ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL provides the high-frequency snapshot backup feature. You can specify a backup frequency that ranges from 15 minutes to 12 hours for your ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance based on your business requirements. This feature is suitable for scenarios in which data is frequently updated, data consistency must be ensured, and downtime-sensitive services are provided. Increasing the backup frequency helps back up data in a more timely manner and ensures business continuity and data security.
Prerequisites
The RDS instance uses Enterprise SSDs (ESSDs) or Premium ESSDs.
NoteYou can change the storage type of your RDS instance from standard SSD to ESSD. For more information, see Upgrade the storage type from standard SSDs to ESSDs.
Serverless RDS instances are not supported.
The AliyunServiceRoleForDBS service-linked role is created by using your Alibaba Cloud account if you use the backup feature of ApsaraDB RDS for the first time.
Billing rules
If the total size of backup files does not exceed the free quota on backup storage, no backup storage fees are generated. If the total size of the backup files of your RDS instance exceeds the free quota, you are charged for the excess backup storage that you use. For more information, see Backup storage fees.
Feature description
If you do not enable the high-frequency snapshot backup feature, you can set the snapshot backup frequency to once a day.
If you enable the high-frequency snapshot backup feature, you can specify a backup frequency that ranges from 15 minutes to 12 hours based on your business requirements.
The snapshot retention policy changes based on the snapshot backup frequency.
Snapshot backup frequency | Snapshot retention policy |
Minutes | All snapshots that are completed within 1 hour are retained. For snapshots that are generated 1 hour ago, ApsaraDB RDS deletes the snapshots except for the first snapshot after the hour. For snapshots that are generated 24 hours ago, ApsaraDB RDS deletes the snapshots except for the first snapshot after 00:00 every day. For example, if you set the snapshot backup frequency to 15 minutes, 33 snapshot in total are retained in a week. Specifically, four snapshots are generated within 1 hour and all snapshots are retained. For snapshots that are generated within the range of 1 to 24 hours, the first snapshot that is completed in each hour is retained, and a total of 23 snapshots are retained within the range. For snapshots that are generated within the range of 24 hours to 7 days, the first snapshot that is completed on each day is retained, and a total of 6 snapshots are retained within the range. |
Hours | All snapshots that are completed within 24 hours are retained. For snapshots that are retained for more than 24 hours, ApsaraDB RDS keeps only the first snapshot after 00:00 every day. For example, if you set the snapshot backup frequency to 6 hours, 10 snapshots in total are retained in a week. Specifically, four snapshots are generated within 24 hours and all snapshots are retained. For snapshots that are generated within the range of 24 hours to 7 days, the first snapshot that is completed on each day is retained, and a total of 6 snapshots are retained within the range. |
For more information, see Retention policies for snapshots generated for backup.
Enable the high-frequency snapshot backup feature
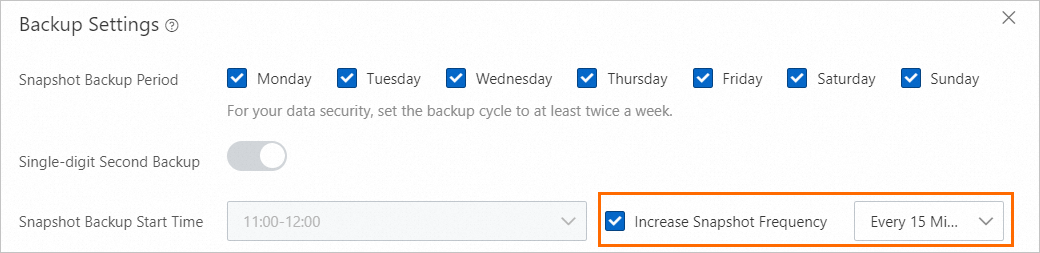
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page of your RDS instance, click Backup and Restoration. On the Backup Strategy tab of the page that appears, click Edit in the Data Backup Settings section to specify a snapshot backup frequency.
Before you can use this feature, you must enable the Single-digit Second Backup feature. If the single-digit second backup feature is disabled, the system automatically enables the single-digit second backup feature when you enable the high-frequency snapshot backup feature.
For more information about other parameters, see Back up an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
After high-frequency snapshot backup files are generated, you can use the files to restore your RDS instance. In addition, the files are automatically uploaded to an Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket for storage. In Task Center, you can filter the tasks of the Back Up Snapshot to OSS type to check the progress of uploading high-frequency snapshot backup files to the OSS bucket.
Before high-frequency snapshot backup files are uploaded to an OSS bucket, locally redundant storage (LRS) is used. After high-frequency snapshot backup files are uploaded to an OSS bucket, the data redundant storage mechanism varies based on the region of your RDS instance. If your RDS instance resides in a region in which you can create ZRS buckets, zone-redundant storage (ZRS) is automatically used. If your RDS instance resides in a region in which you cannot create ZRS buckets, LRS is used.
References
You can also call an API operation to configure the snapshot backup frequency that is specified by the BackupInterval parameter. For more information, see ModifyBackupPolicy.
For more information, see Backup features of an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance or Overview of data restoration methods.