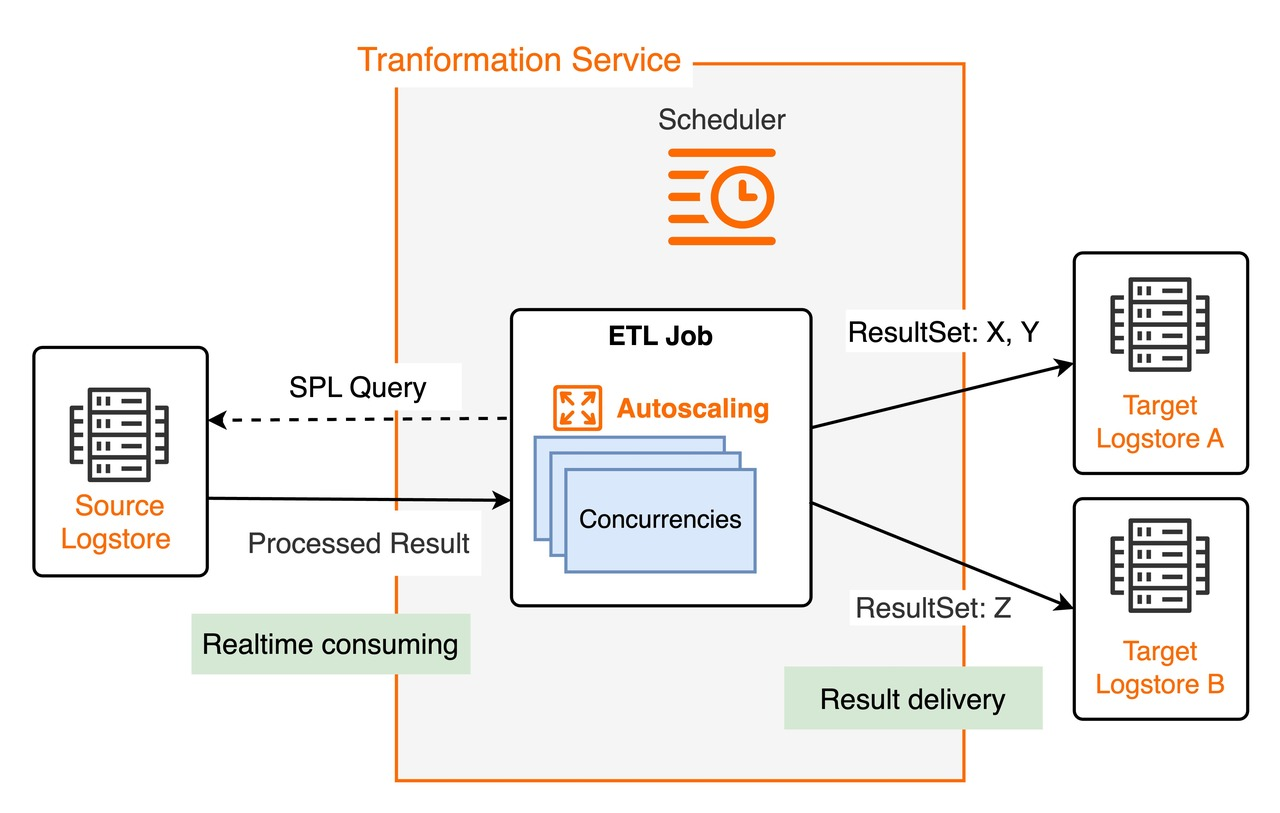
Scheduling mechanism
For each transformation job, the service's scheduler starts one or more instances to process data concurrently. Each instance acts as a consumer and consumes data from one or more shards of the source Logstore. The scheduler adjusts the number of instances based on resource usage and processing progress to achieve elastic scaling. The maximum concurrency for a single job is the number of shards in the source Logstore.
Running instances
Based on the job's SPL rules and destination Logstore configurations, each running instance consumes source log data from its assigned shards using the SPL rules. The instance then distributes and writes the processed results to the corresponding destination Logstore. While an instance is running, it automatically saves the consumption checkpoint of each shard. This ensures that if the job stops and restarts, consumption resumes from the saved checkpoint.
Stop and resume jobs
Automatic stop: If an end time is configured, the job automatically stops after it processes all logs created before that time. If no end time is configured, the job runs continuously. For more information, see ETL.
Resumable processing: When a job restarts after an unexpected stop, it resumes processing from the last saved shard checkpoint by default. This ensures data consistency.
View job status
You can monitor the status of data transformation jobs. For more information, see Monitor a data transformation job (new version).
Scenarios
The data transformation feature is used for scenarios such as data standardization, data forwarding, data masking, and data filtering. These scenarios are described below.
Data standardization and information extraction: Extract fields and convert data formats from logs with inconsistent formatting. This produces structured data to support downstream stream processing and data warehouse analysis.
Data forwarding and distribution:
Collect logs of different types into a single Logstore. Then, distribute the logs to different downstream Logstores based on their characteristics, such as the source service module or business component. This helps achieve data isolation and scenario-specific computation.
If your service is deployed in multiple regions, collect logs in each region. Then, aggregate the logs from different regions into a central region. You can use an acceleration service for cross-region aggregation. This enables centralized global log management.
Data cleansing and filtering: Cleanse invalid log entries or remove unused log fields. Filter out key information and write it to downstream Logstores for focused analysis.
Data masking: Mask sensitive information in data, such as passwords, phone numbers, and addresses.
Benefits
Simple Log Service uses a unified SPL syntax for data collection, querying, and consumption. This removes the need to learn different syntaxes for different operations.
When you write SPL scripts for data transformation (new version), you can use line-by-line debugging and code hinting. This provides a coding experience similar to an Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
Benefit from real-time processing, data visibility in seconds, scalable computing power, elastic scaling based on usage, and high throughput.
Use out-of-the-box data processing instructions and SQL functions designed for log analysis scenarios.
View real-time observability metrics and dashboards. You can also create custom monitoring rules based on operational metrics.
Benefit from a fully managed, O&M-free service that integrates with Alibaba Cloud big data products and open source ecosystems.
Billing
If a Logstore uses the pay-by-ingested-data billing method, the data transformation (new version) service itself does not incur fees. However, you are charged for Internet traffic that is generated when you pull data from or write data to Simple Log Service over the Internet. The traffic is calculated based on the compressed data size. For more information, see Billable items for the pay-by-ingested-data mode.
If a Logstore uses the pay-by-feature billing method, you are charged for the computing and network resources that are consumed by the data transformation (new version) service. For more information, see Billable items for the pay-by-feature billing model.