This topic explains how to configure High Availability (HA) for your PolarDB for MySQL cluster by deploying it across multiple availability zones. A multi-zone deployment provides superior disaster recovery, protecting your database from data center-level failures.
Concept
An Availability Zone (AZ) is an independent data center within a single geographic region. By deploying your cluster across multiple zones, you create physically separate replicas of your data and infrastructure.
If the primary zone experiences a large-scale failure (like a power outage or network disruption), your cluster can automatically or manually fail over to a standby zone or a secondary zone, ensuring business continuity with minimal downtime.
Key features
Architecture and data redundancy
In a multi-zone deployment, both the primary and secondary zones each store a complete, independent copy of your data (3 replicas per zone), resulting in a total of six data replicas for high reliability.
The primary zone hosts the active compute nodes that serve your application traffic. The secondary zone's resources are on standby, ready to take over during a failover.
Failover capabilities
Automatic failover: When you enable the the cross-zone automatic switchover feature, the system will automatically promote the secondary zone to become the new primary if it detects a failure in the original primary zone.
Manual failover: You can also trigger a failover manually at any time. This is useful for performing disaster recovery drills or for strategically moving your database closer to applications (like ECS instances) running in the secondary zone.
To use multi-zone mode, make sure of the following:
Your cluster's region must have at least two zones with available PolarDB resources.
The secondary zone must have sufficient computing resources.
The multi-zone deployment feature is unavailable in the following regions: China (Qingdao), China (Hohhot), China (Chengdu), South Korea (Seoul), Philippines (Manila), and Thailand (Bangkok).
How it works?
PolarDB offers several high availability modes to fit different needs for resilience and cost. The following figure shows the architecture of the different deployment solutions.

Use the table below to understand the key differences and choose the best option for your workload:
Mode | Best For | How it Works (Based on Diagram) | Key Consideration |
Single-zone | Development, testing, and non-critical applications. | All data (3 replicas) and compute nodes are in one zone. (Not shown in diagram) | Lowest cost, but longer recovery time during a full zone failure. |
Dual-zone with Storage Standby | General production workloads requiring high availability. | A full copy of your data (3 additional replicas) is kept in a standby zone. Compute nodes (Primary, Read-only) exist only in the primary zone. | Doubles storage cost for high resilience against data center failure. |
Dual-zone with Storage & Compute Standby | Mission-critical applications that cannot tolerate service degradation after a failover. | A full data copy and a matching set of compute nodes (Secondary, Read-only) are kept in the standby zone. | Higher cost (storage and compute), but ensures full performance after a failover. |
Three-zone with Strong Consistency | Financial services and core enterprise systems requiring zero data loss (RPO=0). | Uses two zones for data and compute replicas, and a third zone for a special Logger Node. This architecture uses the X-Paxos protocol to guarantee a zero-data-loss failover. | Highest level of data protection and availability. The most resilient option. |
High availability modes
Solution overview
Single-zone
Database services are only provided by the cluster in the primary zone. This solution is less costly.
However, it takes longer to recover services when the primary zone fails. If you require cross-zone high availability, we recommend enabling the hot standby cluster feature.

Switching rules
It can be switched to dual-zone (hot standby storage cluster enabled) or dual-zone (hot standby storage cluster and compute cluster enabled).
Scenarios
Small-sized websites and applications
You can offload routine O&M tasks to Alibaba Cloud and focus on developing your applications.
Personal learning
If you are new to PolarDB, you can use the Standard Edition for testing and learning.
Development and testing
PolarDB features lightning-fast provision, allowing you to flexibly scale your database with your business requirements. This significantly improves R&D and testing efficiency.
Dual-zone with storage standby
Data is distributed across multiple zones. The primary zone and secondary zone each store a complete copy of data, ensuring high service level agreement (SLA).
Compute nodes must be deployed in the primary zone. The hot standby storage cluster in the secondary zone is primarily deployed for failover when the primary zone fails.

Switching rules
It can only be switched to dual-zone (hot standby storage cluster and compute cluster enabled).
Pricing
Data is distributed across multiple zones. The primary zone and a secondary zone each contain three replicas of data, resulting in a total of six data replicas. Its storage costs are higher than those of the single-zone (hot standby cluster disabled).
Scenarios
It is suitable for more than 80% of use cases in various industries, such as Internet, IoT, online retailing, logistics, and gaming.
Dual-zone with storage & compute standby
Data is distributed across multiple zones. The primary zone and secondary zone each store a complete copy of data, ensuring high service level agreement (SLA).
In case of primary zone failures, business can be switched over to the hot standby storage cluster in the secondary zone. The number of compute nodes in the secondary zone is the same as in the primary zone. Therefore, the secondary zone can provide sufficient read-only nodes after a failover to prevent service degradation.

Switching rules
It can only be switched to dual-zone (hot standby storage cluster enabled).
Pricing
Compute nodes
When you purchase a cluster, compute nodes are added to the secondary zone where the hot standby storage cluster resides. By default, the number and specifications of compute nodes in the secondary zone are the same as those in the primary zone. The compute nodes in the secondary zone are charged separately.
Storage
Data is distributed across multiple zones. The primary zone and a secondary zone each contain three replicas of data, resulting in a total of six data replicas. Its storage costs are higher than those of the single-zone (hot standby cluster disabled).
Scenarios
It is suitable for large and medium-sized enterprises whose production databases need to process many read requests during peak hours or perform intelligent data analysis. These enterprises include financial institutions, online retailers, automobile enterprises, education enterprises, and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) service providers.
Three-zone
Cross-zone strong consistency. Compared with semi-synchronous and asynchronous methods, the three-node architecture of one primary, one secondary, and one log is adopted. Physical replication is combined with X-Paxos protocol to provide higher disaster recovery capabilities.
When the primary zone fails, a failover is performed between the primary and secondary zones and strong-consistency replication of multiple replicas is implemented across zones to ensure that the recovery time objective (RTO) is less than 60 seconds. This also ensures strong data consistency and provides high financial reliability.

Switching rules
It cannot be switched to other high-availability modes.
Pricing
Compute nodes
Secondary nodes and logger nodes are free of charge. Primary nodes and read-only nodes are charged as common compute nodes.
Storage
Data is distributed across multiple zones. The primary zone and a secondary zone each contain three replicas of data, resulting in a total of six data replicas. Its storage costs are higher than those of the single-zone (hot standby cluster disabled).
Scenarios
It is suitable for large and medium-sized enterprises whose production databases need to process many read requests during peak hours or perform intelligent data analysis. These enterprises include financial institutions, online retailers, automobile enterprises, education enterprises, and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) service providers.
For more information about billing rules for compute nodes and storage, see Billing.
How to configure a high-availability mode
You can enable a high availability mode either when you create a new cluster or by modifying an existing one.
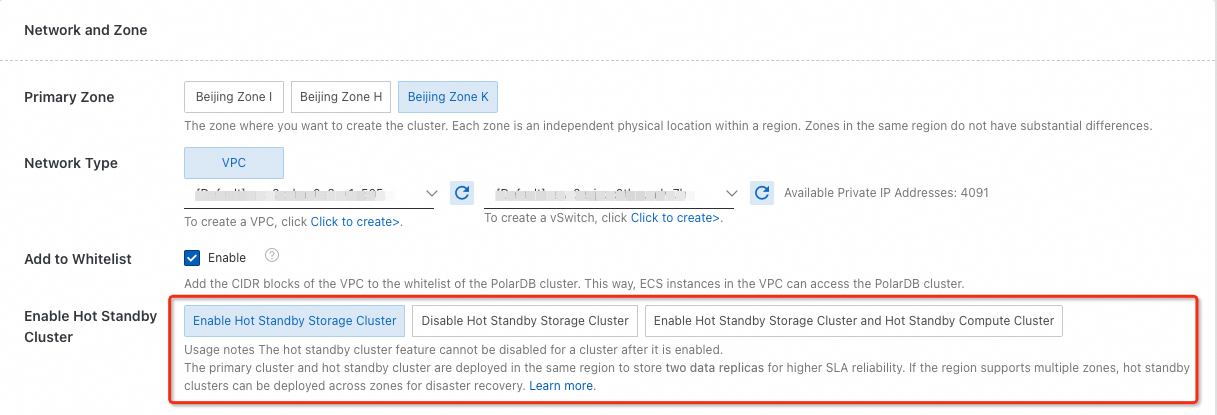
When you purchase a cluster, you can select the high-availability mode in the Network And Zone section.
NoteThe high-availability mode option is limited by the zones and resources available in the region where the cluster is deployed. For more information, see the buy page.
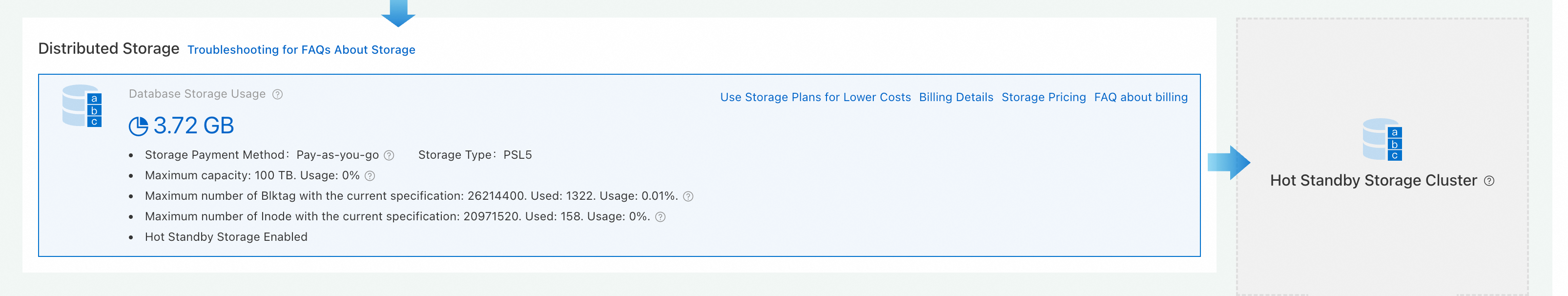
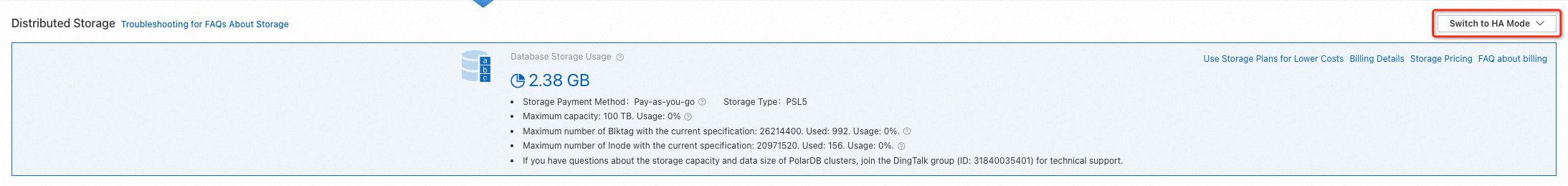
Go to the page. Click the cluster. In the Database Distributed Storage section of the Basic Information page, click Switch To HA Mode.
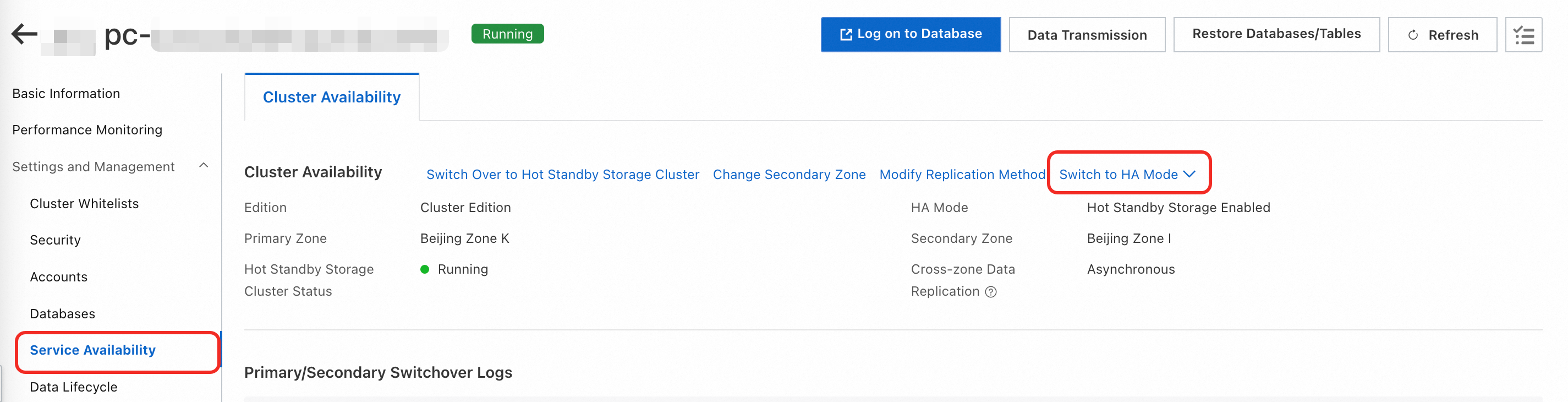
Go to the page. Click the cluster. Choose . On the Cluster Availability tab, click Switch To HA Mode.
Switching HA modes on an existing cluster is subject to resource availability and other limitations. If the option is not available, you must create a new cluster with the desired HA mode and migrate your data using the Data Transmission Service (DTS).